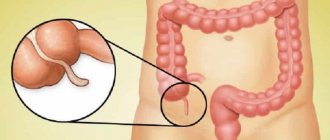
Appendicitis is a purulent-inflammatory process of the vermiform appendix of the cecum - the appendix. Its length is about 10 cm. People wonder what it is for and want to know everything about appendicitis. During the process of evolution, the appendage has lost its original functions, so the body can function normally when it is removed.
At the same time, when an infection occurs inside the appendix, pus begins to accumulate, which can rupture the appendix and lead to peritonitis. For this reason, you need to know how to identify appendicitis and call a help team in time.
Features and causes of inflammation of the appendix
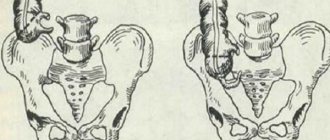
In most people, the appendix is located behind the cecum. The vermiform appendix is capable of rupturing from accumulated pus due to a special septum separating the intestinal lumen from the atavistic cavity. It prevents food waste from entering the appendix.
Inflammation in the appendix develops due to prolonged stagnation of feces, exposure to infections or parasites. Several etiologies of the occurrence of the pathological process are classified:
- helminthic infestation;
- entry of pathogenic microorganisms;
- stagnation theory;
- a consequence of the immune response;
- allergic;
- angioneurotic.
In some cases, the appendix can be compressed by surrounding tissue or twisted, causing damage to the septum and stool leaking into the appendix. After foreign substances enter, the mucous membrane of the organ is damaged, which causes appendicitis.
The infectious process can be triggered by several factors:
- Obstruction of the appendix lumen. The organ cavity is closed, so the contents cannot leave the body through the cecum.
- Vascular pathologies. Thrombosis, vasculitis, impaired tissue microcirculation, or the development of segmental necrosis can provoke putrefactive processes in the process of the cecum, which lead to its subsequent rupture.
- Disorders of the neuromuscular system. Stretching of the appendix or increased peristalsis of intestinal smooth muscles is observed. As a result, mechanical damage can lead to rupture of soft tissues and the development of appendicitis.
The organs of the abdominal cavity are closely interconnected not only by their close proximity to each other, but also by the frequent interweaving of a network of capillary and arterial vessels. Therefore, if the infectious process begins in the intestines, decay products or pathogenic microorganisms can freely enter the appendix due to the general blood flow.
People who have one or more provoking factors are at risk for developing acute appendicitis:
- overeating, nutritional obesity;
- lack of treatment for infections with systemic spread;
- immunodeficiency state;
- predisposition to the development of an allergic reaction.
Your doctor will help you understand what appendicitis looks like and what the consequences are.
What can cause appendicitis?
- husks from seeds, grape seeds, nails, etc. getting into the appendix;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- abdominal trauma;
- weakened immune system;
- severe stress (it provokes a sharp narrowing of blood vessels, which leads to bleeding and subsequent inflammation of the appendix).
What should be the first aid for suspected appendicitis?
Read more >>
Symptoms of appendicitis. First signs
There are several characteristic symptoms that accompany the development of the inflammatory process in the appendage of the cecum:
- The pain syndrome in some cases is accompanied by sudden vomiting, stomach cramps and nausea. Reflex vomiting occurs. If the patient empties the stomach cavity before the onset of pain, this means there is no appendicitis. Otherwise, it is necessary to palpate the abdomen to clarify the discomfort and, if necessary, call for medical help. Reflex vomiting after feeling acute pain is more often observed in patients in childhood and old age.
- In rare cases, the patient develops diarrhea or constipation.
- With inflammation of the appendix, disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the genitourinary system are observed. In 25% of patients, a frequent urge to urinate begins, pain develops in the ureter, and in addition to pain on the right side of the abdomen, a pulling sensation appears in the bladder area.
- Heart rhythm disturbances develop - tachycardia and blood pressure surges occur.
- Against the background of the inflammatory process, body temperature rises to subfebrile levels of +37...39°C. This is due to the release of a large number of leukocytes into the blood, an increase in heart rate and an increase in blood flow speed. The patient feels muscle weakness, begins to feel sleepy, has an aversion to food and a complete lack of appetite.
In the presence of concomitant diseases, the clinical picture of appendicitis is blurred, because the present symptoms may be the cause of the development of another pathological process.
Signs of inflammation of the appendix develop in a complex manner. In rare cases, a chronic form of appendicitis may occur.
Floating pain
At the initial stage, the progressive pathological process does not have precise localization. The pain is felt in the navel area, migrates to the epigastric region and back to the lower abdomen. After 2-3 hours, if there is appendicitis on the right, the pain begins to increase sharply. This effect is due to the spread of the inflammatory process to the soft tissue surrounding the appendix and the parietal peritoneum.
Some patients with gastrointestinal disorders suggest that this floating pain is a sign of gastritis or overeating. But this phenomenon is called Kocher's symptom, which makes it possible to diagnose appendicitis in the early stages of its development and serves as the basis for urgent hospitalization.
Constancy
Acute appendicitis is characterized by constant pain, which can subside at rest and sharply increase with movement. If the symptom lasts more than 2 hours, you should not take analgesics. In this case, you should palpate the appendix area for inflammation. The pain symptom intensifies with physical activity, during muscle contractions, coughing, breathing, turning and moving. The patient's condition sharply worsens if he is turned from the right to the left side.
If the pain suddenly dulls, this may indicate the development of peritonitis due to a rupture of the inflamed appendix.
In such a situation, the risk of death increases by 60%. When the appendix bursts, the purulent contents spread throughout the body along with the blood and affect the nerve tissue. It is necessary to perform a surgical operation on the patient as quickly as possible to remove the remnants of the appendix and cleanse the peritoneum of pus and feces.
Increased pain and increased body temperature
After 4-5 hours from the onset of pain, the discomfort gradually intensifies. Due to inflammation in the blood, the number of leukocytes increases, which causes an increase in temperature above +37.3°C and blood circulation speed. In case of acute inflammation of the appendix, the patient tries not to move, does not walk and lies in one position on the right side to dull the pain. In some cases, the pain can intensify with deep breathing.
Nature of pain
Appendicitis without pain is impossible. The pain symptom remains acute and appears gradually over 2-3 days. Severe pain can spread to the back of the peritoneum and the pelvic area, causing pain in the lower back and lower abdomen. This symptom is called migrating.
If the discomfort does not go away for more than 2 hours, you need to call a medical team. You can start self-diagnosis, but it is strictly forbidden to neglect the help of specialists.
Symptoms
Abdominal pain is often confused with an ailment of the digestive system, but there are distinctive signs that make it possible to recognize suspected inflammation:
- Pain syndrome in the abdominal area. Only at the beginning of the inflammatory process is discomfort felt near the navel, with a gradual movement to the right, to the lower corner, to where the appendix is located. The attack and pain occur unexpectedly, it is impossible to take a deep breath. The pain syndrome intensifies many times when a person begins to cough or laugh.
- Body position. When the appendix becomes inflamed, the human body involuntarily takes a certain position in which the pain is not so strong. A man walks in a bent position. In the supine position, both the adult and the child lie on their sides with their legs pulled up.
- Nausea, vomiting develops. The inflammatory processes occurring inside also affect the intestines, causing a feeling of nausea and regular vomiting, which does not bring relief. In rare cases, gagging occurs 1-2 times; the majority of patients complain of ongoing discomfort. Schoolchildren and teenagers suffer from appendicitis more often, which is why vomiting occurs more often during this period. Adults experience vomiting much less frequently. If the disease develops in an elderly person, such symptoms are not observed.
- Body temperature. When the body tries to cope with any inflammation, the overall temperature rises. As a rule, the thermometer shows 37.5 - 38 degrees. In a child’s body, the temperature can reach 40. An increase in thermometer readings indicates an increase in the inflammatory process and the progress of the disease.
- Defecation disorder. It is rare for an upset bowel symptom to occur. Only if the location of the appendix itself is atypical, then there may be a lack of stool or diarrhea. It is worth noting the state of a person after defecation is liquid. If after the process there is temporary relief, then there is poisoning; if there is no relief, it is appendicitis.
- Feeling of dry mouth and plaque. The appearance of these signs clearly indicates the development of inflammatory processes in the cecal appendage.
In rare cases, pain may occur when urinating. This occurs due to the location of the appendix next to the bladder and pressure on it (sometimes it is believed that the kidney hurts). Pain may appear in the lumbar spine or in the groin. It all depends on the specific position of the appendix in the human body. Sometimes it is difficult to diagnose the disease when children develop a runny nose and a cold cough.
Consequences and complications
When appendicitis bursts, the patient's condition deteriorates sharply and in most cases he loses consciousness. This is the most dangerous outcome of the inflammatory process. Due to damage to the septum between the cecum and the appendix, when the inflamed appendix ruptures, feces and pus are released into the abdominal cavity, and peritonitis develops. The patient requires emergency surgery.
The following symptoms are characteristic of peritonitis:
- sudden spread of pain throughout the abdominal cavity;
- facial features become sharper, pale skin is observed;
- a sharp deterioration in health;
- increase in heart rate up to 130 beats/min;
- loss of consciousness or sudden worsening of anxiety and restlessness.
Many people are interested in whether appendicitis can fail to burst and what the consequences will be. With proper treatment of minor inflammation with medications, positive recovery dynamics are possible. But if the appendix remains inflamed and does not rupture, soft tissue necrosis begins.
What is peritonitis?
Peritonitis (from Latin peritoneum - “peritoneum” + itis suffix indicating inflammation) is inflammation of the peritoneum that occurs when the inflamed appendix ruptures.
Symptoms of peritonitis:
- increasing pain throughout the abdomen,
- nausea, vomiting,
- in severe cases - drowsiness, lethargy, bluish tint to the face,
- pulse up to 120–140 beats per minute, temperature up to 39–40 degrees;
- the tongue is covered with a white coating,
- chapped lips,
- bloated belly.
Inflammation of the appendix in children
Appendicitis in infants and preschool children is difficult to detect. During such a period, internal organs and systems continue to form. The growth of bones and soft tissues leads to a change in the initial location of the intestinal appendix. It is difficult for a child to talk about his feelings. He is experiencing severe stress, not understanding what is happening to him and how to report it. Parents should not ignore the child's constant crying and complaints of pain.
Despite accelerated regeneration, children have a more difficult time withstanding operations and infectious diseases. Therefore, it is important to take your child to the doctor. An inpatient pediatrician will help identify the cause of symptoms and prescribe appropriate treatment.
It is important to remember that children do not like to be left alone in hospitals. Because of this, they often lie about feeling normal and may endure severe pain. In such cases, the child cannot be trusted, because appendicitis poses a threat to his life.
Appendicitis in a child
The most difficult task for a doctor is to determine appendicitis in a small child. If children constantly cry and complain of persistent pain, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Up to 2 years of age, the pathological process develops extremely rarely, which is due to the digestive system being unprepared for complete digestion.
Therefore, in 90% of cases, teenagers are admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of acute inflammation of the appendix.
The clinical picture in children over 7 years of age coincides with the classic manifestations of appendicitis in adult patients. The difficulty in determining pathology arises due to the immature psychological state of the child. He may be capricious and cry from fatigue, and not from pain. Children cannot tell exactly how the pain manifests itself and where it is strongest. Therefore, doctors have identified several distinctive symptoms that are characteristic of a child with inflammation of intestinal atavism:
- when he squats, he holds his stomach;
- curls up in a fetal position and does not allow touching or changing body position;
- after the pain appears, the child will periodically wake up;
- in children, body temperature can rise to +40°C;
- the pain intensifies when bending to the right side and in the process of changing clothes;
- constant nausea and uncontrolled vomiting.
After the first day from the onset of inflammation, the child’s condition worsens sharply. Lethargy develops, there is no appetite and strength for physical activity. When the stomach is touched, children begin to scream and cry.
When visiting the hospital, you should remember that the consequences of surgery greatly affect the child’s body. Therefore, it is important to prevent the development of appendicitis and know in advance for what reasons pathology may appear in childhood:
- Weak immunity. Frequent colds and viral diseases of the respiratory system, flu, infections can lead to depletion of the immune system. The condition can be aggravated by taking antibiotics, which are necessary in the fight against pathogenic microorganisms.
- Parasites and ingestion of foreign objects. Children can eat the seeds with the husk, eat orange peels, or eat the berries with the bone. Indigestible debris can lead to a blockage of the appendix.
- Obesity, frequent overeating and excess protein in the diet.
The appearance of symptoms characteristic of appendicitis cannot be ignored. To exclude the disease, you need to seek medical help.
Why is an appendix needed?
The appendix is a partially vestigial organ, the removal of which does not cause much harm to the human body. The appendix produces immune cells that protect the intestines. It also harbors some beneficial microorganisms that help digest food.
Is it true that the appendix, tonsils and tailbone are not superfluous in the body?
Read more >>
Appendicitis in pregnant women
Appendicitis in pregnant women is a common occurrence that occurs during the second trimester of embryonic development. Pain during the pathological process of the patient is confused with the characteristic pain syndrome from constipation or fetal movements. Against the background of the inflammatory process, a woman’s heart rate increases, shortness of breath appears, and her temperature increases. Nausea and vomiting in this case are not specific signs of damage to the rectal appendage, because they may be signs of toxicosis.
The severity and localization of pain depend on the force of pressure of the uterus on the inflamed appendix. The longer the pregnancy, the more the uterine endometrium begins to put pressure on the appendix. As a result, the appendage of the cecum begins to rise upward, changing the location of the pain.
This increases the risk of premature birth, intestinal failure, placental abruption and peritonitis. Therefore, if appendicitis is suspected, a woman should immediately consult a doctor in order to protect her life and ensure the normal embryonic development of the unborn child.
Acute appendicitis in elderly people
Appendicitis in old age is more difficult to diagnose. This phenomenon is due to the natural aging processes in the body - after 50 years, the pain threshold increases, so patients do not pay attention to the discomfort and tolerable pain in the lower right part of the abdomen.
There is a feature of an attack of inflammation, which manifests itself in the form of a small tumor at the location of the appendix. Swelling develops after 2-3 days of constant pain.
Body temperature practically does not increase, but nausea and vomiting are observed more often than in patients from 20 to 50 years old. Diarrhea or constipation are typical for older people, so patients do not complain about stool retention or changes in stool. Therefore, in 15-35% of cases, doctors may make an incorrect diagnosis.
Chronic appendicitis
A rare pathological phenomenon occurs in only 1% of people over 30 years of age who have previously suffered acute inflammation of the appendix. Signs of chronic appendicitis repeat the classic clinical picture. At the same time, the symptoms are mild, there is no fever. The patient feels pain constantly, the pain intensifies when raising the right leg. In this case, vomiting and nausea develop, which dull the feeling of hunger. After emptying the stomach, there is no relief.
Due to characteristic pain in the abdominal cavity, a person is unable to move independently. The patient reflexively turns over onto his right side and pulls his knees towards his stomach in an effort to reduce pain. If there is a suspicion of chronic appendicitis, it is strictly prohibited:
- take painkillers;
- wrap the patient in a blanket, because the inflammatory process under these conditions can intensify and develop into acute appendicitis;
- refuse to call an ambulance for a patient.
When the appendix ruptures, peritonitis develops, which, if not properly treated, can lead to death within 7 days. Diagnosing chronic appendicitis is more difficult in pregnant women, children and the elderly, in patients with diabetes mellitus, with HIV infection and the presence of a malignant neoplasm. In the latter case, pain from an inflamed appendix is often confused with tumor growth and the spread of metastases.
Appendectomy
The operation to remove appendicitis is performed using a classic appendectomy or laparoscopy. Appendectomy is a classic abdominal operation. Laparoscopy is an operation that does not require abdominal incisions in the skin. It is less traumatic, but has a number of significant contraindications. Classic appendectomy is performed much more often.
Before the operation, general anesthesia is given. Then access to the affected organ is provided. In the case of laparoscopy, small punctures are made in the skin. The appendix is completely removed, after which the abdominal cavity is drained. The final step involves placing stitches on the puncture or incision sites.
Home diagnostics and self-diagnosis
To identify inflammation of the appendix yourself, you will need to perform several steps:
- Ask the patient to take a horizontal position on a flat surface. If the pain is severe, you need to help him roll over onto his back.
- Find the edge of the lower costal process on the right side and lightly tap the phalanges of your fingers on the area located below the rib. The appearance of acute pain indicates the presence of appendicitis. To make sure of this, you should repeat the manipulations on the left side. If there is no characteristic reaction, then acute inflammation of the appendix has occurred.
- Ask the patient to point to the area where he feels the most severe pain. After this, you will need to press your middle and index fingers in this area. With appendicitis, the pain should dull, and if you let go of the fingers, it will intensify several times.
- If you lay the patient on his right side and ask him to pull his legs towards him, temporary relief will come. When returning to the starting position, the patient's condition will worsen.
- An early sign of incipient inflammation is discomfort and dull pain in the appendix area with mild coughing and tension in the abdominal muscles.
If self-diagnosis of appendicitis confirms the presence of inflammation, you need to immediately call an ambulance. The process can only be removed during surgery. Otherwise, if the diagnosis does not confirm the presence of purulent inflammation, you need to take the patient to the hospital. The symptomatic picture that appears may be associated with a disease of the digestive tract, pelvic organs or urinary system.
Only special equipment and a doctor will help to accurately determine the etiology of the pathological process.
How to quickly identify appendicitis in men and women?
In order to avoid peritonitis and other negative consequences when an inflamed appendix ruptures, you should know the clinical manifestations of the disease and have time to diagnose the pathology at home. The first characteristic sign of appendicitis in 95-97% of cases is pain in the right side. The syndrome can be acute and permanent. In some cases, the pain may periodically subside.
In women, the ovary is located next to the appendix, making diagnosis more complicated. The pain that appears may indicate inflammation of the appendages. Therefore, people wonder how to understand what hurts, appendicitis or ovary. The answer to the dilemma will be several signs of acute inflammation of the appendix:
- if you press and suddenly release your fingers from the place where the acute pain comes from, the pain will increase many times;
- unpleasant sensations are constantly present and spread to the lower back;
- the pain should be sharp or stabbing, a pulling sensation indicates inflammation of the ovary;
- abdominal spasms do not allow you to straighten up and move;
- nausea and vomiting are present, after which the state of health does not improve.
In men, in the absence of diseases of the digestive and urinary system, when acute pain appears on the right side or a hard abdomen upon touching, only inflammation of the appendix is diagnosed. You should also pay attention to other accompanying symptoms:
- High body temperature. If for a long time the temperature increases and does not subside, then, with the exception of other infectious and inflammatory diseases, they indicate the presence of appendicitis. Unlike women, men's temperature can rise to +40°C.
- Nausea and vomiting. With inflammation of the intestinal atavism, vomiting occurs as a reflex. A person feels a constant aversion to food. Women empty their stomach more often than men.
- Diarrhea and constipation. These symptoms are rare, but may also indicate the onset of inflammation. At the same time, intestinal disorders often develop due to food intoxication.
It is important to call an ambulance to accurately identify appendicitis and perform timely surgery. When appendicitis ruptures, both men and women experience severe pain, a sudden attack of severe vomiting and loss of consciousness.
The risk of death from peritonitis is higher in the male body, so if the inflamed appendix ruptures, it is important to perform surgery within 30-45 minutes. If after this time help has not been received, then systemic intoxication of the entire body begins. Pus, pathogens and waste products enter the bloodstream and spread to other organs, including the brain.
Tactile test
A tactile test, which allows you to identify the pathological process mechanically, helps to determine appendicitis at home. The patient must be placed on his back on a flat, non-springy surface. You need to ask to relax your stomach so that muscle tension in the abdominal cavity does not provoke pressure on the appendix or other soft tissues and cause pain. If the stomach remains hard, this indicates the beginning of a pathological process.
You need to open your palm and gently press on the area where the appendix is located. After 2-3 seconds, you need to sharply remove your hand. With appendicitis, the layers of peritoneum will come into contact with the affected area, which will cause increased pain. It is recommended to repeat the test from the back if there is no characteristic reaction, because the localization of the appendix is individual for each person.
You can tap with bent fingers along the right side. Mechanical movements also cause friction of the peritoneum, which causes severe pain to the patient. The symptom may be aggravated by tension in the pectoral muscles during coughing, talking and loud laughter. The pain syndrome can migrate or spread to the pelvic area and radiate to the back.
An alternative way to diagnose the inflammatory process is to lightly tap on the right and left sides with the edge of the palm or phalanges of the fingers along the lower edge of the costal processes. Moreover, it is necessary to start from the abdomen and continue the test on the back. The pain should intensify in rhythm with the blows. If there is no discomfort on the left side, this is a clear sign of appendicitis.
How to identify him?
In most people, the appendix is located approximately halfway between the navel and the right ilium. In this place, with appendicitis, the maximum pain is felt. But if the appendix is raised to the right hypochondrium, closer to the liver, pain will appear in this area. And if the appendix is lowered into the lower part of the pelvis, then in women appendicitis is easily confused with inflammation of the appendages, in men - with the bladder.
When the process is located behind the cecum, when it is wrapped towards the kidney and ureter, pain occurs in the lower back, radiating to the groin, leg, and pelvic area. If the process is directed inside the abdomen, then pain appears closer to the navel, in the middle abdomen and even in the pit of the stomach.
Pain occurs suddenly, without any obvious reason . At first they are not too strong - they can still be tolerated. And sometimes, from the first minutes of an attack of acute appendicitis, they become unbearable and proceed like colic.
The pain will torment a person as long as the nerve endings of the appendix are alive. When its necrosis occurs, the nerve cells will die and the pain will subside. But this is no reason to calm down. . ” On the contrary, the resolution of pain is a reason for immediate hospitalization. Acute appendicitis is accompanied by other symptoms. At the onset of the disease, general malaise, weakness, and loss of appetite appear. Nausea and sometimes vomiting may soon occur, but only once. A typical temperature ranges from 37.2 to 37.7 degrees, sometimes accompanied by chills. A white or yellowish coating appears on the tongue.
Simple techniques will help you recognize appendicitis. But keep in mind that self-diagnosis must be carried out very carefully.
Lightly tap with the pad of your bent index finger in the area of the right ilium - with appendicitis it always hurts there.
For comparison, also tap on the left iliac region, which in case of inflammation of the appendix will not cause pain. Attention: you cannot carry out palpation (feeling the abdomen with your hands) yourself, there is a danger of rupturing the appendix, which usually leads to peritonitis.
Try coughing loudly: increased pain in the right iliac region will tell you that you have appendicitis.
Apply gentle pressure with your palm to the area of your abdomen where it hurts the most. Hold your hand here for 5-10 seconds. The pain will ease slightly. Now remove your hand. If pain appears at this moment, this is a sign of acute appendicitis.
Take a fetal position, that is, lie on your right side and pull your legs towards your body. With appendicitis, abdominal pain will ease. If you turn on your left side and straighten your legs, it will intensify. This is also a sign of acute appendicitis.
But self-diagnosis should be limited to this. Do not hesitate to consult a doctor, since appendicitis itself, and all the diseases that it can masquerade as (renal colic, exacerbation of pancreatitis or cholecystitis, peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, acute inflammation of the bladder, kidneys, female organs), require hospitalization!
What should you not do if you suspect appendicitis?
The situation can be aggravated by the following actions:
- Giving the patient analgesics or laxatives for appendicitis, which is strictly prohibited. Painkillers can interfere with the diagnosis of the disease. Laxatives cause increased intestinal motility and muscle spasms in the abdominal cavity, which increases pressure on the appendix. The risk of rupture increases. Peritonitis may occur as a result of taking both drugs.
- Take medications for the stomach or intestinal tract. When a therapeutic effect is achieved, violent biochemical reactions may develop, leading to rupture of the inflamed appendix.
- In the absence of vomiting and nausea, eat. If an emergency appendectomy is required, digested foods may increase the likelihood of complications. In this case, the surgeon may refuse to perform the operation, because when a coma of hydrochloric acid and semi-digested food is released into the oral cavity and pharynx during anesthesia, the patient may suffocate.
- Apply warm compresses to the appendix. An increase in temperature creates intense blood circulation, which accelerates the process of inflammation.
What are the consequences of the operation?
With timely surgical intervention, the prognosis for appendicitis is completely favorable. On the sixth or seventh day, patients have their stitches removed and discharged from the hospital. After the operation, they are prescribed a special diet: in the first days - milk, jelly, thin porridge. On the third day, butter and bread are added to the diet, and from the fourth day, as a rule, the patient switches to a normal diet. Heavy physical activity should be avoided for a month after surgery.
Laparoscopy (from the Greek λαπάρα - “groin”, “womb” + σκοπέω - “I look”) is an operation on internal organs, which is performed through small (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) holes. Punctures (incisions) of the abdominal wall are made with a thin special tube - a trocar.
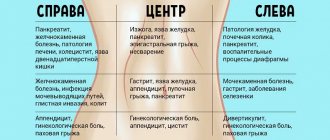
Diseases with similar symptoms
If the patient has a history of a predisposition to developing allergies or diseases of the digestive or urinary system, doctors have no choice but to distinguish appendicitis from other diseases. This attitude is due to the similarity of the clinical picture of some pathologies. What can appendicitis be confused with:
- pyelonephritis;
- inflammation or rupture of an ovarian cyst;
- Crohn's disease;
- inflammation of the uterus or fallopian tubes;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum;
- enterocolitis;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes near the small intestine;
- abdominal muscle rupture or stretching;
- renal colic.
Diagnostics and treatment in a hospital setting
In the hospital, the doctor must determine appendicitis and exclude the presence of other pathologies using palpation, laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Ultrasound or radiography is performed;
- the patient donates blood and urine for tests.
X-rays and ultrasound images will help identify pathological changes characteristic of appendicitis:
- accumulation of fluid in the cavity of the cecum, between the layers of the peritoneum or in the pelvis;
- increase in the thickness of fatty tissue;
- swelling of the intestinal walls located near the appendix;
- modifications of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract;
- increase in size of the appendix, thickening of its walls.
In some cases, when it is difficult to detect the disease, a laparoscopic examination is performed. This procedure allows you to assess the condition of the internal organs and the type of appendicitis. A movable tube with a camera at the end is inserted into a small incision, which transmits the image to the monitor. If cells begin to die and necrotic changes progress, this indicates gangrene. With a high risk of rupture of the appendix with the release of contents into the abdominal cavity, phlegmon develops. In such cases, an appendectomy is performed - removal of the appendix.
Ultrasound and blood tests
To perform laboratory tests for appendicitis, the patient is given blood and asked to provide urine. This is necessary to exclude other diseases of the pelvic and abdominal organs. When examining blood against the background of an inflammatory process, a high level of leukocytes with a predominance of neutrophils is observed. Urinalysis allows you to distinguish pathology of the appendix from damage to the kidneys and urinary tract. If the intestinal atavism is located next to the ureter, then a small amount of red blood cells can be found in the urine.
To identify inflammation of the appendix of the cecum with an intra-abdominal abscess and determine its atypical locations, an ultrasound examination is performed.
The accuracy of ultrasound, depending on the clinical picture of the disease and the anatomical features of the organ structure, varies from 71 to 97%.