Analgin and Ibuprofen are drugs with a combined effect that have analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. They have a quick effect and, if you follow the rules of administration, do not cause side effects.
Analgin and Ibuprofen are drugs with a combined effect that have analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects.
What is the difference and which is better, Analgin or Ibuprofen
Medicines have the following differences:
- Compound. The main component of Analgin is metamizole sodium salt, the second is a substance of the same name, which is a derivative of propionic acid.
- Release forms. Analgin is produced in the form of tablets and solution for injection, the second drug is in tablets, capsules and syrup for children.
- Analgin often provokes negative reactions, which indicates its greater toxicity.
In most cases, to relieve pain symptoms and normalize temperature indicators, preference is given to Ibuprofen. This product has convenient dosage forms, and the raspberry-flavored syrup is used in pediatrics.
Analgin solution for injection is prescribed in cases where tablets or other medications do not give a positive result in relieving painful symptoms of influenza and other diseases accompanied by high fever.
Tablet forms of medications show almost equal effectiveness in pain relief and fever relief. But the advantage of Ibuprofen is that it shows the best result in reducing the severity of inflammatory processes.
Metamizole sodium salt is toxic. Analgin is prohibited in most countries due to the high risks of complications with prolonged or constant use.
The advantage of Ibuprofen is that it shows the best result in reducing the severity of inflammatory processes.
Description of drugs
Analgin and Ibuklin have the same pharmacological properties. Ibuklin belongs to the clinical and pharmacological group of analgesics and antipyretics of a combined composition. Analgin belongs to the category of analgesics-antipyretics.
The main composition of the medicine includes various active components:
- Ibuclina – ibuprofen plus paracetamol;
- Analgina - metamizole sodium.
Properties
The therapeutic effect of Ibuklin and Analgin is due to the properties of the main substances.
Antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic
In addition to the same properties, Ibuklin and Analgin have a common distinctive feature. The mechanism of action of metamizole sodium and ibuprofen is associated with a decrease in the amount of prostaglandids, which are mediators of pain, hyperthermic and inflammatory manifestations. This shows the compatibility of Ibuklin and Analgin.
Forms of release and purpose
The tables below provide an overview of the main types of drugs with a list of indications for use, in accordance with the official instructions for the drugs.
Ibuklin:
Dispersible tablets for children
Analgin:
Rectal suppositories for children
There are also direct analogues of Analgin:
- tablets Analgin-Avexima, Analgin-Ultra;
- Analgin-ExtraCap capsules.
Indications for use
Medicines are prescribed in the following cases:
- pain of various etiologies;
- injuries;
- burns;
- headache and migraine;
- insect bites;
- toothache;
- increased body temperature;
- state of fever;
- neuritis;
- periodic pain in women;
- radiculitis;
- viral, infectious diseases, colds that occur with high fever.
In these clinical cases, the medications show the same therapeutic effectiveness.
Classification of drugs
Migraine is a disease that has been known to mankind since the time of Hippocrates. Even then, people were looking for which medicine would be most effective. However, the development of medicine during the time of Hippocrates was significantly lower. Today, compared to ancient times, there are many ways to overcome migraine attacks.
There are three groups of drugs used in the treatment of migraine, namely:
- Symptomatic.
- Abortive.
- Preventive.
Symptomatic medications
This group is intended to combat the accompanying manifestations of migraine (nausea, vomiting, general painful condition).
As a rule, symptomatic drugs depress the central nervous system, calming it and eliminating the discomfort caused by its excitement.
List of effective drugs in this group:
- phenergan (this drug has an antiemetic effect and can also act as a sleeping pill);
- compazine (depresses the central nervous system, helps stop gag reflexes and nausea);
- Thorazine (a potent sedative that depresses the central nervous system);
- diacarb (promotes the removal of fluid from the body).
Medicines in this group are always prescribed in combination with abortifacients, since only they can help a person get rid of headaches.
Abortion drugs
This group of drugs is aimed at eliminating headaches. Medicines from this group are taken very first, as they help relieve an attack.
This group includes painkillers, both broad-spectrum and narrowly targeted, these include:
- ketanov;
- Nurofen;
- picamilon;
- sumamigren;
- ketorol;
- Actovegin;
- spasmalgon;
- paracetamol;
- nimesil;
- askofen;
- Excedrin;
- aspirin.
Preventive medications
From the name it is clear that these medications are used before the onset of an attack and are designed to prevent it long before its formation.
As a rule, these are drugs that prevent the narrowing of blood vessels in the brain and also increase the patient’s cardiac tone.
Typically, this practice helps patients whose migraine attacks are prolonged.
- neurofulol;
- inderal;
- topral;
- cardizem;
- Cyproheptadine.
Directions for use and dosage
The dose is determined individually; the selection takes into account the age and weight of the person. The recommended amount of Ibuprofen is from 200 to 400 mg/kg per day (for adult patients and children weighing more than 30 kg).
The daily dosage of Analgin depends on the severity of symptoms and averages 0.75-3 g. The maximum permissible amount per day is 3 g.
The solution is administered intravenously in a maximum dosage of 2 g and intramuscularly - no more than 3 g.
For children, a 50% solution is administered at the rate of 0.1 to 0.2 ml per 10 kg of weight, 25% - 0.2 or 0.4 ml per 10 kg.
Medicines are taken after eating food.
The daily dosage of Analgin depends on the severity of symptoms and averages 0.75-3 g.
What are the differences between different antipyretics?
All antipyretics contain one of 4 components: paracetamol, ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid or metamizole sodium.
Paracetamol has a pronounced antipyretic and analgesic effect. It gradually and for a sufficiently long time reduces elevated body temperature, and also relieves the patient of headache and muscle pain. At the same time, paracetamol quite rarely causes complications from the digestive, nervous and hematopoietic systems. It should be taken no more than 4 times a day: adults and children over 12 years old - 500 mg or 1 g, children from 3 months to 12 years - in the age dosage specified in the instructions for the drug.
It is important! To reduce fever in children under 12 years of age, only antipyretics based on paracetamol or ibuprofen are used and only in age-appropriate dosage forms.
Ibuprofen begins to act quite quickly and provides a long-lasting antipyretic effect. In addition, it has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, and recently there has been evidence that taking ibuprofen has a positive effect on the functioning of the immune system. Take it no more than once a day: for adults - for children - in an age-specific dosage.
It is important! Acetylsalicylic acid is used only in patients over 15 years of age, no more than 3 times a day
Acetylsalicylic acid, like ibuprofen, has antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, but it causes side effects much more often: blood clotting disorders, spasm of the respiratory tract, irritation of the gastric mucosa, etc.
Metamizole sodium has a more pronounced analgesic effect and somewhat less antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. To reduce the temperature, this substance is most often used in the form of intramuscular injections - when there is an emergency need to “bring down” the temperature. It is not recommended to take metamizole sodium without a medical prescription, because the risk of severe allergic reactions and hematopoietic disorders is very high.
special instructions
During drug therapy, certain categories of patients need to be careful.
Pregnancy and lactation
Ibuprofen is prohibited for use in the last stages of gestation. In the 1st and 2nd trimester it can be prescribed, but only if there are special indications for this. In the early stages of pregnancy, taking the medication can cause a miscarriage.
Metamizole sodium salt is not prescribed to pregnant and lactating women.
Childhood
Ibuprofen is allowed from 3 months, and the second remedy only from 12 years of age.
Elderly age
Taking medications requires special care and dosage adjustments.
Side effects of Analgin and Ibuprofen
Medicines can cause the following side effects:
- Allergies – hives, skin rashes, itching, redness. Less common are anaphylactic reactions and angioedema.
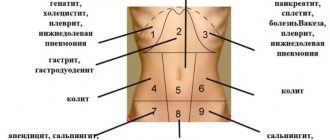
- Disorders of the digestive system - nausea, less often vomiting, gastritis, pancreatitis, formation of stomach or duodenal ulcers, flatulence, diarrhea, stomach pain.
- Impaired liver and kidney function.
- Dyspnea, tachyarrhythmia, bronchospasm.
- Prolonged intense pain in the head area.
- Heart disease, edema, thrombotic complications: myocardial infarction, stroke.
The risk of developing side effects due to the use of medications increases with their long-term use.
Differences and similarities of drugs
Both drugs have anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects. It is necessary to understand the mechanism of action of ibuprofen and metamizole sodium in order to know for which disease it is more effective to use one or another remedy.
Indications for use
Analgin is indicated for use for the following symptoms and phenomena:
- headache and migraine;
- fever due to an infectious disease (taken together with antibiotics);
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs (anemia, neutropenia, leukopenia);
- pain after surgery.
Ibuprofen is recommended for use in the following cases:
- increased body temperature due to an infectious disease or inflammation (additionally take vitamin C);
- joint and muscle pain (arthritis, arthrosis, rheumatism);
- diseases of the respiratory system - sore throat, sinusitis, otitis media, rhinitis (except asthma and bronchitis);
- various types of pain.
The drug is able to block nerve endings, due to which the nerve does not transmit the pain signal to the brain. Thanks to this, the patient does not feel pain.
Directions for use and dosage
Application of Analgin:
- for headache, toothache, menstrual or other pain, just take 1 tablet and drink plenty of water;
- in complex treatment, metamizole is used as an auxiliary antisymptomatic drug, and it should be taken 2-3 times a day, 1 tablet.
Ibuprofen can also be used as an auxiliary or primary drug:
- to relieve pain, you need to take 1 tablet and wash it down with water at room temperature (to speed up absorption);
- when taken systematically during the course of treatment, 1 tablet twice a day.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, the doctor may adjust the dosage.
Side effects of Analgin and Ibuprofen
If the active substance is intolerant or if used incorrectly, Analgin can cause a number of side effects:
- bronchospasm, decreased blood pressure, development of pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- nausea, stool disturbances, pain in the intestinal area;
- renal impairment - olirugia, nephritis, anuria;
- dysfunction of hematopoiesis – anemia, agranulocytosis, etc.
If you are intolerant of the active substance or if used incorrectly, Analgin can cause nausea.
Side effects from Ibuprofen:
- from the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, bleeding of ulcers;
- from the nervous system: excessive irritability, insomnia, fatigue after sleep;
- from the senses: decreased visual acuity, tinnitus;
- allergic reactions: Quincke's edema, itching and rash on the skin.
If any symptom occurs, you should stop taking the drug and consult your doctor.
Contraindications
Analgin is not always used, as there are a number of contraindications for taking metamizole sodium:
- individual intolerance to the components of the drug;
- bronchial and aspirin-induced asthma;
- thyrotoxicosis (thyroid disease);
- heart diseases - ischemia, heart attack, cardiosclerosis, tachyarrhythmia;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- liver and kidney failure.
Children under 3 months are not recommended to use Analgin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Before taking the drug, you should consult your doctor so as not to cause complications.
Analgin is not always used, since there are a number of contraindications for use, for example, pregnancy.
There are also a number of contraindications for the use of Ibuprofen:
- hypersensitivity to the components of the composition;
- stomach diseases, gastrointestinal erosions, pancreatitis;
- asthma, bronchitis, pulmonary edema;
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs, bleeding disorders;
- liver failure;
- liver dysfunction;
- heart failure, myocardial infarction.
Contraindications to the use of Analgin and Ibuprofen
Drugs are not prescribed in the following cases:
- hypersensitivity to certain components;
- stomach diseases;
- duodenal ulcer;
- tendency to internal bleeding;
- perforation of the walls of the abdominal organs;
- severe heart failure;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- severe renal and liver failure.
Additional restrictions on taking Analgin include:
- bronchial asthma;
- hemolytic type anemia;
- suspicion of acute surgical pathologies.
Antipyretics: instructions for use
Fever, or hyperthermia, is the body’s response to an infectious-inflammatory process. As the temperature rises, infectious agents multiply more slowly, and the immune system is activated - more immunoglobulins and interferons are formed. Therefore, it is not always necessary to lower the temperature. Temperatures up to 38°C are protective and help the body resist.
Antipyretics, like any medicine, have side effects. Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) irritates the gastric mucosa, can cause an allergic reaction (aspirin-induced bronchial asthma), and in children it often provokes Reye's syndrome (a very severe disorder accompanied by damage to the liver and brain). Metamizole sodium (analgin) can interfere with the formation of blood cells and provoke internal bleeding and severe allergic reactions. Paracetamol can affect the condition and functioning of the liver and may have a hepatotoxic effect. Ibuprofen and many other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are known to have a risk of gastropathic effects (nausea, vomiting, irritation of the gastric mucosa), in addition, they can negatively affect the cellular composition of the blood and kidney function.
It is important! Antipyretics should not be abused and should not be used for mild ailments.
When taking antipyretics, you need to follow the recommended dosage and frequency of administration. Combined cold medications in the form of effervescent tablets and powders for preparing hot drinks are themselves reliable and effective remedies, but the dosage form in which they are produced promotes unreasonably frequent use. Many people use them as an invigorating and warming remedy, instead of a regular mug of tea.
Interaction with other drugs
Ibuprofen should not be taken together with other non-steroidal drugs. Take with extreme caution with diuretics, cardiac glycosides, and medications that have an antiplatelet effect.
Analgin should not be taken together with penicillin antibiotics, diuretics, medications that inhibit bone marrow activity, NSAIDs, or vitamin C.
Ibuprofen and Analgin cannot be taken at the same time. Such a combination will lead to a doubled therapeutic effect and provoke complications in the form of intense adverse reactions.