Sometimes your head and stomach start to hurt at the same time. The reasons can be quite harmless, for example, banal fatigue. But if the condition is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, upset stool and other symptoms, then you should consult a doctor.
The causes of a condition in which the head and stomach hurt can be:
- rotavirus infection;
- food poisoning;
- toxic infection;
- gastritis;
- appendicitis.
Rotavirus infection
Most often, abdominal discomfort appears against the background of an existing headache. But in the case of rotavirus infections, a person first develops gastrointestinal symptoms, and only then headaches appear. The disease is diagnosed both in the adult group of patients and in childhood, including babies in the first year of life.
Food becomes the source of infection. After the virus enters the body and attacks the human gastrointestinal tract (GIT), it is excreted naturally along with feces. Typical signs of the disease are:
- general malaise and weakness;
- headache;
- pain in the abdomen;
- increased body temperature over 38 degrees;
- diarrhea;
- nausea and vomiting.
There are also external symptoms of rotavirus infection: redness of the sclera of the eyes, inflammation of the mucous membranes of the throat and pharynx. The duration of the incubation (hidden) period can reach 5 days. Recovery occurs approximately 4–7 days from the onset of primary symptoms.
How to get rid of headaches with gastritis
There are simple ways to get rid of the ailment: put white cabbage leaves on your forehead. Just lie down a little and the pain will disappear. In 30 min. Dill oil helps get rid of ailments. It should be applied to the forehead and temples.
Traditional analgin can help you get rid of headaches with gastritis. But this will not solve the problem, since the cause of the malaise is gastritis. Therefore, if discomfort occurs, it is recommended to take an antacid. Drinking herbal teas and valerian infusion before meals gives good results. To eliminate spasms, “No-spa” is recommended.
It is important to pay attention to the overall picture of digestion. If the inflammatory process is accompanied by constipation, then toxins enter the blood from the intestines, which negatively affect the state of the nervous system.
To solve the problem of headaches arising from gastritis, you need to treat the disease itself
Developed intoxication is accompanied by headaches, which are difficult to relieve with medication without eliminating the cause. In this case, the person complains of sleep disturbances, fatigue, and irritability.
Any painkiller will relieve the symptom for a short time, but the main problem will remain. To solve the problem of headaches that occur against the background of gastritis, you need to treat the disease itself. It is important for the patient to follow a diet, quit smoking and alcohol, and avoid stress. If inflammation worsens, physical activity should be limited.
There may be several reasons why a headache occurs with gastritis: reflex pain, manifestation of astheno-vegetative syndrome, intoxication due to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract or improper use of medications.
Depending on the cause, the headache will vary in nature and may require different medications to relieve it. Painkillers may help in one case, but not provide relief in another. Before taking pills, you need to figure out what is causing your headache.
Gastritis is usually associated with stomach pain and nausea, especially on an empty stomach; the patient cannot eat salty, spicy or fried foods. But some of its symptoms may not be directly related to the gastrointestinal tract and food intake. For example, the fact that gastritis can cause a headache is not obvious at first glance. But, nevertheless, headaches, dizziness and nausea with gastritis occur quite often.
Sources:
- https://netmigraine.com/golovnaya-bol-pri-gastrite-prichiny-lechenie/
- https://gastritinform.ru/zdorovayagolova.ru/iz-za-chego-mozhet-bolet-golova/mozhet-bolet-golova-pri-gastrite.html
- https://sputnik.by/society/20171230/1032790433/prosto-o-zdorove-kak-ponyat-ot-chego-bolit-golova.html
- https://kiwka.ru/gastrit/golovnaya-bol.html
- https://zdorovajagolova.ru/lechenie/obezbolivayushhie-ot-golovnoy-boli/ot-golovnoj-boli-pri-gastrite.html
Food poisoning
Headache and stomach pain may be a sign of food poisoning. Sometimes such symptoms accompany a drug overdose. The most common causes of food poisoning are meat, canned food, dairy products, and mayonnaise.
Health problems arise from consuming expired foods and those that have been stored improperly. In this case, they contain a large amount of toxic substances and pathogenic bacilli. In most cases, infection occurs with Salmonella bacillus.
Signs of food poisoning include:
- sharp cramping pain in the gastrointestinal tract - the stomach twists strongly, diarrhea develops;
- headaches - appear somewhat later (as the condition worsens as a result of increased general intoxication);
- general weakness, lightheadedness, flickering of spots before the eyes;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- increase in body temperature to significant levels;
- chills;
- severe thirst, as the body intensively loses moisture.
First aid consists of gastric lavage and subsequent administration of adsorbent drugs. To prevent dehydration, you need to drink as much water as possible and special rehydrating preparations - Gidrovit, Regidron - that restore lost electrolytes. It is recommended to adhere to the principles of dietary nutrition.
Food poisoning can be accompanied by severe intestinal pain and headaches
If there is no result and the patient’s general condition worsens, hospitalization is necessary.
Child's pain
If a child develops both a headache and abdominal pain, it is necessary to consult a doctor. This becomes relevant when additional symptoms appear: nausea, vomiting and increased body temperature. Most cases are associated with food poisoning or rotavirus infection. Pathogenic bacteria enter the child’s body along with unwashed vegetables and fruits, developing the following symptoms:
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Headache;
- Weakness, redness of the eyes;
- Sore throat, pain when swallowing;
- Body temperature reaches 39 degrees;
- Diarrhea with liquid feces.
Every parent should pay attention to what their child eats. Fruits and vegetables should be treated with boiling water, and hands should be washed with soap.
Toxic infection
Bacterial toxins can be the reason why a person has a headache, a stomach ache, and at the same time feels sick. The causative agents can be: Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus bacteria, clostridia, botulism bacteria.
Staphylococcal infections
After the pathogen enters the body, a person develops certain pathological symptoms.
Abdominal pain and vomiting
This is pain in the abdomen and epigastric region, nausea ending in severe vomiting, a drop in blood pressure - the patient becomes dizzy, the limbs become cold, and the vision darkens.
Staphylococcal toxicoinfection, despite severe symptoms, is characterized by rapid recovery. Stabilization of the condition occurs approximately 3 days after the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease. But weakness and dizziness may persist for another two to three days.
Clostridia infection
Clostridia poisoning is much more severe. The onset of the pathology is accompanied by bloating and severe abdominal pain, localized in the projection of the small intestine - the peri-umbilical region. Later, other symptoms appear: darkening before the eyes, nausea, uncontrollable vomiting, severe diarrhea (up to 20 times a day). All this causes dehydration of the body.
Botulism
You can become infected with botulism bacteria by eating low-quality foods. Most often this is meat, fish and home-canned mushrooms and vegetables. Symptoms of botulinum toxin infection include:
- severe abdominal pain;
- indomitable vomiting that does not bring relief;
- repeated diarrhea.
If left untreated, they are accompanied by muscle weakness, drooping of the eyelid and paralysis of the respiratory tract, which leads to death. First medical aid consists of gastric lavage, taking sorbents and rehydrants.
Astheno-vegetative syndrome
Astheno-vegetative syndrome appears only in the chronic form of gastritis, as well as in other chronic diseases. It is formed due to the participation of immune mechanisms, the central nervous system, and regular stressful situations, which subsequently cause chronic disease. The difference from reflex pain in this syndrome is that pain in the head occurs regardless of whether the patient has taken food.
The nature of the pain in this case is not constant. They often intensify at night or with heavy stress on the body. In addition, additional symptoms appear in the form of weakness, fatigue, apathy, and dizziness at the end of a hard day. However, nausea and characteristic stomach upsets are observed quite rarely here. Due to headaches with gastritis, it is enough to establish an accurate diagnosis, since this symptom is inherent in almost all diseases and it is not always possible to determine the cause of the pain the first time. A feeling of nausea can also occur after headaches, as a consequence of untimely treatment. Medicines aimed directly at relieving headaches will not help as effectively as expected. The pain may subside, but may return stronger over time. To cure astheno-vegetative syndrome during exacerbation of gastritis, you need to take a course of vitamins, strengthening medications, and also begin to treat the underlying disease.
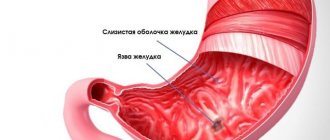
Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa, occurring in acute and chronic format. The pathology is accompanied by pain that occurs after eating.
Gastritis typically develops pain some time after eating.
Signs that a person has a sick stomach include:
- periodic nausea - sometimes a person feels nauseous all the time;
- pain in the epigastric region - in some cases, pain is felt in the lower abdomen, in its left quadrant, which is caused by strong distension of the stomach;
- increased saliva production;
- dyspeptic symptoms - heartburn, belching, unpleasant aftertaste.
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix (an appendage of the cecum) in the bulk of all diagnosed cases involves surgical treatment - the inflamed appendage of the intestine is excised. Symptoms of appendicitis include: pain in the lower abdomen on the right side, diarrhea (sometimes constipation), increased body temperature (indicators depend on the current stage of appendicitis).
Nausea and vomiting occur, as well as pain in the area of projection of the inflamed appendix. In acute complicated appendicitis, the patient experiences a sharp increase in pathological symptoms and a deterioration in general condition. If the pain does not stop for more than 6 hours, then the patient needs hospitalization.
The pain in this pathology is described as bursting, pulling, initially spreading to the entire abdomen and gradually shifting to the lower right quadrant. It becomes constant and intensifies when a person lies on his left side.
In rare cases, the area of pain associated with appendicitis is completely atypical: the person has a tightening/pain in the lower back. This is due to the anatomically atypical location of the appendix - it is directed posteriorly, towards the kidneys and spine, and not towards the anterior abdominal wall.
Pregnancy period
During pregnancy, a woman may often feel nauseous and have a headache. These symptoms are not considered dangerous, and they are especially noticeable in the morning. Sometimes there may be a tugging in the lower abdomen; a similar symptom is characteristic of the initial stage of pregnancy. In some cases, unpleasant symptoms occur late in life, and gradually the symptoms go away.
It should be understood that if you experience intense pain, you should definitely consult a doctor. It is quite possible that they signal some abnormalities in the body. You definitely need to be examined by a doctor, because not only the woman’s health, but also the life of the unborn child depends on this. You may need to perform an ultrasound of the pelvis and esophagus, as well as a general blood test. You will need to visit a gynecologist, he will be the one who will decide on further treatment.
Other reasons
Other pathological conditions can become other causes of simultaneous abdominal pain and headaches. These include:
- Traumatic brain injuries. In most cases they are accompanied by a concussion. This condition is characterized by headaches, as well as nausea and vomiting.
- Meningitis (inflammation of the membranes of the brain). The disease is characterized by severe headaches and abdominal discomfort. At the same time, the patient has a high fever and bouts of vomiting. A typical sign of meningitis is the inability to lower the head down due to too much tension in the neck muscles.
- Oncopathology. Malignant neoplasms can cause headaches and discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract. Bloating and increased body temperature are possible.
- Hypertension. People with abnormally high blood pressure may suffer from abdominal pain, headaches, nausea and dark vision.
Diseases
If you have discomfort in the stomach and dizziness, this condition can be caused by many reasons.
Rotavirus
After an infection enters the body, a person feels pain in the stomach area. When infected, severe dizziness and cephalalgia are observed. This clinical picture of malaise is often found with intestinal flu. The disease most often affects preschool children, although the infection is also dangerous for adults.
The main route of infection is through the consumption of contaminated foods, and therefore the stomach and intestines are usually affected. In this case, weakness, nausea, severe headache, vomiting and fever are noted, and the mucous membranes of the eyes and throat become inflamed. The illness lasts up to five days.
Poisoning
Another reason for stomach pain and dizziness is poisoning. It is provoked by Salmonella bacillus, which is always present in products that have expired or are stored in unsuitable conditions. Muscle weakness, stomach irritation, vomiting and upset bowel movements lead to significant dehydration, which causes extreme thirst.
In such a situation, it would be wise to ensure that you drink plenty of fluids (at least two liters) and resort to gastric lavage with a weak solution of potassium permanganate in combination with taking a sorbent that will absorb toxins and remove them from the body. Refusal to eat heavy foods will have a positive effect on the patient’s condition.
If there is no relief within the next two days, you should seek help from a specialist.
Toxic infection
Other “problem” bacteria include clostridium (its toxins provoke the most severe stomach pain) and staphylococcus. When infected, the following symptoms appear:
- significant decrease in blood pressure;
- darkening of the eyes;
- coldness in hands and feet.
Recovery usually takes several days, although the feeling of weakness will persist for a long time.
Other reasons
There are a number of other factors that can cause a simultaneous attack of headache and stomach pain:
- psychological problems, stress;
- taking medications without a doctor's prescription;
- pancreatitis;
- TBI (traumatic brain injury);
- meningitis;
- oncological diseases;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- hypertension.
Each ailment requires an individual approach to treatment.
Other pathological conditions can become other causes of simultaneous abdominal pain and headaches. These include:
- Traumatic brain injuries. In most cases they are accompanied by a concussion. This condition is characterized by headaches, as well as nausea and vomiting.
- Meningitis (inflammation of the membranes of the brain). The disease is characterized by severe headaches and abdominal discomfort. At the same time, the patient has a high fever and bouts of vomiting. A typical sign of meningitis is the inability to lower the head down due to too much tension in the neck muscles.
- Oncopathology. Malignant neoplasms can cause headaches and discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract. Bloating and increased body temperature are possible.
- Hypertension. People with abnormally high blood pressure may suffer from abdominal pain, headaches, nausea and dark vision.
A disease in the body can simultaneously cause an attack of headache and abdominal pain.
Infection of the body is manifested by gastrointestinal cramps, then a headache. According to medical statistics, rotavirus infection affects adults; pediatric cases were recorded only in babies in the first year of life.
Contained in food. Once in the body, it penetrates the gastrointestinal tract, where it causes an unpleasant symptom and is excreted naturally through bowel movements.
Symptoms of rotavirus infection:
- Weakness and malaise;
- Headache;
- Painful sensations in the stomach;
- High temperature exceeding the permissible threshold of 38 degrees;
- Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
External signs of infection: the sclera of the eyes turn red, the throat and pharynx become inflamed. The incubation period of the disease lasts no more than 5 days. It is eliminated from the body a week after the first symptoms appear.
Gastritis
An inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa, occurring in acute and chronic forms. The disease manifests itself as pain in the epigastrium after eating.
The affected stomach is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Constant attacks of nausea;
- Pain is observed in the gastric region and on the left side as the organ is stretched;
- Heavy secretion of saliva;
- Heartburn, belching with a sour taste.
Appendicitis
The inflamed appendage of the cecum can radiate to any part of the body. The problem is solved by surgical removal of the organ. Symptoms felt by the patient: pain on the right side, lower abdomen, diarrhea, fever.
Then nausea, vomiting and pain appear at the location of the inflamed appendix. Patients characterize the unpleasant symptoms as bursting, pulling, spreading throughout the entire body and gradually converging to the lower right corner.