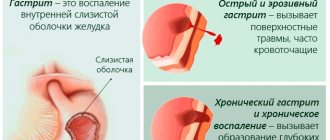
The tissues of the esophagus are most sensitive to the effects of chemicals. If a person swallows anything from aggressive solutions or suffers thermal injuries, a burn of the larynx or esophagus occurs. Symptoms usually appear immediately. Severe pain, swelling, and vomiting occur. Depending on the degree of injury, different treatment methods are prescribed. The therapy is carried out in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor.
The most severe damage occurs as a result of ingestion of acids and alkalis. A significant part of the victims are children whose parents did not look after them. Burns of the esophagus in young children are the most dangerous, since the child cannot always tell what substance he drank.
If the necessary measures are taken in time, the possible consequences of a burn to the esophagus are reduced to nothing. In this article we will look at emergency measures, signs of damage, and how to treat different types of burns.
Signs of a burn
In adults, poisoning occurs in most cases either through negligence or due to a suicide attempt. When an injury occurs, various symptoms occur. First of all, nerve endings and tissues are damaged. Against this background, severe pain occurs. It spreads to the mouth, throat and the esophagus itself.
Subsequently, the patient begins to experience tissue swelling, which moves from top to bottom. It becomes more difficult to breathe and wheezing appears. The person stops swallowing normally, then vomiting begins. It often contains blood and mucus. The following symptoms are also noted:
- dyspnea;
- nausea;
- spasms;
- attacks of suffocation;
- cough;
- the occurrence of ulcers;
- increased salivation;
- tachycardia.
Severe damage may affect internal organs. The liver, kidneys, heart and brain are primarily affected.
Signs of thermal and/or chemical damage
Burns of the esophagus in children and adults are accompanied by severe pain felt in the upper abdomen, behind the sternum and in the neck. Also, traces of burn injuries are determined by swelling on the lips and oral cavity. In addition, the person experiences shortness of breath, hoarseness in the voice, or the ability to pronounce sane sounds completely disappears. The impact of an aggressive environment on the mucous surface destroys the cellular structure and leads to tissue necrosis, which entails a physiological narrowing of the esophagus, and as a result, the person begins to suffocate.
With a chemical aggressive lesion, the wall of the esophagus can collapse with the formation of a hole, and in especially severe cases, an esophageal-tracheal fistula is observed, accompanied by suffocation, uncontrollable coughing and the release of sputum with food fragments. As a rule, patients after a burn of the esophagus with chemically active compounds are admitted to a medical facility in a state of shock or unconsciousness. Treatment often requires resuscitation measures.
Severity of burns
Depending on how badly a person was injured, one of several degrees may be assigned:
- the first, the easiest type of damage, is characterized by the fact that injuries appear on the superficial tissues, while the internal ones do not suffer. Signs include swelling, redness, and mild pain. All symptoms disappear after a few days and do not require medical intervention;
- with a more serious degree of damage, the second, the muscles are also affected, severe swelling develops, and ulcers appear. Provided you contact a medical facility in a timely manner, the injury will not have serious consequences, the tissues will heal within a month;
- the last, third degree, is characterized by the most severe damage to all tissues of the esophagus and stomach. Intoxication occurs in the internal organs that are located nearby. The patient is suffering from severe pain. If medical care is provided in a timely manner, the chance of recovery increases. However, possible consequences of a burn to the esophagus at this stage are most likely to appear. Scars form in place of damaged tissues; a very long period of rehabilitation will be required. If help was not provided on time, the person will die.
Types and causes of burns
This injury can be chemical or thermal in nature.
In the first case, damage occurs as a result of exposure to aggressive chemicals, acids, alkalis, and even alcohol burns are possible. In the second case, the mucous membranes are burned under the influence of excessively high temperatures. Thermal burn of the esophagus occurs as a result of eating excessively hot food, boiling water, or ingesting steam. Chemical burns of the esophagus can occur when ingesting alcohol, peroxide, acetic acid, ammonia, and household chemicals.
Young children are most susceptible to chemical damage. Injuries occur due to the child’s curiosity and lack of parental care. Therefore, it is very important to store all household chemicals and other aggressive substances in a place inaccessible to children!
Adults rarely receive such injuries, either by accident or deliberately, during a suicide attempt. Patients suffering from chronic alcoholism, in the absence of the opportunity to purchase high-quality alcoholic beverages, often drink medical or industrial alcohol, which also leads to severe damage to the stomach and esophagus.
According to statistics, the most common type of injury among this type is a burn to the stomach caused by hot food. Specialists divide burn injuries into several categories, depending on the severity of the depth of damage to the esophageal tissue:
- The first degree is characterized by damage to the superficial epithelial layers, without damage to the internal soft tissues, which is accompanied by mild swelling. The patient experiences moderate pain that disappears within a few days, even without medical measures.
- In the second degree, mucous membranes and muscle tissue localized in the area of the stomach and esophagus are affected. The development of severe edema and ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane is observed. In this case, the patient requires qualified treatment. With timely assistance, the damage heals within a month.
- Third degree - characterized by damage to all deep layers in the area of the stomach and esophagus, the spread of damage to nearby internal organs. The injury is accompanied by the development of painful shock and severe intoxication of the body. Even with timely treatment, such injuries require long-term recovery.
Damage to the stomach and esophagus requires mandatory examination by a qualified specialist, since it is quite difficult to independently determine the severity of the damage. Not only the health, but also the life of the victim largely depends on the timeliness of seeking medical help!
First aid
First aid for burns of the esophageal mucosa is to remove the aggressive substance, and thereby reduce the negative impact. The choice of method depends on the type of damage. For thermal injuries, the victim drinks cold water in small sips. To eliminate painful sensations, anesthetic components are added to it.
In case of poisoning with chemical components, it is important to know exactly what product got inside. Further actions depend on this. There are often recommendations for artificially inducing vomiting, but doctors do not recommend using such measures at home, since this will cause aggressive components to again enter the mucous membrane. In addition, excessive vomiting sometimes provokes rupture of the walls.
To neutralize chemicals, an opposing component is used. For alkali poisoning, use a weak acid solution; for acid poisoning, use an alkaline solution (soda dissolved in water). If it is not known what the victim drank, he is given milk, which will reduce the impact of aggressive drugs until the patient is hospitalized.
In a medical facility, the victim is given a tube through which all the contents of the stomach are removed, then medication is selected.
Regardless of the extent of the injury, the victim must be hospitalized and shown to a doctor. If this cannot be done immediately, assistance should be provided on the spot until paramedics arrive. First aid for various esophageal burns includes the following steps:
- wash your mouth with plenty of water;
- in case of poisoning with chemicals, drink 2 glasses of milk; in case of thermal injury, you need to drink cold water in small sips. Novocaine can be added to the liquid to reduce pain;
- It is not recommended to artificially induce vomiting. The decision on this is made only in a medical institution;
- it is necessary to neutralize the effect of chemical components if hazardous substances have been ingested. Depending on their type, an opposing reagent is selected.
In any case, the victim should be taken to the hospital for an accurate diagnosis and the necessary treatment.
Classification
We use the following classification of caustic injuries of the esophagus:
- 0 - no damage
- 1 - erythema and swelling
- 2 - ulceration is not circular
- 3 - circular ulceration
- 4 - perforation
There are also more detailed classifications:
- 1st degree - erythema and edema (damage is limited to the superficial layers of the mucosa, their rejection with subsequent epithelization without scar formation is possible).
- 2a degree - vulnerability, hemorrhages, erosions, exudate, blistering (mucosal, submucosal and muscular layers are involved).
- 2b degree - the same as 2a plus deep or circular ulcers.
- Grade 3a - deep ulcers, “gray or black esophagus” (transmural lesion).
- Grade 3 - extensive necrosis.
Related articles:
- Articles: ENDODIAGNOSTICS FOR ESOPHAGUS BURNS WITH ALKALI
- Articles: FEDERAL CLINICAL GUIDELINES “Toxic effect of corrosive substances”, “Toxic effect of soaps and detergents” 2014
- Articles: Zargar classification - assessment of damage to the esophagus when swallowing caustic (caustic) substances
CLASSIFICATIONS section
Chemical burn of the esophagus and stomach
Damage resulting from the internal use of aggressive solutions is most common. They are treated in a medical facility. The greatest danger is the process of absorption of components into deep tissues. This happens in the absence of first aid.
Inflammatory processes gradually cover the upper gastrointestinal tract. The greatest danger is posed by ingested alkaline solutions, which quickly penetrate deep tissues, affecting internal organs. With this type of lesion, esophagitis often develops.
After first aid is provided, the victim is prescribed agents that promote the formation of a protective film on the mucous membranes. The complex uses antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and painkillers.
In most cases, patients are unable to eat anything on their own, even liquid meals, since the tissues are severely damaged and their sensitivity is increased. Therefore, during the recovery period, nutrient solutions are additionally used, which are administered using droppers.
Damage caused by the use of chemicals is quite common. Most often, people mistakenly or intentionally swallow vinegar, acid, alkali, ethyl, phenol, etc.
When aggressive components enter the mucous membrane, they cause severe damage to first the superficial tissues, then penetrate deep into the body. If the victim is not provided with timely assistance, a rupture of the esophagus, the appearance of pus, and bleeding may occur. Chemicals tend to penetrate deep into tissues and be absorbed into the blood. Subsequently, they enter the internal organs and cause disruptions in their functioning. The most severe cases cause death within 2–3 days.
Acid burn
When acid penetrates into the body, tissue death occurs. Exposure to chemicals causes extensive damage to the mucous membrane and pulmonary edema. The person has difficulty breathing, which worsens the general condition.
Tissue restoration processes take a long period and last up to six months, depending on the severity of the damage. After healing, scars form on the walls. In severe cases, deformation of the esophagus occurs, and scarring lasts for several years, periodically causing pain in the victim.
If it is known for sure that a person drank a solution containing acid, its effect must be neutralized with alkali. To do this, use regular soda, which is dissolved in water in a proportion of 1 tsp. per 1 liter of liquid.
Alkali burn
When consuming an alkaline solution, the risk of death increases. It can cause rapid and deep tissue damage. Acid is used to neutralize alkalis. At home, you can use lemon or vinegar. To prepare the solution, take 3 g of the substance and 1 liter of water.
Vinegar burn
When vinegar is ingested, not only the walls of the larynx, but also the internal organs can be affected, since it is quickly absorbed into the blood. To provide first aid, the victim is given an alkaline solution (soda mixed with water) to drink.
Treatment
Treatment for a burn of the esophagus is carried out on an individual basis, prescribed by a doctor after examining the victim and conducting diagnostics. Typically, comprehensive therapy is required, consisting of the following measures:
- gastric lavage using a tube (the procedure is painful, so painkillers are often administered before it);
- spasm relief;
- prescription of antibiotics;
- infusion of saline solutions and other means to maintain the normal functioning of the liver and other internal organs;
- general strengthening procedures.
The table below shows commonly used drugs:
| Painkillers | Analgin, Morphine |
| Antispasmodics | Atropine |
| Sedatives | Relanium |
| Antishock | Sodium bicarbonate, Reopoliglucin |
| Antibiotics | Ampiox and others, broad spectrum |
In case of severe damage to the esophagus, the victim is taken to a medical institution, whose specialists can perform an operation. Surgery is required to remove the affected areas of the esophageal mucosa by excision.
Treatment of thermal burns of the esophagus
If a thermal injury occurs due to one-time consumption of a large amount of hot food or boiling water, the same measures must be applied as in the case of a chemical injury. In most cases, gastric acid damage due to poor diet or alcohol abuse occurs over a long period of time and gets worse.
For therapy to be successful, complete abstinence from alcohol and dietary adjustments are required. Medication is mandatory because if left untreated, complications may arise. Due to a thermal burn, esophageal stenosis also appears and the functioning of the digestive system is disrupted.
Doctors advise treating damage to the esophagus with drugs of three groups, taking them simultaneously:
- alginates that create a protective film around the mucous membrane: Almagel, its analogues;
- drugs that accelerate metabolism: Motilium, Motinol;
- drugs that normalize acid levels: Lanza, Nolpaza.
If damage to the esophagus by alcohol or hot food is serious, immediate hospitalization is required. As with chemical burns, particularly severe cases may require surgery.
Elimination of burn strictures
Burn strictures of the esophagus – scar formation. They usually occur with severe chemical burns. To eliminate them, an operation is prescribed, which is recommended to be performed at least 1 month after the injury.
Depending on the degree of the inflammatory process, there are two types of burn strictures:
- complete – there is no lumen in the esophagus;
- incomplete - a small gap remains.
The stricture can be of any length, sometimes it affects neighboring internal organs, especially the stomach. Doctors make diagnoses using radiography.
Various diagnostic methods may be prescribed to help the doctor determine the parameters of burn strictures.
After this, a decision is made to choose one of the possible treatment methods for burn strictures:
- Bougienage. It appears to be effective in the treatment of short burn structures.
- Surgical intervention. It is prescribed if bougienage does not bring results or the burn strictures are too long.
The doctor prescribes one of the treatment options, explaining to the patient the essence of the procedure.
Thermal burn of the stomach or esophagus
Thermal injuries are usually caused accidentally. When this type of injury occurs, treatment can be done at home using traditional medications. Typically, victims are prescribed antibacterial agents, painkillers, and antispasmodics.
In addition, medications are prescribed to prevent the development of scars. During therapy, it is necessary to drink plenty of cool water, and also give preference to soft foods at room temperature. Treatment lasts about a month.
A special case is the burn of the walls of the esophagus by gastric juice. This disease can cause esophagitis and requires professional treatment.
Food burn
You can burn your mouth and mucous membranes with hot food if you eat food whose temperature exceeds the norm. Food whose temperature is above 40 degrees Celsius is not recommended. A symptom of injury will be pain. To neutralize the effects, you need to drink cold water in small sips.
Boiling water burn
If you drink a liquid that is too hot, its effects should also be neutralized with cold water. For any type of lesion, you need to see a specialist so that he can prescribe a medicinal solution in cases where it is necessary.
Causes
Radiation and thermal burns are extremely rare; if a person is burned by something hot, it is usually a superficial injury that does not require special treatment. The most common cause is the use of chemical substances.
The most common causes of burns:
- inattentive use of chemical liquids and ingestion;
- taking dangerous liquids by mistake, for example while intoxicated;
- suicide attempts with the deliberate use of aggressive chemical compounds.
Treatment of a burn of the esophagus must be carried out as quickly as possible, therefore, at the first symptoms, the victim should be taken to the hospital for a detailed examination, diagnosis and a course of therapy.
Burn of the esophagus and stomach in a child
Most often, parents of young children go to medical institutions for diagnosis. More than half of the cases of mucosal injuries occur in minors. This is due to the fact that they love to break taboos and try new things.
To avoid accidents, it is necessary to remove all potentially dangerous substances upstairs, where children cannot climb. Vinegar, alkaline solutions, and household chemicals should be stored out of the reach of children.
Parents should know how to treat burns in young children. Therapy takes place in a medical facility to avoid possible consequences. Often the problem is to determine what the child has drunk. The babies' stomach is washed and appropriate treatment is prescribed.
The danger is that in young children all processes proceed faster, and, therefore, the risk of intoxication of internal organs is higher. Therefore, it is important to call an ambulance as soon as you discover that your child has drunk a chemical.
Burn of the esophagus with hot food - can you burn the esophagus with hot tea or soup?
Temperature burns of the esophagus usually have a favorable prognosis and are not accompanied by severe lesions in the area of the esophageal wall.
This is due, first of all, to reflex defense mechanisms - if hot food gets into the oral cavity, all attempts will be made to remove it from there.
The temperature at which the protein of the mucous secretion begins to coagulate is quite high - about 70 degrees . The maximum possible temperature of water-based food products cannot exceed 96 degrees. Given such a small range, significant burns do not occur - in 98% of cases, a first-degree burn is diagnosed.
An exception may be oil-based products . Boiling vegetable oil can reach temperatures of 200 degrees or higher, so if such an agent gets into the esophagus, burns of any degree can occur.
Alternative treatment for burns of the esophagus or stomach
All traditional methods refer to remedies that can only be used for minor injuries. Be sure to wait for the first symptoms of poisoning to subside, and also consult with your doctor about the advisability of using certain medications. The most popular folk methods include the following:
- Sea buckthorn and olive oils reduce the manifestations of pain syndrome. They envelop tissues and reduce sensitivity. They should be consumed 1 tbsp. l. on empty stomach;
- Chamomile provides an anti-inflammatory effect due to its rich composition. The natural antiseptic also relieves discomfort in the larynx area. Brew flowers at the rate of 1 tbsp. per glass of boiling water. Let the broth brew and cool, then consume orally 2 – 3 times a day;
- A popular recipe that uses flaxseed is popular. 12 tsp. The plants are boiled for 10 minutes in 1 liter of water. The solution is decanted and cooled. After this, you can drink it several times a day. Flaxseed will have an analgesic effect;
- milk helps cope with the effects of chemical damage. It is drunk undiluted, after being cooled in the refrigerator. You can drink 2 – 3 cups of drink per day.
However, you should not rely only on folk recipes. Conservative treatment should be prescribed by a specialist.
If a chemical or thermal injury occurs, it is important to provide timely assistance to the victim. Despite the fact that mild burns go away quickly and do not require hospital treatment, only a doctor can decide on the need for therapy. Therefore, in any case, you need to call an ambulance to clarify the diagnosis, especially if we are talking about a minor.
Etiology of the phenomenon
Vinegar
Poisoning statistics show that the following chemicals are most commonly ingested and cause a burn to the esophagus:
- acids – acetic essence, sulfuric and hydrochloric acids;
- alkalis - caustic soda, sodium hydroxide, etc.
- other substances - ethyl alcohol, iodine, sublimate, ammonia, silicate glue, potassium permanganate solution, acetone, hydroperite, all kinds of stain removers and solvents.
In addition to the esophagus, chemical liquids affect the mucous membrane of the mouth, throat and stomach. More than 70% of the victims are children, who, due to their curiosity, try to taste everything. Of the remaining 30% of adults who accidentally or intentionally drank poison, the majority are women. Alkali burns are considered more destructive than acid burns.
Due to the effects of acid, the mucous surfaces are covered with a kind of membrane, which slows down further penetration of the substance into the lower tissues of the stomach. The acid concentration is also affected by the fluid secreted by the affected areas of the esophagus after a chemical burn.
When alkalis get inside, they cause completely different consequences - they destroy proteins and fats, dissolving stomach tissue and turning them into viscous jelly. Alkali causes necrosis (death) of the walls of the esophagus and its perforation (the appearance of holes).
The main cause of chemical burns of the esophagus in children is the presence of such dangerous things in accessible places. The child is fascinated by the colorful wrappers of household chemicals, and he tries to taste the contents of these containers. It is also a mistake to pour chemicals into glass jars and bottles without labels, which also leads to accidental consumption.
Possible complications
Anemia
As noted above, when consuming chemical components, the chemical drug ingested has a toxic effect on the activity of all organs and leads to damage to the heart, liver, and kidneys. With simultaneous chemical burns of the gastric tract and respiratory organs (larynx, trachea, bronchi), there is a danger of pulmonary edema and suffocation. Such consequences are caused by exposure to vapors of acids and alkalis.
According to statistics, 70% of all poisonings and burns from chemical substances are caused by poisoning with vinegar essence, which causes such consequences as blood acidification and hemolysis of red blood cells - toxic hepatitis develops with complications in the liver and kidneys, a decrease in the level of bilirubin, hemoglobin, anemia, urine turns dark red fleshy color.
When burned by alkali elements, dehydration (dehydration) and softening of the tissues of the esophagus are observed, as a result of which toxic alkalis penetrate into deep tissues and cause necrosis, bleeding and perforation of the digestive organs (fistulas).
Important: Applying a burn patch
Pathological complications that begin to develop in the digestive tract go through 4 stages: necrosis of mucous and soft tissues, formation of ulcerations and granulations, the beginning of scarring, ending with cicatricial narrowing of the esophagus.
The most painful stage, causing suffering to the patient, is the 1st stage (during the first week). The victim experiences severe pain in the mouth, chest and abdomen. There is profuse salivation, vomiting, and a little later - rapid breathing, increased temperature, severe tachycardia and a decrease in pressure until shock occurs.
Stage 2 (7-30 days) – the stage of imaginary improvement, when the patient is able to take liquid food. This period is characterized by the beginning of the rejection of dead tissue and, as a result, bleeding. In especially severe cases, perforation, fistulas, and blood poisoning may occur.
At the 3rd stage (1-2 months), scarring of the superficial affected areas begins. Stage 4 ends with scarring of deep areas, narrowing and obstruction of the esophagus. The process can last from 2 to 6 months. In special cases, deep scarring can begin decades after the accident.
Why does a burn occur?
When aggressive substances enter the stomach, other digestive organs - the esophagus and liver - are affected, and the function of the kidneys and adrenal glands is impaired, which leads to a life-threatening condition.
The most common types of burns that occur are thermal and chemical burns. When the provoking component enters the stomach, the epithelium is damaged and dies. Long periods of healing and scarring of tissue lead to narrowing and complete obstruction of the stomach. The following unfavorable factors precede the condition:
- large amounts of strong alcohol consumed on an empty stomach;
- accidental ingestion of household chemicals containing alkalis or acids;
- drinking vinegar in its pure form (not diluted with water or as a food additive);
- taking too hot food or liquid.
Help with alcohol burns
If there is a burn to the stomach from alcohol on the face, then the victim urgently needs to receive help. It is as follows:
- The first step is to wash off traces of alcohol-containing substances. This is done by inducing vomiting by drinking large amounts of water.
- Take the person to the hospital.
Basic treatment for burns consists of the following procedures:
- Taking medications that have an analgesic effect. Suitable: “Promedol”, Analgin.”
- Using medications that can relieve esophageal spasm. Atropine will cope with this effectively.
- Means for normalizing the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- Prevent exposure of the body to toxic substances.
- Help the patient cope with shock. For this purpose, Prednisolone injections and saline solutions administered intravenously are used.
- To avoid complications and infection, it is recommended to take antibacterial agents, for example, Ampiox.
- Relanium will help calm the victim.
- Dehydration of the body requires the installation of a drip to restore water-salt metabolism.
In the first time after a burn, it is recommended to take medications that reduce the secretion of gastric juice. Famotidine and Omeprazole are suitable.
For a victim of an alcohol burn for the first time, it is recommended to take any vegetable oil; it will speed up the healing process. Eating is not recommended.
For severe burns, gastroendoscopy is not performed at first to avoid additional injury to the walls of the esophagus.
A common consequence of a burn is narrowing of the esophagus. To avoid this, doctors use the bougienage procedure. It consists of expanding the lumen of the organ using probes made of elastic material. Each time the diameter of the probe increases. The procedure can begin no earlier than 5-7 days after the esophagus burn and continue for several months after healing.
It is important that the patient understands during treatment that only complete exclusion of alcohol from his life can guarantee successful therapy. Even 100 grams of an alcoholic drink will reduce all the efforts of doctors to zero.
Diagnostic methods
Before treating a chemical burn of the esophagus, the doctor determines the type of substance that caused the damage, its volume and concentration. Since a severe burn may cause a perforation of the esophageal wall, instrumental diagnostics are not performed in the first 3 days.
In the future, the following methods are used:
- fluoroscopy - thickening of the folds of the mucous membrane and symptoms of hyperkinesia can be detected;
- esophagogastroscopy - you can detect swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane, ulcers and erosions, dilatation and stenosis.
Scars of the esophagus discovered during a diagnostic study may look like valves, rings, or pipes. In rare cases, malignancy of scar changes develops.