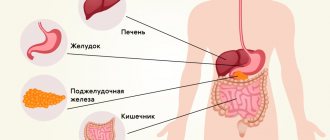
Vomiting and acute abdominal pain are symptoms indicating intoxication of the body, both in adults and children. Poisoning is caused by the entry of pathogenic microorganisms and toxins into the body. Another common cause may be surgical pathology.
In addition to the usual poisoning from poor-quality food or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, vomiting in adults can occur due to such diseases or pathological disorders. Namely:
- Pathologies of the digestive system.
- Hepatitis.
- Brain diseases, such as hydrocephalus or malignant tumors.
- Pathologies of the heart and vascular system.
- The appearance of problems with the mental and nervous system.
- Rupture of cerebral vessels or formation of a hematoma inside the skull.
- Diseases of the inner ear (dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus);
- Endocrine disorders.
- Migraine.
- Meningitis.
- Anorexia.
- Bulimia.
Vomiting also occurs in pregnant women due to impacts or falls, as well as a weakened vestibular system when driving.
If a child is vomiting, ordinary parents will not be able to independently determine the cause of this condition, but they can make the first assumptions. They are based on accompanying symptoms, the nature of the pain and the baby’s previous menu.
Causes of vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal pain
The following are the main diseases that cause vomiting and abdominal pain::
- Acute intestinal infection. She is accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature, with loose, frequent stools, vomiting and general malaise. With this infection, waste products of bacteria accumulate in the body, which got there with low-quality food. You can assume the disease by analyzing what food was recently consumed, since from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first symptoms, 2 to 12 hours pass.
- Appendicitis. In the initial stage it resembles a common eating disorder. The pain comes on suddenly. First it is localized around the navel. Then he clearly gives it to the lower right side. The temperature rises sharply, vomiting and diarrhea begin.
- ARVI . There is a group of viral infections that cause severe vomiting and diarrhea. Young children are susceptible to the disease. The disease is accompanied by a high temperature of up to 39 degrees and abdominal pain.
- Helminthiasis. The pain is spasmodic in nature. Both loose stools and frequent constipation are observed. Nausea, poor appetite, general anxiety. And with severe infection - vomiting and skin rashes.
All accompanying symptoms should be carefully monitored. They will help diagnose the disease more easily.
Vomiting in children
Poisoning in children occurs frequently. Usually the reason is due to poor quality products. Vomiting in a small child must be treated with special attention and proper care must be provided. If the case is not isolated, is accompanied by diarrhea and high fever, or the baby complains of pain, consult a doctor. In an adult, poisoning is much easier than in a child. The child’s body is not strong enough and is unable to cope with the infection on its own. Medications may be required.
Drinking regime
The first thing to do during and after vomiting is to provide the child with plenty of fluids. Drinking regime is important, as for adults: water helps remove toxins faster. A water-salt solution will help get rid of vomiting. The volume of liquid is calculated based on the child’s weight - 150 ml per kilogram. Young children are given a teaspoon of water at room temperature every 10 minutes.
When the nausea has stopped, it is better not to eat right away. It is recommended to wait until the next day. Products should be selected that are easy to digest. Infants do not need any other nutrition; mother's milk normalizes the activity of the stomach. The mother must follow a diet. It is necessary to choose foods that are easier to digest. From the age of one year, start feeding porridge with milk diluted with water, gradually introducing baby cottage cheese, vegetable puree, and juices into the diet. At first, it is recommended that older children be given rice and buckwheat porridge with water. Oatmeal is fine. The porridge should be boiled and unsweetened. If desired, instead of sugar, add dried fruits, focusing on your well-being.
The following foods will improve stomach function:
- banana puree (bananas are an essential source of microelements);
- baked apples remove toxins and reduce nausea;
- decoction of dried fruits;
- boiled vegetables (carrots, broccoli);
- plain yoghurts;
- non-acidic kefir.
Products should not irritate the gastric mucosa; it is better to prepare semi-liquid food and grind solid food using a blender. The food is cooled to a comfortable temperature. If the child is not hungry, there is no need to force him to eat. The body will independently determine the optimal amount and frequency. After one or two days, you can diversify your diet with low-fat dishes, boiled or steamed. It is extremely important to replenish the animal protein content. Liquid chicken broth perfectly soothes the mucous membrane and saturates the body with nutrients. Gradually, the menu includes stewed vegetables and familiar dishes. It is recommended to consume food in small portions, but often. Gradually portions and intervals are increased.
Additional actions
Recovery lasts up to three weeks, depending on the duration of vomiting. During this period, the body needs vitamins and minerals. The doctor may prescribe medications high in vitamins A, B and C to improve metabolism and increase the body's resistance. In case of prolonged vomiting, a vitamin complex is required.
To avoid re-poisoning, check the expiration date and quality of the products. If the diet does not help, the nausea does not go away, you need to take medicine and call a doctor. After prolonged vomiting, severe dehydration occurs. Prolonged vomiting can lead to serious consequences, chronic diseases, and death. You should pay close attention to your health and determine what is causing your prolonged illness. The doctor will prescribe treatment based on the specifics of the disease.
Causes of vomiting with fever
Vomiting with an increase in body temperature indicates severe intoxication of the body. It can be caused by various toxins and poisons.
If diarrhea is not accompanied by vomiting, this indicates the development of pathological processes in the liver, gall bladder or organs of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
Sometimes such symptoms indicate cancer.
We can distinguish the following group of diseases in which vomiting is not accompanied by diarrhea:
- Peptic ulcer disease. The pain is paroxysmal in nature. It often appears after eating food. Experts say that this disease is caused by the bacterium Halicobacter pylori.
- Acute gastritis. When the surface epithelium of the stomach becomes inflamed, the temperature begins to rise, the stool changes, mucus impurities can be found in it, and bad breath appears. After eating food, attacks of nausea and vomiting are observed.
- Increase in the number of ketone bodies. Simply put, “acetone” in children. Children under 12 years of age suffer. In addition to severe vomiting and cutting pain around the navel, there may be an increase in temperature, a specific smell from the mouth, dizziness and general weakness.
- Intestinal obstruction. The patient has a long absence of bowel movements. Vomiting does not bring even temporary relief.
- Acute cholecystitis. The pain is concentrated in the right hypochondrium. This indicates an inflammatory process in the gallbladder. The younger the patient, the more intense the pain.
Vomiting with fever without loosening stools is a serious symptom indicating a dangerous disease.
What tea can you drink if you are poisoned?
Be sure to drink warm, sweet tea.
Sugar in tea normalizes the amount of glucose and blood pressure in the body, and actively removes toxic microbes from the body. Patients with high blood pressure drink green tea, and those with low blood pressure drink black tea. Sweet tea is contraindicated for diabetics. In case of food poisoning, if you drink tea or other drinks with lemon, they will help destroy pathogenic microbes and bacteria, but it is better to consume in moderate doses so as not to irritate the intestines. Honey, when used properly, has a positive effect on the gastrointestinal tract, its microflora and mucous membranes. In the first days after poisoning, you should not consume honey, but when you feel a little better, you can drink decoctions with honey. For example: - take a teaspoon of dill seeds and pour it into a glass of boiling water. Leave for 20 minutes, strain, add a teaspoon of honey. The decoction is ready for use. There are other recipes: - dried fruits and honey. Pass dried apricots and prunes through a meat grinder, add honey, bringing to a thick consistency. This mixture is used after poisoning and returns lost vitamins and microelements to the body.
First aid for vomiting at home
Vomiting is the eruption of the contents of a person’s stomach through the oral cavity, accompanied by a specific sound. In anticipation of vomiting, nausea and the urge to vomit are observed. The attack is one-time or repeated many times within a short period of time.
In addition to food debris with vomit, a large amount of liquid comes out. Frequent and profuse vomiting is dangerous for children. To avoid dehydration, you need to give your child something to drink between attacks. Do not give large amounts of liquid. Repeated drinking in small doses is what you need.
Experts do not recommend giving medications that block nausea. If vomiting is associated with food poisoning, then the more contaminated contents come out of the stomach, the less pronounced the consequences of intoxication will be.
If vomiting is repeated often, does not bring relief, and other alarming symptoms are added to it - frequent bowel movements, chills, high temperature, then you should call an ambulance. This is justified for both children and adult patients.
After each attack, the mouth is rinsed with boiled water and the face is washed. If the contents of the stomach begin to come out through the nose, be sure to rinse it.
The patient needs rest. To avoid choking on vomit, it must be placed on its side.
If the cause of this condition is not clear, you should hold off on taking any medications. To relieve pain, you can use Doloren or No-Shpu. Other drugs can blur the picture of the disease and complicate the diagnosis.
You should refrain from eating food, especially in the first day, but clean drinking water should be consumed in large quantities.
What can you eat and drink if you are poisoned?
Poisoning is a fairly common and extremely unpleasant problem.
The possibility and danger of encountering it follows the heels of modern man - from unwashed hands, non-compliance with food preparation and storage regimes, to all sorts of microbial or chemical reasons. Serious clinical manifestations or illness in children force (force) to seek medical help. In case of mild cases, rest and proper diet - drinking and appropriate foods - will help you “get back to shape.”
Folk remedies for nausea and vomiting
Before using folk remedies for nausea and vomiting, it is necessary to understand the cause of their occurrence. Non-traditional recipes can be used when overeating, drinking alcohol or eating low-quality foods.
The following recipes are most effective:
- Strong tea. You can cook green or black with lots of sugar.
- Potato juice. Grate 1-2 potatoes on a fine grater and squeeze out the resulting mass using gauze. 1 tbsp is enough. l. to relieve an attack of nausea.
- Apple vinegar. Can only be used by adults. 1 tsp vinegar is diluted in 200 ml of warm water. You can drink throughout the day until the urge stops.
- Peppermint decoction. Preparation: 2 tbsp. dry raw materials, pour 200 ml of boiling water. Place the container with the broth on the fire and boil for 1-2 minutes. Leave for 30 minutes and strain. Drink in small sips throughout the day.
- Green tea leaves. Large green tea leaves should be chewed but not swallowed. The nausea goes away quickly.
- Honey with lemon. This remedy is suitable for relieving seizures in children. You need to mix 1 tsp. honey with a finely chopped lemon slice. The resulting mass is poured into a glass of warm boiled water, stirred and allowed to brew for 10-15 minutes. In the absence of allergies, you can give 1-2 tbsp. l. funds every 10 minutes.
Traditional medicine does not always help with nausea and vomiting, which may indicate a more serious cause of the disease that is not related to food intake.
Duration of recovery period
The duration of rehabilitation depends on the duration of vomiting, the reasons for its occurrence and the general health of the patient. In the standard case (for poisoning, inflammation and gastrointestinal infections), a gentle diet is prescribed for 2-3 weeks. For gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis and colitis, some restrictions remain permanently. Following a therapeutic diet allows you to avoid exacerbation of the disease and improve digestion.
For acute liver infections, a gentle diet is prescribed for at least 6 months.
Features of nutrition during vomiting
It is important to know not only what you can eat when vomiting, but also how to eat food. During vomiting, it is worth reducing the load on the digestive system. It is necessary to eat in small portions and replenish the lack of water in the body, since vomiting leads to dehydration.
What can you give your child to eat?
Typically, when children vomit, they experience a high fever and frequent loose stools. This condition is dangerous for the baby, as a lot of fluid is lost. In this situation, it is difficult for parents to determine what their child can eat when vomiting.
While the bouts of vomiting continue, you cannot eat anything. To avoid dehydration, you need to give your child plenty of fluids:
- Warm tea. You can infuse it with herbs (chamomile, St. John's wort, sage) or use regular loose-leaf black tea.
- Rose hip decoction. Perfectly replenishes the loss of vitamins and fluids. You shouldn’t give it to your baby a lot, as rosehip works as a diuretic.
- Still mineral water. To remove gases, pour water into a glass and stir well with a fork. Most of the gases will evaporate.
- Dried fruits compote. Restores strength and water balance of the body.
A day after the vomiting stops, you can give the child light food.
What can you eat if an adult is vomiting?
If there was a single attack, after which there was relief, then there is no need for a serious change in the daily diet.
If bouts of vomiting are repeated many times and are accompanied by diarrhea, then you should stop eating.
A fasting break for an adult can last from 24 to 48 hours.
The longer the patient can withstand without food, the faster the inflammation of the stomach and intestinal mucosa will pass. You cannot fast for more than 2 days. Therefore, it is important to decide on a list of what you can eat or drink when vomiting and what you cannot.
What not to eat when vomiting
In the first days after the cessation of vomiting, it is necessary to organize dietary nutrition. The following products should be removed from the menu for a while:
- any meat;
- any fish;
- fresh fruits and vegetables. Eating plums, pears and grapes can be especially harmful. They provoke bloating and resumption of diarrhea;
- juices and carbonated drinks;
- fresh bread;
- cereals: pearl barley, semolina and wheat;
- pasta;
- mashed potatoes;
- confectionery.
These products have a negative effect on irritable intestines and stomach. If they are consumed, diarrhea and vomiting may resume. Before giving the patient any food, you need to make sure that it can be eaten while vomiting.
Drinking water when vomiting
Through vomiting and diarrhea, the human body gets rid of toxins. As a result, with each bowel movement or bout of vomiting, fluid and minerals are lost.
The patient should receive as much fluid as possible. The best option is regular drinking water. It must be consumed in small portions between attacks.
You can use ice cubes. Dissolving one every 10 minutes.
To alleviate the patient's condition, it is necessary to restore the water-salt balance. Add 1 tsp to a glass of drinking water. sugar and 1/3 tsp. salt. Pharmacy drugs restore electrolyte balance well:
- Regidron;
- Citroglucosolan.
If the patient vomits after drinking, he should continue to be given water. Small child 1 tsp. water every 10 minutes, adults 1 tbsp. spoon.
Menu for stomach poisoning
It is preferable to eat according to the following scheme:
- Breakfast - liquid semolina, jelly;
- Lunch – light chicken soup (preferably homemade chicken), liquid mashed potatoes, herbal decoction;
- Afternoon snack - jelly;
- Dinner - thin rice porridge, jelly.
Until the body has fully recovered, you should not consume:
- High-calorie, difficult-to-digest foods;
- Sweet and baked;
- Porridge made from pearl barley, millet;
- Canned products;
- Coffee drinks;
- Raw fruits and vegetables;
- Milk, eggs;
- Cocoa and products based on it (chocolate, etc.).
What food can be poisoned at home:
- Fish and fish products;
- Meat;
- Greenery;
- Conservation;
- Mushrooms.
Before preparing food, you should carefully check the products; if in doubt, it is better not to use them for the sake of maintaining your health.
Mushroom poisoning is a very common type of intoxication. To prevent this poisoning, you need to know the types of mushrooms, which ones are edible, how to prepare them, and, if necessary, know first aid techniques for poisoning. There are many types of edible mushrooms and they can be cooked without pre-processing. There are mushrooms that must first be soaked for a long time in salt water, washed for several hours in running water, and cooked, draining the water several times. There are also poisonous mushrooms that are strictly prohibited to consume (mortality rate up to 98%).
General signs of mushroom poisoning (occur after 1 hour):
- Constant pain in the abdominal area;
- Be sick;
- Vomiting without stopping;
- Hourly diarrhea.
You also need to know what fungus caused the poisoning in order to prescribe the necessary treatment method. There are mushrooms that affect the mucous membrane, and there are those that affect the liver and kidneys, bypassing the digestive organs.
If you suspect mushroom poisoning, you must immediately notify an ambulance.
Where to start first aid before the ambulance arrives:
- Give a lot of water or manganese water to drink to empty the stomach;
- If there is no diarrhea, give a laxative;
- For the patient to take several tablets of activated carbon;
- For normal blood circulation, place heating pads under your feet and in the abdominal area.
Is a diet necessary after vomiting - when is it needed?
Vomiting is a symptom of the disease. Therefore, for each specific case, its own treatment regimen and diet are selected.
After prolonged vomiting, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Refusal to eat for 24 to 48 hours.
- Frequent small drinks.
- Restoring electrolyte balance.
- Unloading the digestive tract with diet.
- A gradual return to the usual daily diet, without including harmful foods in it: canned food, spicy and highly fried foods, alcohol, etc.
The diet is mandatory. Its duration and scheme are based on the diagnosis of the disease. If it is gastritis, ulcers or other gastrointestinal pathologies, then you will have to adhere to a specific diet for the rest of your life. The main thing is that after stopping the attack, you should not overeat. You can eat during vomiting and after it ends only easily digestible foods that do not irritate the walls of the stomach and intestines.
Meals on the first day
In order to quickly restore normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, feeding after vomiting should be light and gentle. 4-5 hours after the last attack of vomiting, you can give the patient biscuits or a baked apple.
If he does not start to feel sick, then he can eat allowed foods.
Meals on the second day
Experts recommend eating only after restoring the body’s water-salt balance, i.e. from the second day.
All dishes are finely ground using a sieve or blender. It is worth completely eliminating any seasonings and limiting the use of salt. Food is taken in small portions 5-6 times a day.
Food should not burden the stomach. You should start eating with simple foods: crackers without additives, biscuits with sweet black tea. If the patient feels well, then for lunch, meat broth is cooked in second water. Low-fat varieties of meat are selected for it: rabbit, quail, chicken breast.
Meat should not be consumed on the second day. Therefore, it is removed from the broth. You should refrain from eating fresh bread. Crackers or Lenten cookies are served with the broth.
Oatmeal is the first thing you can eat after vomiting.
You can make oatmeal without milk or butter. Baked potatoes will also not harm your stomach.
What can you eat after vomiting stops?
On the third and subsequent days after vomiting, the patient’s diet can be diversified by including additional foods.
The following dishes are allowed for consumption:
- Porridge: oatmeal, rice, buckwheat. Prepared in water without oil.
- Vegetable soups with meat broth. (In the first 2-3 days they should be crushed).
- Boiled lean fish.
- Steamed meatballs or meatballs
- Baked potato.
As the patient's condition improves, low-fat cottage cheese, milk, and kefir can be added from day 5. Then gradually sour cream and butter are included in the diet. You can’t suddenly return to the usual menu. This will provoke a new attack.
What can you eat if you are poisoned?
What to consider when creating a menu for the victim, what foods can be eaten if poisoned?
- Crackers and biscuits (dry) cookies.
- Light porridge (buckwheat or rice) on water.
- Lenten (vegetable) puree soups.
- Non-acidic fruits (apples, bananas, pears) - preferably boiled or baked.
- Boiled lean meat and fish when the condition stabilizes (not earlier than the 5th day).
- Curd soufflé or casserole (after the 5th day).
It is also advisable to adhere to the principles of fractional (small portions) and frequent (every 2-3 hours) meals, exclusively freshly prepared dishes from permitted products. It should be steamed or boiled, it is advisable to bring it to a liquid or puree consistency before serving.
Thus, a strict diet should be followed for at least 3-4 days after poisoning, and then not consuming prohibited foods for up to two weeks.
Compliance with an appropriate drinking and nutrition regimen, the use of medications as necessary, and proper rest contribute to rapid recovery and restoration of the digestive tract, including the function of the liver and gall bladder.
source
Features of preparing food for a child after vomiting
Vomiting, nausea and diarrhea lead to severe irritation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. In order for nutrients to be properly absorbed, it is necessary to observe some features of processing foods for baby nutrition.
All ingredients must be boiled, stewed, baked or steamed. Fried foods should be completely excluded from the menu for a long time.
In the first few days, all food is finely ground. This especially applies to dense foods: meat and vegetables.
Food and drink should not be cold or hot. Any canned foods and spices are completely excluded, and the use of salt is limited.
By determining what you can eat when vomiting and following the right diet, you can quickly restore the normal functioning of the body’s digestive organs and regain your good health.
Menu for the day
Example of a diet menu for 1 day:
- breakfast – rice porridge with water and milk (1:1) with baked apples;
- lunch – 2 dry toasts with tea;
- lunch - meat or fish soufflé, 2-3 tbsp. vegetable puree;
- afternoon snack – diluted juice, 2-4 biscuits;
- dinner - steam omelette of 1-2 eggs;
- second dinner – jelly or a cup of natural yogurt.
As a snack between meals, you can eat 1-2 crackers with a cup of rosehip broth.
Fish soufflé is a light but nutritious dish, useful for gastrointestinal disorders
Contraindications
Despite the wide range of beneficial characteristics of raisins, you should carefully study the list of contraindications to eliminate possible harm to health.
The use of raisin decoctions is prohibited if the following pathologies are identified:
- pancreatic diseases,
- enterocolitis,
- open form of tuberculosis,
- diabetes,
- acute heart failure.
Caution must be exercised if you are prone to obesity and have diagnosed peptic ulcers. Stop taking it if an allergy to raisins or components included in self-made decoctions is detected.