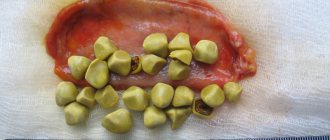
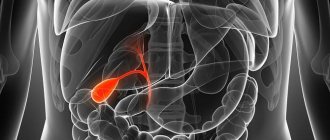
Gallstone disease is a common chronic disease that affects adults. In terms of frequency of occurrence, it comes after cardiovascular pathologies and diabetes mellitus. Among the reasons, there are a number of factors, which include hereditary predisposition, taking certain contraceptives and increased cholesterol levels. Removing stones from the gallbladder is one of the effective ways to combat the disease.
Diagnosis of gallstone disease, its symptoms and causes
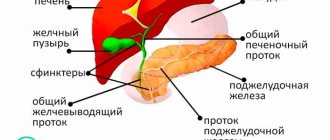
Gallstone disease develops over a long period of time. It takes 5-10 years from the initial stages of stone deposit formation to the first symptoms. This can be explained by the fact that a person does not feel the presence of stones. It is worth learning about symptoms and treatment in advance. The appearance of pain indicates that stones have entered the bile ducts, which begin to be injured. The common bile duct drains digestive fluid from the bile duct to the duodenum. It can become clogged with a stone, which will cause stagnation of bile.
The first symptoms of pathology include:
- yellowing of the skin, sclera, oral mucous membranes,
- a feeling of bitterness in the mouth is one of the main signs of bile stagnation,
- nausea, heaviness in the stomach - these sensations persist even after vomiting,
- pain in the right hypochondrium.
Such symptoms indicate the passage of stones from the gallbladder. At the same time, it is dangerous to leave them unattended. In some cases, there is a stone impacted into the neck of the gallbladder. There are also main symptoms of the disease:
- Liver colic.
- Vomit.
- Weakness.
- Diarrhea.
- Yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyes.
Additional symptoms include fever, increased sweating, discoloration of stool, pain in the liver, and cramps. Symptoms are expressed depending on the location of the blockage of the bile ducts. If a gallstone does not bother you, this does not mean that it does not need to be removed. This may harm the patient's health.
The reasons why gallstones form in the gallbladder include:
- stagnation of bile or its high concentration,
- disruption of metabolic processes,
- hepatitis,
- anemia,
- pathologies of the structure of the gastrointestinal tract,
- dyskinesia of the bile ducts (disturbances in the functioning of the bladder and its ducts),
- insufficient functioning of liver cells,
- scars, adhesions or neoplasms of the bile ducts,
- development of infection.
Large stones are called stones from 2 mm. They can only be removed by abdominal surgery. This operation is performed for acute cholecystitis. Factors contributing to the development of gallstone disease:
- unhealthy diet
- being overweight
- allergy,
- sedentary lifestyle,
- pregnancy,
- age after 70 years,
- taking certain medications, which include estrogens, contraceptives, fibrates (lowering cholesterol levels),
- eating hot, spicy and fried foods,
- gender – the risk of cholelithiasis in women is higher,
- hereditary factor.
Gallstone disease is diagnosed in several ways. The appearance of symptoms is related to the number of stones. There are the following examination methods:
- anamnesis - collecting information from the patient’s words,
- MRI,
- bile and blood analysis,
- radiography,
- oral cholecystography - the patient first drinks a contrast agent, and then he is given an x-ray.
Modern medicine makes it possible to remove stones from the gallbladder quickly and safely.
Causes
An increase in the diameter of the canals occurs due to a weakening of the tone of their walls or the presence of foreign bodies inside. This is rare in congenital cases and is called Caroli's disease. With it, dilation of the large intrahepatic bile ducts is observed.
If the disease is accompanied by changes in small pathways and liver fibrosis, Caroli syndrome occurs. It is caused by genetic disorders and is inherited. There is also an increase in the diameter of extrahepatic canals – common bile duct cysts.
With the hypotonic form of dyskinesia, the tone of the entire biliary tree decreases, which complicates the passage of bile.
The disease can arise for completely different reasons: due to hormonal imbalance, frequent nervous tension, unhealthy lifestyle, allergies, and parasite activity. Dyskinesia often develops as a complication of another ailment.
Foreign bodies in the tracts also contribute to an increase in their lumen. This occurs with the following ailments:
- Choledocholithiasis is a gallstone disease. They enter the ducts mainly from the bladder, although the formation of stones directly inside is possible. Most often it occurs due to infectious inflammation of bacterial etiology.
- Helminthic infestations - expansions appear in places where parasites accumulate. The most common are: echinococcus, various types of flukes (Siberian, lanceolate, Chinese, liver), Giardia. Ascoridosis invasion is a rare phenomenon, observed when the patient is significantly weakened in advanced stages.
- Neoplasms – papillomas, adenomas, polyps, cancerous tumors. Usually formed at the bottom, as they grow, they expand the lumen of the channel on both sides of themselves.
Tumors, stones, and accumulations of worms can clog one of the segments of the biliary tract. The closed bile bursts the ducts and returns back to the liver.
During inflammation, the channels also expand. This provokes the development of different types of cholangitis. Its characteristic signs: fever, pain under the right rib, jaundice are called Charcot's triad.
There is a physiological increase in the diameter of the tracts that does not require correction. This occurs after cholecystectomy. A person needs bile occasionally, during meals.
Its reserve is contained in the bladder and, if necessary, is excreted into the duodenum, where it promotes the disinfection and digestion of food and the absorption of nutrients.
After the organ is removed, the duct system takes over its functions and expands to accommodate the required supply of fluid.
How to get rid of gallstones
The disease does not manifest itself in any way until a late stage. The patient may not suspect a problem until a certain point. Therefore, emergency surgery is often required. Since stones from the bladder begin to spread throughout the internal organs and scratch their walls, inflammatory processes are possible. This explains why it is worth starting treatment after the first signs appear. Removal of stones from the gallbladder is carried out in accordance with the patient's condition.
Often, patients diagnosed with gallstones go to the doctor only after severe biliary colic appears. High fever and nausea may occur. The sclera of the eyes may turn yellow. Your doctor will help you figure out how to remove stones.
If the patient does not seek help for a long time, dangerous complications may arise. As a result of inflammation, ailments such as pancreatitis, cholecystitis and duodenitis appear. There are several ways to remove gallstones.
Therefore, the fight against gallstone disease should be started in a timely manner. The sooner a patient visits a doctor, the higher the chance of curing the disease without abdominal surgery to remove gallstones. You can get rid of stones in three modern ways:
- drug treatment (when small particles dissolve in the gallbladder),
- crushing (without removing the gallbladder) produces many small fragments,
- surgery - through punctures or an incision.
The first option includes not only the use of drugs, but also ultrasound lithotripsy. In this case, no internal intervention is carried out. This method of removing stones from the gallbladder is effective only when the diameter of the stones is small and their number is small. Can a stone dissolve on its own? Without the use of special tools this is unlikely.
A laser is used in the crushing process . This is a minimally invasive method. In case of emergency, surgery will be prescribed. The method for removing stones depends on the condition of the organ. Sometimes laparoscopy helps (gallbladder stones are removed through punctures); in others, abdominal surgery is required. Your doctor will help you figure out how to get rid of stones.
Before any operation, a thorough examination is carried out. It is important to make a diagnosis and find out what type of stones are located in the gallbladder.
They may differ significantly in composition. This is important to know when a doctor prescribes medication. If medications are ineffective (when stones do not disappear), laser or ultrasound is prescribed. In advanced situations, stones are removed through surgery. This is the only way to remove large gallstones.
Surgery to remove stones while preserving the gallbladder
There are several methods for removing gallstones. However, not all allow the preservation of an organ capable of functioning normally. The operation to get rid of gallstones is designed to relieve the patient from disturbances in the digestive tract. Among the ways to keep an organ are:
- laparoscopic - this is the name of the method in which no incision is made,
- laparotomy - when an incision is necessary.
Endoscopic surgery to remove gallstones (laparoscopy) is now increasingly used to treat gallstones. This method of treatment requires certain qualifications, as well as the use of special equipment.
The operation is performed using a laparoscope. The surgeon makes a puncture in the abdominal cavity, then inserts an endoscope there and monitors the progress of the operation on the screen.
Laparotomy is performed by making an incision on the anterior wall of the peritoneum. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. This method is considered classic. During the procedure, the surgeon is given the opportunity to examine nearby organs and understand whether they have pathologies. This operation is prescribed if the gallbladder is located atypically, which requires caution during the manipulation process. If the procedure is performed without an incision, organ rupture and liver pathology are possible. A large fragment can get stuck in the bile duct, so crushing is carried out when the diameter of the stones is no more than 2 cm. To eliminate the problem, an operation is performed to remove the stones using the cavity method .
Advantages and disadvantages
Removing stones while preserving the gallbladder has several pros and cons. The advantages of laparoscopy include safety and a small number of contraindications. The method is less traumatic, and there are no cosmetic defects left on the skin. It can be performed without general anesthesia. The disadvantages of laparoscopy include the complexity of the operation and the need for highly qualified surgeons.
Possible consequences
Any operation on the gallbladder to remove stones, be it a conservative treatment method or an invasive one, can be associated with unpleasant consequences for the patient’s body.
Possible risks can be divided into 2 main groups:
Associated with stone crushing:
- injury to the walls of the bladder with sharp edges of fragments,
- blockage of the duct with large stones,
- damage to the bladder with surgical instruments,
- laser burns,
- relapses as a result of organ-saving procedures,
General operating rooms:
- rupture of postoperative sutures,
- pain syndrome,
- infectious processes,
- bleeding.
Complications after stone removal are quite rare.
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy of the gallbladder
This method of removing stones from the bile ducts began to be used in 1968. Until today, this method of treatment is practiced mainly by German doctors. It can be found much less often in other countries. For example, in the USA there is no official permission for this operation.
Crushing is carried out by exposing the stones to the energy of shock waves. With a parabolic reflector, energy is focused on the stone. At a certain point the energy becomes maximum. The result is to break the stone - it splits into many small fragments. The stones in the gall bladder are crushed, and the resulting sand and small stones are released through the ducts.
Small particles are removed through the cystic duct. Then, through the common bile ducts, they rush into the intestines. Larger fragments that are unable to pass through the cystic duct remain. The effectiveness of the operation can be increased by the use of bile acids, which dissolve the remaining stones. Ultrasound lithotripsy is possible for medium-sized stones.
Advantages and disadvantages of using ultrasound
The main advantage of the technique is the ability to remove stones without punctures or cuts. This allows you to significantly shorten the recovery period and has a positive effect on the general condition of the patient. However, there is a possibility of not getting the desired result. This is especially true in cases where the stones are too large.
The stone may fragment into smaller ones, but also unable to pass through the bile ducts. In the worst case, their lumen will become clogged, which will lead to obstructive or subhepatic jaundice.
The main disadvantage of this method is the high risk of relapse. The stones may appear again. After 5 years, the relapse rate is 50%.
Laser crushing of stones
The use of this method of treatment involves creating a puncture to access the diseased organ. A laser beam is introduced into the action area, and then the stones are split. The procedure lasts 20 minutes. This method is similar in technology to ultrasonic crushing.
Contraindications to crushing gallstones:
- the patient's weight is more than 120 kg,
- serious condition of the patient,
- patient over 60 years old.
Laser removal of medium-sized gallstones is called lithotripsy. It is effective if cholesterol stones are found.
Laser crushing of gallstones is increasingly used in medicine. It happens that surgical intervention is impossible. In this case, laser treatment is used. It becomes relevant if general anesthesia fails.
For patients with lung and heart diseases, gallstones are crushed with a laser. This allows you to completely remove stones from the organ while maintaining its functionality.
Laser crushing of stones is carried out at the moment when the beam reaches the stone. First, the doctor needs to make a puncture at the location of the organ. All actions are visible to the surgeon on the screen. A catheter is then placed (with a laser placed on it) to break up the gallstones.
Through the puncture, the beam crushes the stones. Then the crushed stones are removed through the bile ducts. Removing stones from the gallbladder with a laser lasts half an hour . The patient does not require hospitalization.
Before receiving a referral for stone removal, the patient undergoes a full examination. Sometimes the patient is in the hospital, preparing for laser crushing. This applies to older people and children. Additionally, maintenance therapy may be provided. Laser stone removal is a painless procedure.
Advantages and disadvantages of using laser
Crushing gallstones with a laser is a modern technique that allows you to remove stones from the body without performing abdominal surgery. Using a laser makes it possible not to completely remove the organ.
Among the main advantages of laser crushing of gallstones are:
- the possibility of not using general anesthesia,
- minimum contraindications and complications after surgery,
- painlessness of the procedure,
- this method is bloodless and gentle.
The number of possible deviations is reduced to a minimum . After the operation, the patient recovers within a few days.
The disadvantages of the procedure include:
- the possibility of a burn to the mucous membrane, which can cause an ulcer,
- injuries to the walls of the gallbladder - occur when stones move,
- the need to use high-tech equipment.
This method is quite effective and painless.
How to avoid relapse?
Removing gallstones does not solve health problems.
Source of vitamins and minerals
Enter in menu
In order to protect yourself from a new operation, you must:
- Fractional meals. The formation of stones is facilitated by long intervals between meals, since in this case less bile acids are produced.
- Watch your weight. The greater the body weight, the higher the risk of stone formation. Avoid sudden weight loss.
- Avoid refractory animal fats, smoked meats, coffee, cocoa, marinades, and pickles.
- Eat lean meat and fish (boiled and steamed).
- Avoid rich and fatty broths.
- Limit consumption of simple carbohydrates.
- Avoid dehydration (recommended amount of fluid per day is 2 liters).
- To live an active lifestyle. Walking and playing sports help combat bile stagnation.
Prohibited!
Give it to the enemy!
Food should be rich in pectins. This will help improve intestinal motility and remove toxic substances from the body. Products with a high content of magnesium are useful, which eliminates spasms of the biliary tract and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Precious gift of nature
Essential products:
- bran;
- oatmeal and buckwheat porridge;
- low-fat fish varieties (rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, which have a lipotropic effect);
- seafood (contain iodine, which helps bind cholesterol);
- pumpkin and sunflower seeds (a source of magnesium and vegetable oils);
- alkaline mineral waters;
- beets, pumpkin, carrots (rich in pectins);
- dairy products (alkalize bile, which prevents the formation of stones).
Self-discipline will help you maintain your health for many years.
Removing gallstones through the mouth
The essence of this treatment method is to insert a thin probe through the mouth and stomach, and then into the duodenum. A contrast liquid is applied to the obstruction that is stuck in the duct and an image is taken. This is necessary to determine the cause of jaundice. Often its source is a stone that is stuck in the duct. Removing stones through the mouth is a fairly common way to combat gallstone disease. The procedure can be seen on video.
Less commonly, a polyp or tumor is detected. If the cause of the blockage is a stone, the surgeon can use special instruments to crush it directly in the duct itself. Then a second photo is taken to ensure that the bile is flowing normally through the duct. The disadvantage of this method is that if large stones are detected, abdominal surgery will have to be performed.
Advantages and disadvantages of oral removal
The advantages of the operation include painlessness, because it does not require an incision. The procedure is carried out quickly, and the patient does not need to go to the ward for several days.
However, this method is not suitable for everyone . There are several complications and unpleasant consequences. The method is contraindicated for obese people suffering from cardiovascular diseases and problems with the respiratory system. Removal without an incision is not carried out for those who have large stones (more than 2 cm in diameter).
Recovery and rehabilitation after removal of gallstones
Once the stones are removed from the gallbladder, it is important to follow certain activities for 4-8 weeks. These actions will ensure normal liver function. Under normal conditions, the liver produces 600 to 800 ml of bile every day. This amount goes to the gallbladder for storage. When the bolus of food approaches the duodenum, the accumulated bile begins to be released into it.
If abdominal surgery was performed, the patient should not move after recovery from anesthesia for at least 6 hours. Then you are allowed to rise and turn around. On the first day, it is forbidden to eat. Only still water is allowed. On the second day you can drink jelly or low-fat kefir.
For 3-4 days you are allowed to eat vegetable puree, some boiled meat and lean fish. This diet is followed for the next 4 days. Then the patient switches to fractional meals. Meals should be frequent. It is unacceptable to eat fried foods. The products are crushed and heated until warm.
During recovery (rehabilitation) after stone removal, the following is excluded from the diet:
- fish, meat, canned vegetables,
- roast,
- smoked products,
- pickles and marinades,
- spicy,
- offal,
- mushrooms,
- bread - rye and white,
- green peas, raw vegetables.
This diet should be discussed with your doctor.
Preparation for surgical treatment
Before carrying out measures to remove gallstones in the gallbladder, preparatory manipulations are carried out. As prescribed by the doctor, laboratory diagnostics are carried out, including the following tests:
- blood chemistry;
- clinical examination of urine and blood;
- clotting and electrolyte analysis;
- the acid-base state of bile is established.
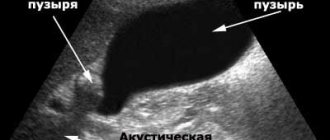
An ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is performed. It will allow you to determine whether it is realistic to save the gallbladder or whether it is necessary to remove the stones along with the gallstone.
If the patient takes any medications on an ongoing basis, he should notify the doctor about this. Prescribed antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants are discontinued.
The patient must follow general rules of conduct before surgery:
- 3–5 days before the expected date, reduce physical activity;
- the patient's nutrition should be complete and fractional;
- Alcohol must be excluded;
- two days before surgery, the amount of food taken is reduced;
- 12 hours before the process it is forbidden to drink and eat, this is due to the need to use general anesthesia;
- Immediately before the operation, the patient is given an enema and urine is removed using a catheter.
If the patient is restless, administration or oral administration of sedatives is indicated.
Where can I remove gallstones and how much will it cost?
In Moscow, the operation costs from 24 thousand rubles. For example, when contacting the Cosmeton clinic, the price can reach up to 60 thousand. There are quite a lot of average offers up to 30 thousand. There are clinics that remove gallstones from the gallbladder in most large cities:
- Penza,
- Saratov,
- Vladivostok,
- Saint Petersburg.
You can find many worthy offers from private clinics. You can figure out how much the procedure costs after a consultation at the chosen institution. The cost of laser gallstone removal can vary greatly depending on the region.