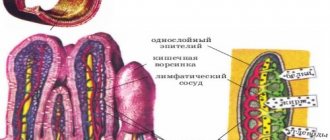
A test for occult blood in stool is prescribed if occult bleeding is suspected. Normally, 1 g of feces of a healthy person contains no more than 2 mg of hemoglobin, that is, less than 2 ml of blood is released with feces during the day. With significant gastrointestinal bleeding, the color of the stool changes.
When the source of bleeding is highly localized (stomach, duodenum, small intestine), they become dark, tarry in color (melena), and when low, blood in the stool is detected visually. If blood is present in the stool, but is not detected either visually or during microscopy, it is called hidden, and bleeding, accordingly, hidden. It can be detected by laboratory methods of analyzing stool for occult blood:
- test with benzidine (Gregersen reaction) or guaiac resin;
- quantitative immunochemical method.
The detection of blood in the stool indicates that the patient has diseases of the stomach or intestines that occur with a violation of the integrity of their mucous membrane.
Causes of gastrointestinal bleeding
The following diseases lead to the development of bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT):
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- polyps, benign and malignant tumors of the gastrointestinal tract;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- diffuse familial polyposis;
- haemorrhoids;
- anal fissures.
Patients suffering from these diseases should be regularly tested for occult blood in the stool.
A special disposable container for collecting stool to determine hidden blood in it can be purchased at a pharmacy
After reaching 50 years of age, each person is recommended to undergo a fecal occult blood test annually; it is included in the algorithm for early diagnosis of malignant intestinal neoplasms, the incidence of which increases significantly at this age. The appearance of a positive test for occult blood in the stool in adults, especially those over 50 years of age, is the basis for further in-depth examination.
Decoding the analysis results
In the absence of any pathologies, a stool blood test will be negative. A positive test result may indicate the presence of various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, characterized by bleeding: gastric ulcer, ulcerative colitis, helminthiasis, intestinal tuberculosis, Crohn's disease, tumors, etc.
When assessing the results of the analysis, the fact that detected bleeding may not always relate to parts of the gastrointestinal tract is taken into account. A positive test result may be the result of nosebleeds, pharyngeal bleeding, periodontal disease, stomatitis, or hemorrhoids. A repeat test may be ordered to confirm the results.
Stool analysis is one of the first stages of studying the patient’s condition and subsequent diagnosis. Bleeding in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract is a symptom of a pathology, which in many cases can significantly threaten the patient’s life. Severe bleeding can be detected visually, but in the early stages of the disease, the presence of blood in the stool can only be determined through analysis.
The essence of the study
In order to understand how the presence of occult blood is determined during a stool examination, you need to know what this analysis is. It is based on the Gregersen method, during which the change in the level of hemoglobin formed during the destruction of blood cells in the lower intestine is determined. A reagent is added to the sample, which helps detect the presence of hemoglobin.
The analysis has a significant drawback - the hypersensitivity of the research method. The reagent tends to react to the presence of even the slightest amount of hemoglobin, including that contained in the meat of the animal consumed by the patient the day before. Therefore, preparing for a stool occult blood test is a separate process.
Preparing for analysis
Before prescribing a patient for a study, the doctor must instruct the patient. Before submitting stool for analysis, it is forbidden to use supplements that help increase hemoglobin levels for a week. This ban also applies to the following products:
- meat;
- chicken;
- fish;
- offal;
- apples;
- spinach;
- white beans.
Eating these products will interfere with obtaining a true research result.
Another important condition that must be met before the analysis is the absence of invasive examinations of the gastrointestinal tract two days before the test. Therefore, it is forbidden to do enemas, fibrogastroscopy and irrigoscopy, which can negatively affect the mucous membrane, causing the test results to be incorrect
In this case, it is necessary to refrain from the usual morning and evening procedure - brushing your teeth, as this can cause gum bleeding.
False result
It happens that the patient regularly followed all the doctor’s recommendations, but a stool test for occult blood gave a positive result, which was not later confirmed. This is because there are several factors that negatively affect the test. First of all, it is worth noting the bleeding of the gums, which the patient himself may not notice, because very little blood is required to disturb the authenticity of the result.
A reason that is not accidental, but is considered more serious, is periodic bleeding. If it is not constant, but occurs from time to time, then there is a risk that during the repeated donation of stool for blood, it will stop and, if pathology is present, the analysis will give a negative result.
Factors that interfere with a true result are observed extremely rarely, but nevertheless specialists have learned to protect themselves from them by repeatedly collecting stool for occult blood. Thus, the patient prepares for the test within a week, but after completing the test, he still complies with the recommendations, since a repeat test is carried out after two to four days. Because of this, we can conclude that given the existing risks, stool testing for occult blood is still a reliable diagnostic method that can be trusted.
Benzidine test
The benzidine test (Gregersen-Adler reaction) is a chemical reaction used to detect blood impurities in biological material (urine, gastric juice, feces). In the presence of blood, after adding the reagent, the color of the test material becomes bright green or blue.
This analysis requires patient preparation, since it is possible to obtain a false positive result due to hemoglobin contained in meat foods, some vitamins and other substances.
To exclude a false positive result, you must follow a diet. 72 hours before the study, exclude foods of animal origin (fish, poultry, meat) and some vegetables (tomatoes, zucchini, herbs, green apples, horseradish, cucumbers, cauliflower, broccoli) from the diet.
In an infant, the cause of a false positive result may be cracked nipples in the mother. During feeding, these cracks bleed, and children swallow the released blood along with breast milk.
Diet during preparation for the study:
- dairy products (ryazhenka, kefir, cheese, feta cheese, cottage cheese, milk);
- porridge (oatmeal, rice, millet);
- vegetables (potatoes, carrots, white cabbage);
- fruits;
- weak tea, still mineral water;
- sweets and confectionery.
Important Nutrition Principles
First of all, the results of this analysis will depend on nutrition. If your doctor has prescribed a test such as a stool test for occult blood, the diet must be followed. Let's consider the basic principles of nutrition that must be followed before the procedure:
- Eliminate foods containing large amounts of protein from your diet. This includes legumes, eggs, as well as meat or fish.
- Eat in small portions; you should not feel even the slightest heaviness in your stomach.
- Be sure to include dairy products in your diet, as well as boiled potatoes and cereals.
- Completely avoid sugary drinks, coffee and tea. If desired, you can replace them with compote or juice. But still, doctors recommend giving preference to purified still water several days before the procedure.
The diet when testing stool for occult blood should consist only of light foods. Therefore, cook food by steaming or boiling. Avoid frying with oil completely. After all, the maximum number of calories you can consume per day should not exceed 2,200. You need to eat in small portions, but often. According to experts, the diet when donating stool for occult blood allows you to get the most accurate results from this procedure.
Immunochemical analysis of feces for occult blood
Old methods for determining hidden blood in feces, including the benzidine test, react not only to human hemoglobin, but also to animal hemoglobin contained in meat products, so it is not always possible to accurately determine whether a positive result shows hidden bleeding or errors nutrition.
The immunochemical method does not have this drawback and reacts specifically to human blood. This means that it does not require the patient to follow a special diet.
Types of analysis
Testing for occult blood in stool is carried out in three ways.
| Type of analysis | What it reveals, how it is carried out |
| Gregersen method (reaction), reaction with benzidine | This test is prescribed to detect bleeding in the upper and lower digestive tract. The reaction occurs both to human hemoglobin and to foreign hemoglobin (contained in meat). Therefore, before the analysis, it is recommended to follow a strict diet with a complete exclusion of meat products from the diet. |
| Immunochemical analysis | This study gives a more accurate result. Diagnostics, as a rule, is prescribed for suspected development of pathologies of infectious origin in the lower parts of the digestive tract - intestines (this test cannot detect bleeding in the stomach and esophagus) and colon cancer. The sensitivity of the test is so high that it can detect even 0.05 mg of hemoglobin per 1 mg of feces. The only drawback of the study is its length. The result is announced only after 14 days |
| Guaiac test (Weber test) | When carrying out this diagnosis, particles of the patient's excrement are placed on special filter paper. Guaiac, acetic acid and hydrogen peroxide are then applied to them. This method is still carried out in many laboratories and gives many false reactions. Today there are tests in which guaiac is pre-applied to a strip of plastic. This allows you to detect even the smallest amount of blood in the stool. |
Only a doctor should determine what type of research should be performed, depending on the specific case.
The reaction with benzidine is used quite rarely in modern medicine. This type of study can detect only 15 ml of blood in excrement. In addition, this diagnosis is characterized by multiple false results.
Rules for collecting material for occult blood analysis
Three days before the test, you should stop taking iron and bismuth supplements, and the day before - vitamin C (ascorbic acid) and Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid).
72 hours before the study, it is necessary to exclude any diagnostic or therapeutic manipulations affecting the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, i.e., colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, or X-ray contrast examination of the digestive tract should not be performed.
The day before taking a stool occult blood test, the patient is not recommended to brush his teeth, since a brush, especially with hard bristles, can injure the gums, causing them to bleed.
Feces for examination should be collected only after spontaneous bowel movements. It is unacceptable to take laxatives or perform an enema before the study, as this will distort the result.
With a high localization of the source of bleeding, the stool becomes dark, tarry in color, and with a low localization, blood in the stool is detected visually.
It is necessary to take measures to ensure that urine or vaginal discharge does not get into the material; to do this, before defecation, you should urinate, and then wash and dry the perineum with a towel. During bowel movements, you should not strain excessively.
Immediately after defecation, material is collected from 3-4 sections of feces and placed in a disposable container with a lid and a spatula, which is obtained in advance in the laboratory or purchased at the pharmacy. 1/3 of the container is enough for research. The collected material must be delivered to the laboratory as quickly as possible.
The process of examining stool for the presence of blood
The study is carried out using the Gregersen method (sometimes also called the benzidine test). The point of the analysis is that a stool sample is examined in a laboratory for the presence of hemoglobin.
As red blood cells pass through the lower intestines, they are destroyed and the structure of hemoglobin changes. If hemoglobin is present in the stool sample, a special chemical reagent will determine its presence.
The benzidine test for fecal occult blood is very sensitive. This is its advantage and at the same time its disadvantage. The reaction occurs even if a small amount of hemoglobin is present in the sample, which may be caused by meat consumed the day before the test. Therefore, you need to prepare before submitting a stool sample for research and follow all the rules.
Preparing for a stool test
Everyone, without exception, including people with low hemoglobin levels, with anemia, a week before taking a stool test, should avoid taking medications that contain iron and other supplements that help increase hemoglobin levels. It is also unacceptable to take medications that contain bismuth. Laxatives are also contraindicated.
3-4 days before the test, you need to start following a special diet, which involves excluding meat products, fish, beans, spinach, apples and other foods that contain iron and increase hemoglobin levels.
48 hours before the test, it is not allowed to conduct studies of the gastrointestinal tract, such as irrugoscopy, fibrogastroscopy, enemas, etc. All these procedures can disrupt the integrity of the mucous membrane and cause a false result.
The day before the analysis is collected, it is forbidden to brush your teeth and eat hard (solid) food. Bleeding gums can also cause incorrect results.
Decoding the research results
A stool test for the presence of occult blood may be false. This often happens if the process of preparing for its delivery was disrupted. Damage to the gums or bleeding from the nose can allow blood to enter the gastrointestinal tract and cause a positive result.
There is a possibility of getting a false negative result. If the bleeding is intermittent and occurs for a short period of time and then goes away, the test will not detect the presence of blood in the stool sample.
To avoid a misdiagnosis, it is recommended to re-test your stool to check for blood. It is recommended to conduct it 5 days after the first study. As statistics show, if a repeated stool analysis gives the same result as the first time, then it can be considered correct.
If a positive result was obtained and it was confirmed by a repeated benzidine test, this means that you need to undergo a set of additional examinations, which are prescribed by the doctor individually for each patient. Their goal is to identify the true causes of blood in the digestive organs. Based on them, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes an appropriate course of treatment.
A positive test result cannot be ignored. There are many causes of gastrointestinal bleeding: it could be an ulcer, a severe inflammatory process or cancer. The main thing is to remember that any treatment will be much more effective if it is started as early as possible.
Doctors' advice
It would be a grave mistake to think that diet is not that important when testing for occult blood in the stool. According to experts, it is a mandatory stage of preparation before conducting an analysis. Doctors advise adhering to it strictly, because the correctness of further treatment will depend on it. Do not under any circumstances consume prohibited foods, and do not overeat. Eat small meals five to six times a day. You shouldn't feel overfull, but you shouldn't feel hungry either.
It is very important to avoid certain medications as they may affect test results. Be sure to tell your doctor about the medications you take. You can refuse them only if a specialist gives the go-ahead. Also, avoid serious sports activities. It is best to replace it with walks in the fresh air.
Why eat right before the test?
Please note that specialists pay great attention to preparing for this procedure for a reason. After all, the test results will depend on this, so follow all the requirements that your doctor tells you about. Failure to comply with these requirements may result in particles of hemoglobin getting into the stool, and this will spoil the entire picture of the analysis, after which it will have to be done again.
If your doctor has prescribed you to undergo such a procedure, this means that you have serious indications for this, so under no circumstances ignore your diet when testing stool for occult blood.
If you follow the nutritional principles before conducting the study, you will not only get the right results, but also cleanse your body of harmful substances, improve digestion, and even lose a little weight.
How to test your stool yourself
If a person constantly experiences discomfort and pain in the abdominal area, but does not have the opportunity to quickly seek help from a medical facility, conducting a primary diagnostic study is possible at home. For this, special test strips are used.
You can purchase a rapid test at any pharmacy. The sample is collected in compliance with all recommendations.
Next, a small amount of stool is placed in a container with an applicator. The reagent is applied to the sample. When two stripes appear, the result is interpreted as positive, which requires an immediate visit to a specialist.
Examination of feces for occult blood plays an important role in determining internal bleeding. In some cases, the presence of hemoglobin is enough to understand that pathology is developing in the intestines.
In order to detect violations in a timely manner and take the necessary measures, it is necessary to undergo this study at least once a year as a preventative measure.
How long should you follow a special diet?
Not all patients understand what the nutritional system should be like. And also how long it must be observed before donating stool for occult blood. Nutrition needs to be adjusted several days before the test. Typically, doctors advise their patients to follow a dietary regimen from three days to a week, depending on the individual characteristics of each patient’s body. After you have passed the test, return to your previous eating regimen. However, nutritionists recommend not to do this quickly. Gradually add familiar foods to your diet. This way your body will experience minimal stress.
When is it necessary to get tested?
A screening test for blood in stool is carried out for the following indications:
- dyspeptic disorders of unknown etiology (frequent nausea, heartburn, flatulence, stool instability);
- regular pain in the abdominal area without a clear cause;
- anemia of unknown origin in a clinical blood test;
- rapid weight loss;
- loss of appetite;
- discomfort and pain during bowel movements;
- intoxication syndrome of unknown etiology (unmotivated rises in temperature, chronic fatigue syndrome due to decreased appetite, weight loss);
- age after 40 years;
- family history of cancer or autoimmune intestinal pathology.
Be sure to read:
How to take a stool test for intestinal microflora?
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- How to check the intestines for oncology?
- Details about bowel cancer: stages, symptoms, treatment and prognosis
- Stool analysis for calprotectin: what does it show and how to take it?
- How to take a stool test for Giardia?
- Rectal cancer: symptoms, stages, treatment and prognosis for life
- Bacteriological culture (tank culture) of feces: essence, preparation and analysis
- Analysis of stool for disgroup: essence, preparation and delivery of analysis
- Preparing and submitting a stool test for dysbacteriosis in infants
- Details about the coprogram: preparation, conduct and interpretation of the analysis
- Preparation and testing for food intolerance
Dairy based diet
Doctors say that a preparatory nutrition system will make sense if you make dairy products the basis of your diet. This way you won't have to test your stool again for occult blood. Before the diet, of course, you need to set yourself up. The diet itself is based on the use of large amounts of low-fat dairy products. This includes cottage cheese, kefir and milk. However, vegetables and fruits should still be present in small quantities on the menu.
You can prepare porridge based on milk, and make casseroles from cottage cheese. In this case, it is allowed to add small amounts of sugar or honey to them. Of course, in addition to milk, you can drink water, various compotes and jelly.
How to take the test correctly
To obtain a reliable result, you must adhere to the delivery algorithm. It consists of the correct collection of material and preparation for analysis.
Preparing for the test
Before taking the test, it is necessary to warn the patient about a false positive result if the recommendations are ignored. For reliability, you must adhere to the preparation rules:
- follow dietary recommendations;
- brush your teeth carefully to prevent blood from gingivitis from entering the gastrointestinal tract;
- do not take the test during menstruation;
- avoid taking medications;
- feces should be obtained only in a natural way; the use of auxiliary means is unacceptable.
So, you can't:
- 3 days before the study, eat fish and meat dishes, seafood, foods containing iron (broccoli, apples, asparagus and others);
- a week before the study, exclude any laxatives: suppositories, micro- and regular enemas, oral laxatives;
- 3 days in advance, stop taking medications containing iron (for example, vitamin preparations), as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aspirin, ibuprofen, paracetamol).
Be sure to read: How to test stool for pathology at home?
Preparing containers
The material must be collected in sterile containers.
It can be purchased at every pharmacy. A container for collecting feces consists of a container that is tightly screwed on with a lid, and a spatula for collecting material. The container is sterile, so after opening it is necessary to immediately collect the material and screw the lid tightly. A more budget-friendly option is to use food jars. It is preferable to use glass or plastic containers, which must first be boiled. Metal, especially iron, boxes are unacceptable, as a false result is possible.
Collection of material
- The container from which feces are collected must be clean, without additional impurities such as water, secretions, or urine. Also, it should not be metal. It is recommended to purchase a plastic pot, which needs to be boiled before testing. Taking material from the toilet is prohibited!
- It is advisable to collect morning feces from a sterile pot using a clean spatula.
- Sampling is carried out from different departments, several factions.
- About 2/3 of the volume is filled into the container (this is about half a teaspoon).
- Close the lid tightly.
How and for how long can the material be stored?
Store the material at a temperature of +4-+8 - this is the temperature of the refrigerator compartment. The shelf life of stool is up to 12 hours.
If the ambient temperature is higher, then the material must be delivered to the laboratory within two hours. Otherwise, the result will be unreliable.
Read on topic: Basic stool parameters for self-assessment