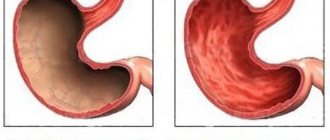
Subatrophic gastritis is an inflammatory pathology characterized by damage to the mucous membrane lining the stomach. This form of the disease is accompanied by gradual death and atrophy of the inner layer of the organ, which leads to a decrease in secretory function. Without targeted treatment, this pathological condition can create conditions for the formation of a malignant neoplasm.
Types of subatrophic gastritis
Depending on the nature of the pathological changes and the degree of damage to the gastric mucosa, this form of gastritis can be:
- antral;
- chronic;
- superficial.
Antral subatrophic gastritis is the most severe form of pathology. Superficial and chronic varieties occur with less severe symptoms.
Surface
Superficial subatrophic is characterized by damage to only the upper epithelial layer. At this stage of the pathological process, gastric juice is produced normally. The symptoms are vague, so during this period the disease is detected extremely rarely. At this stage, gastritis can be treated without medications. Often a gentle diet and exclusion of provoking factors are sufficient.
Antral
Antral subatrophic gastritis is characterized by the appearance of an inflamed defect in the area of the inlet valve, designed to separate the stomach from the duodenum. In this part of the system, the acidity of gastric juice rapidly increases.
Often this form is complicated by duodenitis, i.e. inflammatory damage to the duodenum. This is caused by the fact that the gastric glands affected by the inflammatory process begin to work too actively. Stomach juice backs up into the intestinal area, causing irritation.
A defect that occurs on the wall of the stomach penetrates into the deeper layers. It often increases due to the activity of Helicobacter pylori. Antral gastritis can occur in both acute and chronic forms. Initially, this pathological condition leads to acute symptoms. Subsequently, the process becomes chronic. This type of gastritis must be treated comprehensively. Without targeted therapy, there is a high probability of the defect transforming into a malignant tumor.
Chronic
Chronic subatrophic gastritis is characterized by infiltration of deep tissues and often becomes the cause of the development of an oncological process. With chronic gastritis, atrophy of the functional glands of the stomach occurs. This leads to a decrease in the production of gastric juice and indigestion. Damaged cells are replaced with connective tissue. The process quickly becomes diffuse, so a large part of the stomach can be affected in a short time.
Most often, this form of subatrophic gastritis develops as a result of a malfunction of the immune system. Antibodies produced in the body go astray and begin to destroy the glandular tissue of the stomach. The damage is irreversible. Increasing infiltration contributes to the spread of the pathological process to neighboring organs and tissues.
General concepts
The term “atrophy” is commonly understood as the process of loss of function and structural changes in living tissue.
Subatrophic gastritis is characterized by the destruction of glands that secrete gastric secretions. When examined, dead areas of mucous membrane are found on the internal mucous membrane. There is a gradual thinning of the walls.
The prefix “sub” indicates that the disease is at an initial stage and the development of the pathology has not yet gone far. Modern experts no longer use the term “subatrophic” to refer to progressive inflammation, considering it obsolete.
Today the disease is called “atrophic gastritis”. In the international qualification system, the disease is assigned code K29.4.
Causes
Many factors of the external and internal environment can negatively affect the state of the digestive system and cause a number of pathologies. From an anatomical point of view, the stomach is a multilayered organ. The outer layers consist of muscle and connective tissue, and the inner layers are represented by glandular cells and mucous membrane. Thanks to this structure, the organ can withstand the effects of various unfavorable factors for a long time.
Most often, subatrophic gastritis develops against the background of increased activity of Helicobacter microflora. These bacteria normally live on the stomach lining of all people. As long as the immune system controls their numbers, they do not provoke inflammation and other undesirable effects. However, under certain conditions they affect the mucous membrane and begin to multiply rapidly.
Often this phenomenon is observed against the background of poor nutrition. Inclusion in the diet of foods low in microelements and vitamins, as well as high in fats, carbohydrates, preservatives and other harmful substances, leads to a decrease in both local and general immunity, which contributes to the activation of opportunistic microflora. Violation of the diet creates conditions for the development of gastritis. Factors that increase the risk of developing this pathological condition include:
- intoxication of the body;
- smoking;
- systematic overeating;
- alcohol abuse;
- living in environmentally unfavorable areas;
- genetic predisposition;
- being in stressful situations;
- autoimmune processes;
- chronic infections, etc.
The development of subatrophic gastritis can be triggered by taking medications in the form of tablets and capsules. Many medications contain substances that have a detrimental effect on the gastric mucosa and cause the formation of foci of erosion. A special risk group for developing subatrophic gastritis includes people suffering from enterocolitis and pancreatitis.
The role of proper nutrition and diets in the treatment of illness
For gastritis, diet and proper nutrition are very important components of treatment, without which it will be ineffective.
Proper nutrition in this case implies a gentle regime for the digestive organs and activates the secretion of glands. Products considered beneficial for gastritis:
- low-fat soups;
- eggs;
- stewed and pureed vegetables;
- lean boiled meat;
- porridge;
- fruit puree;
Unhealthy foods include fried and fatty foods (dairy products, fatty meats and fish), as well as pickled foods, raw vegetables and fruits, canned food, legumes, coffee, and sweets. Spicy and salty foods are also extremely undesirable. All these foods and dishes irritate the walls of the stomach, so you should avoid them.
Alcoholic drinks and smoking should be prohibited for people with gastritis.
During an exacerbation, it is necessary to follow a diet consisting of cereals, low-fat broths and soups. Food should be of uniform consistency. On the day when the patient suffered an attack, it is better to completely refuse food. This will reduce pain and relieve the gastrointestinal tract.
The period of following the diet after an exacerbation of the disease will last about half a month. At the end of this period, it is necessary to gradually include new foods in food.
Even after some time, it is advisable to eat dishes made from soft ingredients so that they contain vitamins (especially C, E and B), animal proteins, and microelements. This diet will promote remission.
Clinical picture
In the early stages of gastritis, manifestations can be mild, so the patient often cannot independently determine what it is and what consequences relatively harmless symptoms can have. The development of such a pathology is indicated by the appearance of a white coating on the tongue and bad breath.
In addition, already at an early stage of development of the pathology, deterioration in well-being and general weakness may be observed. The patient's appetite and weight decrease. Often a person does not pay attention to these symptoms, attributing them to a temporary decrease in immunity, fatigue or mild poisoning. As the pathological process worsens, the following symptoms occur:
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- increased sweating;
- stabbing pain in the right hypochondrium;
- belching;
- constipation, etc.
Patients often suffer from apathy and depression. When deep layers are involved, the digestion process is disrupted and the absorption of nutrients is reduced. This leads to the development of anemia and the appearance of a number of other problems in the body. Possible deterioration of vision, as well as the condition of the skin and nails. If there is a severe deficiency of nutrients, hair may fall out. Some patients develop intolerance to dairy products against the background of progressive subatrophic gastritis.
Diagnostics
At the initial stage, the clinical picture of gastritis of various etiologies is poorly distinguishable. To clarify the diagnosis, a comprehensive examination of the patient is carried out, including:
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy,
- fluoroscopy;
- histological tissue;
- intragastric pH-metry;
- Ultrasound of the digestive organs,
- probing,
- laboratory tests of stool, blood and urine.
FGDS is always prescribed, as it is the most effective method of examination.
Bacteria are detected during the examination of biopsies of the gastric mucosa. In other cases, the patient is prescribed an instant urease test with urea.
Cytological examination reveals Helicobacter pylori in gastric mucus. The analysis is also carried out to identify tumor processes at an early stage. To prescribe effective therapy for a disease caused by bacteria, studies are carried out to determine the sensitivity of the gastritis pathogen to antibiotics.
Treatment
With subatrophic gastritis, the patient requires complex treatment. First of all, you need to change your lifestyle. In addition, the patient needs a special gentle diet. Depending on the nature and degree of damage to the stomach, drug therapy is selected. Additionally, some folk remedies can be introduced into the treatment regimen.
Drug therapy
For subatrophic gastritis, doctors prescribe medications to suppress the active process and restore the functioning of the stomach. In addition, medications are selected to eliminate the symptomatic manifestations of pathologies.
When identifying Chilicobacter, a combination of antibiotics such as Clarithromycin and Amoxicillin is used. If the pathogenic microflora has obvious resistance to this drug, the use of other antibiotics may be indicated. In addition, drugs are prescribed to restore the mucous membrane. De-Nol is one of these products.
Additionally, patients are given medications that activate the production of gastric juice. Rosehip decoction and mineral water have a similar effect. To normalize digestion and improve the absorption of nutrients in the intestines, enzymes are selected. These medications include:
- Pancreatin.
- Mezim.
- Festal.
In some cases, patients are prescribed antacids. Such agents include Omeprazole, Pepsan, Almagel, etc. These agents have an enveloping effect, increasing the protection of the mucous membrane from hydrochloric acid. Among other things, patients are prescribed multivitamins and iron supplements according to indications.
Nutritional Features
Therapy for subatrophic gastritis requires adherence to a strict diet. You need to eat strictly on a schedule. Food must be taken in small portions. Food should be warm. You cannot eat anything that is too hot or cold. Adjusting the diet involves including in the patient’s diet such foods and dishes as:
- kefir;
- cottage cheese;
- slimy porridge;
- chicken bouillon;
- vegetable soups;
- stew;
- non-acidic fruits;
- lean meat;
- boiled fish;
- weak tea;
- jelly;
- mashed potatoes;
- unhealthy baked goods;
- cocoa with milk;
- compotes, etc.
It is recommended to boil, steam or bake food. It is not advisable to add a lot of salt and spices. Gastritis imposes great restrictions on the selection of products and dishes. Prohibited use:
- yeast baking;
- garlic;
- legumes;
- cabbage;
- meat with veins and cartilage;
- strong meat and vegetable broths;
- chocolate;
- strong coffee;
- canned food;
- pickles;
- mushrooms;
- smoked meats;
- semi-finished products;
- fried foods, etc.
If you have gastritis, you should avoid drinking alcohol. Even a small amount of alcohol can make the condition worse.
Folk recipes
Formulations based on medicinal herbs and natural components can be used as therapeutic aids in addition to drug treatment and diet. Before using any traditional recipes, you should consult a doctor. To suppress the inflammatory process in the stomach during gastritis, it is recommended to use a decoction of the following herbs:
- thyme;
- yarrow;
- rose hip;
- dill;
- sagebrush;
- St. John's wort.
To prepare a healing drink you need to take 1 tsp. selected herb and pour 1 cup of boiling water. Then the composition must be put on fire and boiled for 2-3 minutes.
In addition, an infusion made from mint, plantain and chamomile leaves can be of great benefit. All components need to be taken 1 tbsp. l. They must be thoroughly crushed and mixed. Then the collection is poured with 250 ml of boiling water and left in a thermos for 1 hour. After this, the composition is filtered. The finished product should be consumed 3-4 times a day, 70 ml. It is advisable to drink the product 1 hour before meals. You should be treated with this composition for 30 days.
For gastritis, it is also recommended to use a composition based on oat grains. To make this remedy, you need 2 tbsp. l. pour 500 ml of boiling water of this herbal ingredient. After this, the composition is thoroughly mixed. The container is covered with a lid and insulated with a towel. In this position, the product is infused for 6 hours. Then the product must be strained and drunk ½ glass 30 minutes before meals 3 times a day. The product must be treated for at least a month.
Some traditional healers for subatrophic gastritis recommend taking fresh potato juice on an empty stomach. To obtain it, the root vegetable should be thoroughly washed and grated on a fine grater. Then the juice is squeezed out of the pulp. You need to drink 50 ml per day. The juice should not be stored. The course of treatment with this remedy is 20 days. Potato juice will help reduce the acidity of gastric juice.
Diet
Treatment of atrophic gastritis necessarily includes diet. For this disease, patients are shown table 2 according to Pevzner. The following are excluded from the menu for this disease:
- fresh bread,
- baking,
- soups and porridges with milk,
- legumes,
- fatty dairy products,
- smoked meats,
- pickles and preserves,
- mushrooms,
- fresh onion,
- rutabaga,
- radish,
- marinades,
- fish and meat with high fat content,
- kvass,
- grape juice,
- dates,
- figs,
- gooseberry,
- currants
- millet,
- pearl barley, corn and barley grits.
Spicy seasonings and sauces, fried foods, and hard-boiled eggs are contraindicated. It is recommended to exclude chocolate confectionery, cream cakes, coffee, and strong tea.
On our website: How to cure erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis?
The Pevzner diet allows the use of:
- dried bread,
- biscuits,
- soups with a weak broth of vegetables, poultry and fish,
- cranberry juice,
- lean types of meat (rabbit, lamb, veal),
- boiled or steamed lean fish,
- fruit, berry and vegetable purees without additives,
- turkey and chicken meat,
- fermented milk products with minimal fat content,
- vegetable and butter,
- eggs in the form of an omelet, steamed or soft-boiled,
- beets,
- potatoes,
- zucchini,
- cauliflower,
- green peas, fresh or frozen,
- carrots,
- ripe tomatoes and cucumbers.
It is allowed to eat rice, oatmeal, semolina or buckwheat porridge with water. You can season dishes with dill and parsley, cinnamon, and vanilla.
It is better to add lemons or oranges to tea, sauces, and infusions. Allowed sweets include marshmallows, marshmallows, jam, honey, and jelly marmalade.
Sample menu for table No. 2
1st day
Breakfast: mashed potato tubers in water, steamed fish, mint tea. Snack: fruit jelly. Lunch: chicken broth with noodles, baked pumpkin, cranberry jelly. Afternoon snack: rosehip decoction. Dinner: cheesecakes, tea with lemon, a spoonful of honey.
2nd day
Breakfast: steamed omelet, cocoa, biscuits. Snack: rosehip decoction with honey. Lunch: mashed potato soup with chicken meatballs, zucchini casserole with minced turkey, dried apricot compote (without berries). Afternoon snack: baked apples. Dinner: cottage cheese seasoned with sour cream and honey, tea with mint and chamomile.
3rd day
Breakfast: sticky rice porridge, green tea with a slice of orange. Snack: raspberry jelly. Lunch: vegetable cauliflower soup seasoned with cream, minced chicken soufflé with stewed zucchini, compote. Afternoon snack: baked pumpkin with honey. Dinner: boiled potatoes, steamed fish, cocoa.
4th day
Breakfast: 2 eggs, lean ham, rose hip decoction. Snack: blueberry jelly. Lunch: pureed carrot soup with rice, steamed meatballs with buckwheat in white sauce, green tea. Afternoon snack: apples baked with honey. Dinner: baked chicken breast with zucchini puree, cocoa.
5th day
Breakfast: boiled diet sausages, semolina pudding, tea. Snack: apple juice. Lunch: chicken broth, cauliflower and zucchini puree with veal, tomato juice. Afternoon snack: toast with jam, tea. Dinner: baked buckwheat pancakes, pear jelly.
6th day
Breakfast: viscous buckwheat porridge, cocoa. Snack: blueberry jelly. Lunch: vegetable puree soup with chicken broth, turkey cutlets with potatoes, apple compote. Afternoon snack: green tea, marshmallows. Dinner: boiled tongue with zucchini puree, tomato juice without salt.
On our website: Chronic erosive gastritis: symptoms, treatment, diet
7th day
Breakfast: oatmeal, egg, tea with rosehip. Snack: fruit juice. Lunch: vegetable soup with meatballs, baked turkey steak, jelly. Afternoon snack: chamomile tea with marmalade. Dinner: buckwheat, steamed cutlets, tea with lemon.
Before going to bed, it is recommended to drink a glass of yogurt or kefir. Berry fruit drinks and fresh juices will help replenish your diet with vitamins.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention of subatrophic gastritis. To prevent the development of this pathological condition, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle. You need to follow a meal schedule. It is advisable to give preference to steamed, stewed or boiled dishes.
Stressful situations should be avoided. In addition, you need to get at least 8 hours of sleep at night. It is imperative to observe the rules of personal hygiene. The presence of chronic foci of bacterial and viral infection should not be allowed. Such diseases need to be identified and treated promptly. It is necessary to undergo regularly scheduled examinations to ensure timely detection of pathology.
What do patients complain about?
With minor lesions of the mucous membrane, there may be no complaints at all, or they are insignificant: heaviness after eating, belching of air. If multiple areas are involved in the pathological process, then clinical symptoms become more obvious.
With atrophy of the gastric glands and thinning of the mucosa, a decrease in the secretion of HCL and pepsinogen is observed, and the production of gastric juice decreases. And patient complaints will indicate this:
- the appearance of a feeling of fullness in the stomach after eating a small amount of food, heaviness, dull pain in the epigastrium
- belching either air or rotten
- loss of appetite
With low production of gastric juice and a low content of hydrochloric acid, carbohydrates entering the stomach do not undergo sufficient breakdown and quickly enter the small intestine, being actively absorbed there. This causes the following symptoms to occur: after eating, weakness, sweating and even dizziness develop.
With large subatrophic lesions, vitamin B-12 is not absorbed on the atrophically changed mucosa. Symptoms indicating B12 deficiency anemia occur:
- “jams” in the corners of the mouth
- hair loss, brittle nails
- pale skin
Superficial diffuse gastritis
If the inflammation covers only the superficial layer of the stomach, even with a chronic course, the disease responds well to treatment. Medication therapy and a balanced diet contribute to long-term remission. The risk of progression to severe forms is minimal and depends entirely on the patient’s habits and behavior.
However, it is not always possible to begin treatment of a common superficial process on time, because in the initial stages the disease does not manifest itself in any way. The patient associates rare dyspeptic disorders with overeating or, on the contrary, a strict diet, stress, lack of sleep and other circumstances, and does not consult a doctor.
With this approach, there are no obstacles to further progression, and diffuse inflammation begins to invade the deeper layers of the mucosa. Over time, superficial inflammation transforms into another form - diffuse subatrophic gastritis.
Nutritional Features
The presence of a disease is always the basis for changing the system and quality of nutrition. This is also relevant in the case of the development of subaternal gastritis.
It is acceptable to eat vegetarian soups, low-fat fish, and white bread. Porridge and non-sour fruits are healthy. You should avoid eating food with temperatures above 60 °C and below 15 °C - this causes intense irritation of the gastric mucosa. Excessive consumption of food and deviation from the established system are prohibited.
Laboratory research
Many diseases have symptoms similar to those of gastritis, so the attending physician may conduct additional examinations to differentiate the pathology. The diagnosis of antral subatrophic gastritis is established on the basis of a combined study:
- biochemical blood tests will reveal the presence of iron deficiency anemia (low hemoglobin and erythrocyte sedimentation rate) or vitamin B12 deficiency;
- an increase in the level of serum gastrin, a decrease in pepsinogen in the blood serum indicates the presence of antral subatrophic gastritis;
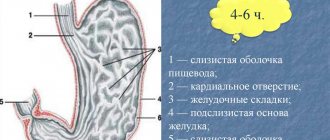
- performing endoscopy of the stomach is the most informative diagnostic procedure: if the patient’s subatrophic gastritis is already in a chronic form, the natural folds in the proximal stomach will be atrophic, while the tissues of the distal or antral stomach may remain unchanged;
General recommendations
Gastritis requires complex therapy, including not only medication, but also diet, proper rest, and physiotherapeutic treatment. It is important to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, minimize alcohol consumption, and give up cigarettes.
Uncontrolled use of medications is also dangerous for gastritis. Before using any remedy, you should consult your doctor.
The patient's meals should be regular. Overeating is not allowed. The volume of food absorbed does not exceed the size of the stomach. Recommended serving weight is 200-250 grams.
Food is taken 4-6 times a day, in a calm environment, chewing each piece thoroughly. You should not eat food that is too hot or cold.
source