Causes of adhesions
Appendicitis removal surgery is one of the most common surgical procedures.
In general, if there are no problems with the appendix, the recovery process after this operation takes only a couple of weeks.
However, often as a result of certain provoking factors, adhesions begin to form in the body.
Useful article? Share the link on VKontakte
Such a process is considered a complication and should not be neglected. As soon as the first symptoms of adhesions appear, treatment should begin.
If it is possible to eliminate the symptoms at the very beginning of the development of the disease, then pathological changes in tissues can be stopped.
Adhesions form after surgery if there is an inflammatory process in the body. Thus, the combination of these 2 reasons leads to the formation of connective tissue compactions - adhesions.
The most common provoking factors:
- the technique of the operation is violated;
- leaving objects foreign to the body in the wound after surgery;
- impaired blood circulation in tissues for a long time;
- Bleeding started during the operation;
- failure of the patient to comply with a special diet;
- lack of physical activity after surgery.
What is the danger of adhesions after appendicitis surgery?
If adhesions appear after surgery, you should immediately begin treatment for this pathology, because it can cause serious complications:
- Intestinal obstruction. It develops as a result of compression of intestinal loops by cords of adhesions. As a result, the contents of the intestine cannot move through it normally.
- Infertility. If after an appendectomy a woman cannot become pregnant, this may indicate damage to the appendages by adhesions, or a violation of the patency of the fallopian tubes.
- The necrotic process is the most dangerous complication. Adhesions, putting pressure on the tissue, can compress the blood vessels, which will lead to poor circulation in part of the intestinal tissue. The drained area begins to die and necrosis forms. In this case, immediate surgical intervention is required to remove the affected tissue and stop the necrotic process.
Return to contents
Symptoms of the disease
According to statistics, adhesions appear in almost 90% of people after surgery. The formation of compactions begins a few days after the operation.
Gradually, adhesions limit the functionality of the intestines, at which time the first symptoms of the disease begin to appear.
It should be noted that with minor pathological changes, symptoms may be partially or completely absent.
The main symptoms of the appearance of seals:
- pain in the lower abdomen, which can change in nature when the weather changes, and also intensify with physical activity.
- decreased appetite;
- weight loss;
- heartburn and belching due to indigestion;
- with prolonged development of the disease, constipation is possible;
- Women may have problems conceiving.
The process of formation of adhesions can cause the development of intestinal obstruction, which interferes with the release of intestinal gases and feces.
When obstruction occurs, pain increases significantly, symptoms of intoxication of the body appear, body temperature increases, and sometimes symptoms include severe vomiting with fecal particles.
Video:
This complication can often be identified by severe bloating of the abdomen, upon palpation of which the pain intensifies.
Quite often in women, inflammation spreads to the appendages, which leads to an obstacle to conception.
Therefore, if a woman cannot become pregnant for a long time without obvious reasons, and has recently had operations in the gastrointestinal tract, then it is worth conducting an examination for the presence of adhesions that could disrupt the patency of the fallopian tubes.
Treatment of intestinal obstruction is mainly carried out with the help of surgery, since it is important to carry out the intervention as soon as possible.
Symptoms of exacerbation of adhesive disease include acute pain, constipation, and some signs of intestinal obstruction.
Complications
Adhesive formations can provoke some complications. Most often, doctors encounter acute intestinal obstruction. It is formed from compression of the intestine, which impairs the passage of food through the gastrointestinal tract. Doctors also diagnose necrosis of a certain area of the intestine - the blood supply to the intestine is disrupted, which leads to compression of the artery by the adhesion, as a result of which the walls of the organ die. With such serious complications, the patient needs to undergo additional surgery to completely remove the intestine or just the affected part.
In addition to these complications, adhesions can lead to the following consequences:
- peritonitis;
- infertility;
- disrupted menstrual cycle;
- bend of the uterus;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment of the disease
The doctor selects treatment for adhesive disease depending on the stage of pathological changes.
If the damage is minor, then treatment most often consists of the following procedures:
- drug treatment: use of folic acid, vitamin E, Aloe preparation in the form of ampoules. Remember that only a doctor can prescribe medications and determine the dose; self-medication can worsen your health;
- treatment using physiotherapy: magnesium, zinc or novocaine electrophoresis, paraffin applications on the abdominal area. Such procedures are especially effective at the initial stage of the disease.
If treatment with the above remedies does not help eliminate unpleasant symptoms, then surgery is performed to remove adhesions.
Surgical intervention can be performed using an electric knife, laser or traditional methods.
Video:
In no case should you neglect the treatment of adhesions, because this disease will not go away on its own, and with prolonged development it can lead to serious disorders of metabolism and digestive processes. The most severe complications are intestinal necrosis and intestinal obstruction.
At the first suspicion of adhesions, you should inform your doctor so that he can prescribe the necessary tests for diagnosis.
Remember that the sooner you start treating the disease, the faster you can get rid of it and stop the inflammatory processes.
Diagnostics
It is almost impossible to determine adhesive disease in the early stages of development, since there is no clinical picture. As symptoms increase, the patient seeks medical help and undergoes a series of examinations:
- General and biochemical blood test. Some changes indicate an inflammatory process: an increase in the number of leukocytes, an increase in the ESR rate, the presence of C-reactive protein in large quantities.
- Ultrasound. Connective tissue is poorly visualized, and gas bubbles interfere with the diagnostic search. Information using ultrasound can only be obtained in case of advanced disease.
- X-ray with the introduction of a contrast agent. Allows you to determine the area of narrowing and tissue structure.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy. The most informative method, it can be used to determine the exact localization of adhesions and decide on repeated surgical intervention.
Therapy consists of two directions: conservative and surgical. Conservative treatment involves the use of a number of medications and procedures.
At the very beginning, doctors try to reduce the severity of pain using enemas, if it is caused by constipation and flatulence, and taking antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Papaverine).
To suppress the inflammatory process and further proliferation of connective tissue, NSAIDs (Ketorol, Ibuprofen, Nimesil) are used. Administered orally or intramuscularly.
Particular attention is paid to the patient's nutrition. He needs to focus on foods enriched with plant fiber: cereals, fresh vegetables and fruits
Complex carbohydrate stimulates peristalsis and promotes the excretion of feces.
Excluded from the diet:
- carbonated drinks;
- legumes;
- White cabbage;
- corn;
- baking;
- black bread;
- whole milk.
All these products increase gas formation in the intestines and the severity of abdominal pain.
Of the physiotherapy treatments, preference is given to paraffin baths, diathermy, mud baths and iontophoresis. Physical activity and heavy lifting should be temporarily avoided.
During the operation (during surgical treatment), doctors move apart the adhesions; if necrotic tissue is detected, the area is removed, intestinal patency is restored, or a stoma is performed. Doctors must take preventive measures to reduce the risk of re-formation of connective tissue cords. These include:
- making wide cuts;
- timely removal of spilled blood and complete stop of hemorrhage;
- eliminating drying out of the layers of the abdominal wall.
At the end of all manipulations, surgeons introduce enzymes and medications that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Preventive measures
To prevent adhesions from appearing after removal of appendicitis, you should take some preventive measures, and most importantly, strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Preventive measures:
- After several hours after the operation, you can, while lying in bed, perform some movements to avoid physical inactivity. On the second day you can walk around the ward for a short time;
- It has been proven that the appearance of adhesions can be avoided by performing the operation using the endoscopic method. This eliminates the risk of infection and minimizes the impact on internal tissues. Thus, the suture heals much faster after surgery and adhesions do not appear;
- for the purpose of prevention, an auxiliary one is added to the main course of treatment, consisting of the use of drugs such as Fibrinolysin, Streptokinase and Trypsin. Such agents dissolve the substance that forms in the area of adhesions - fibrin. Doctors also often prescribe antibiotics and drugs that help relieve inflammation.
Prevention of adhesions and any complications after removal of appendicitis necessarily includes following a certain diet.
In the first week after surgery, it is best to eat chicken broth and steamed or boiled foods.
The diet may contain porridge with water, various casseroles and omelettes with vegetables. Make sure that dishes and products do not contain a lot of salt, sugar and do not increase acidity.
The following products are prohibited:
- fatty fermented milk products: kefir, cream, cottage cheese with a high percentage of fat content;
- rich soups with fatty meat - it is better to replace them with light chicken or vegetable broths;
- legumes in any form;
- any spicy or too salty foods;
- smoked or pickled products;
- bakery;
- stringy or fatty meat, because it greatly irritates the gastrointestinal tract;
- any ready-made sauces;
- vegetables such as peppers and tomatoes.
Honey, dried fruits and other foods with a lot of sugar or fiber should also be consumed with caution; it is better to completely eliminate them from the diet.
Such restrictions must be observed during the first month after the operation.
This will avoid the occurrence of adhesions and other complications, and also normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
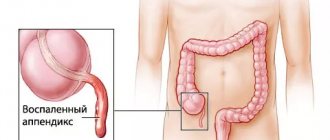
One of the most common diseases in people who need surgery is inflammation of appendicitis.
The atrophied part of the large intestine is the appendix; it looks like a vermiform appendix of the cecum. The appendix forms between the large and small intestines.
The causes of this pathology are usually attributed to the occurrence of worms and the development of parasites, but it is impossible to say for sure what actually causes inflammation of the appendix.
Doctors note that it is quite difficult to predict and prevent the disease. Experts do not recommend taking painkillers in case of appendicitis.
The appointment will prevent the doctor from making a correct diagnosis of the patient. This should be done exclusively by a specialist who will prescribe an ultrasound.
Thanks to them, it will be possible to understand what shape the inflamed appendix has. It may be clogged or swollen. It can only be removed surgically.
Types of appendicitis
Today there are 4 types of appendicitis known. These are: catarrhal, phlegmonous, perforative; gangrenous.
The diagnosis of catarrhal appendicitis is made by a doctor if the penetration of leukocytes into the mucous membrane of the worm-shaped organ has been noted.
Phlegmonous is accompanied by the presence of leukocytes in the mucosa, as well as other deep layers of appendix tissue.
Perforated is observed if the walls of the inflamed appendix of the cecum have been torn, but gangrenous appendicitis is the wall of the appendix affected by leukocytes, which is completely dead.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease include:
- acute pain in the abdominal area, or more precisely in the right half in the area of the inguinal fold;
- increased body temperature;
- vomiting;
- nausea.
The pain will be constant and dull, but if you try to turn your body, it will become even stronger.
It should be noted that it is possible that after a severe attack of pain the syndrome disappears.
Patients will mistake this condition for the fact that they feel better, but in fact, the subsidence of pain carries a great danger, indicating that a fragment of the organ has died off, and it is not for nothing that the nerve endings have ceased to respond to irritation.
Such pain relief ends with peritonitis, which is a dangerous complication after appendicitis.
Problems with the gastrointestinal tract may also be observed in symptoms. A person will feel a feeling of dry mouth, he may be bothered by diarrhea and loose stools.
Blood pressure may jump and heart rate may increase to 100 beats per minute. The person will suffer from shortness of breath, which will be caused by impaired heart function.
If the patient has a chronic form of appendicitis, then all of the above symptoms do not appear, with the exception of pain.
The most common complications after appendicitis
Of course, doctors set themselves the task of eliminating all complications after appendicitis removal, but sometimes they simply cannot be avoided.
Below are the most common consequences of appendicitis.
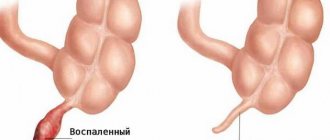
Perforation of the walls of the appendix
In this case, there are ruptures in the walls of the appendix. Its contents will end up in the abdominal cavity, and this provokes sepsis of other organs.
The infection can be quite severe. A fatal end is not ruled out. Such perforation of the walls of appendicitis is observed in 8-10% of patients.
If it is purulent peritonitis, the risk of death is high, and exacerbation of symptoms cannot be ruled out. This complication after appendicitis occurs in 1% of patients.
Appendiceal infiltrate
These complications after surgery to remove appendicitis are observed in the case of adhesions of organs. The percentage of such cases is 3-5.
The development of complications begins 3-5 days after the formation of the disease. Accompanied by pain of unclear localization.
Over time, the pain subsides, and the contours of the inflamed area appear in the abdominal cavity.
The infiltrate with inflammation acquires pronounced boundaries and a dense structure, and tension in nearby muscles will also be observed.
In about 2 weeks the swelling will go away and the pain will stop. The temperature will also subside, and blood counts will return to normal.
In many cases, it is possible that the inflamed part after appendicitis will cause the development of an abscess. It will be discussed below.
Abscess
The disease develops against the background of suppuration of the appendiceal infiltrate or surgery if peritonitis is diagnosed.
As a rule, it takes 8-12 days for the disease to develop. All abscesses need to be covered and debrided.
In order to improve the outflow of pus, doctors install drainage. During the treatment of complications after appendicitis, it is customary to use antibacterial drug therapy.
If there is a similar complication after appendicitis, urgent surgery is necessary.
After this, the patient will have to wait for a long rehabilitation period, accompanied by drug treatment.
Complications after appendectomy
Even if the operation to remove appendicitis was performed before the onset of severe symptoms, this does not guarantee that there will be no complications.
Many cases of death after appendicitis make people pay closer attention to any warning signs.
Below are the most common complications that may occur after removal of an inflamed appendix.
Spikes
One of the most common pathologies that appears after removal of the appendix. Accompanied by nagging pain and discomfort.
It is difficult to diagnose, because ultrasound and x-rays cannot see them. It is necessary to carry out a course of treatment with absorbable drugs and resort to the laparoscopic method of removing adhesions.
Hernia
The phenomenon is really common after appendicitis. There is a prolapse of part of the intestine into the area of the lumen between the muscle fibers.
If the doctor’s recommendations were not followed, then often such complications after appendicitis cannot be avoided. All physical activity is excluded after appendicitis.
A hernia looks like a tumor in the suture area, increasing in size. Surgical intervention is provided. The surgeon will sew it up, trim it, or remove part of the intestine and omentum.
Abscess
Occurs in most cases after appendicitis with peritonitis. It can infect organs.
A course of antibiotics and special physiotherapeutic procedures is required.
Pylephlebitis
A very rare complication after surgery to remove appendicitis. Inflammation is observed, which spreads to the area of the portal vein, mesenteric vein and process.
Accompanied by fever, severe liver damage, and acute pain in the abdominal area.
If this is an acute stage of the pathology, then everything can lead to death. Treatment is complex, requiring the introduction of antibiotics into the portal vein systems.
Intestinal fistulas
Occurs after appendicitis in 0.2-0.8% of people. Intestinal fistulas form a tunnel in the intestines and skin, sometimes in the walls of internal organs.
The reasons for their appearance may be poor sanitation of purulent appendicitis, surgeon errors, tissue inflammation during drainage of internal wounds and foci of abscess development.
It is difficult to treat the pathology. Sometimes doctors prescribe resection of the affected area, as well as removal of the top layer of epithelium.
It should be noted that the occurrence of complications is facilitated by ignoring the doctor’s advice, failure to comply with hygiene rules, and violation of the regime.
Deterioration of the condition can be observed 5-6 days after surgery.
This will indicate the development of pathological processes in the internal organs. During the postoperative period, it is possible that you will need to consult with your doctor.
You should not avoid this; on the contrary, your body gives signals that other ailments are developing, they may not even be related to the appendectomy.
It is important to pay due attention to your health and do not hesitate to seek help from a doctor.
Increased body temperature
The inflammatory process can also affect other organs, and therefore the occurrence of additional health problems is possible.
Women often suffer from inflammation of the appendages, which makes diagnosis and the exact cause of the disease difficult.
Often, the symptoms of acute appendicitis can be confused with similar pathologies, and therefore doctors prescribe an examination by a gynecologist and an ultrasound of the pelvic organs if the operation is not emergency.
Also, an increase in body temperature indicates that an abscess or other diseases of the internal organs are possible.
If the temperature rises after the operation, then you need to undergo an additional examination and be tested again.
Digestive disorders
Diarrhea and constipation may indicate a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract after appendicitis. At this time, the patient is having a hard time with constipation; he cannot push or strain, because this is fraught with protrusion of hernias, ruptured sutures and other problems.
To avoid indigestion, you need to stick to a diet, making sure that the stool is not fixed.
Pain attacks in the abdomen
As a rule, there should be no pain for 3-4 weeks after surgery. This is how long it takes for tissue regeneration to take place.
In some cases, pain indicates hernias or adhesions, and therefore there is no need to take painkillers, you should consult a doctor.
It is worth noting that appendicitis is often encountered in the medical practice of doctors. The pathology requires urgent hospitalization and surgery.
The thing is that inflammation can quickly spread to other organs, which will entail many serious consequences.
To prevent this from happening, it is important to visit a doctor in a timely manner and call an ambulance. Do not ignore those signals from the body that indicate the development of the disease.
Appendicitis is dangerous; even with a successful operation, deaths have been observed more than once, let alone when patients neglect their health.
Prevention
There are no special preventive measures for appendicitis, but there are some rules that should be followed to reduce the risk of developing inflammation in the area of the appendix of the cecum.
Below are some useful tips:
- Adjust your diet. Moderate your intake of fresh herbs (parsley, green onions, dill, sorrel, lettuce), hard vegetables and ripe fruits, seeds, fatty and smoked treats.
- Take care of your health. It is worth paying attention to all signals about a malfunction in your body. There have been many cases in medical practice where inflammation of the appendix was caused by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into it.
- Detect helminthic infestations and provide timely treatment.
Summing up
Although appendicitis is not considered a dangerous disease, the pathology has a high risk of developing complications after surgical removal of the appendix of the cecum. Typically, they occur in 5% of people after appendicitis.
The patient can count on qualified medical care, but it is important not to miss the moment and see a doctor in a timely manner.
It is imperative to follow all the specialist’s recommendations during the rehabilitation process after appendicitis.
You need to wear a bandage, women can wear panties. This measure will help not only to eliminate complications after appendicitis, but also to keep the seam neat, without causing it to become defective.
Pay attention to your health, and even if appendicitis has been detected, try to do everything that the doctor directs to avoid problems in the future.
Useful video
Patients who have undergone surgery to remove an inflamed appendage of the cecum (appendix) need to be aware of possible adhesions after surgery in the abdominal cavity. Having studied the symptoms of adhesions after appendicitis, you can monitor your own well-being and, even at the slightest suspicion of pathology, consult a doctor to avoid serious complications.
Pain at the site of appendix removal - symptoms of adhesions
Symptoms and first signs
As medical practice shows, after appendectomy, cords form in more than 85% of patients . The main sign of a complication is severe pain in the area of the removed appendix. Discomfort is felt on the right side under the ribs.
It is worth considering that the pain will not be constant: the discomfort intensifies after physical activity, when changing position and due to sudden movements. In addition to discomfort in the operated area, intestinal dysfunction is observed, accompanied by the following symptoms :
- flatulence, bloating;
- feeling of heaviness in the abdominal cavity;
- difficulty with bowel movements;
- constant nausea (35% of patients experience vomiting);
- general weakness, headaches, dizziness;
- increase in body temperature up to 38°C;
- frequent heartburn and belching;
- intoxication of the body;
- decrease in blood pressure.
Patients with cardiovascular diseases may experience disruptions in myocardial function.
It is worth considering that the first time after surgery to remove appendicitis, neoplasms will practically not make themselves felt. The patient will only exhibit symptoms indicating bowel dysfunction. As the pathology progresses and the size of the tumors increases, other signs appear: problems with bowel movements, heaviness in the abdomen.
To minimize the risk of subsequent complications , you need to consult a doctor in a timely manner, who, after an examination, will tell you what to do next.
Such symptoms cannot be ignored , since the formation of adhesions is a dangerous pathology. In the absence of timely treatment, the disorder leads not only to intestinal obstruction and tissue necrosis, but also negatively affects the condition of the pelvic organs. Adhesions are especially dangerous for women, as they often spread to the ovaries, which causes difficulties in conceiving a child.
Reference. If adhesions have formed after removal of appendicitis, the abdominal area will be particularly painful during palpation.
Intestinal adhesions after surgery
Adhesions are most often associated with abdominal surgery. Adhesions serve as a natural obstacle in the peritoneum to limit the inflammatory process in it. The bad thing is that this disrupts the normal interaction and functioning of the internal organs of not only the abdominal cavity, but also the pelvic organs. There are also frequent cases of inability to get pregnant for a similar reason.
Attention! If we talk about the mechanism of formation of adhesions in medical terms, then many aspects of adhesive disease will remain unclear, but we don’t need to know all the nuances. It is important to understand that any surgical intervention in the abdominal area, performed even by the best surgeon in the best hospital, can provoke the formation of adhesions.
Doctors cannot in any way prevent the occurrence of adhesions, but they must inform the patient about the possible symptoms of adhesions and how to reduce the risk of their formation. Follow all medical instructions and the chances of adhesive disease will be significantly reduced.
What are adhesions?
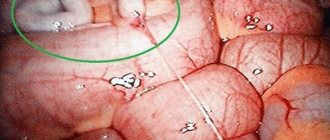
Adhesions after appendicitis are the most common consequence of surgery. As a result of surgical intervention, unwanted connective tissue formations appear to one degree or another in a third of patients. Strands, as these formations are called, arise between the intestinal loops and other abdominal organs. In this case, there is a kind of gluing, merging of their serous membranes with each other. Adhesive disease is promoted by the peritoneum's ability to adhere.
Formation of adhesions in the intestines
Interesting to know! The peritoneum is a membrane, multiple thin serous surface that envelops the organs. It is formed by two layers - visceral and parietal, passing into each other to form a closed sac - the cavity of the peritoneum, which is filled with serous contents.
If for some reason an inflammatory focus occurs in the abdominal cavity, the membrane of the peritoneum is securely attached and adheres to the inflamed area, thereby preventing the pathology from spreading further. One could say that this is a good protective function, but sometimes a similar process occurs with deformation of organs and disruption of their functioning. Constriction of blood vessels and narrowing of the intestines are often detected.
The main causes of adhesions after appendicitis
There are several factors that can cause adhesions after appendicitis. Among them are of particular importance:
- Surgical intervention. With laparoscopic access, the risk of adhesions is slightly lower than with laparotomy.
- Long-term inflammatory process. With the constant migration of immunocompetent cells into the zone of infection, connective tissue gradually grows.
- Poorly performed operation. If there is a cotton ball or bandage in the wound, chronic inflammation is formed with subsequent complications.
- Vascular coagulation. During the cauterization process, the doctor may touch adjacent tissues and damage them.
After appendectomy for catarrhal appendicitis, adhesions rarely form. This is the result of common or severe forms of the disease, including perforated appendicitis and peritonitis. When removing a process that has not undergone significant changes, the scope of the operation is minimal. Accordingly, adhesions are not formed.
Symptoms of adhesive disease
Symptoms of adhesions after appendicitis, as after any operation or serious injury in the abdominal area, are manifested primarily by periodic pain at the site of intervention - in the lower abdomen on the right side. Most often, the patient begins to notice a painful sensation during physical activity or sudden movements.
Adhesive disease does not have pathognomonic symptoms, but consists of all the symptoms that determine the patient’s condition as a whole. Basically, these are various types of functional intestinal disorders, but not only:
- abdominal pain;
- flatulence;
- frequent constipation;
- nausea, vomiting;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- decreased blood pressure;
- general weakness.
Note! Symptoms of intestinal adhesions after appendicitis are pronounced only in the acute form of adhesions. Symptoms appear when there is already a threat to the patient’s health and another operation is required. Monitor your health: abdominal pain and severe constipation should alert you.
It is not possible to detect adhesions using ultrasound. Laparoscopy is used for accurate diagnosis, but such a modern minimally invasive procedure is not available everywhere and it is still an operation.
Diagnostic methods
If you experience abdominal pain after surgery, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. To make a diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a special examination:
- Anamnesis collection. The doctor conducts an initial examination and records the patient’s complaints. If there is a suspicion of adhesive disease, especially if the person has had appendicitis relatively recently, further examination is prescribed.
- Laboratory blood test. Detects the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
- Ultrasound. Using this method, the presence, location and size of adhesive strands are revealed. The patient must adhere to a special diet for several days before the procedure.
- Radiography. The procedure is performed using a contrast agent. Shows a general picture of intestinal damage.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy. A special device equipped with a camera and a light system is inserted into the abdominal cavity through a small incision. Allows you to clearly see the existing cords on the intestines.
Return to contents
How to remove adhesions?
Treatment of adhesions after appendicitis depends on the exact stage of development at which they were detected. If the process has just begun, you can try to stop it conservatively. Modern pharmacology can offer a wide range of drugs, but taking them without consulting a doctor is strictly prohibited!
If adhesions do not allow the patient to live normally, an operation is prescribed, which is similar to appendix removal, which can be either traditional or laparoscopy. The latter method is preferable, because after it the adhesions are removed forever, and the operation itself does not leave scars.
Removal of adhesions using laparoscopy
What to do to prevent adhesions from occurring? After surgery on the appendix, the patient is under observation for some time. To avoid adhesions in the intestines, surgeons recommend starting to move very soon after the operation.
It is important to follow all recommendations and not feel sorry for yourself! Move within reasonable limits, walk, try to keep your body in an upright position more often. If the body moves, there will be some movement in the internal organs, and this is enough in most cases to prevent symptoms of adhesions after appendicitis from occurring.
Treatment methods
The treatment regimen is selected taking into account the stage of the pathological process, concomitant disorders and the patient’s age. If the complication was identified at the initial stage, in most cases conservative treatment is prescribed :
- Taking medications. You can cure adhesions with the help of aloe in ampoules, tocopherol and folic acid. The dosage and duration of administration are determined individually for each patient.
- For severe pain caused by constipation and flatulence, painkillers such as Papaverine and Drotaverine are prescribed.
- To block the inflammatory process and further proliferation of connective tissues, NSAIDs are prescribed: Ibuprofen and Ketorol.
- Physiotherapy. The technique is effective only in the initial stages of adhesions formation. The most effective is considered to be a course of electrophoresis with magnesium, as well as paraffin applications to the abdominal cavity.
Particular attention is paid to diet. It is advisable that it be based on foods rich in plant fiber: cereals, vegetables and fruits. Complex carbohydrates stimulate the intestines and promote the excretion of feces.
During treatment, exclude from the diet:
- carbonated drinks;
- canned food;
- fast food;
- peas and beans;
- cabbage;
- corn;
- baked goods;
- natural milk.
These products increase gas formation , so if there are adhesions, their use increases pain.
If drug therapy and physiotherapy do not produce results and the patient continues to complain of painful symptoms, surgery is prescribed. During it, the surgeon cuts the adhesions. The operation can be performed using the classical method, using a laser or electric knife. If necrosis is detected, the affected tissue is removed.