The gallbladder is an important internal organ that helps digest food. How a person’s gallbladder works depends significantly on the way they eat and the correct composition of their diet.
Excess fatty and fried foods lead to overload, the formation of gallstones and organ damage.
Problems with this organ in people are common, and most often affect middle-aged and older people; pathologies occur in both women and men.
Let's take a closer look at where the organ is located and how it hurts.
What is the gallbladder and where is it located?
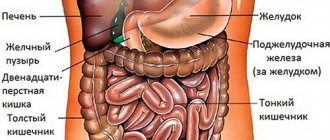
Where is the gallbladder located in humans? This organ (Latin: Vesica Felley) is located on the underside of the liver in a small depression (see photo below). This is a small bag, the size of a lemon, about 40-70 cm.
Its main function is to store and concentrate bile, so it can be said to be a bile reservoir.
Bile is produced in the liver, and “liver bile” is much less concentrated. The bubble takes water from it, and retains the rest - concentrated.
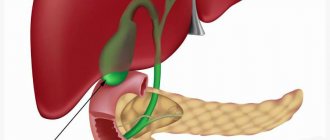
Its outlet (bile duct) emerges from the bladder, which, after about 3 centimeters, connects with the hepatic outlet (common hepatic duct) and continues further as the bile ducts (ductus choledochus).
At the final stage, the bile ducts connect to the pancreatic outlet and enter the first part of the small intestine - the duodenum (duodenum).
Bile is produced in quantities of approximately 0.7 to 1.2 l/day. Its main components are bile acids, cholesterol and bilirubin (a biliary pigment dye).
Bile is secreted after eating, due to the influence of a nerve impulse. It is designed to help mainly with the digestion and absorption of fats, but also, together with pancreatic juice, neutralizes gastric digestive juices, thus protecting the intestines from damage.
Anatomical structure of the gallbladder
It is a muscular-membranous hollow organ that is pear-shaped. The narrowest end - its neck passes into the duct, which is connected to the common hepatic duct. The widest part is the bottom; it is in contact with the parietal peritoneum. The middle part is the body; it is in contact with the stomach in its lower part, as well as with the duodenum and transverse colon. The walls of the gallbladder are quite thin, the organ itself is dark green in color. It does not exceed 8-10 cm in length, and the width at the widest part is approximately 5 cm.
Functions of the gallbladder in the body
Proper functioning of the gallbladder is an important factor in the digestive process, focusing mainly on the digestion of fats. It supports the digestive process by emulsifying fat and neutralizing acid from food that passes from the stomach to the duodenum.
The organ also supports intestinal motility (movement) and nutrient absorption by preventing putrefaction.
The main causes of bladder pathology
In humans, the main problems of gallbladder pain are determined by infection and stagnation of the contents with overstretching of the walls. These reasons are aggravated and form a vicious circle: when bile stagnates, favorable conditions are created for pathogenic microorganisms, and inflammation changes the composition and viscosity of bile and contributes to stagnation.
Infection occurs:
- directly from the intestines (parasites, pathogenic strain of E. coli, helminths);
- from the liver - for hepatitis, abscess, echinococcosis;
- with blood when infection spreads from untreated chronic foci (in men more often - prostatitis, sinusitis, in women - adnexitis, tonsillitis).
Obesity and low physical activity are the main causes of damage to the biliary system in women.
Predisposing factors include:
- obesity - disrupts the composition of bile, causing an increase in cholesterol concentrations;
- hormonal disorders - it has been found that sex hormones affect the elimination of cholesterol; decreased activity during menopause contributes to gallbladder disease.
In the last trimester of pregnancy, the mechanism of compression and stagnation operates.
Provoking reasons may be:
- irregular meals with long breaks, subsequent overeating;
- using fasting diets for weight loss;
- increased blood cholesterol in older people;
- structural anomalies (deformation, bends, curvature);
- metabolic disorders in diabetes mellitus;
- diseases of the pancreas and liver;
- functional disorders of contraction coordination in diseases of the nervous system.
Great importance is attached to: professional contact with toxic substances at chemical industry enterprises, low human physical activity, chronic intestinal atony, stress, long-term use of certain medications (Octreotide, Clofibrate, Ceftriaxone), drugs with a diuretic effect, statins, oral contraceptives.
Composition of bile
Bile is produced in the liver. Leaving the liver, it enters the gall bladder, where, like in a reservoir, it is stored and available to perform its functions. It is necessary for the degradation of fats supplied with food.
Its density is regulated by the nervous system in a humoral manner, depending on the fat content in the diet.
The organ is connected to the small intestine through ducts. Depending on the type and amount of fat contained in the food taken, it is emptied into the small intestine.
Bile contains bile pigments, mainly cholesterol and acids:
- primary, free, which are formed in the liver (for example, bile acid);
- secondary (for example, deoxycholic acid), which arise in the intestine from primary acid due to exposure to bacteria; these are not free acids, but bound to glycerol or taurine; the connection occurs due to protein breakdown.
Cholesterol is a white, odorless, tasteless fatty substance that is abundantly present in nerve tissue and bile, respectively, and in gallstones. It occurs together with lecithin, indicating their physiological function.
What to do if you have pain in the gallbladder?
It is possible to get rid of pain in the gallbladder only by eliminating the pathological changes that have occurred in the digestive organ. However, there is a general algorithm that can effectively eliminate painful sensations:
- Diet food. If you have pain in the gallbladder, you should avoid eating food that negatively affects the functionality of the organ. Experts recommend excluding: fatty, smoked, spicy, fried foods. The diet includes the consumption of lean varieties of fish and meat, fermented milk products, vegetables and fruits. You need to eat small portions up to 6 times a day. You should avoid eating at night;
- Etiotropic treatment. Drug and surgical therapy is used to eliminate the cause of pain;
- Symptomatic treatment. Therapy allows you to get rid of pain in the gallbladder, restore the functionality of the organ, and eliminate signs of intoxication in the body.
Major diseases of the gallbladder
Stones
The overall health of a person depends significantly on how the organ works.
However, for various reasons, disruption of the bile fluid may occur, such as the excretion of crystalline substances.
As a result, several small stones appear in the gall bladder or one large stone.
If, over time, many small stones accumulate in the gallbladder, it is said to be sand. In the case of creating one large stone, it is called single.
The presence of stones in the gallbladder or ducts is professionally called cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis). Sooner or later, gallstones cause colic, i.e. spasms.
The spasms shoot into the back under the right shoulder blade and can be very persistent and painful.
Colic
As already mentioned, bile is produced in the liver. This organ contains bile ducts, which can also be affected by colic.
Nutritional errors or mental disorders may be involved in the occurrence of colic.
Biliary colic begins with a sudden severe pain in the upper abdomen, which radiates to the back under the right shoulder blade, often accompanied by vomiting, but without fever.
After half an hour or several hours, the pain may suddenly subside, and rapid recovery occurs.
Inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis)
The next disease of the gallbladder is its inflammation (cholecystitis).
As a rule, it begins with manifestations of spasms. Later, fever or chills occur, and sometimes a slight yellowing of the conjunctiva. After the worst pain has subsided, more or less severe pain remains.
How does a person’s gallbladder hurt?
When the gallbladder hurts, the pain can be localized in various parts of the abdomen. The intensity, nature and location of the pain syndrome is determined by the pathological process. So how can you tell if your gallbladder is hurting? Painful sensations have the following characteristics:
- With cholelithiasis, the following symptoms of pain in the gallbladder occur: a sharp pain syndrome on the right, which radiates to the right shoulder blade, shoulder or back;
- Chronic cholecystitis causes constant pain, which is intensified by spicy, fatty foods, alcohol and carbonated drinks;
- How does it hurt with gallbladder dyskinesia? Characteristic is the appearance of acute paroxysmal pain, the duration of which does not exceed 20 minutes;
- With cancer, a dull pain syndrome develops that is not relieved by analgesics.
Important! In the initial stages, the gallbladder hurts in the evening or at night, the discomfort intensifies during coughing and deep breathing. In the later stages, the pain syndrome becomes constant, sharp, and intense. In severe cases, painful shock may develop.
In some pathologies, the symptoms of pain in the gallbladder are accompanied by external and internal symptoms. The development of the following symptoms is characteristic:
- Itching of the skin;
- Heartburn;
- Bitter taste in the mouth;
- Decreased appetite;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Increased gas formation;
- Pronounced sweating;
- A sharp decrease in body weight;
- The appearance of shortness of breath while walking;
- Chills and increased body temperature to high values;
- Abdominal muscle tension.
Symptoms of gallbladder disease
Problems with the gallbladder are manifested by the following symptoms:
- constant belching;
- pressure behind the sternum;
- pain in the right side of the chest, radiating to the right shoulder blade;
- prostration;
- pressure and nausea after eating.
The organ is often characterized as “a sensor that determines the abilities to evaluate and decide.”
Causes and risk factors for symptoms
Factors such as stress, poor diet and obesity are associated with gallbladder problems as they can promote inflammation or can cause dangerous visceral fat to form around the digestive system and other vital organs.
Obesity has been shown to increase cholesterol levels in the liver and can contribute to many different digestive disorders.
Visceral fat can be seen by looking at a person's widened waist.
Other causes and risk factors for developing gallbladder disease:
- unhealthy eating and/or suffering from nutritional deficiencies;
- pregnancy and other hormonal changes;
- taking birth control pills/oral contraceptives;
- diabetes;
- high levels of triglycerides in the body (a type of fat in the blood);
- low cholesterol (high-density lipoprotein (HDL));
- sedentary lifestyle/lack of physical activity;
- family history of diseases associated with the organ;
- autoimmune disease, viruses or infections that interfere with the normal functioning of the immune system.
Gallbladder diagnostic methods, tests
Signs of organ pathologies cannot be ignored! You should also not resort to self-diagnosis and self-medication. Only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis, so if you have pain in the right hypochondrium, you should go to the clinic.
Where does the examination begin? First, the doctor conducts a survey and orders a laboratory blood test. The analysis will reveal inflammation, if any. Then you will need to perform duodenal intubation - collecting bile. The laboratory will determine the chemical composition of the liquid, conduct a study for the presence of cancer cells, etc.
An ultrasound examination may also be prescribed. Ultrasound will reveal pathologies such as:
- bend of an organ;
- change in the thickness of its walls;
- the presence of polyps, stones in the organ and its ducts.
If cancer is suspected, a biopsy of the gallbladder is required. The following may also be assigned:
- X-ray with the introduction of contrast fluid to correctly assess the size of the organ and identify possible deformation;
- MTR (magnetic resonance imaging);
- CT (computed tomography).
How to help the gallbladder and normalize its functioning at home?
Normalizing the functioning of this organ can have a significant impact on the overall health of a person. Let's talk about how and how to treat the gallbladder.
To transport bile to the intestines, the proper functioning of the liver and gallbladder is necessary.
Many popular medications to support these organs are based on the healing power of plants, and their effectiveness has been proven by many studies.
The following herbs promote the secretion and transport of bile into the intestines; they can also have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects; they can be purchased at a pharmacy (herbs are cheap) or collected in the forest in the summer.
Real bedstraw infusion
Speaking about normalizing the functioning of the gallbladder, we should mention the interesting results shown by studies studying the healing properties of bedstraw (galium verum). It has been proven that this plant can normalize the functioning of the gallbladder and dissolve gallstones and kidney stones.
During the test tube study, a stone with a diameter of 10 mm was poured with an infusion of bedstraw (1 teaspoon of the herb infused in a glass of boiling water). Within 48 hours there was no trace left of the stone.
After several repetitions of the study, which showed a similar result, experts came to the conclusion that drinking bedstraw tea (3-4 times a day) can help the gallbladder perform its functions, flush the intestines, dissolve stones and cleanse the bile ducts.
The following herbs and infusions are also used:
- burdock - it is recommended to drink tea made from flowering tops or alcohol extract;
- milk thistle - extract used; You can chew whole seeds or drink tea made from crushed seeds (crushed seeds quickly lose their effectiveness, so grind them immediately before preparing tea);
- dandelion - tea from roots and leaves or alcohol extract is used;
- yarrow - tea made from flowering tops or alcohol extract is used;
- chicory (also sold in stores) – a drink made from soluble chicory normalizes the functioning of the entire digestive system;
- centaury - tea from the flowering tops is used.
Detoxifying a given organ can be done as a general process where the entire body is cleansed, or as a specific action where only the target organ is cleansed.
How to treat the gallbladder
Prescription of drugs begins taking into account the diagnosis. So, if stones are present, the following may be prescribed:
- conservative therapy with the use of bile acid drugs;
- shock wave lithotripsy method (small stones, up to 2 cm);
- removal of the gallbladder - cholecystectomy.
Infectious diseases require the use of antibiotics; for large polyps, surgical intervention is necessary; in some cases, drug treatment or traditional methods are effective.
Treatment of the gallbladder with drugs
What medications can be prescribed for diseases of the organ? To relieve pain symptoms, the most effective antispasmodics are used: Drotaverine, No-shpu, Spazmalgon, etc.
For uncomplicated cholelithiasis, choleretic drugs are prescribed:
• Ursosan;
• Holosas;
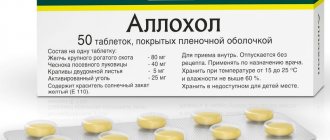
• Allohol;
• Cholenzyme;
• Flamin, etc.
It is unacceptable to choose treatment on your own! This should only be entrusted to a specialist!
Treatment of the gallbladder at home
Folk remedies are used to cleanse the organ and remove stones from it.
One of the popular home treatment options is olive oil cleansing. For these purposes, vegetable fat is taken for three days, three times a day, 30 ml. The oil is drunk before meals, washed down with freshly squeezed citrus juice (grapefruit or lemon).
Chicken eggs, or rather their raw yolks, are successfully used to cleanse the gallbladder. In the morning, drink two yolks and wash it down with fresh lemon juice. Reception is carried out on an empty stomach for 14 days.
This recipe is contraindicated if cholesterol is high. There is also a danger of infection with salmonellosis - the bacterium can be present in raw eggs!
An excellent remedy for enhancing the secretion of bile, which also has a general strengthening effect, is rosehip. They use both infusions and decoctions from the berries themselves, as well as ready-made pharmaceutical preparations, for example, Holosas. The roots of the plant are also used.
To clean the gallbladder, use the following recipe:
- 2 tablespoons of washed and finely chopped rosehip root are poured with a glass of boiling water;
- boil the mixture over medium heat for 25-30 minutes;
- filter;
- take 1/3 of the prepared infusion three times a day for two weeks.
Traditional methods of treatment are not only potential benefits, but also risks - this is worth remembering!
Inappropriate use or incorrect dosage of medications can cause the movement of large stones and lead to serious complications!
Diet for illnesses
People with various gallbladder pathologies are concerned with the question: what products are included in the list of permitted products for their disease, and what should be avoided? Nutritionists say that in case of gallbladder diseases, dietary restrictions are very small and concern not so much the products themselves as the methods of their preparation.
So, what can you eat?
- Vegetable, cereal and milk soups;
- Steam cutlets, meatballs, soufflé and goulash made from poultry (chicken or turkey), rabbit, veal and lean beef;
- Egg whites - mainly in the form of an omelet;
- Low-fat dairy products - milk, sour cream, yogurt, kefir, low-fat cottage cheese);
- Porridge with water or milk - semolina, buckwheat, rolled oats;
- Sweet fruits - bananas, pears, juicy varieties of cherries, apples (fresh and heat-treated);
- Vegetables - zucchini, pumpkin, carrots, cabbage, legumes in limited quantities, except for green pea puree.
Soups, vegetable dishes, salads can be sprinkled with finely chopped parsley and dill, seasoned with a small amount of vegetable or butter.
It is allowed to consume some sweets - jam, marmalade, homemade preserves from sweet fruits, honey, marshmallows and marmalade, drinks - weak black tea, compote, jelly, rose hip decoction and sweet juices mixed with water.
Vegetables and fruits that must be consumed for various pathologies of the gallbladder:
- Pumpkin;
- Carrot;
- All types of cabbage;
- Beet;
- Sea kale;
- Apples;
- Dates;
- Dried apricots;
- Dog-rose fruit.
All these products are rich in substances necessary for the normal functioning of the gallbladder, and can be used for both therapeutic and preventive purposes.
The list of products that are prohibited is very short. This:
- Alcohol and carbonated drinks;
- Meat and fish of fatty varieties;
- Lard and smoked meats;
- Mushroom dishes;
- First courses cooked in strong broth;
- Vegetables with a spicy taste;
- Chocolate;
- Strong coffee and tea;
- Sweet pastries and pastries with rich cream.
Dyskinesia
Symptoms
With hypermotor dyskinesia, transient jaundice develops and the outflow of bile is disrupted. This results in discolored stool that turns white or gray. Hypotonic dyskinesia is also characterized by dull pain in the right hypochondrium, which many patients characterize as a feeling of heaviness. This often results in nausea while eating and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. Many patients often cannot even tolerate the smell of food.
Treatment of the disease
The choice of treatment method for dyskinesia depends on the form of the disease. Maintaining a proper diet is of great importance. You need to eat in small portions, at least 5 times a day. It is advisable to eat less foods that cause strong contraction of the gallbladder. These include, in particular, vegetable oil, beer, cakes, and carbonated drinks. For the patient, it is better to steam or boil foods. It is important to exclude spicy and fatty foods. But you can eat fresh fruits and berries all the time.
Usually, for this disease, the doctor prescribes treatment with antispasmodics, for example, No-shpa . Choleretic drugs help well, among which are Cholenzym and Holosas. Traditional medicine is also widely used: peppermint, corn silk, eleutherococcus, ginseng and rose hips.
An important treatment method is mineral water with medium and low mineralization. These are mineral waters such as Smirnovskaya, Narzan, Essentuki. Often, a doctor prescribes tubage with mineral water, that is, washing the bile ducts. Modern methods of treating dyskinesia are also acupuncture and laser treatment.