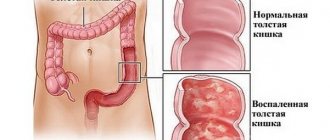
What is hemorrhagic colitis? Hemorrhagic inflammation of the intestine, one of the types of infectious colitis, is an inflammatory process that occurs on the mucous membrane and on the walls of the large intestine. The disease begins to develop when E. coli enters the body and is capable of producing a specific toxin.
Pathology can develop at any age (both in adults and children); hemocolitis is especially common in children under 5 years of age (it occurs in infants when they abuse diapers) and in the elderly.
Causes of pathology
The main cause of the development of this type of intestinal colitis is considered to be toxic E. coli, which lives in the intestines of cattle. An increase in its number in the human intestinal microflora becomes a source of formation of a large number of toxins that negatively affect the intestinal mucosa and disrupt the structure of the walls of blood vessels.
Infection can occur when:
- consumption of unpasteurized cow's milk;
- insufficient heat treatment of beef (eating rare steak).
This pathology can also spread:
- through shared cutlery;
- fecal-oral route;
- through unwashed hands after the street.
The disease is transmitted from person to person, and young children are the main risk group.
In children, this pathology may be a consequence of food allergies. Children who suffer from diathesis and indigestion are often susceptible to the disease.
Hemorrhagic colitis in some cases can be triggered by heredity and unhealthy diet, and can be a consequence of long-term use of medications and abuse of cleansing the body with enemas.
Blood in the stool in infants and young children
In infants and newborns, blood in the stool may be due to the following reasons:
Ingestion of mother's blood during childbirth (newborns)
Ingestion of blood by infants during breastfeeding from the mother's cracked nipples
Microbial contamination of the infant intestine
Allergy to certain foods (usually to proteins contained in cow's or goat's milk)
Infectious intestinal diseases (dysentery, amoebiasis, rotavirus infection, salmonellosis, shigellosis, giardiasis)
Congenital intestinal diseases (Hirschsprung's disease, Meckel's diverticulum)
Anal fissures (for chronic constipation)
Trauma or foreign body
Recommendations on what to do:
If bloody stool appears in a child of the first year of life, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible
Symptoms of the disease
Hemorrhagic colitis is characterized by a sudden onset and rapid development of symptoms, which in a short time lead to a significant deterioration in health.
The main symptoms of this disorder are:
- Acute pain syndrome spreading throughout the entire abdominal area.
- The appearance of large amounts of blood in the feces.
- Profuse diarrhea (stool has a watery texture).
- Severe increase in temperature.
- Violation of blood composition and the appearance of anemia.
- Development of renal failure.
These signs are characteristic of an adult organism. The duration of the disease is 7-10 days. In children under 5 years of age and the elderly, symptoms may appear within two weeks. This pathology can lead to serious consequences.
When an infection enters the child’s body, the following signs are added to the above symptoms:
- rapid weight loss, up to the development of anorexia;
- upset stool, alternating diarrhea and constipation (feces of different structures);
- general weakness;
- feeling of nausea, vomiting;
- pain (usually in the navel area), which has a long-term aching character, occurs before going to the toilet, with sudden movements, after eating.
Diagnostics
An infectious disease specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Before prescribing examinations, the doctor conducts a survey of the patient or parents (if the patient is a child), this is required to determine the time of the first manifestation of the disease and the intensity of symptoms. The doctor also finds out the history of the disease to determine the route of infection into the patient’s body. In addition, palpation of the anterior abdominal wall and temperature measurement are performed.
After carrying out the above procedures, laboratory and instrumental studies are prescribed, consisting of:
- blood test. It reveals signs of the inflammatory process;
- bacteriological culture of feces;
- microscopic examination of stool. Particles of the pathogen can be found in it;
- colonoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy. It helps to assess the condition of the inner surface of the colon mucosa.
Be sure to carry out differential diagnosis with:
- ischemic colitis;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- dysentery.
Blood in stool in older children and adolescents
If traces of blood appear in the stool of your child (older age, teenager), this may be due to the following diseases:
Anal fissures (for chronic constipation)
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
Infectious intestinal diseases (dysentery, amoebiasis, rotavirus infection, salmonellosis, shigellosis, giardiasis)
Trauma or foreign body
Varicose veins of the esophagus in liver cirrhosis
If your child has bloody stool, consult a doctor.
Dear parents, if you notice blood in your child’s stool, on toilet paper or in the toilet, you need to contact a pediatrician or gastroenterologist as soon as possible for a competent and accurate diagnosis so as not to miss serious diseases!
Chikunov V.V., Candidate of Medical Sciences, pediatrician-gastroenterologist, assistant at the Department of Childhood Diseases with a postgraduate course at Krasnoyarsk State Medical University named after. prof. V.F. Voino-Yasenetsky.
blood in baby's stool
Attentive parents always monitor very closely any changes and deviations in the child’s behavior and well-being. And if something worries you, then you should definitely show your child to your doctor. Especially if you find blood in your child's stool. Komarovsky voices a variety of reasons, and in some cases they can be really serious and lead to bad consequences.
To prevent this from happening, you need to diagnose a developing disease in time, if, of course, it exists, and begin immediate treatment.
Komarovsky about why the child has bloody stool.
Don’t immediately panic if you find blood in your child’s stool. Dr. Komarovsky names several types of rectal bleeding (this is what this alarming phenomenon is called).
- Bleeding from the upper digestive system. In this case, all the baby’s feces will be black and have a tar-like consistency. This is due to the fact that iron in the blood, under the influence of hydrochloric acid produced in the stomach, is converted into hematin hydrochloride, which gives the discharge its color.
- Bleeding in the lower gastrointestinal tract (rectum, colon, anus). In this case, you will find streaks of blood in the child's stool. Komarovsky also says that the feces themselves may be mixed with fresh, bright-colored blood.
In any case, if you do not like the look of your child’s discharge or have at least the slightest doubt, then you should immediately contact your pediatrician for examination and examination. In this case, it is better to play it safe.
How is pathology treated?
When the diagnosis is confirmed, isolation of the patient is required, since the disease is contagious. Treatment of hemocolitis is carried out only by conservative methods; for this type of pathology, surgical intervention is not provided.
Therapy consists of:
- taking antibacterial agents;
- use of antipyretics and other medications to relieve symptoms;
- following a strict diet;
- bed rest.
For complicated hemorrhagic colitis, therapy may also include:
- plasmapheresis;
- hemodialysis.
Diet
For hemorrhagic colitis, it is necessary to follow a diet, the rules of which imply adherence to the following principles:
- eat frequently and in small portions;
- eating food at a comfortable temperature - all food consumed should be warm;
- the presence of a large amount of protein products in the diet;
- It is advisable to prepare dishes using gentle methods - boiling and steaming;
- the food consumed should also be well chopped, and chewed thoroughly while eating;
- It is recommended to remove from the diet foods that irritate the intestinal mucosa - pickled, smoked, fatty foods, all types of beans, raw vegetables, alcoholic and carbonated drinks, coffee.
Treatment
Treatment of hemorrhagic colitis in children is always inpatient. The child is hospitalized for differential diagnosis, to exclude parasitic infestations, dysentery, and acute dysbacteriosis. In complicated cases, resuscitation, hemodialysis, and plasmapheresis may be required.
Nutrition
An important aspect in treatment is compliance with the rules of clinical nutrition. Prescribing a therapeutic diet has two main objectives:
- sparing the mucous organs of the digestive system;
- reduction of digestive load.
Be sure to read:
Carminative drugs for adults and children: list of medicines
In the first days of treatment, it is important for the child to drink plenty of fluids and reduce the level of digestive load. On days 3-5, the baby begins to be fed in accordance with the following recommendations:
- small and frequent meals (one serving should not exceed more than 100-200 ml according to the child’s age);
- the temperature of the food must be comfortable and warm;
- plenty of protein food to restore the intestinal mucosa (in the absence of contraindications);
- cooking method - steaming, stewing, cooking;
- It is recommended to eat the dishes semi-liquid or liquid.
It is important to exclude any irritating foods from your diet. The list of permitted or prohibited products is established in each individual case separately.
When drawing up the menu, the level of stomach acidity, the age of the child, allergic reactions and other criteria are taken into account. An approximate generally accepted list is as follows:
| Recommended Products | Not Recommended Products |
|
|
It is important to drink a lot of clean water, a decoction of rose hips without sugar, dried fruit compote, and green tea.
Drugs
Therapy for hemocolitis is conservative and involves the use of the following drugs:
- Antibiotics. The drugs are selected taking into account the sensitivity of bacterial strains to the active substance. Their main purpose is to stop the inflammatory process and prevent its spread throughout the body.
- Antipyretics. Prescribed as a symptomatic treatment for inflammation and high fever.
- Iron-containing preparations. Medicines are necessary to correct anemia due to blood loss.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Prescribed for pain relief. Some medications act as both antipyretic and anti-inflammatory.
In case of severe pain, injectable antispasmodic drugs and serious analgesics are prescribed. Usually, on days 5-7, with an uncomplicated course of the disease, children feel much better.
It is important for parents to understand that hemocolitis cannot be cured with any folk recipes at home. The intensity of clinical manifestations is pronounced, and symptoms increase rapidly. The younger the child is, the sooner he should be hospitalized in a specialized department.
Disease prognosis
In most cases, the prognosis for hemorrhagic colitis is favorable, and complications are quite rare.
References: msdmanuals.com/ru/home/digestive-disorders/gastroenteritis/hemorrhagic-colitis https://www.zdorovieinfo.ru/bolezni/gemorragicheskiy_kolit/ https://www.gastroscan.ru/patient/disease/kolit/ https://yandex.ru/health/turbo/articles?id=5281 med.vesti.ru/articles/zabolevaniya/vospalenie-tolstoj-kishki-simptomy-i-lechenie-kolita/ https://ru.wikipedia.org /wiki/Colitis https://icj.ru/spravochnik-boleznei/gg/613-gemorragicheskiy-kolit.html Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/18/2020
Prevention
Painful colic is an inevitable symptom of hemorrhoids, which disappears only after the disease is cured, and this is a long process. However, their intensity and frequency can be controlled if you adhere to the following recommendations from doctors:
- Avoid spicy foods. It stimulates blood flow to the anus, which can cause painful bleeding.
- Fill your diet with fiber. It improves intestinal motility, resulting in easier bowel movements, so constipation occurs less frequently.
- Don't sit without moving for a long time. If this is not possible, change your body position periodically.
- Control physical activity and avoid overexertion.
- Don't take too hot baths.