The human stomach contains glands that digest food. These include parietal cells. When the glands function normally, a person does not experience any unpleasant or painful sensations. Proper nutrition is required for the body to function properly. If a person often eats unhealthy food, the glands of the stomach, including the parietal cells, suffer.
Digestion in the stomach
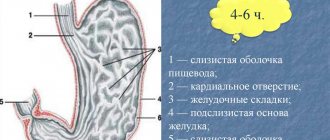
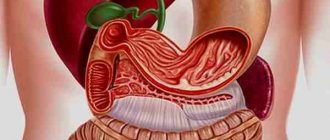
The stomach consists of three parts:
- cardiac - located near the esophagus;
- fundamental - the main part;
- pyloric - near the duodenum.
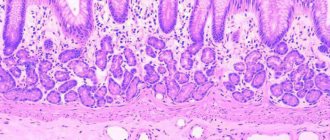
Inside there is a mucous membrane that is the first to come into contact with food coming from the esophagus. In addition, there is a muscular and serous membrane. They are responsible for motor and protective functions.
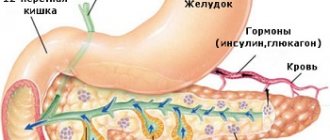
The mucous membrane contains an epithelial layer, which contains a large number of glands. They secrete a secretion that allows them to digest food. Gastric juice is produced constantly, but its amount is influenced by hormones and the brain. Thoughts about food and the smell make the glands work more actively. Thanks to this, up to 3 liters of secretion are produced per day.
Glandular cells secrete mucus in the stomach
Mucus in the stomach, which in professional language is called “mucin,” is a gel-like substance produced by the cells of the organ and located on the surface of the stomach. If this substance is not produced, the walls of the stomach will become covered with ulcers, and micronutrients will no longer be absorbed correctly.
Failure of the activity of glandular cells can lead to increased production of mucus, which will also negatively affect the functioning of the organ and lead to disruption of food absorption. The production of mucin in a certain amount occurs constantly, this process is natural and is not considered a deviation. Mucin is produced daily to maintain the walls of the organ. If the stomach tissues are damaged, mucus production increases significantly; this is a protective reaction.
If left untreated, they will increase in size and develop into peptic ulcers. Such neoplasms injure the epithelium of the organ and provoke various diseases, some of which are difficult to treat.
Failure of the activity of glandular cells can lead to increased production of mucus, which will also negatively affect the functioning of the organ and lead to disruption of food absorption
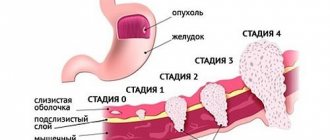
Long-term gastritis and mucosal hypertrophy can even cause stomach cancer. To prevent such negative consequences, at the first signs of illness you need to immediately visit a specialist.
Mucus in the stomach is secreted by glandular cells
Failure of the activity of glandular cells can lead to increased production of mucus, which will also negatively affect the functioning of the organ and lead to disruption of food absorption. Mucin is secreted by glandular cells, it is necessary for processing food (due to it, hydrochloric acid is also processed) and protecting the stomach. In a healthy person, the mucous membrane is about 1.5 mm thick; in appearance it resembles jelly and has a fairly viscous structure.
Depending on which cells produce the substance, the mucus may be cloudy, pink, or foamy (this type is the worst to dissolve). The production of mucin in a certain amount occurs constantly, this process is natural and is not considered a deviation. Doctors associate an excess of this substance with poor diet and certain human habits.
Mucin is produced daily to maintain the walls of the organ. If the stomach tissues are damaged, mucus production increases significantly; this is a protective reaction. Since a large amount of mucin indicates the beginning of the atrophic process and the death of some glands, the disease cannot be left to chance; the consequences of such ignoring can be very sad.
Hydrochloric acid is produced by glandular cells in the stomach
Hydrochloric acid is part of gastric juice. As the name suggests, it is produced by parietal cells that are found in the gastric mucosa. Thanks to this composition, gastric juice creates an acidic environment in the stomach.
Hydrochloric acid is part of the gastric juice; it is produced by parietal cells that are located in the gastric mucosa
This is necessary for the proper functioning of the enzyme pepsin, which breaks down proteins into monomers. Pepsin is active only in an acidic environment, so when the acidity of the stomach is low, proteins are poorly broken down. The mucous membrane contains special cells that protect the stomach from acid.
The proenzyme pepsinogen is secreted by glandular cells of the stomach
Proenzymes of the digestive enzyme of the stomach (pepsin), used as biochemical markers of the condition of the gastric mucosa. Pepsinogens are inactive precursors (proenzymes) of the main digestive enzyme of the stomach - pepsin.
There are 2 types of pepsinogens, which differ slightly in structure and functional properties:
- pepsinogen I and pepsinogen II. Pepsinogen I is produced mainly by the glands of the mucous membrane of the fundus of the stomach;
- pepsinogen II - also in the cardiac, antral and duodenal mucosa.
They are converted into pepsin under the influence of hydrochloric acid of gastric juice - while high acidity is optimal for pepsinogen I (pH = 1.5-2.0), and lower acidity for pepsinogen II (pH = 4.5). In small concentrations, pepsinogens enter the blood.
A study of the level of pepsinogens in blood serum is used to assess the condition of the gastric mucosa. Pepsinogens are used as a marker of atrophic gastritis (a condition regarded as precancerous), but not as a tumor marker.
What to do so that the glandular cells in the stomach are normal
If an ultrasound examination shows that the thickness of the mucin layer has changed, the first step is to advise the patient to change the diet and prescribe a special diet. If the body begins to produce mucin in excess, it is necessary to adhere to certain nutritional rules and follow a regimen.
You need to exclude low-quality and unhealthy foods from your diet, especially fast food, fatty, fried foods and carbonated drinks. Consumption of foods with added carcinogens and large amounts of fat will sooner or later negatively affect the activity of the gastrointestinal tract. The sooner they are excluded, the better. In order for the stomach to function properly and be healthy, you need to drink at least one and a half liters of filtered water per day and not eat dry food.
Sources:
- https://gastritinform.ru/m.ekamedcenter.ru/articles/anatomiya-zheludka-stroenie-zheludka-lechenie-zheludka.html
- https://ashgb.ru/gastrit/cliz-v-zheludke-prichiny-i-lechenie-patologii-chto-delat-i-kak-izbavitsya.html
- https://studbooks.net/2483696/meditsina/zheludok
- https://kaz-ekzams.ru/biologiya/uchebnaya-literatura-po-biologii/biologia-repetitor/588-stroenie-i-funkcii-pishhevaritelnoj-sistemy.html
- https://invitro.by/analizes/for-doctors/486/10429/
- https://vseozhivote.ru/zheludok/sliz-prichini-ilecheniye.html
Post Views: 624
Types of stomach glands
The glands in the stomach have a variety of shapes. The number is in the millions. Each gland has its own function. They come in the following types:
- The cardiac glands are responsible for the production of chlorides and bicarbonates.
- Fundus produces gastric juice. There are most of them. They are found throughout the stomach, but the largest amount is concentrated in the lower part.
- Parietal cells create hydrochloric acid. In addition, they have to create the Castle factor, which is involved in hematopoiesis. Removing the part of the stomach in which these cells are located leads to the development of anemia.
Gastric glands
The main functional role of the gastric glands is the production of gastric juice. Each section of the stomach secretes its own glands, which are responsible for the primary processing of incoming food, for its digestion and for the formation of the food bolus. Enzymes produced by the glands break down the complex components of the food bolus into simple structural bricks. The secretion affects the function of the stomach, helps cells absorb substances. Therefore, the correct functioning of the glandular structures of the organ is the key to the health of not only the stomach, large intestine, but also the entire gastrointestinal tract.
What is a parietal cell
The cell is shaped like a cone or pyramid. The number is higher in men than in women. Parietal cells secrete hydrochloric acid. For the process to occur, the participation of histamine, gastrin and acetylcholine is required. They act on the cell through special receptors. The amount of hydrochloric acid is regulated by the nervous system.
Previously, in case of gastric ulcer, part of the organ was removed for better functioning. But in practice it turned out that if the part in which the parietal cells were located was cut out, then digestion slowed down. The patient had complications after surgery. At the moment, this method of treatment has been abandoned.
Features and Functions
A distinctive feature of parietal cells is their single location outside the mucous cells. They are larger than other epithelial cells. Their appearance is asymmetrical; the cytoplasm contains one or two nuclei.
Inside the cells there are tubules responsible for transporting ions. From the inside, the channels pass into the external environment of the cell and open the lumen of the gland. There are villi on the surface, microvilli are located inside the tubules. Another feature of cells is a large number of mitochondria. The main function of parietal cells is to produce ions that contain hydrochloric acid.
Hydrochloric acid is required to destroy pathogenic bacteria and reduce the rotting of food debris. Thanks to it, the digestion process goes faster, proteins are absorbed more easily.
Factors affecting the functioning of the glands
The following factors influence the proper functioning of the gastric glands:
- healthy eating;
- emotional state of a person;
- stressful situations;
- chronic diseases of the liver and gall bladder;
- alcohol abuse;
- long-term use of medications that irritate receptors;
- chronic gastritis;
- stomach ulcer;
- smoking.
If there are disturbances in the functioning of the gastric glands, chronic diseases occur. Failure to follow the rules of a healthy lifestyle provokes the risk of healthy cells degenerating into malignant neoplasms. Stomach cancer is not immediately recognized. The fact is that the process begins gradually, and the patient does not see a doctor for a long time.
The functioning of the glands is important for the digestion of food, so it is important to prevent the development of stomach diseases, undergo regular medical examinations and, if possible, avoid surgery.
Autoimmune gastritis
Sometimes a person develops autoimmune gastritis. A disease in which the body perceives its own cells as enemies and begins to destroy them. In practice, such gastritis is rare and is characterized by the death of the gastric mucosa and the destruction of the gastric glands.
As a result of a malfunction in the body, the production of gastric juice is reduced, and problems arise with the digestion of food. At the same time, the level of internal Castle factor decreases and vitamin B12 deficiency appears, which leads to the development of anemia.
Typically, autoimmune gastritis develops into a chronic form. In this case, the patient has concomitant thyroid diseases. The disease is difficult to diagnose and cannot be completely cured. Patients take medications throughout their lives.
The appearance of antibodies to Castle factor and parietal cells is detected by immunoglobulins, which indicate that vitamin B12 has ceased to be absorbed.
Types of gastric glands
The glands of the stomach differ in location, the nature of the secretion produced and the method of its secretion.
Exocrine
Digestive secretions are released directly into the lumen of the organ cavity. Named according to their location:
Own
This type of gland is very numerous - up to 35 million; they are also called fundic bodies. They are located mainly in the body and fundus of the stomach and produce all the components of gastric juice, including pepsin, the main enzyme of the digestive process.
The gastric glands are divided into 3 types:
- the main ones are large in size, combined into large groups; needed for the synthesis of digestive enzymes;
- mucous membranes are small in size and produce protective mucus;
- Parietal cells of the stomach are large, single, and produce hydrochloric acid.
Parietal (parietal) cells occupy the outer part of the main or fundal bodies located on the bottom and body of the organ. Outwardly they look like pyramids with bases. Their function is the production of hydrochloric acid and internal Castle factor. The total number of parietal cells in the body of one person approaches a billion. The synthesis of hydrochloric acid is a very complex biochemical process, without which food digestion is impossible.
Causes and symptoms of autoimmune gastritis
The exact causes of the development of this disease are still unknown. But there are a number of assumptions explaining what can trigger the process of self-destruction in the body:
- Genetic factor. According to statistics, 10% of diseases arose due to hereditary disorders.
- Failure in the immune system. There is an assumption that disruption of the endocrine system allows the body to be reprogrammed to destroy individual cells.
- Alcohol and smoking can increase the risk of developing various diseases.
- Rough, poorly chewed food irritates the gastric mucosa and can contribute to the development of autoimmune gastritis.
The symptoms of the disease differ little from other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. First of all, patients pay attention to:
- pain in the stomach;
- heaviness and discomfort after eating;
- nausea;
- bowel dysfunction;
- burping;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- constant flatulence.
In addition to the main signs, a person may be tormented by symptoms to which he does not attach importance. Low blood pressure, constant fatigue, sweating, weight loss and pale skin are secondary signs of the disease. For doctors, the main reason indicating autoimmune gastritis is the condition that antibodies to parietal cells are elevated.
What does their work depend on?
The gastric glands produce secretions under the influence of the visceral nervous system. The quantity and quality of released enzymes are influenced by the nature of the food, the regularity of its intake, and the presence of inflammatory pathologies in the gastrointestinal system. The functioning of the glands is affected by the use of certain medications, a person’s hormonal levels, and his emotional state. A proper daily routine, regularity and good quality of nutrition, stress control and moderate physical activity help harmonize the functions of the glandular formations of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune gastritis
To make a diagnosis, the doctor collects data about the patient. Anamnesis and current complaints suggest what disease is tormenting the person. To confirm or refute the diagnosis, the following measures are required:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- immunological analysis for antibodies to parietal cells;
- level of gastric juice secretion;
- FGDS;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- determination of vitamin B12 levels.
Based on the examination, the doctor determines the diagnosis. Autoimmune gastritis cannot be treated. All medications are aimed at reducing discomfort and improving quality of life.
For severe pain, painkillers and antispasmodics are prescribed. Additionally, it is necessary to take enzymes to improve food digestion. A course of B vitamins and folic acid is taken. A diet is prescribed that excludes foods that have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa.