Reasons: adults, pregnant women, children
The appearance of belching is inevitably associated with eating food, especially in large quantities. The absorption of fast food and air-containing products (milkshakes, souffles) leads to the accumulation of air in the stomach. Active smokers also often suffer from belching due to active swallowing of air.
The main factors for the appearance of belching:
- Binge eating;
- Presence of pathogenic microorganisms (poisoning);
- Incorrect combination of products;
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
In pregnant women, belching is considered normal, resulting from hormonal changes and a slow digestion process. Carrying a fetus - mainly in the second half of pregnancy - leads to compression of the esophagus and the appearance of undesirable processes.
In children, belching of air occurs due to the rapid process of absorption of food. Capturing air, the baby swallows it along with food, which after a while comes out in the form of belching.
Diseases in which this symptom occurs
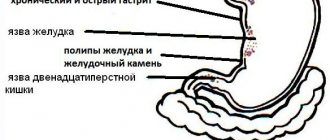
Among the gastrointestinal diseases that provoke belching are:
- Gastric stenosis,
- Kink in the stomach
- Gastritis,
- Inflammation of the esophagus.
Dysbacteriosis, leading to frequent disorders, equally provokes active gas production.
Gastroesophageal reflux is accompanied by the backflow of food into the esophagus from the stomach, which provokes increased formation of gases.
Problems with the liver and gall bladder disrupt the functioning of the intestines, and therefore are concomitant diseases to the manifestation of unhealthy gas formation in the stomach. Nervous diseases, primarily nervous aerophagia, are characterized by the weakening of many body systems, including disruption of the stomach.
Medical causes of belching
Since belching, flatulence and diarrhea (diarrhea) are natural reactions to abdominal discomfort, there should be other symptoms for various diseases that will allow the doctor to make the correct diagnosis.
Reasons that can lead to burping include:
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): a condition that causes stomach or duodenal contents to flow into the esophagus.
- Paresis (also called delayed gastric emptying): a condition in which the muscles in the stomach wall are weakened. This results in delayed digestion, and the abdominal muscles are needed to push food through the digestive tract.
- Belching with gastritis occurs due to inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Gastritis is often accompanied by belching of hydrogen sulfide. Due to atrophy of the gastric mucosa, decreased acidity of gastric juice and decreased motor function of the stomach walls, gases belched after eating acquire the smell of rotten eggs. Due to gastritis, belching with a large amount of saliva is painful even after sleep (it is called “hungry belching”).
- Peptic ulcers on the esophagus, stomach and upper small intestine.
- Inability to properly digest lactose. This ingredient is found in dairy products. This condition is often accompanied by diarrhea.
- The body's inability to properly digest fructose and sorbitol. This condition, like lactose intolerance, is often accompanied by diarrhea.
- The bacteria Helicobacter pylori causes stomach infections, which can make belching worse. These same bacteria can cause gastritis, peptic ulcers and GERD.
- In persons with diseases of the nervous system (hysteria, neurasthenia), so-called nervous belching or pneumatosis of the stomach sometimes occurs. Its causes are the accumulation of a large amount of air in the stomach with the subsequent formation of a gas bubble.
- With thoracic or cervical osteochondrosis, belching and nausea occur while eating. Also, with osteochondrosis, due to muscle spasm, a feeling of a lump in the throat often appears, regardless of food intake.
Less common causes of belching:
- celiac disease: intolerance to gluten, an ingredient in many flour products;
- dumping syndrome: a disorder in which incompletely digested food passes from the stomach to the intestines;
- The pancreas is unable to produce enough enzymes needed for digestion.
Diagnosis of pathological processes
The patient assesses the process of gas release based on additional criteria. Particular attention should be paid to the taste indicators of belching.
Diagnosis of belching by taste:
a rotten taste indicates the presence of low stomach acidity and gastritis- a sour aftertaste indicates gastritis with high acidity
- putrid taste is formed from the decomposition of food in the stomach (usually due to overeating at night)
- sour or bitter with foam - chronic or acute gastritis
- bitter belching - liver problems
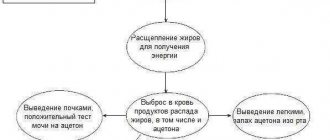
- acetone taste is a symptom of the presence of diabetes mellitus in humans
You should also pay attention to the duration of the belching, which should not last several seconds. If you have a foreign taste, prolonged belching and increased discomfort, you should contact a therapist or directly a gastroenterologist.
A person who consults a doctor is traditionally sent for urine and blood tests (if diabetes is suspected, additionally for sugar testing), as well as an FGDS test. Assumptions regarding intolerance to certain foods will require an immunological study (blood is taken from a vein).
Belching mucus from the stomach
Every healthy person has a certain amount of mucus in the stomach. Mucus itself is a natural biological gel with a complex composition responsible for protecting the stomach. If a person experiences belching of mucus from the stomach, then it is worth thinking about suspected rigid and hypertrophic gastritis. Most likely, excessive secretion of mucus from the stomach occurred under the influence of medications, alcohol, rough and unhealthy foods. Despite its protective functions, the natural biological gel simply could not resist the onslaught and was expelled from the stomach.
In order to further prevent belching of mucus from the stomach in the future, the following enzyme preparations should be taken: Festal, Creon, Mezim, Enzistal.
Mucus in the stomach: causes
In this case, you don’t have to go far. Mucus in the throat has very common causes:
- Regular consumption of unhealthy and unhealthy foods.
- Drug therapy “cleaned” the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Passion for alcohol and carbonated drinks.
- Protracted illnesses without proper treatment.
- Being depressed or in a stressful situation.
The reasons are quite simple at first glance, but in order to restore the normal functioning of the stomach, serious treatment and the right approach to your health are required.
Mucus in the throat from the stomach
Periodically, mucus does not have proper release for a long time. Therefore, it actively accumulates on the way to its exit. Mucus in the throat from the stomach collects and very often comes out at one time in copious amounts. True, this requires a strong impact on the gastrointestinal tract with medications or food.
Treatment
Unpleasant conditions that last more than 2-3 weeks require the use of auxiliary medications to eliminate the frequent release of gases.
Drugs and drug treatment
When choosing a drug, the doctor is based on the causes of belching.
- Almagel, Smecta eliminate symptoms of heartburn and flatulence;
- Pancreatin improves digestion and blocks the formation of belching due to poor digestion;
- Omeprazole, Gastal are indicated for increased stomach acidity, reflux and ulcers;
- Passazhix neutralizes gagging, eliminates hiccups and improves gastric motor function.
Taking medications helps to quickly and effectively eliminate belching, but if there is no long-term effect, you need to return to the clinic.
Goodbye burp!
Folk remedies and treatment at home
Elimination of the feeling of heartburn and the belching caused by it is done by taking a solution of soda (half a tablespoon per cup of water). A decoction of mint and linden (leaves) has an enveloping effect, taken for up to 10 days in small portions (35-40 ml no more than 3 times a day). A decoction of flax seeds is also useful for inflammation of the stomach.
For a normal digestion process, nutritionists advise eating a pear or apple immediately after eating. The disorder caused by nervous manifestations is eliminated by taking tincture of valerian, hawthorn or mint at night (course about 20-30 days).
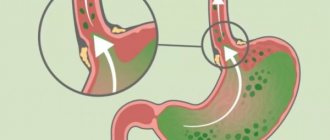
Gastroesophageal reflux
Belching can occur for various reasons. It almost always happens after eating. This is a completely normal and natural phenomenon, so there is no need to panic.
However, if belching is accompanied by foam systematically, most likely the person suffers from gastroesophageal reflux.
Symptoms of this disease almost always appear at night. Why? The fact is that when a person is in a supine position, gastric juice enters the esophagus.
Belching with foam after eating is not the only symptom of GERD. Signs of this pathology:
- A person has a feeling of a lump in the throat. In medicine, this phenomenon is called dysphagia.
- After eating there is a sharp pain in the chest. Painful sensations are present even when a person drinks water.
- Heartburn. Belching with GER is often accompanied by heartburn. This occurs due to an increase in the amount of saliva. After eating, heartburn goes away in about 40-60 minutes. Heartburn will bother a person if he takes a lying position after eating.
- Diarrhea.
- Frequent cough. There is not always phlegm present in the lungs, but dysphagia forces a person to reflexively cough up a lump in the throat.
- Frequent vomiting, nausea.
This is a universal symptom of GERD, however, not every person suffering from this disease will experience everything from the above list.
Signs of this disease may appear suddenly. They disappear in the same way.
To alleviate the patient’s condition, it is necessary to prescribe appropriate medications. Usually, after taking them, he begins to feel better.
If this syndrome is not treated promptly, damage to the esophagus is possible. Specifics of foamy belching with GERD:
- Foamy burps occur within 30 minutes after eating.
- It appears when a person is lying down.
- Belching with the release of liquid appears after eating spicy foods, such as garlic and onions. It also appears after eating fried foods and sour foods. Therefore, patients with GERD should not eat citrus fruits.
- This type of belching occurs after eating chocolate and mint.
When going to the hospital for examination, a patient with GERD should describe in detail all his symptoms, as some of them may indicate damage to the esophagus.
Also, this disease can negatively affect the digestive process, resulting in pathologies in the functioning of the duodenum and stomach.
Prevention
The process of active accumulation of gases caused by poor nutrition is neutralized by following a diet and adjusting the diet.
Avoid foods that cause belching:
- carbonated drinks (cola, lemonade, mineral water);
- fatty, spicy and rich foods;
- chewing gum (long chewing).
The most gas-forming foods are all legumes (peas, beans), cabbage, and dairy products. Food should be chewed thoroughly, without haste, and conversations should not be allowed at the table.
Eating more frequently, but in small portions, reduces the likelihood of belching.