Basic information
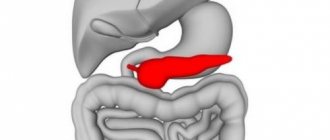
The pancreas in children and adults is the most important organ of the digestive system, which is located deep inside the abdominal cavity.
According to experts, the pancreas consists of several types of tissue and, due to its anatomical location, is characterized by rather difficult access. Therefore, it is impossible to diagnose inflammation of this organ by palpation. At the same time, the presence of any problems with it can only be detected based on the results of ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging.
Diagnosis and treatment of pathologies
Diagnosis begins with a detailed clarification of complaints, anamnesis, and objective examination.
Clinical signs of tail damage in all pathologies are similar to diseases of the entire pancreas. Symptoms of tail inflammation manifest themselves with the same symptoms as pancreatitis, which affects the entire gland:
- pain localized in the right hypochondrium or in the epigastric region, with irradiation to the precordial region, lower back,
- loss of appetite,
- bowel disorders,
- temperature increase.
Tumors, cysts, lipomas, fibromas, hemangiomas do not manifest themselves clinically for a long time. Symptoms occur when these formations reach enormous sizes.
It is impossible to determine the enlargement of the tail of the pancreas during an objective examination: due to its retroperitoneal location, it is not palpable. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of changes in the tail part, it is necessary to contact a specialist to prescribe special laboratory and functional examination methods.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the identified pathology. If the tail of the pancreas is enlarged, the underlying disease is treated. Methods also depend on changes: surgical treatment is used in the presence of neoplasms, both malignant and benign. Sometimes surgical treatment is used for abscesses, huge cysts, and pseudocysts. For inflammatory lesions, pancreatitis is treated.
Diagnostic methods
Screening methods include ultrasound examination (US), which has received positive feedback from doctors of various specialties. Sonography is convenient because it does not require complex preparation, takes little time, and is well tolerated by both children and elderly people. Using this technique, the following are determined:
- sizes,
- presence of formations,
- clarity of boundaries,
- increased or decreased echogenicity (density) of tissues,
- condition of the Wirsung duct.
When performing sonography, in some cases the tail of the altered pancreas is not located. It may be partially and inconsistently visualized. According to the literature, the detection rate of the pancreatic tail on echography is approximately 40-100%. It is better to locate the significantly enlarged tail part of the organ, especially when there are large echo-positive formations in it.
Therefore, additionally:
- MRI,
- radiography,
- CT with contrast agent,
- cholangiopancreatography (endoscopic and magnetic resonance),
- EFGDS (esophagofibrogastroduodenoscopy).
Laboratory research methods include:
- a general blood test to determine the presence of inflammation (increased ESR, leukocytosis),
- sugar in blood and urine,
- during an attack of insulinoma - insulin in the blood,
- glucagon,
- fasting blood test for gastrin.
All studies are prescribed by a doctor, who analyzes what their results may mean, and based on them, medications are prescribed to treat the identified pathology.
First aid when identifying signs of disease
Tail enlargement can become acutely manifest when there is a pronounced inflammatory process and developing pancreatic necrosis. Intense pain occurs, there may be vomiting and diarrhea. Necessary:
- call an ambulance immediately,
- Before her arrival, place the patient on his side with his knees bent to his stomach - this can reduce pain,
- create complete peace, comfortable conditions,
- apply a heating pad with ice to your stomach,
- observe hunger (you can only drink warm mineral alkaline water without gas),
- give an antispasmodic tablet if there is no severe vomiting (No-Shpu, Drotaverine, Papaverine), painkillers are prohibited.
In case of hyper- or hypoglycemic coma (with glucagonoma or insulinoma), the patient also needs emergency care.
How to treat the tail of the pancreas?
Treatment tactics for an enlarged pancreatic tail depend on the identified pathology. For pancreatitis, a course of drug therapy is prescribed. Its goal is to restore the functions of the organ. If the clinical picture is severe, inpatient treatment is required using a complex of several drug groups:
- antispasmodic, anticholinergic drugs, analgesics - pain relief,
- protease inhibitors – reduce the activity of aggressive pancreatic enzymes,
- somatotropin (growth hormone produced in the pituitary gland) – limits the area of necrosis,
- drugs from the group of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) - reduce the production of hydrochloric acid, which stimulates the synthesis of pancreatic enzymes,
- antibiotic – to treat or prevent infection,
- detoxification solutions,
- detoxification - neutralization of toxins formed during cell breakdown.
In some cases, if there are formations in the tail of the pancreas, surgical intervention is indicated. Minimally invasive medical technologies developed in recent years lead to maximum preservation of the organ itself and its functions, reduction of complications, and reduction of rehabilitation time. Their use improves prognosis and quality of life. For tumors, laparotomy and lumbotomy (with opening of the retroperitoneum) techniques are often still used.
False alarm
It should be especially noted that if the pancreas is enlarged in a child, this does not always indicate a serious pathology. The fact is that this organ has separate sections (for example, the tail, body or head), the sizes of which may be non-standard due to the peculiar reaction or characteristics of a particular organism, including in the case of a congenital anomaly that does not pose a threat to life sick.
It should also be noted that sometimes it is possible to misdiagnose a pathological condition such as an increase in the size of the body of the pancreas or its tail. To make a more accurate diagnosis, you should undergo not only a laboratory examination, but also an instrumental one.
A little about enzymes
If babies or older children have symptoms of flatulence, then taking enzymes would be a good idea. They improve digestion and facilitate the functioning of the pancreas.
Currently, the pharmacy has a wide selection of these drugs. But you shouldn’t rely on the advice of your friends; it’s better to listen to your doctor and buy the remedy he prescribed. Most often, experts prescribe the following medications:
- Creon;
- Festal;
- Enzistal;
- Pancreatin forte;
- Panzinorm.
You must take the enzyme at every meal. When the child’s health becomes better, it will be possible to correct intestinal problems. In this case, fermented milk products and special medications containing bifidobacteria, such as Bifidumbacterin or Bifacil, can help. Thanks to these measures, the child’s digestion will not only normalize, but the size of the pancreas will also decrease.
If the child is healthy, then his development, both mental and physical, will not suffer. Much depends on the baby’s nutrition. If his diet contains healthy foods, and parents control their child’s diet, then problems with the pancreas will not arise. If the organ is already enlarged due to congenital pathologies, then it is better to contact a specialist who will help in resolving this issue.
Enlarged pancreas of a child: reasons
Treatment of this abnormal phenomenon should be carried out only after consultation with a doctor. It is also necessary to identify the causes of this pathology.
Modern medicine knows 2 types of enlargement of the organ in question:
- local;
- total.
The first type is characterized by a proportional process, and with the second, an increase in any one area of the internal organ is observed.
So why is the pancreas enlarged in a child? The reasons for this phenomenon are manifold. However, the most common of them include:
- mucosal ulcer;
- closed types of injuries to organs located in the abdominal cavity;
- a consequence of exposure to various toxins;
- autoimmune processes;
- acute or chronic inflammation;
- cystic fibrosis;
- diseases of the duodenum;
- abnormal development of the pancreas.
When does pathology appear?
Everything in the human body is interconnected. And the pancreas not only ensures normal digestion, but itself depends on the general state of health. Its work is especially strongly influenced by the nature of nutrition, hormonal levels and the psychological state of the child. Therefore, there are several important periods for the pancreas of children when it is most susceptible to pathologies. This is the time when the child’s diet changes and serious changes occur in his life. In this case, the pancreas often enlarges.
This can happen when introducing the baby’s first complementary foods or when switching to artificial feeding, as well as when introducing new foods. If such a change in diet is accompanied by nausea, frequent vomiting, or changes in behavior, you should be examined by a doctor as soon as possible. This will help to detect in time that the child has an enlarged pancreas.
A similar state can also be observed during severe emotional upheavals. For example, when adapting to kindergarten or entering school. At this time, children are often capricious and eat poorly. In addition, the pancreas can be enlarged in adolescents. This is most often due to hormonal changes in the body or a violation of the diet.
If complementary foods are introduced incorrectly or untimely, the baby's pancreatic function may be impaired.
Reasons for the disproportionate increase
Enlargement of the head of the pancreas, its body or tail can also be caused by completely different reasons. As a rule, these include the following:
- the occurrence of a true or false cyst;
- tumors of various origins (can be benign or malignant);
- development of abscess and suppuration of the pancreas;
- replacement of some areas of glandular connective tissue;
- blockage of Wirsung's ducts.
Treatment of enlarged pancreas in children
If there are problems with the pancreas, the child must be examined in a hospital.
Before starting treatment, you should examine the pancreas and conduct an ultrasound examination, which will help determine the type of pancreatitis. Very young children should have a blood test to check for digestive enzymes.
If the organs of the digestive system are enlarged, treatment takes place in a hospital under the strict supervision of doctors. Children are required to follow a strict diet during the first two days after an exacerbation. On these days you are allowed to drink only still water. When the pain begins to subside, the baby is gradually introduced to food following a diet that should be followed for six months.
To reduce pain and reduce toxic substances entering the blood, the patient is prescribed medications. In extreme cases, when the pain is too severe, the baby is prescribed narcotic analgesics, which are administered intravenously, intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Take the tablets orally when the pain decreases. Even when your baby's diet consists entirely of food, he should still take medications to reduce pancreatic enzymes, which help food digest. If pancreatitis is complicated by cysts or abscesses, then antibiotics are prescribed according to a special regimen that the doctor will tell you.
To alleviate the condition, use herbal infusions.
Folk remedies can help cope with the inflammatory process of the pancreas, the use of which should be agreed with your doctor. Traditional therapy is based on taking infusions and decoctions of herbs, which can be made with your own hands or purchased in pharmacy chains. You can use herbs provided they are fully tolerated, there is no allergic reaction and depending on the stage of the disease. Recipes for relieving the inflammatory process in the digestive organs are as follows:
- Tincture of string, elecampane and mint. For cooking you will need 3 tbsp. l. herbs and 400 milliliters of boiling water, which is poured over the collection. Leave the broth to simmer for 5 minutes, then let it brew. The tincture should be consumed in the morning and evening before meals.
- Tincture of sage, wormwood, St. John's wort, calendula, string, chamomile and elecampane. A pinch of herbs is poured with 200 milliliters of boiling water and left to infuse. Drink the tincture in the morning, at lunch and in the evening before meals.
- A decoction of three parts of mint leaves and dill, two parts of immortelle and hawthorn flowers and one part of chamomile flowers. Pour the mixture with 200 milliliters of boiling water and steam in a water bath for half an hour. After which the broth is allowed to cool and after 60 minutes, squeeze out and drink. The medicinal decoction should be consumed in the morning, at lunch and in the evening 60 minutes after meals.
In addition to decoctions, breathing exercises will help the baby; it can be done in a playful way and together with parents. Massage has a beneficial effect on internal organs thanks to proper inhalations and exhalations. You can ask your doctor how to do therapeutic exercises correctly.
Why is the pancreas enlarged in a child?
Experts say that childhood problems associated with an enlarged pancreas are similar to those that affect adults. At the same time, children at any age must be examined for enlargement of this organ. This is due to the fact that over time and as the child grows, he is able to grow several times. However, such an increase is not always proportional and safe.
It often happens that the growth of the pancreas does not correspond to generally accepted graphs and tables, but it is proportional to all other surrounding organs.
It should also be said that pancreatic disorders are detected for the first time in early childhood. In this case, you should contact your pediatrician, who will prescribe appropriate treatment.
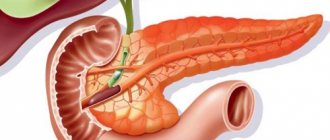
Normal sizes of the tail of the pancreas according to ultrasound in children and adults
The size of the pancreas is one of the objective criteria of its health. With pathology, it can increase evenly or only in its individual components or, on the contrary, decrease. Since it is impossible to determine the size and even palpate the pancreas by palpation, an ultrasound examination is performed, which gives accurate indicators. In cases where it was possible to palpate the gland during an objective examination, you need to think about its pathology - its size in this case is significantly increased.
While the largest parameters are at the head of the pancreas (35 mm), at the body of the pancreas they are 25 mm, the establishment of the size of the tail of the pancreas by ultrasound is normally no more than 7 to 27 mm in adults. In children, the size of the pancreas and its individual parts depends on the age and weight of the child. At birth, the length of the entire pancreas is 5 cm, it reaches its maximum values by the age of 18, then it no longer grows. At the age of 1 month to 1 year, the tail size is 12-16 mm, from 1 year to 10 years - 18-22 mm.
What does an enlarged pancreatic tail indicate?
Due to the topographic location of the tail of the pancreas, it is not always possible to detect its lesion in a timely manner. This is also associated with clinical manifestations: there are no specific subjective signs of changes in the tail. The patient has complaints inherent in the pathology of any organ of the digestive system. Especially if it concerns the inflammatory process. According to statistics, in only 1 out of 4 cases of inflammation of the pancreas, the focus is located in the tail.
If a detailed examination reveals an increase in only the tail part of the gland, it is necessary to show oncological alertness: a change in size may indicate the presence of a malignant neoplasm. Tail cancer disrupts the functioning of the entire organ and can lead to the death of the patient within a few months of the onset of the disease. But without special examination methods, it is difficult to suspect this pathology in the initial stages: in most cases it is detected when the tumor reaches a large size. On sonography, it can significantly increase echogenicity.
If the tail enlargement is due to a tumor, symptoms appear slowly. Even with a significant excess of all sizes, except for weakness, constant malaise, disturbed sleep and decreased appetite, there may be no other complaints.
An increase in the caudal part of the pancreas is observed with the development of benign neoplasms. These tumors:
- are not prone to metastasis,
- maintain tissue differentiation,
- grow only within one organ or part of it.
In addition, exceeding the normal size of the end part of the pancreas can be caused by a local inflammatory process, which will subsequently cover all parts of the organ, but at the initial stage, swelling and changes in the tissues of the tail develop.
If there is dysfunction in the tail section, the following are of concern:
- intense pain in the lower back,
- decreased appetite,
- weakness.
Damage to the tail of the pancreas leads to the development of diabetes mellitus due to a sharp hormonal imbalance.
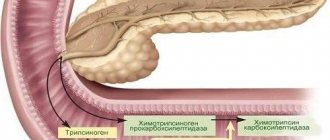
Endocrine functions in the pancreas are performed by the islets of Langerhans, which are localized in large numbers in the tail and produce hormones. Tumors are formed from their cells under certain circumstances. They are divided:
- for benign adenomas,
- for malignant adenocarcinomas.
Clinical manifestations depend on:
- from the cells from which the neoplasm appeared,
- from the hormone synthesized by them,
- on the size of the tumor.
Main symptoms
How to treat and how does inflammation of the pancreas manifest? Symptoms and treatment of this pathological condition depend on the causes of its occurrence.
Regardless of the gender and age of a person, diseases of this organ can occur in different ways. Very often such pathological conditions manifest themselves acutely. But sometimes the symptoms are hidden, which requires a number of additional studies.
How does inflammation of the pancreas manifest? The symptoms and treatment of this disease should only be identified and prescribed by a doctor. This pathology is characterized by bright and increasing symptoms.
With cystic neoplasms and various tumors, signs may appear after some time. In such cases, a correct and quick diagnosis is possible only by observing several specific symptoms, which include the following:
- repeated vomiting, an unpleasant feeling of bitterness in the mouth, nausea, complete lack of appetite, belching;
- pain (burning, aching) of varying degrees, which can be localized in the upper abdominal cavity and radiate to the back or arm;
- problems with stool, manifested by diarrhea without any impurities;
- jumps in body temperature.
Signs of an enlarged pancreas
In children of different ages, the disease will progress differently, and everything will depend on the cause of the enlargement of the pancreas. For some, the symptoms are pronounced, while for others the disease occurs in a latent form. Increasing symptoms are characteristic of the presence of inflammation in the organ.
If there is a tumor or cystic formation, then the pathology will be hidden for a long time.
It is during this period that it is important to diagnose the disease in a timely manner in order to cope with it faster.
Later, the following symptoms may occur:
- Pain. It can be aching or burning, arising in the upper abdomen and radiating to the arm or back.
- The appearance of vomiting and belching, bitterness appears in the mouth, and due to constant nausea, appetite disappears.
- Diarrhea without additional impurities in the stool.
- Increased body temperature.
Parents need to know that if a child has an enlarged pancreas, this may indicate very serious reasons. Enlarged parts of the pancreas can put pressure on neighboring organs. In particular, the enlarged head can compress the duodenum, which often leads to intestinal obstruction.
Complications
What complications can arise if the tail of the pancreas in a child or other parts of this organ are enlarged? This pathological condition is quite dangerous, regardless of what causes it. What is this connected with? The fact is that there are other organs around the pancreas, which can easily lead to their compression. This is especially true for the head of the gland, since it is its large size that can exert strong pressure on the duodenum of a small child.
There have been cases when, with such enlargements of the organ, the patient developed intestinal obstruction.
Etiology of the phenomenon
Why can the pancreas become enlarged? To find out the reason for the enlargement of this organ, it is necessary to find out what it consists of. The basis of the gland is the head and tail. Enlargement of the pancreas in a child can be complete or partial, for example, some parts of the pancreas: either only the head, or only the tail. There may be reasons for this. Most often, this condition is caused by the following circumstances:
- Systemic autoimmune disorders.
- Closed abdominal injury.
- Congenital pathologies, most often cystic fibrosis, which is characterized by the release of thick secretion.
- Drug poisoning.
- Congenital anomalies, for example, the structure of the gland may resemble a horseshoe.
- Duodenal ulcer.
- The presence of chronic or acute inflammation in the organ.
An enlarged pancreas is not always preceded by illness. This may be completely normal. For example, when a child experiences growth in all organs.
You just have to wait a little and everything will return to normal.
If we talk about the reasons for local enlargement of the organ, i.e. when the tail of the pancreas or only its head is enlarged, then the following most common factors can be identified:
- Cyst - can be false or true.
- A tumor that can be located on the gland itself or in the duodenum.
- Chronic pancreatitis, against the background of which organ tissue changes.
- Abscess (suppuration).
- Presence of stones in the pancreas.
Important information: What hormones do the pancreas produce and their functions?
All these causes are identified through diagnostic measures. Most often, congenital pathologies such as cystic fibrosis are diagnosed in childhood. The treatment will be complex.
Diagnostic methods
As mentioned above, the pancreatic ducts and the mentioned organ itself are located deep in the abdominal cavity. Therefore, with a minor inflammatory process or any other pathologies, it is not possible to detect the presence of a particular disease by palpating the patient. The only exceptions are those cases when the pancreas has become so large that it can be detected even with normal palpation.
In connection with all of the above, we can safely conclude that problems with this organ are often diagnosed based on the symptoms that have developed, which were described in this article. But what to do if clinical signs of the disease are completely absent? In this case, doctors recommend resorting to instrumental research methods. These include ultrasound and MRI.
Despite the high cost of such methods, they allow you to immediately determine whether there really is an enlargement of the pancreas, as well as the causes of this pathological condition.
Diagnostic measures
If there are problems with the pancreas, only in the acute period may visible symptoms appear, such as:
- pale skin;
- nausea and vomiting;
- pain under the ribs of a girdle nature;
- tension in the anterior abdominal wall;
- inflammation can increase body temperature;
- heavy sweating, general weakness.
The doctor initially conducts a visual examination of the child and uses the palpation method. If necessary, children with a diseased organ are sent for an ultrasound scan.
In very young children there are periods in life when the risk of pancreatic growth increases:
- during the period of introduction of complementary foods;
- when breastfeeding is replaced by artificial or mixed feeding;
- at the moment of eruption of baby teeth;
- if the child goes to kindergarten for the first time;
- going to first grade;
- during the transition period in adolescents.
Important information: Which doctor should I consult for pain in the pancreas?
When acute inflammation of the pancreas, called pancreatitis, occurs, no special diagnosis is required. A doctor can identify the disease by its obvious symptoms.
How to treat?
How can such a pathology be treated if the child is one month old? The pancreas is enlarged - you should immediately contact your pediatrician. After all, only an experienced doctor will be able to determine the true cause of the development of such a pathological process, as well as identify its threat to a small organism.
It should be especially noted that each individual case of pancreas enlargement in children requires its own individual treatment. According to experts, such therapy can be conservative and surgical.
If we talk about the general principles of treatment, they boil down to the following scheme:
- Reducing swelling of the pancreas by applying cold compresses to the affected area.
- Mandatory adherence to a strict diet, which includes the complete exclusion of spicy, fatty, and fried foods. Also, many experts strongly recommend abstaining from eating for at least a few days. In some cases, doctors even inject nutrients into the patient's body (so-called parenteral nutrition).
- Maximum reduction in the activity (secretory) of the organ in question by taking special hormones, proton pump inhibitors or histamine receptor blockers.
- A surgical intervention performed to eliminate dead tissue or inflammation.
- Additional introduction of artificial digestive enzymes in order to correct the functioning of the internal organ.
How to return the gland to normal size
To understand this issue, you will need the help of a gastroenterologist. If you are sure that your child has an enlarged pancreas, then start giving your baby mineral alkaline water more often.
If you feel pain, apply cold to this place (as a rule, it is located just to the left of the navel). If the pain is severe, call an ambulance. The doctor will choose treatment tactics based on diagnostic data. There are 2 types of therapy: conservative and surgical.
Approximate scheme of the treatment process:
- Secretory activity is suppressed with the help of proton pump inhibitors. Histamine receptor blockers are administered and hormones are prescribed.
- To reduce swelling, apply a cold heating pad to the sore spot.
- To correct the functioning of the pancreas, enzyme preparations are prescribed.
- Parenteral nutrition is possible, i.e. injections with vitamin components are given.
- An operation to eliminate inflammation or dead tissue.
Since the pancreas is often enlarged due to pancreatitis, in this case it is advisable for the child to fast for a while. At this time, various nutrient solutions can be introduced into the body.
If you prescribe a diet, it will be called table No. 5, which provides nutrition aimed at restoring the functioning of the pancreas. This diet provides for the following food intake rules:
- Lean meat should be either boiled or steamed.
- Dairy products are not fatty.
- Porridges cooked in water, except millet. Over time, the water can be gradually replaced with milk.
- Boiled or steamed vegetables.
- If it’s tea, it’s not strong, with a small amount of sugar. It is also recommended to drink rosehip decoction.
- Fruits baked without adding sugar and honey.
- Bread in the form of crackers or dried in the oven.
- Biscuits.
Spices and sugar should be present in minimal quantities. Fatty, smoked, fried and spicy foods are prohibited. You should not eat sour fruits and berries, as well as the following vegetables - garlic, radish, radishes, onions. Sweets in the form of candies, chocolate, and cakes are also excluded. If you eat even a little of all these forbidden foods, the pancreas will enlarge again.
Diet
Treatment of children with large pancreatic glands without normal and proper nutrition is impossible. As a rule, with such a pathology, the doctor prescribes a special diet No. 5 for the child. It involves avoiding fatty foods and other fatty components. In return, the patient should include in his diet protein foods that have a beneficial effect on his body.
It should also be noted that diet No. 5 involves a complete rejection of foods such as:
- any types of juices, including fresh ones;
- sweets in the form of ice cream, chocolate or jam;
- fruits and vegetables in their natural state (that is, not thermally processed);
- dairy products with high fat content (cream, sour cream, whole milk);
- fatty broths, decoctions, as well as various dishes cooked on their basis.
Instead of the listed products, it is better to offer your baby:
- vegetables, steamed or stewed;
- boiled and stewed meats and dishes that were made based on them;
- black tea with a little sugar;
- dairy products with a small percentage of fat content;
- baked fruits, as well as desserts based on them;
- any types of porridges cooked in plain water;
- crackers, dried bread, biscuits.
What to feed a child with an enlarged pancreas
Proper nutrition is an essential part of treatment tactics. It is important to follow all dietary recommendations for any form of pancreatitis.
First, types of food are excluded from the menu, the digestion of which requires the active operation of the enzyme secretion system. These include products with a large amount of proteins and fats of animal origin (fatty meats and fish, dairy products with high fat content, etc.). The consumption of sugar, sweets, sweets, etc. is limited. Fried and smoked foods, as well as pickles and other canned goods are prohibited. The presence of rich bakery products, egg yolk, seasonings and spices in the diet is also undesirable.
Instead, the emphasis is on moderate-carbohydrate meals. These are mainly cereals and legumes (rice, oatmeal, beans), from which you can prepare porridge. In addition, the diet should be based on a fractional principle, that is, food should be taken in small portions 6-7 times a day.
Permitted and prohibited products
An important point is the method of preparing the products. Dishes must be steamed. Before cooking, food must be grated or finely chopped - this will also greatly facilitate the functioning of the digestive system. This rule is of particular importance in acute pancreatitis. The most suitable in this regard are milk porridges and vegetable purees.
For many gastroenterological diseases, especially those associated with impaired bile flow, a special drinking regime is recommended. The child should drink a lot. Simple boiled or mineral degassed water, compotes or green tea are suitable for this.
For two weeks after the first attacks of exacerbation of the disease, a strict diet should be followed. When relieving acute symptoms, the menu can be supplemented with dishes made from unprocessed products.
Examination by a pediatrician
Other treatments
It should be especially noted that there are cases when using only one diet is inappropriate, and also ineffective for different groups of children (for example, with neoplastic processes in the child’s body). With this diagnosis, no nutrition, as well as a strict diet, will affect the rate of tumor growth in the pancreatic gland. The only treatment for this disease is surgical removal of the affected area.
With the development of acute pancreatitis, diet also turns out to be powerless. That is why, in case of such diseases, it is very important to consult a pediatrician in time, and not to self-medicate, which, by the way, can quite easily lead to disastrous consequences.