Does your stomach hurt under your ribs? Pain in the upper abdomen under the ribs is a common symptom, especially characteristic of the following pathologies:
- Gastritis;
- Stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- Pancreatitis;
- Cholecystitis.
Cuts under the ribs on the right side are also characteristic of liver diseases. Lung pathology is indicated by subcostal pneumalgia, occurring on the right, left, in the middle, and aggravated by coughing. The same floating pain under the ribs is also characteristic of vegetative-vascular dystonia. This article will discuss pain in the upper abdomen that is related to dysfunction of the digestive system.
Gastralgia
Inflammation of the stomach
Dull, or, on the contrary, sharp pain in the anterior hypochondrium of the abdominal cavity causes inflammation of the stomach with high or normal acidity. This pathology is characterized by the occurrence of painful sensations in a state of hunger, due to the fact that gastric juice irritates the inflamed gastric mucosa.
But eating does not alleviate the condition, but on the contrary, it can increase the pain, because after eating, the inflamed mucous membrane is irritated by the food taken, especially if it is hard and high in acids. Therefore, patients with gastritis are recommended to eat starch-containing soups, jelly and other dishes that envelop the walls of the stomach.
Gastritis with high acidity is also characterized by symptoms such as heartburn, unstable stools prone to constipation. Aching pain and a feeling of heaviness under the solar plexus indicate the presence of gastritis with low acidity. This condition is especially worse after eating.
One of the signs confirming this diagnosis may be belching something bitter, sour, or something eaten. Vomiting with this form of gastritis brings relief. Malabsorption leads to decreased body weight, increased sweating of the hands and feet, chronic anemia, and vitamin B12 deficiency.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of pain in the upper abdomen in the middle largely depends on the specific pathology identified, its neglect and the general symptoms of the patient. Also, when selecting therapy, the attending physician must take into account the person’s age, the presence of additional diseases, a tendency to allergies and the form of the underlying pathology (acute, chronic).
Traditional therapy can be medication and surgery. Typically surgery is required in the following cases:
- With peritonitis.
- When cancer pathology is detected.
- When detecting an acute form of cholecystitis and ulcers, which is accompanied by internal gastric bleeding.
- Diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.
If other pathologies are detected, a person requires long-term drug therapy. It is advisable to carry it out in a hospital setting under close medical supervision.
Typically, the following groups of drugs are used for acute pain:
- Analgesics are prescribed for pain. They can be in the form of injections, tablets or syrups.
- Antipyretic drugs are needed when observing high body temperature (Paracetamol).
- Enzyme medications and bifid drugs are prescribed to normalize digestion (Linex, Hilak Forte, Mezim, Pancreatin).
- Antiemetic drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (excluding peptic ulcers)
- Medicines to normalize stool.
The duration of treatment depends on the specific disease identified. Thus, it can last from 1-2 weeks to several months. It all depends on the complexity and neglect of the pathology.
In order for the therapy to be successful, during its implementation the patient is strongly recommended to completely stop smoking and drinking alcohol. It is also important to avoid physical activity and stress.
In addition, nutrition plays a very important role. The diet includes the following:
- The patient needs to adhere to a fractional diet plan. Thus, you need to eat at least five times a day, but at the same time, portions should be no more than a handful. This way you can avoid starvation, but at the same time, do not overload your stomach with food.
- Complete refusal of seasonings, hot sauces and spices. It is also important to minimize the consumption of salt and foods with added salt.
- Refusal to eat solid, hard-to-digest foods (white cabbage, fatty meat, salted fish, etc.). Instead, the basis of the diet should be liquid dishes and pureed food.
- The menu should regularly include vegetable soups, cereals and boiled meat. Low-fat fermented milk products are also allowed.
- It is better to avoid most fruits during the treatment period, as they are sour. Only sweet fruits or those fruits that have undergone heat treatment (baked apples) are allowed.
- The temperature of food for consumption should be optimal - not too hot and not too cold.
- Complete avoidance of coffee, sweets and black tea, as they can increase the production of gastric juice, which in turn can cause a new attack of pain in a person.
Important! To further support the body in this condition, a person can take vitamin complexes. It is advisable that they be prescribed by the attending physician. This will help the body recover faster.
Source
Stomach and duodenal ulcers
Gastric ulcers are characterized by sharp pain localized in the left half of the hypochondrium.
Gastric and duodenal ulcers are characterized by sharp pain, localized in the left half of the hypochondrium, starting from the middle of the abdomen. Often discomfort occurs at night. The disease worsens in the off-season, that is, in spring or autumn. The pain sometimes radiates under the left rib, into the back and lower back. To alleviate the condition, the patient is forced to take a position that allows him to press the painful part of the abdomen:
- Lie on your stomach
- Sit on your haunches with your hands on your stomach,
- They press themselves against the table.
Read: A child has a stomach ache at night: possible causes of the problem
Ulcers, like gastritis, are characterized by “pain on an empty stomach”, which appears one and a half to three hours after eating. Physical stress and nervous disorder can be a provoking factor for the occurrence of pain. Antacids help in this condition. Some patients use a heating pad and soda solution.
Sometimes the pain occurs due to bleeding from the part of the stomach affected by the ulcer, and this can be dangerous. Additional symptoms indicating the presence of stomach and duodenal ulcers are heartburn, flatulence and constipation. With a long-term illness, patients lose weight, they develop headaches, weakness, and increased irritability.
Gastrointestinal diseases
In the case where pain in the upper abdomen is chronic, this may be a sign of pathological processes in the stomach or duodenum. Ulcerative damage to these organs leads to aching, dull or cutting, stabbing pain in the abdomen, which is associated with meals.
A gastric ulcer is characterized by the appearance of discomfort 15-45 minutes after eating, a duodenal ulcer manifests itself as pain after an hour and a half. In addition, peptic ulcer disease is characterized by the occurrence of unpleasant sensations on an empty stomach and at night; they can radiate to the area of the shoulder blades and chest. Other symptoms of the disease are also observed: bloating, problems with stool, nausea, vomiting. What is characteristic: vomiting in this case brings relief; with pathologies of other organs, such an effect is not observed.
If you experience unbearable, piercing, stabbing pain in the abdomen, you should immediately seek medical help, as this may be a sign of a perforation of the ulcer.
The presence of heartburn, belching, or a burning sensation behind the sternum may be a sign of inflammatory or ulcerative damage to the esophagus. This happens with GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease). The appearance of symptoms after eating, being in a horizontal position, bending or lifting heavy objects, and their disappearance after taking antacids - all this is confirmation of this disease.
Acute, dagger pain with perforation of the stomach and duodenum
Perforation of the stomach or duodenum is characterized by acute dagger pain.
Perforation of the stomach or duodenum is characterized by acute dagger pain. This pain forces the patient to assume the fetal position - lying on his side with his legs pressed to his stomach. At first it concentrates in the epigastric region, that is, “under the stomach,” but then moves to the right, under the last rib.
This is the contents of the stomach spilling into the abdominal cavity. After an acute attack, temporary relief may occur. If the patient does not receive timely treatment, the perforation will result in peritonitis, which will cause the patient’s death. Therefore, a patient diagnosed with a stomach and duodenal ulcer needs to be more attentive to his body.
And if acute stabbing pain occurs, immediately call an ambulance. Because in this situation there is only one way out - surgical intervention. Is it possible to avoid ulcerative perforation when the ulcer damages an organ through and through? Yes, you can, if you don’t let the disease progress and treat it in a timely manner, follow diets and all doctor’s instructions, take medicinal herbal infusions and decoctions, and avoid stress and anxiety.
Why does pain occur?
Painful sensations of this nature can occur for various reasons. Discomfort may be felt in the presence of pathologies of internal organs. Hollow organs, such as the stomach or intestines, may be bothersome due to their spasms. In this case, the person suffers from cramping, burning, pressing or pulling pain.
Discomfort is also possible if the organ capsule is damaged or stretched, which has the appearance of a dense shell of connective tissue with good innervation. In the presence of a tumor, injury or inflammation, the capsule stretches. At the same time, unpleasant sensations can be both strong and barely noticeable. If the capsule ruptures, the pain becomes pronounced.
Ischemia (poor blood supply) also often causes pain in the abdominal area. This condition occurs, for example, with atherosclerotic lesions or blockage with a blood clot.
Another cause of pain can be irritation of the mucous membrane that covers the walls and organs of the abdominal cavity (peritoneum). It has many nerve endings, so any aggressive impact on it leads to severe cutting pain. In medicine, this condition is called “acute abdomen.” It is an indication for emergency hospitalization.
In addition, pain in the abdominal area may be a consequence of its irradiation from other areas. This condition occurs due to the structural features of the human nervous system. When referred pain occurs, there are usually areas where the pain is more intense. From here the pain radiates to other areas.
Stomach cancer
Pain in the stomach area, that is, in the middle under the ribs with a transition to the left, is characteristic of stomach cancer in the last stages. The initial stage of oncological pathology is always asymptomatic, and this is where the insidiousness of oncological growths lies. At an early stage the following are noted:
- weight loss,
- change in taste preferences,
- aversion to meat dishes,
- anemia,
- signs of jaundice,
- decreased performance.
Read: Uterus. Some diseases, pathologies and serosometer of the uterus
Cancer occurs with gastritis with low acidity, develops from polyps and against the background of an ulcer of the cardial part of the stomach. Therefore, patients with these diseases need to be more attentive to their body so as not to miss the formation of a malignant tumor.
Why does the upper abdomen hurt - causes and types of diseases
Doctors say that if the upper abdomen hurts, it is recommended to undergo an urgent examination. This symptom is a warning sign of serious problems. There are many reasons why this condition occurs. But when making a diagnosis, it is worth considering an additional symptomatic picture.
Causes of painful feeling in the upper abdomen
Spasms in the upper abdomen do not always indicate that problems have arisen with the functioning of those organs that lie in this area. Often, during the period of diagnostic measures, blood diseases, disturbances in the production of hormones and metabolic processes are detected.
The cause may be hidden in another part of the body. Therefore, taking medications on your own can only cause even more harm.
Doctors highlight a list of the main reasons as follows:
A timely visit to the doctor and an examination will allow you to correctly diagnose and select treatment therapy.
Oncological problems in the abdomen
The upper abdomen rarely suffers from the development of a malignant process. But despite this, all tissue structures and organs are susceptible to cancer. If the upper abdomen hurts, then the formation of a tumor may be the cause. In the early stages, pathology rarely makes itself felt. Pain occurs only when the tumor is of impressive size.
There are several types of cancer, which are accompanied by a painful feeling in the upper abdomen.
- Neoplasms in the pancreas. According to statistics, it is more often diagnosed in men over 50 years of age. This is due to the fact that the male body is more exposed to adverse factors. A painful feeling is detected at the last stage and is characterized by signs of jaundice, a sharp decrease in body weight, and bloating.
- Neoplasms in the gallbladder. The decisive factor is the long course of cholelithiasis and regular exacerbations of chronic cholecystitis. The symptomatic picture is similar to pancreatic cancer. But at the same time there are constant problems with stool.
- Liver tumor. It is formed against the background of prolonged cirrhosis or the presence of hepatitis B and C. Pain in the upper abdomen is observed. There are also accompanying symptoms in the form of an increase in temperature, the formation of fluid in the abdominal cavity and an increase in the size of the organ.
- Tumor of the gastric cavity. A characteristic symptom is prolonged constipation. The risk category includes men over 40 years of age and people with polyps in the stomach, gastritis and other inflammatory processes.
- Tumor of the esophageal tube. If the lower part of the esophagus is damaged, the pain moves to the upper abdomen and chest. One of the main signs is a violation of swallowing function. When eating, the patient feels a lump in the larynx, which causes the urge to vomit.
A rare type of cancer called peritoneal carcinomatosis is also detected. Characterized by the spread of metastases to the peritoneal area.
Neurological problems
Why does my upper abdomen hurt? One of the common causes of discomfort in the upper abdomen is considered to be damage to the spinal roots. The main source of unpleasant symptoms is osteochondrosis.
The spinal cord is interconnected with the organs of the digestive system. If nerve fibers or roots are pinched in the spinal column, this leads to pain in the middle of the abdomen or in the upper part of the peritoneum.
Other symptoms of the pathological process also occur in the form of:
It is not possible to completely cure osteochondrosis, since tissue structures undergo irreversible changes. Symptomatic therapy is carried out, which is aimed at eliminating unpleasant symptoms, improving blood microcirculation and eliminating spasms in muscle fibers.
Concept of diaphragmatic hernia
A diaphragmatic hernia is usually understood as a violation of the normal state of the diaphragm in the area of the esophageal opening. The cause of the pathology is a concussion of the body, which led to stretching and weakening of the muscle tissue structures.
Subsequently, the opening of the diaphragm expands, and this process threatens the digestive organs prolapse into the chest cavity.
With a diaphragmatic hernia, he experiences pain in the upper abdomen. Acute pain syndrome occurs with prolonged absence of treatment for the disease. Leads to pinching of blood vessels and degeneration of muscle tissue.
Peritoneal injury
The blunt type of abdominal injury is characterized by the absence of open wounds and external bleeding. But despite this, damage to internal organs is diagnosed.
Damage can be caused by impact with a blunt object, strong shaking, or falling from a great height.
In medicine, there are several types of injuries.
- Hematoma. A hollow formation is formed, which is filled inside with inflammatory fluid or blood. A painful feeling occurs after the blow. The affected part of the abdomen becomes swollen and bluish.
- Rupture of the spleen. Observed after a strong blow to the left side under the ribs. The spleen has a good blood supply, so after an impact there is an immediate and large loss of blood. There is a possibility of loss of consciousness due to painful shock.
- Fractured ribs. After such a process, the patient experiences acute pain in the middle or on the side where the fracture occurred. In addition to all this, the stomach begins to put a lot of pressure on top. Increased discomfort occurs when walking and deep breathing.
The danger of blunt abdominal trauma is that a person does not react immediately to it. Then serious complications and death of tissue structures occur.
Myocardial infarction
During an attack, heart muscle tissue is rejected. The cause of the pathological process is a violation of blood flow and nutrition of the organ.
Before the attack, the patient complains of pain in the upper abdomen. This symptom is similar to other pathologies, so it rarely goes unnoticed. Discomfort can vary in intensity and can be felt under the ribs.
During an attack, the pressure drops sharply, the patient loses consciousness and becomes pale. In such cases, you should immediately seek help from a doctor.
Diseases of the digestive organs
Sharp pain can occur in any part of the peritoneum. To determine the type of pathological process, you need to rely on the accompanying symptoms.
Liver diseases
Common ailments include:
These diseases do not immediately make themselves felt. But in the absence of therapeutic measures, for a long time the center of the abdomen begins to strongly pull and constantly vomit. The pain syndrome begins on the right side, but can migrate to any side of the peritoneum.
In the initial stages, treatment involves following a diet and taking medications. In more serious cases, surgical procedures are performed.
Stomach diseases
Severe stomach cramps may occur. The cause is a number of diseases such as:
Gallbladder diseases
The pathological process occurring in the gallbladder is commonly called cholecystitis. The formation of stones in the organ is observed. The reason is a decrease in immunity and metabolic disorders.
The upper layer of the gallbladder is susceptible to adverse factors. The resulting stones constantly injure him, which causes pain in the upper abdomen. Often the pain syndrome becomes shingles in nature.
The pathology requires urgent surgical intervention. If help is not provided in a timely manner, severe pain leads to loss of consciousness and the development of serious complications.
Spleen damage
The spleen is one of the important organs of the digestive tract. But most often it is she who is adversely affected. Doctors can diagnose:
In addition to the painful feeling, the person complains of nausea and the urge to vomit. Inflammation is treated with medications. In other cases, an operation is required.
Pathologies of the pancreas
Pathology of the pancreas
Sudden, unbearable, girdling pain under the ribs indicates acute pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas. The pain occupies the entire upper abdominal region, and responds under both shoulder blades. Quite often it is accompanied by vomiting, which can increase the pain.
The provoking factor for vomiting is the desire to eat something or drink water. Therefore, during acute attacks of pancreatitis, there is no need to offer the patient food and drink. Acute pancreatitis is also indicated by a bluish tint of the skin, pinpoint hemorrhages in the navel area, a drop in blood pressure, all this occurs due to blood poisoning by enzymes entering the bloodstream from the inflamed pancreas.
One of the causes of acute pancreatitis is drinking too much alcohol. Therefore, the number of patients with attacks of acute inflammation of the pancreas increases sharply in the post-holiday days. Doctors managed to nickname pancreatitis “New Year’s disease.”
At the first signs of pancreatitis, do not try to self-medicate. The patient must be immediately sent to the hospital.
Chronic pancreatitis
This disease is characterized by girdling pain, covering the entire upper abdominal area under the ribs, and responding under the shoulder blades. Appears after fatty foods. The pain worsens when the patient lies on his back, so during an attack of pain the patient tries to sit leaning forward. Exacerbation of the disease is characterized by impaired absorption, which leads to greasy stool and diarrhea.
As a result of digestive disorders, the body does not receive enough necessary nutrients, causing the patient to lose weight and develop general exhaustion of the body and vitamin deficiency.
Pain in the upper abdomen: causes, diagnosis, treatment, medications
Among the direct indications for hospitalization in a surgical hospital, not the least place is occupied by complaints of acute pain in the upper abdomen. Some of them are completely justified and after a thorough examination, doctors identify in such patients a serious pathology of the abdominal organs, requiring intensive and sometimes surgical treatment.
However, in other cases, patients are discharged almost the next day, with a recommendation to be observed by a local physician at their place of residence. The bewilderment of these people who had to endure a very difficult time of waiting for an ambulance and staying within hospital walls is understandable.
In this article we will talk about why pain in the upper abdomen occurs and what to do about it.
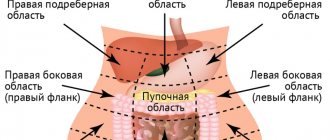
Briefly about the anatomy of the epigastrium
Epigastric organs
The upper part of the abdomen, located just above the navel, is called the epigastrium in medical literature (from the Greek words “epi” - “above” and “gaster” - “belly”). From above this area is limited by the costal arches and the xiphoid process of the sternum, and from below by a conditional line passing through the lowest points of the edges of the X ribs.
The immediate causes of pain in the upper abdomen can be both organs located in this part of the abdominal cavity, as well as nerve fibers and muscles. Most often, the stomach above the navel hurts due to pathology :
- Stomach.
- Duodenum.
- Pancreas.
- Gallbladder and bile ducts.
However, sometimes doctors have to deal with complex cases of pain in the upper abdomen, when it is not caused by pathology of the abdominal cavity.
Diseases of the stomach and duodenum
This is the most common cause of aching and nagging pain in the upper abdomen, as well as other complaints that make up gastric dyspepsia syndrome . This symptom complex is caused by the pathology of the stomach and duodenum and includes:
- Discomfort in the upper abdomen, which occurs both on its own and in connection with food intake.
- Nausea, sometimes vomiting of recently eaten food.
- Heaviness after eating.
- Belching is sour, bitter and rotten.
- Regurgitation, or a kind of analogue of regurgitation in adults.
- Feeling of early satiety, and many other symptoms.
These clinical manifestations, including pain in the upper abdomen, fully describe the picture of chronic gastritis - one of the most common diseases of our time. The causes of this pathology are:
- long-term errors in diet;
- frequent intestinal infections;
- hereditary predisposition;
- autoimmune processes;
- carriage of the bacterium Helicobater pylori.
The latter is the main culprit of gastric ulcer . The disease can be asymptomatic, but most often with an ulcer, patients complain of pain in the upper abdomen that occurs during or half an hour after eating.
This differs from a duodenal ulcer , in which pain occurs on an empty stomach and at night - such patients, as a rule, love to eat and they perceive food as a pain reliever.
In the absence of proper treatment, the ulcer can be complicated by extremely dangerous pathologies that require urgent surgical care:
- Perforation or perforation of an ulcer . In this case, a through hole is formed in the wall of the hollow organ, through which the entire contents of the digestive tract penetrates into the abdominal cavity and causes peritonitis. Clinically, this condition is manifested by dagger pain in the upper abdomen, sharp tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall and a rapid deterioration in general well-being.
- Penetration of an ulcer or penetration of an ulcer into nearby organs. The pancreas is most often affected and clinically this condition manifests itself in almost the same way as perforation. But the described complaints are quickly joined by symptoms of acute pancreatitis, including girdle pain in the solar plexus area.
- Bleeding from the bottom of the ulcer , which can be either minor or very pronounced. This complication is manifested by weakness, low blood pressure, bloody vomiting or melena (smelly, tarry stool). Paradoxically, often with the development of bleeding, stomach pain is significantly relieved.
- Stricture or the formation of a pronounced narrowing of the stomach as a result of scarring of the ulcer. Clinically, this is manifested by faster satiety, vomiting of recently eaten food, pain above the navel and rapid weight loss.
The most serious reason why the upper abdomen may hurt is stomach cancer . Unfortunately, externally it often looks like an ulcer, including clinically, and final diagnosis is possible only on the basis of gastroscopy with biopsy.
If a middle-aged or older person experiences symptoms of a peptic ulcer, a prolonged increase in temperature (up to 37-37.9 degrees), loss of appetite and weight loss. Then he definitely needs to be examined for cancer.
Pathology of the pancreas
Another common cause of discomfort in the epigastric region is acute and chronic diseases of the pancreas. Three pathologies are of greatest importance here.
Acute pancreatitis , or an acute inflammatory process in the tissue of the pancreas, is accompanied by sharp, often girdling abdominal pain in the solar plexus area, repeated vomiting and a rapid deterioration in general condition. The causes of this disease are:
- Alcohol abuse and improper use of alcoholic beverages (for example, combining lard or other very fatty foods with vodka).
- Addiction to energy drinks and alcoholic cocktails.
- Taking certain medications (such as anticonvulsants for epilepsy and emotional disorders).
- Gallstone disease and some other conditions.
If acute pancreatitis develops, the patient should be immediately hospitalized in a surgical hospital to prevent the development of pancreatic necrosis or complete necrosis of the organ.
Dull aching pain in the upper abdomen, especially if it is accompanied by weight loss and frequent loose stools, may indicate chronic pancreatitis .
With this disease, the function of the organ is reduced to one degree or another, and first of all, the process of breaking down dietary fats is disrupted. They are excreted unchanged from the body and lead to steatorrhea - loose, foul-smelling stool, in which feces are poorly flushed from the walls of the toilet.
A very serious cause of pain in the upper abdomen is pancreatic cancer . This disease is extremely difficult because the tumor mechanically compresses the common bile duct. In patients with pancreatic cancer, the digestive processes are severely disrupted, jaundice with lightening of the stool and typical symptoms of a malignant process are observed.
Diseases of the biliary tract
In some patients, diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract may be accompanied by acute and prolonged pain in the abdomen above the navel. Although these diseases are more characterized by the localization of pain in the left hypochondrium.
Most often, the upper abdomen hurts due to cholelithiasis , a disease characterized by the formation of hard stones in the lumen of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
When one of them begins to pass through the ducts, it mechanically injures their wall and causes excruciating and unbearable pain, which is called biliary or hepatic colic . The pain syndrome can be localized both in the left hypochondrium and in the upper abdomen under the ribs, and if it appears, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Rare causes of upper abdominal pain
It is not always possible to establish the reason why a particular patient has pain in the upper abdomen. Often patients do not understand why they undergo “extra” tests, such as ECG, chest x-ray and detailed urine tests. However, there are reasonable reasons for everything:
- In older people, acute pain above the navel may be the first signal of a myocardial infarction . Especially if there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure and sweating. Most often, this situation occurs in patients suffering from diabetes mellitus, since the functioning of the autonomic nervous system is disrupted due to impaired glucose metabolism.
- Sometimes pain in the upper abdomen is associated with pleurisy or acute inflammation of the pleura - the membrane surrounding the lungs. This is a complication of severe pneumonia, although there may be other reasons for the development of pleurisy.
- In difficult cases, when the patient, in addition to cramping pain in the upper abdomen, experiences severe watery diarrhea, attacks of suffocation, a feeling of flushing in the face and trembling of the hands, one can suspect carcinoid syndrome - a specific set of symptoms that occurs when there is a malignant neuroendocrine tumor in the body.
There are other reasons for the appearance of pain in the epigastrium, but they all require in-depth laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
What to do if your stomach hurts in the upper abdomen
Epigastric pain is a dangerous symptom that you should never turn a blind eye to. Since very often its cause is acute surgical pathology, the slightest delay in seeing a doctor can lead to very sad consequences.
Therefore, if a sharp acute pain appears in the abdomen above the navel, you should immediately call an ambulance, and to reduce the pain, you can take No-Shpu.
Patients with chronic diseases of the digestive system (chronic gastritis or pancreatitis) first of all need to follow a strict diet.
Spicy, fried and sour foods are not allowed in the daily diet. It is necessary to limit the consumption of smoked meats, spices, as well as sauces and other seasonings.
Meals should be frequent, at least 4-5 times a day and divided into small portions. If, against the background of chronic gastritis, the stomach suddenly hurts in the stomach area, then to reduce discomfort you should take antacid medications (for example, phosphalugel).
If, based on the results of the examination, a diagnosis of gastric ulcer was made, then intensive eradication therapy . It is aimed at destroying Helicobacter pylori and normalizing the acidity of gastric juice.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HYUfjceQ-Fk
The treatment regimen should be selected by a gastroenterologist or therapist, but usually it combines 3-4 drugs, including:
- Antibiotic (from the group of penicillins, macrolides, tetracyclines or metronidazole);
- A proton pump inhibitor (omez, esomeprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole and others) or bismuth preparations (for example, De-Nol).
Therapy should be continued continuously for at least 7 days, after which a repeat gastroscopy should be done.
Source: https://zhivotu.net/bol-vverhu-zhivota/
Hepatic colic and cholecystitis
Chronic cholecystitis manifests itself as moderate pain under the right rib, radiating under the right shoulder blade or into the epigastrium. As a rule, pain occurs when the diet is violated, when eating spicy and fatty foods. Accompanied by bitter belching, vomiting, nausea, heartburn. Chronic cholecystitis is complicated by cholelithiasis, which requires surgical intervention.
Read: Why does tingling occur in the right side under the ribs? Treatment of diseases
Acute cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis may be indicated by acute pain in the front of the abdomen under the right rib.
Acute cholecystitis or inflammation of the gallbladder may be indicated by acute pain in the front of the abdomen under the right rib. Unbearably acute pain forces the patient to rush around in search of a position that would help make the pain less acute.
In this case, the patient suffers from fever and incessant vomiting. The disease is accompanied by yellowing of the skin and eyeballs. If inflammation of the gallbladder is suspected, the patient must be hospitalized in the surgical department.
The occurrence of hepatic colic is associated with the entry of a stone into the bile duct. She is characterized by a stabbing pain under the ribs on the right. But there are no chills or vomiting. An attack of hepatic colic, provoked by the movement of a stone, can go away on its own after a few hours. It can be treated with antispasmodic drugs.
Diagnostics
If a person detects pain in this localization, it is recommended that a person contact several specialists at once - a surgeon, a therapist, a gastroenterologist and a neurologist. If necessary and if other pathologies are suspected, the doctor may refer the patient to specialists in a different medical field.
After the initial examination, history taking and palpation of the abdomen, the doctor will prescribe the following mandatory diagnostic measures:
- General clinical blood and urine tests. These studies will show the general picture of the patient’s health condition and identify the inflammatory process, if any, in the body.
- Advanced biochemical blood test.
- An abdominal ultrasound will immediately determine whether there is fluid in the abdominal cavity, inflammation of internal organs or other pathologies.
- Endoscopic examination (EGD), which will help to see erosions, ulcers or bleeding in the stomach and intestines.
- MRI and CT are prescribed if cancer is suspected.
These are classical methods of diagnostic procedures that are mandatory when identifying an “acute abdomen” with pain in its upper part. If more advanced diagnostics are needed, the doctor may prescribe additional procedures.
Subphrenic abscess
Injuries to organs can lead to subdiaphragmatic abscess.
The cause of subphrenic abscess is surgical interventions in the abdominal cavity, injuries to organs located in the abdominal area. An abscess can also occur as a consequence of complicated liver inflammation, accompanied by tissue suppuration, which can also affect the diaphragm.
But this rarely happens when liver disease is not treated. The impetus for this pathology can also be peritonitis that develops as a result of appendicitis or cholecystitis. With a subphrenic abscess, acute pain appears in the anterior part under the ribs on the right or left side, which intensifies with a sharp sigh, coughing, or sneezing.
The pain radiates to the shoulder blade or collarbone of the side where it is localized, and is accompanied by a fever and signs of poisoning of the body. If pain of this kind occurs for the first time, do not try to self-diagnose and self-medicate, do not suppress it with painkillers.
Through pain, your body lets you know that it needs help, and above all medical help. Contact a professional to get the correct diagnosis. If the diagnosis is in doubt, get examined at two or three different medical institutions. This advice is especially relevant when the diagnosis requires surgery. Because erroneous diagnosis, and especially the dishonest attitude of doctors who think not so much about the recovery of patients, but about personal enrichment, still occur in our society.
Read along with this article:
- What diseases can cause pain in the hypochondrium?
- Pain in the epigastric region - what does it mean?
- How to relieve stomach pain: first aid
- What is in a person’s left side and what can hurt there?
- 20 reasons why there is a stabbing pain in the left side under the ribs
- Let's become invulnerable, or how to identify a stomach ulcer in...
- Is a sour taste in the mouth always a warning sign?
- Why does nagging pain in the stomach occur, what pathologies...
- Want to know the reasons for morning sickness?
Pain in the upper abdomen - causes, diseases, diagnosis, prevention and treatment
Pain in the upper abdomen in the middle is a very dangerous symptom, which is a harbinger of the development of various pathologies and dangerous diseases.
Negative manifestations can form suddenly or increase gradually. Some go away in a short period of time, others annoy the patient over a long period.
With increasing intensity and intensification of symptoms, you should contact a professional specialist. The patient must undergo a diagnosis of the body and find out why certain symptoms appeared.
After passing diagnostic methods, appropriate treatment should be prescribed.
The upper abdomen hurts for various reasons. They are an indicator of all kinds of conditions. Diseases may manifest differently in each patient. Some patients experience more pain, while others experience less pain.
Since pain itself is considered a subjective feeling, relying on just one symptom is not recommended. It is impossible to make a correct diagnosis based only on the manifestations of pain. Therefore, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the body. It is also worth considering that diseases have a specific nature of pain.
Independent and professional diagnosis of pain in the upper abdomen
Many people don’t know what to do if there is severe pain in the upper abdomen, what should be the treatment for pain in the upper abdomen, and in general, who to turn to if there is pain in the upper abdomen above the navel - a therapist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, pulmonologist? Ideally, you should visit each of the above specialists. You can start with a therapist - he will collect anamnesis, prescribe the necessary tests and write a referral to a specialist.
Before going to the doctor, it is recommended to take the following steps:
1 Take a horizontal position and carefully palpate the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, lightly pressing on it with your fingertips.
Palpation will help identify the source of discomfort - an organ whose dysfunction or damage has led to a person having pain in the upper abdomen.
This information will be useful in the future, when it is time to answer the doctor’s questions, so do not neglect this procedure.
2 Analyze the actions preceding the onset of pain.
Pain syndrome can be a consequence of recently experienced stress, taking strong medications, excessive physical exertion, poisoning with low-quality food or alcohol, overeating, exacerbation of chronic ailments - it is important to establish the factor that provoked the deterioration of the general condition, the specific causes of pain in the upper abdomen on the left, right or in the middle. This is necessary, first of all, so that the doctor can prescribe adequate treatment before the patient develops dangerous complications: if he does not know where to start, what to start with when making a diagnosis, the examination will be delayed - during this time the person’s condition will change. who comes in with complaints that he has pain in the upper peritoneum, it can worsen sharply.
3 Determine the nature of the pain. Cutting, twisting, encircling, pulling, burning, aching, sharp, floating - the variety of sensations can at first lead to a stupor. What type of pain in the upper abdomen and its causes can hardly be determined immediately, but over time a person will definitely figure out what’s what.
No one except himself can say with certainty what exactly he feels, so every effort must be made to recognize the types and types of pain in the upper abdomen, what it could be - pain, tingling, burning, distension - since this is essential will facilitate making a preliminary diagnosis.
To find out the true cause of the ailment, you will have to undergo additional examination at a medical institution. The following instrumental types of diagnostics will help to clarify the picture of what is happening:
1 Ultrasound examination of the abdominal and pelvic organs.
2 Magnetic resonance and/or computed tomography.
3 Radiography.
4 Colonoscopy.
5 Fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
6 Electrocardiogram.
Ultrasound, MRI, CT and radiography allow you to assess the general condition of internal organs and the quality of their work. Colonoscopy is prescribed if there is a suspicion of the presence of tumors or other formations in the intestines.
With the help of FGDS, it is possible to identify diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract - the esophagus, stomach and the adjacent part of the duodenum. An ECG can help rule out heart problems, which often make themselves felt through pain in the epigastric zone.
The patient will also need to take blood, urine and stool tests - their results will show how the body reacts to changes and what it is missing at the moment.
When to go to the doctor?
In many ways, the manifestations of cancer are determined by the localization of the process. If atypical structures grow in the esophagus, in addition to pain in the upper center of the abdomen, the patient notices problems with swallowing. There may be a feeling of weakness in this part of the body.
Sometimes there are problems with stool. If esophagitis is diagnosed, it is necessary to especially carefully evaluate any painful manifestations and other questionable symptoms. Conditions such as stomach and intestinal polyps and peptic ulcers are potential precursors of cancer.
As can be learned from medical statistics, many patients do not pay attention to the primary manifestations of the disease, and come to the doctor when the pathology has already progressed to the third, sometimes fourth stage.
One of the problems of the cancer process in the esophagus is the high rate of progression of the pathology.
Doctors recommend that at the first signs of discomfort or stable unpleasant symptoms, you undergo a comprehensive examination, which will help eliminate any suspicions or confirm the disease. This means it will be possible to start treatment in a timely manner.
Source: https://PrioritetMed.ru/simptomatika/pochemu-bolit-verh-zhivota.html
How to behave if your stomach hurts
Regardless of the nature of the pain, consultation with a specialist is necessary. This will help establish the correct diagnosis and avoid possible complications.
You cannot take painkillers before the doctor arrives; this interferes with making an accurate diagnosis, and the result can be disastrous.
When your stomach hurts, you should never use a heating pad until the cause of the pain has been determined. You can apply ice.
You should be wary if abdominal pain is accompanied by fever, diarrhea and vomiting. This may be a sign of a serious pathology.
Irregular pain that occurs from time to time usually does not indicate a serious illness. But if discomfort occurs very often and has become a pattern, you should consult a doctor. To facilitate diagnosis, you should pay attention to the severity and nature of pain, location. As for treatment, naturally, it should be aimed primarily at eliminating the pathology that causes such unpleasant symptoms for the patient.
Information about the possible causes of abdominal pain, of course, can help a person understand his condition. But still, to maintain health and even life in the presence of alarming symptoms, it is necessary to seek qualified medical help.
Abdominal pain is an unpleasant symptom. But what do we mean when we talk about abdominal pain? Essentially, the stomach is a cavity in which the internal organs are located, and any of them can cause painful spasms. In order to make a preliminary diagnosis, you need to find out where the pain is localized, and then you can guess which organ we are talking about. What do cramps in the upper abdomen mean?
Abdomen hurts with cramps at the top - clinical significance of the symptom
When painful spasms appear in the upper abdomen, you need to pay attention to the organs that are projected onto the upper region of the anterior wall of the peritoneum. These include the stomach, liver, pancreas, duodenum, spleen, and gall bladder.
In addition, we must not forget that such pain signals possible diseases of the sternum organs, which are located next to the abdominal cavity and are separated only by the diaphragm. For example, spasms in the right hypochondrium indicate possible right-sided pneumonia, and pain in the epigastrium is evidence of myocardial infarction.
Also, the abdomen in the upper part can hurt with such diverse pathologies as:
- exacerbation of gastralgic osteochondrosis;
- preperitoneal lipoma;
- inflammation of the abdominal cavity.
We must not forget that most of the organs of the peritoneum are hollow, and pathologies in them can be in the form of blockage or rupture of the walls, and this leads to very serious consequences.
As you can see, the clinical picture is quite heterogeneous, and knowing just the place where it hurts is not enough to make a diagnosis. If you experience sudden sharp pain for more than half an hour, then this is a sure signal to seek emergency medical help.
Cardiovascular diseases as a cause of pain
Coronary heart disease can provoke discomfort in the upper abdomen. Their most common cause is acute myocardial infarction. Referred pain occurs in the upper abdomen. They can be very pronounced, which is why doctors sometimes misdiagnose acute abdomen. Heart attack pain also has other symptoms: a feeling of squeezing in the chest, shortness of breath, a drop or sharp increase in blood pressure, severe weakness, cold sticky sweat, rhythm disturbances, etc.