Over the past few decades, a large number of people have experienced digestive difficulties, particularly stomach problems. According to statistics, more than seventy-five percent of the Russian population have symptoms similar to those of gastritis and stomach ulcers.
Unfortunately, more than half of the sick do not attach much importance to the unpleasant sensations that arise and do not consider it necessary to seek medical help.
Doctors explain the inexorable statistics by insufficiently attentive attitude towards one’s own health, poor nutrition, leading to a deficiency of vitamins in the body.
Symptoms of gastritis of the stomach in adults are observed much more often than among the child population of the country, although statistics show that children are also susceptible to the disease.
Cases often occur: minor ailments associated with the stomach develop into a serious disease, which not only provokes complications in the body, but leads to death. Let's look at how gastritis manifests itself and its causes. Knowledge will help reduce the risk of complications (ulcers, internal bleeding, stomach cancer).
Commonly occurring diseases in the gastrointestinal tract include gastritis and stomach ulcers.
Table of contents
- Causes of diseases
- What are the symptoms of stomach ulcers and gastritis Symptoms of gastritis
- Signs of a stomach ulcer
- Endoscopic signs
- Antibacterial therapy
Perforation
This is the most common complication of this disease and can lead to death. If an ulcer is not treated, it eats away at all layers of the stomach wall. And through this hole the contents are released into the abdominal cavity. This leads to peritonitis, which can cause death within a short time. Signs of a perforated stomach ulcer are difficult to confuse with something else. The main symptom is acute, very severe pain in the abdomen. Patients describe it as a blow from a dagger. The pain does not subside, but only increases. And it gets worse with coughing, any movement, and even taking a deep breath. In addition, there are signs of bleeding: vomiting blood, weakness, dizziness and tinnitus. Hydrochloric acid and other stomach contents cause inflammation of the peritoneum.
Causes of diseases
External and internal factors play a role in the development of inflammation and the appearance of mucosal defects. They lead to changes in epithelial cells, which contributes to disruption of hydrochloric acid production and changes in acidity in the stomach. But there is a difference between these states. Gastritis can have different pH levels. This is its main difference. An ulcer is characterized by high acidity of gastric juice. The duodenum is also subjected to aggressive action with the formation of lesions in the area of the bulb.
Pathological conditions arise due to the following reasons:
- Infection with Helicobacter pylori is the main etiological factor, which is detected in 80-90% of patients.
- Poor quality nutrition with consumption of harmful foods.
- Psycho-emotional stress, stress, overwork.
- Taking certain medications for a long time - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, sulfonamides.
- Endocrine system disorders.
- Diseases that provoke an increase in pH are carcinoid syndrome, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, gastrinoma.
- Autoimmune pathology.
- Exposure to occupational factors - alkali vapors, acids, radiation, coal and metal dust.
- Smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Hereditary predisposition.
Causes
The main cause of the development of pathology today is considered to be the bacterium Helicobacter Pelori, the causative agent of peptic ulcers, gastritis and gastroduodenitis. The presence of bacteria is determined during an endoscopy procedure when scrapings are taken from the mucous membrane.
Dietary disorders are considered the leading cause, these include:
- eating fatty, smoked and spicy foods;
- irregular meals;
- the presence of a large amount of dry food in the diet;
- ingestion of poorly chewed foods;
- binge eating.
Among the reasons are also:
- alcohol and smoking;
- stress and nervous disorders;
- taking selected medications (painkillers, anti-inflammatory and other drugs that irritate the stomach);
- autoimmune diseases;
- hereditary predisposition;
- lack of vitamins.
What are the symptoms of stomach ulcers and gastritis?
Changes in the mucosa, which are characterized by inflammation and the formation of defects, have similar clinical signs. The conditions differ in their chronic course. In recent years, classic symptoms of gastritis and gastric ulcers affecting the duodenum have been observed less frequently. Often there is a hidden form of disease. However, there are features that help differentiate the type of pathology.
Symptoms of gastritis
Chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa has distinctive signs. Depending on the pH level, patients experience different symptoms of gastritis. Hypersecretion of gastric juice causes reflux and inhibits intestinal motility. When epithelial cells are destroyed, secretion ceases to be produced, and a hypoacid state occurs. Low production of hydrochloric acid leads to difficulty digesting food and impaired absorption of vitamins and nutrients. The pathology variant can be distinguished by symptoms independently.
Manifestations of gastritis with high acidity include:
- aching pain in the upper abdomen;
- burning in the epigastrium;
- belching with a sour taste, with bile reflux - with an admixture of bitterness;
- frequent vomiting after eating;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- increased saliva production;
- disruption of intestinal function in the form of constipation.
A decrease in pH in the stomach can be suspected if the following signs are present:
- nausea after eating;
- belching with an unpleasant putrid odor;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- discomfort or dull abdominal pain that occurs 20-30 minutes after eating;
- bloating;
- unstable stool, diarrhea;
- dry, brittle hair and nails;
- anemia.
The progression of the pathology leads to nutritional deficiency and loss of body weight. There is general weakness, decreased performance, and lethargy. There is a violation of vascular tone, which leads to the formation of hypotension. Therefore, when the disease worsens, loss of consciousness occurs.
Signs of a stomach ulcer
Constant exposure of the mucous membrane to an aggressive environment leads to the appearance of defects. The lesions come in different sizes - from 0.3 cm to 5 cm in diameter. They can be localized in the stomach and duodenum. Depending on the clinical variant of the disease, certain signs of a stomach ulcer are observed. The pathology is characterized by a chronic course with periodic relapses. In severe cases, there are complications such as:
- bleeding;
- perforations;
- penetration - when the process can spread to adjacent organs;
- stenosis;
- malignancy.
The main manifestations of peptic ulcer disease are:
- belching with sour contents;
- heartburn;
- pain that occurs mainly at night or on an empty stomach;
- vomiting and nausea after eating;
- progressive weight loss;
- anemia – if there is bleeding from a peptic ulcer.
If complications occur, other symptoms appear that reflect damage to the corresponding organ. Given the disruption of the outflow of gastric juice, chronic duodenitis, biliary tract dysfunction and secondary pancreatitis develop in adults. Destruction of the mucous membrane leads to perforation (rupture). This is an acute condition that requires emergency surgery. Modified tissues of a peptic ulcer can degenerate with the formation of stomach cancer.
Definitions
Gastritis is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa of varying intensity; as a result of the disease, secretory function is impaired. The disease is milder than a stomach ulcer. Simple forms can be treated with only a special diet. In connection with the above, a person often does not attach importance to his own ailments. The longer the patient neglects the symptoms, the greater the likelihood of inflammation of the submucosal layers.
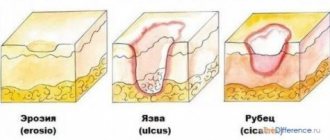
When the proper functioning of the inner lining of the stomach is disrupted, wounds - erosions - form on the mucous membrane. Erosive, or ulcerative, gastritis is much more severe and is considered the first stage of peptic ulcer disease. During an exacerbation, the patient suffers from incessant pain and vomiting after eating.
Stomach ulcer
Peptic ulcer is a pathological change in the stomach wall of a certain localization. Occurs as a result of constant exposure to aggressive acids on the gastric mucosa.
What is the difference between an ulcer and gastritis?
The mechanism for the development of inflammation and the formation of a mucosal defect has common features. Focal changes in the stomach are a consequence of excessive exposure of the epithelium to hydrochloric acid. Therefore, the diseases are similar not only in pathogenesis, but also in manifestations. However, patients often have a question: how to distinguish gastritis from an ulcer?
Pathological conditions can be identified by symptoms. Features are reflected in Table 1.
Table 1. How gastritis differs from a stomach ulcer
| Signs | Gastritis | Stomach ulcer |
| Pain syndrome | After eating 20-30 minutes | Intensifies at night and on an “empty stomach” |
| Belching | Sour, bile - with excess production of gastric juice, with a putrefactive odor - with low pH | Sour |
| Character of the chair | Alternating constipation and diarrhea | Constipation |
| Anemia | Most often hypochromic due to deficiency of nutritional iron | Most often normochromic due to bleeding |
| Asthenic syndrome | Moderately expressed | Progressing |
| Bleeding (stomach) | Not marked | Occurs during periods of exacerbation |
What foods are prohibited for stomach diseases?
During an exacerbation, the patient must follow a certain diet - table No. 1a. This is fractional nutrition in small portions. Hot, cold, irritating and fatty foods are completely excluded. Bakery products and vegetables are also prohibited.
General list of products not recommended for consumption even during remission:
- sausage, lard, liver and other fatty foods
- nuts and seeds - irritate the mucous membranes
- mushrooms and raw vegetables - high in fiber
- fried, heavy and spicy dishes - shish kebab, cutlets, dumplings
- poorly digestible meat - fatty beef, lamb, pork
- sour juices and fruits - pomegranate, grapes, lemon.
A looser diet is table No. 1b, which is followed at the beginning of remission. After some time, determined individually based on the results of the examination, it is allowed to move to table No. 1. It is prescribed for the first six months to a year after an exacerbation of the disease.
Diagnostics: how to check the stomach for gastritis and ulcers
Examinations for pathology of the digestive system are carried out in accordance with the protocol. The appearance of unpleasant symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract is an indication to consult a gastroenterologist. The specialist clarifies the patient’s complaints, medical history and assesses the objective status in order to distinguish gastritis from an ulcer. The next stage is additional diagnostics.
The following methods are prescribed:
- General clinical blood test with mandatory determination of hemoglobin, red blood cells, hematocrit.
- Biochemical examination.
- Identification of the pathogen - carrying out a respiratory urease test for Helicobacter, microscopy of mucus smears for quantitative analysis, qualitative research using PCR, immunohistochemistry.
- pH metering - to determine the acidity in the stomach.
- Analysis of feces for occult blood with a coprocytogram.
- X-ray examination with contrast of the stomach and intestines.
- Fibrogastroesophagoduodenoscopy with biopsy and subsequent histology of the material.
Important!
General clinical data indicate the severity of the pathology. Instrumental studies help determine how gastritis differs from a stomach ulcer.
Ultrasound diagnostics is used as an auxiliary method. However, an ultrasound will not show changes in the mucous membrane. Such an examination reveals concomitant pathologies and complications of the underlying disease.
Endoscopic signs of gastritis and ulcers
Visualization of the mucosa using FGS is the main research method. Signs of gastritis and stomach ulcers cannot always be distinguished by symptoms. However, endoscopy allows a definitive diagnosis. There are diagnostic features to differentiate diseases.
Endoscopic photo shows signs of gastritis and stomach ulcers
Table 2. Endoscopic signs of gastric ulcers and gastritis
| Criteria | Signs of gastritis | Signs of an ulcer |
| Nature of folds | Evenly spaced, easily expanded with air, thickened in the presence of edema and infiltration | Concentrated near the pathological area of the mucosa |
Mucosal color | Red in color, in places with small dotted inclusions similar to enanthema in scarlet fever - in a hyperacid process. Pale gray or cyanotic color, sometimes alternating light and pink areas that resemble a mosaic with the formation of “false” hyperemia | Hyperemia in the area of inflammation, in places there are scars of connective tissue, initially red and then pale |
| Presence of defects | No | A rounded lesion with an edematous ridge, a depression in the center, covered with a gray or yellow coating |
| Bleeding | Determined when the instrument comes into contact with inflamed and swollen mucosa | Marked at the bottom or edges of the ulcer |
| Vascular pattern | Clearly visible during the atrophic process; not detected in hyperacid gastritis | Moderate in remission, not detected during exacerbation of the disease |
How to properly prepare for gastric endoscopy
Differences between individual forms of disease
But some patients may also develop ulcerative gastritis. This type of disease is considered the most dangerous and is practically no different from an ulcer. The greatest threat to human health from this form of the disease is that pathological inflammation of the mucous membrane begins almost immediately after its irritation occurs. Often, almost a few hours are enough, and after half a day, all the main symptoms of the pathology clearly manifest themselves in a person.
Only the attending physician can tell you how to distinguish it from a peptic ulcer, but still there are practically no differences in the symptoms of these two diseases. This can be seen if you familiarize yourself in detail with the clinical signs of ulcerative gastritis:
- loss of appetite by a person;
- nausea, quickly followed by bloody vomiting, which can often contain bile or blood;
- distension and acute pain in the epigastric region.
In addition to these general signs, general symptoms also appear, which include a significant increase in temperature, increased blood pressure and the appearance of weakness and apathy.
Treatment of gastritis and stomach ulcers with drugs
After making a final diagnosis, the doctor draws up an action plan that includes diet, medication and alternative methods. Treatment of gastritis and ulcers involves an integrated approach. This promotes rapid recovery and reduces the likelihood of disease recurrence. The protocol helps the specialist to navigate and prescribe the optimal treatment for the patient. The treatment regimen for gastritis and stomach ulcers is practically the same; the drugs are suitable in both cases. The list is presented by the following groups:
- Antibacterial substances – for step-by-step therapy to eradicate Helicobacter pylori.
- Proton pump blockers - which reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid.
- Antagonists of H2-histamine receptors.
- Antacids - in order to reduce the aggressive effect of gastric juice on the mucous membrane.
- Bismuth preparations are an antiulcer medicine that can create a protective film and have a bactericidal and cytoprotective effect.
- Antispasmodics – eliminate spasms and reduce pain.
- Alginates – prevent the development of reflux due to a gel barrier on the surface of the mucosa.
Attention!
The tactics of the gastroenterologist is to prescribe medications to reduce acidity and antibiotics at the same time, based on the data obtained after examining the patient.
Antibiotics for gastritis and stomach ulcers
The main drugs used to treat pathology are antibacterial agents. This approach is necessary to destroy Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium that causes inflammation in the digestive tract. The scheme provides for stepwise therapy; the list of medications is presented in Table 3.
Additionally, other drugs are used to eradicate the bacteria. The duration of therapy is from 10 to 14 days.
Table 3. Groups of antibiotics used for gastritis and ulcers
| Group | Drug name |
| Penicillins | Amoxicillin 1000 mg 2 times a day |
| Macrolides | Clarithromycin, Fromilid, Klacid 500 mg 2 times a day |
| Imidazole derivatives | Metronidazole, Trichopolum, Tinidazole 500 mg 2 times a day |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline 500 mg 4 times a day |
| Fluoroquinolones | Levofloxacin 500 mg once daily |
| Rifampicin group | Rifabutin 300 mg once daily |
The combination drug Pilobact Neo is presented on the pharmaceutical market. Each package contains three first-line substances for the treatment of gastritis and ulcers. For most patients, this is the best medicine for ease of use and cost benefits.
Painkillers for gastritis and stomach ulcers
Along with antibacterial substances, additional drugs are prescribed that eliminate hypersecretion and reduce discomfort. Excess hydrochloric acid irritates the mucous membrane, which is manifested by pain and heartburn. Auxiliary therapy is aimed at pain relief for gastritis and gastric ulcers. The following medications are used for these purposes.
Table 4. Drugs used to relieve pain from ulcers and gastritis
| Groups of medications | Name |
| Proton pump blockers | Omeprazole, Omez, Nolpaza 40-80 mg per day in 2 divided doses |
| Histamine H2 receptor antagonists | Ranitidine, Famotidine 1 tablet 2 times a day |
| Bismuth preparations | De-nol, bismuth subcitrate 120 mg 4 times a day |
| Antacids | Phosphalugel, Maalox (liquid forms) 2-3 packets per day, but no more than 6; Sucralfate – tablets 1 piece 4 times a day |
| Antispasmodics | No-spa, Riabal, Dicetel 1 tablet 2-3 times a day |
Carefully! Antipyretics and traditional painkillers (Analgin, Paracetamol, Solpadeine) are not used to eliminate pain. Because they are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and can increase the production of hydrochloric acid.
Diet and features of therapeutic nutrition
The success of treatment largely depends on proper diet. The diet for gastritis and stomach ulcers is aimed at reducing the irritating effect of food. The frequency of meals is increased to 5-6 times a day. In the acute stage of the disease, products must be consumed after heat treatment. You can boil, bake or steam food. You need to eat regularly and avoid fasting. What you can eat and what you can’t eat is shown in Table 5.
Table 5. Allowed and prohibited foods for gastritis and stomach ulcers
| Allowed | Limit or exclude |
| Lean meat products (beef, pork, chicken breast) | Fatty meats, lard; By-products (skin, cartilage, liver) |
| Lean fish pelengas, pike perch, perch | Fatty fish mackerel, salmon, belan |
| Milk porridge | Bean dishes |
| Fruits and vegetables (neutral) bananas, peaches, pumpkin, potatoes, beets, carrots | Fruits and vegetables (sour) apples, berries, plums, tomatoes, white cabbage, radish, turnip, garlic |
| Spices cinnamon, ginger, thyme, curry, turmeric | Spices hot red and black pepper |
| Low-fat milk, yogurt, non-sour cottage cheese, hard cheeses | Dairy with a high percentage of fat content cream, fermented baked milk, fatty cheeses, kefir |
| Vegetable soups | Sour borsch; meat, mushroom, fish broth |
| Compotes, jelly | Sour fruit juices, fresh juices, carbonated drinks, coffee |
| Unfortunate bread | Baking with yeast |
The list of products for inflammatory diseases of the stomach corresponds to diet No. 5.
What foods are good for the stomach?
Folk remedies
Along with medication, alternative prescriptions are used. In most cases, folk remedies for gastritis and stomach ulcers contain substances of plant origin. Non-traditional methods practically do not cause any side reactions or complications. Therefore, they remain widely in demand among patients. The most famous medicinal products based on natural ingredients are presented in Table 6.
Table 6. Folk remedies for the treatment of gastritis and ulcers
| Folk remedy | Mode of application |
| Water-based propolis elixir | Ready-made extract of beekeeping products – 7-10 drops of liquid 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals |
| Infusion of cinquefoil | 1 tablespoon of crushed raw materials is poured into 200 ml of boiling water in a thermos. Leave for 2 hours. Drink 1/3 cup of tea 1 hour before meals |
| Sea buckthorn with honey | Brew 3 tablespoons of berries in a glass of boiling water, strain, add 3 tablespoons of honey. Take 1 teaspoon on an empty stomach |
| Infusion of yarrow and buckthorn | A mixture of equal parts of herbs is poured into 1 liter of boiling water. Leave for 2 hours. Drink 1 glass in the morning on an empty stomach |
| Licorice root infusion | 2 teaspoons of crushed root are poured into 1 liter of boiling water. Leave for 24 hours and filter. Take 100 ml 3 times a day before meals |
| A mixture of chamomile, yarrow and celandine | Dry grass is poured with 1 liter of boiled milk and infused in an enamel bowl for 2 hours. Take small sips throughout the day |
How to drink potato juice for gastritis
Ulcer treatment
Gastric ulcers are treated comprehensively. If Helicobacter is detected, the main therapeutic agent will be a set of narrow-spectrum antibiotics. If there is no bacterial infection, then drugs that suppress the secretion of hydrochloric acid come to the fore.
Antimicrobials
The modern treatment protocol includes antibiotics of two groups. First, a “triple” scheme is assigned:
- Clarithromycin or another macrolide drug
- "Amoxicillin" is a penicillin drug; can be replaced by a medicine with a wider spectrum of action - Metronidazole
- proton pump inhibitor of choice
Treatment is prescribed for a period of 1 to 2 weeks. Afterwards, research is carried out to identify Helicobacter in the body. In 9 cases out of 10, the infection is destroyed after one course. If success is not achieved immediately, then therapy is prescribed according to a four-component scheme:
- broad spectrum antibiotic of the tetracycline group
- "Metronidazole"
- "Omez" or another PPI
- bismuth tripotassium dicitrate - "Vis-Nol"
Secretion regulators
To reduce the acidity of gastric juice, proton pump inhibitors are most often used. This class of agents inhibits the transport of hydrogen ions at the cellular level by blocking the transport enzyme. Typical representatives:
- Omeprazole is the very first PPI and is still widely used today.
- "Esomeprazole"
- "Lansoprazole"
New compounds are characterized by a longer period of suppression of secretion and fewer side effects.
Reducing the acidity of gastric juice should be done carefully, selecting the dose separately for each patient. Excessive suppression of secretion leads to slow digestion and fermentation of food in the stomach. Dysbacteriosis is also possible. Insufficient dosage does not bring the expected result: the mucosal defect heals too slowly, a scar often forms, and the risk of complications increases.
Antacids
In addition to antisecretory drugs, antacids are used - alkaline compounds that react with acid. The pH of the stomach is neutralized and reduced for a short time. Such drugs are not used very often. They are divided into absorbable and non-absorbable.
The first group includes:
- baking soda
- calcium and magnesium carbonates
- magnesium oxide
These drugs act quickly, but do not last long, have many undesirable effects, and therefore are unpopular relative to the second group.
Non-absorbable antacids:
- aluminum phosphate - the lower the pH, the more actively it neutralizes acid (“Phosphalugel”)
- aluminum and magnesium hydroxides - rarely used independently
- various combinations of the above compounds with barrier substances - “Almagel”, “Gaviscon”
Non-absorbable antacids are effective for up to 3 hours after administration, but the effect does not appear immediately.
Other medicines
Separately, it is worth noting enveloping agents and other drugs with a protective effect:
- decoction of flax seeds - forms a kind of mucous film in the stomach, due to this it protects wall defects for a short period of time from the influence of acid and food
- bismuth subcitrate - stimulates the formation of a protective layer on the surface of the stomach, inhibits the development of Helicobacter, accelerates the healing of mucosal defects
- alginates - create an elastic and viscous protective film
Vitamin supplements speed up the healing of the stomach wall with ulcers or gastritis.
Pantothenic acid affects the level of HCl; with a lack of this substance, acidity increases. An amino acid called vitamin U lowers pH and has a mild analgesic effect. Contained in egg whites and cabbage juice.
Prevention of gastritis and stomach ulcers
Prevention of relapse of the disease is the main task of the gastroenterologist. Prevention of gastritis and ulcers includes a number of measures aimed at restoring the full function of the digestive organs and eliminating unpleasant symptoms. The main stages of patient rehabilitation can be noted:
- Elimination of provoking factors.
- Proper nutrition.
- Taking medications to prevent exacerbations.
- Phytotherapy.
- Physiotherapy.
- Spa treatment.
Secondary prevention includes taking medications that restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and promote tissue healing. Unlike the acute stage, antibacterial substances are not used during remission. Recommended medications are presented in Table 7.
Table 7. Drugs for the prevention of exacerbation of ulcers and gastritis
| Means | Therapeutic effect |
| Histamine receptor blockers – Ranitidine, Kvamatel | They exhibit antisecretory effects. Prescribed for a long period of 2 to 5 years at half the therapeutic dose |
| Cytoprotectors – Methyluracil, Potassium orotate, Solcoseryl | They have healing properties, stimulate the process of mucosal regeneration |
| Vitamins | Eliminate element deficiency |
| Antidepressants | Increase stress resistance, stabilize the psycho-emotional background |
ethnoscience
As an addition to the main treatment of erosive gastritis, folk remedies may also be recommended. Plants and oils that have an anti-inflammatory effect, accelerate tissue regeneration, and form a protective film on the gastric mucosa (enveloping) will help eliminate the symptoms of erosive gastritis.
Before using decoctions, infusions based on herbs or oils, you should definitely consult a gastroenterologist
One of the popular remedies is sea buckthorn oil. It heals wounds and relieves inflammation. For gastritis, you can use oil purchased at a pharmacy or prepared yourself (mix sea buckthorn juice and olive oil in equal proportions and let it brew for three days). You need to drink a teaspoon of oil daily on an empty stomach for two weeks.
Propolis tincture quickly relieves pain and helps eliminate inflammation. You need to drink it three times a day for three weeks before meals, after diluting it in warm water (20 drops per glass of liquid).
Wheat sprouts are also useful for gastritis. The cereal is sprouted for several days, then the sprouts are crushed and mixed with olive oil and left to infuse in a glass container for 5 days. You need to take the medicine for 5 days, a teaspoon an hour before your first meal.
Treatment of gastritis with honey and bee products has been used for a very long time and is effective. But it should be remembered that in case of illness, honey should be limited, and products based on it should be used in courses. Honey and aloe have an anti-inflammatory effect and promote regeneration. To prepare the product you will need 5 tablespoons of honey and the same amount of aloe leaves.
A paste is made from the plant and mixed with honey. Take a teaspoon on an empty stomach for three weeks. In order for the effect of treatment to be more pronounced, it is recommended to take leaves of a plant that are older than three years and let them lie in the cold for a day.
Chamomile helps restore mucous membranes and relieves inflammation. Therefore, it is beneficial to drink tea from this plant. Watermelon rinds can also be used to treat erosive-ulcerative gastritis. They are crushed and scalded with boiling water, boiled for half an hour and left to brew. Drink a glass of decoction daily in 4 doses before meals. Watermelon improves the condition of the gastric mucosa, relieves inflammation, is rich in vitamins and microelements, and improves the functioning of blood vessels.
Symptoms of erosive gastritis and ulcers most often occur against the background of increased acidity of gastric juice. To reduce the production of hydrochloric acid, it is recommended to drink alkaline mineral water “Borjomi”, “Essentuki”. For medicinal purposes, water should be selected by the attending physician, taking into account the sodium bicarbonate composition. You need to drink it warmed up, in one gulp, an hour before meals. The course continues for a month.
Disease prevention
For the purpose of prevention, as for other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, exercise, and be sure to undergo regular preventive examinations with a doctor in order to avoid the dangerous consequences of gastritis and stomach ulcers.
List of references: https://www.kp.ru/guide/simptomy-i-priznaki-gastrita.html https://www.kp.ru/guide/simptomy-jazvy-zheludka.html https://www.gmsclinic .ru/diseases/peptic-ulcer https://www.segodnya.ua/lifestyle/food_wellness/kak-ponyat-chto-u-vas-yazva-ili-gastrit-771424.html https://www.wmj.ru /stil-zhizni/zdorove/simptomy-gastrita-i-yazvy-zheludka-lechenie-narodnymi-sredstvami.htm https://www.nrmed.ru/rus/dlya-vzroslykh/gastroenterologiya/yazvennaya-bolezn/ https:// www.msdmanuals.com/ru/professional/diseases-of-the-gastrointestinal-tract/gastritis-and-peptic-ulcer/peptic-ulcer https://luch-tv.ru/2011-11-16-10-28-01 /publikacii-za-avgust-2014/item/8249-kak-otlichit-gastrit-ot-yazvy.html https://students.kpfu.ru/node/14061 https://fakty.ua/319271-yazva-zheludka -chasto-voznikaet-u-teh-kto-kurit-nervnichaet-est-odin-dva-raza-v-den-i-pet-mnogo-kofe https://setpol.ru/publications/gastrit-i-yazvennaya- bolezn-zheludka-i-dvenadcatiperstnoj-kishki.html https://www.piluli.ru/medspravochnik/ot_gastrita_i_yazvy Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/18/2020
Ulcer symptoms
The symptoms of an ulcer are similar to the symptoms of gastritis, but there are some peculiarities. Ulcer pain usually appears some time after eating and subsides after taking antacids. The pain radiates to the back and spreads to the entire abdominal cavity. Nausea, possible vomiting, abdominal pain, loss of appetite and flatulence may occur - as with gastritis. But with an ulcer there is no fever, diarrhea or dizziness. Periods of exacerbation are typical for ulcers, usually in spring and autumn. The development of ulcers is provoked by stress, prolonged fatigue, decreased immunity and the use of certain medications.
The symptoms accompanying this disease depend on the individual characteristics of the patient: age, location of the ulcer, stage of the disease, gender, presence of other gastrointestinal diseases, etc.
There are several main syndromes by which the disease is determined:
- painful. It is localized in different areas of the body and is the main sign of an ulcer. With an exacerbation of a peptic ulcer, the pain is aching, paroxysmal. More often it occurs after a long fast or several hours after eating; pain from the stomach can radiate to the back;
- dyspeptic. It includes: heartburn (occurs in 99% of cases), nausea, vomiting, belching or bitter belching, etc. In addition, constipation can often develop, which is associated with increased acidity, characteristic of the acute stage of the disease. Since peptic ulcer disease is a chronic disease, usually dyspeptic and pain syndromes appear in autumn and spring;
- neurocirculatory dystonia and nonspecific intoxication. This syndrome refers to various disorders of the cardiovascular, nervous and other systems of the body. All of these manifestations occur during an exacerbation of the disease. When it is in remission, pain and other symptoms are less intense.
During the acute course of the disease, the patient quickly loses weight. Anemic syndrome occurs due to bleeding due to a peptic ulcer. With a pyloric ulcer, there may be periodic spasms.
Duodenal (intestinal) ulcers occur more often in men after 50 years of age, but both women and younger people are susceptible to this disease. The clinical symptoms of ulcerative lesions intensify during inclement (rainy or windy) weather.
Symptoms of a stomach ulcer opening
There are specific signs of an open ulcer:
- vomiting with pain;
- irritability;
- nervous tension.
After the gag reflex, symptoms may temporarily stop.