Cramping pain in the abdominal area is the most common phenomenon that a person experiences. They are associated not only with minor problems in the digestive system, but also with diseases that require close attention.
The discomfort that appears in the internal organs indicates a disruption in their functioning. The causes are judged by the location of painful symptoms. Determined by the doctor. There are two main causes of discomfort: physiological causes and diagnosed diseases.
Physiological cause of pain
The cause of such pain is infection, bacteria, parasites or selected diseases. More often associated with the nervous system and other body functions.
Neuralgic disorders
Stomach pain that is spasmodic in nature can appear in emotionally unstable people who are subject to frequent stress and are in a state of nervous tension. Lack of proper rest, poor diet, snacks on the run, and dry food are considered by doctors as the main causes of functional disorders, expressed by contractions in the stomach.
Allergic reactions
A possible situation: if the patient has a weak immune system, the body tries to digest inappropriate foods or there is a lack of necessary enzymes, indigestion and acute pain develop. The symptoms are accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting.
Intoxication
Often occurs with abuse of alcoholic beverages or medications. In case of intoxication of the body, the necessary medical care is: gastric lavage and administration of a drug to destroy toxic substances and remove them from the body. Otherwise, death cannot be ruled out.
Food poisoning also happens. Symptoms: vomiting and diarrhea. As a rule, the consumption of low-quality products leads to intoxication of the body.
Abdominal injuries
Getting hit in the stomach or falling on your stomach should not be ignored. The subsequent tension in the abdominal region and gripping pain can cause rupture of organ walls and internal hemorrhages. Hospitalization followed by surgery will be required.
A common feature that unites all physiological disorders is that trouble disappears when there is no external factor. The necessary measures are taken and body functions are restored.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
The patient complains that his stomach hurts, but no problems were found in the digestive system. This may be a symptom of an abdominal aortic aneurysm or another disease related to the blood vessels.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
The vessel increases in size and threatens to rupture, followed by severe bleeding into the abdominal cavity. The patient feels a nagging, dull pain that occurs intermittently. A symptom that immediately indicates the source of pain is a noticeable pulsating area in the peritoneum.
Thrombosis of intestinal vessels
In the blood vessels supplying the intestines, one or more blood clots form, which are located across the movement and block the flow of fluid. As a result, oxygen starvation and necrosis of organ tissue occurs. The disease most often affects older people, but both men and women are affected. The causes of blood clots in blood vessels are found in diseases of the human cardiovascular system. There are sensations of pain radiating to the middle of the abdomen and ribs.
Embolism
Blockage of blood vessels by a particle - embolus. It could be air, part of the fat, or a broken blood clot. Typically, emboli enter the bloodstream:
- As a result of a mechanical disorder (impact, fracture, injury).
- Heart surgery can also be a source of particles.
- Incorrect administration of medication. The drug, intended for intramuscular administration, is injected into a vein, and oil forms are formed.
- Varicose veins, atherosclerosis.
- A perforating wound can carry pieces of bone fragments from the rib into the bloodstream.
Abdominal pain reflects peripheral arterial embolism. Pallor of the skin, cold hands and feet are also observed.
Abdominal myocardial infarction
The symptoms are similar to gastritis. The patient feels abdominal pain, nausea, and the urge to defecate. If other vascular diseases cause them to dilate, then with an abdominal infarction the blood artery narrows. Symptoms of the disease:
- Vomit;
- Nausea;
- It begins to hurt severely, sharply, and burns;
- Bloating, flatulence;
- Heart rhythm disturbances;
- A sharp decrease in blood pressure.
Medical statistics note that the main causes of cardiovascular diseases can be stress, heredity, blood pressure disorders, and injuries.
Diseases
Unfortunately, when an infection or disease occurs in an internal organ, there is no external factor. Normal functioning is not possible.
Ascariasis
Parasites called helminths accumulate inside the human body. The main symptom appears at night. Increased gas production, vomiting, lack of bowel movements, thirst, gripping pain - this is helminthiasis.
Gastritis
It manifests itself as cramping pain in the stomach area and under it. The mucous membrane of the organ becomes inflamed and is accompanied by heartburn, belching with a sour taste, and nausea. The disease has wave-like spasms with periods of exacerbation and remission. Exacerbations occur in spring and autumn. The causative agent of gastritis is considered to be the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. A possible cause of the disease is an excited psychological state.
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix of the colon. Accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, headaches, weakness. The body temperature gradually rises, but not higher than 38. If the operation is not performed on time, peritonitis begins.
Volvulus
It is considered a hereditary disease. If a person is engaged in hard physical work or active sports, and eats mainly while running, there is still a possibility of pain in the lower abdomen, accumulation of gases, and bloating. Also, feces accumulate inside the intestines, which the organ is not able to move for natural emptying.
Medical statistics indicate that 25% of patients die from volvulus due to ignoring symptoms and not seeking help from a doctor.
Hernia
A protrusion appears on the patient’s body, accompanied by pain and lethargy. This indicates a hernia - prolapse of part of the intestine through a weak intestinal wall. As a rule, this is observed in the navel area or at the site of surgery. In such cases, surgery is rarely done without surgery.
Peptic ulcer
Appears when there is a disturbance in the gastric mucosa. Subsequently, non-healing wounds - ulcers - are formed. Cramping pain appears when eating food and stops after digestion.
Stomach ulcer
The intensity of the pain syndrome depends on the degree of destruction of the mucosa. The provocateur of this phenomenon, like gastritis, is Helicobacter pylori infection or excessive nervous tension, forcing the stomach to eat its own walls.
Renal colic
Cramping pain localized in the lower abdomen is a symptom of a disease such as renal colic. There are a number of reasons for the appearance of spasms: urolithiasis, inflammation and oncology.
With urolithiasis, a spasm appears when a stone, descending through the ducts into the ureter, blocks the lumen.
During the inflammatory process, a blood clot, pus, or a piece of dead tissue enters the lumen.
The cancerous tumor, disintegrating, passes through the ureteral canal and clogs the lumen, which causes a sharp cramp-like spasm.
Acute pain
Sharp pain that a person cannot tolerate can occur in the following cases:
- Angina pectoris, with a prolonged attack. This condition may be a signal of a strong coronary spasm, activation of the thromboembolism process. Such a protracted attack cannot be relieved with the help of drugs from the nitrate group.
- Heart attack. In this case, there is a cutting pain in the region of the heart, which indicates necrosis of myocardial tissue. The pain is pronounced, protracted, and accompanied by severe anxiety and fear of death.
- Cardiac aneurysm, namely aortic aneurysm. With the development of this pathology, pain is sudden, tearing in nature, which occurs behind the sternum and spreads to the scapula.
- Pulmonary embolism. This is another reason why cutting pain occurs in the heart area. Its intensity depends on the size of the vessel affected.
- Fracture of the rib bones. With this injury, the pain is acute, but over time it becomes aching.
- Stomach diseases. A condition accompanied by severe pain is perforation of a cardiac ulcer. Patients characterize this condition as if a dagger is stabbing into the heart.
- Spontaneous pneumothorax is another condition that causes sharp cutting pain in the heart area. With this pathology, air begins to enter the pleural cavity. This condition is also accompanied by tachycardia, shortness of breath, pallor, and acute pain in the chest.
Childhood pains
If a child, for no apparent reason, begins to draw his legs to his chest, is capricious, has sleep disturbances, and is restless, this indicates intussusception. This disease occurs in children between 6 and 12 months of age. Intussusception is a process that occurs inside the intestine when one part of it penetrates into another part and the conductive channel becomes blocked. The child develops a fever and vomits.
Symptoms appear abruptly and disappear abruptly, then the child calms down, eats, and plays. The pain syndrome differs in frequency: the greater the pathology, the more intense the pain and the more frequent and longer the attacks.
Doctors attribute the onset of the disease to improper introduction of complementary foods containing fruits and vegetables.
What to do if you have stomach pain
Severe pain in the abdomen does not always threaten the patient’s life. However, in order to avoid complications caused by possible pathology, it is recommended to urgently consult a doctor. More details about what to do if your stomach hurts can be found in the article on the topic.
If the painful sensations are not intense and are not accompanied by concomitant symptoms, and the patient is feeling stable, you can contact more specialized specialists, including:
- therapist;
- gastroenterologist;
- surgeon;
- urologist;
- traumatologist.
When contacting a specialist, it is necessary to talk about the nature of the painful sensations and their exact location. The pain syndrome can be acute or gradually increasing in nature, reminiscent of a dagger strike or reminiscent of cramping pain. Pain in the abdomen may be accompanied by a rise in body temperature, vomiting, flatulence and bowel dysfunction.
All symptoms play an important role in making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment. If the pain in the middle of the abdomen suddenly stops or becomes less intense, it is necessary to determine the exact cause of the condition.
After the doctor listens to the patient's complaints, the patient will be examined and palpated in the abdominal cavity. The patient may be prescribed the following additional studies:
- clinical blood test;
- blood chemistry;
- radiography with contrast to detect intestinal obstruction, intestinal ulcers and perforation, inflammation of the peritoneum, cancer, abscess;
- angiography to determine vascular diseases, including aortic aneurysm, thrombosis, internal bleeding in case of abdominal trauma;
- computed tomography, necessary for the diagnosis of aneurysm, inflammatory and oncological pathologies of the abdominal organs, intestinal obstruction and other diseases;
- ultrasound examination, which is necessary to detect tumors, cysts, formed hematomas, inflammation of the pancreas, peritonitis and other diseases of the digestive system;
- blood tests, defecation products, biopsy materials for the presence of viruses, parasites and intestinal pathogens in the body.
Only guided by the results of the examination of the patient and his tests, the doctor will be able to prescribe appropriate treatment and relieve the patient of the illness that provoked the pain syndrome.
Among women
Women experience cramping pain in the lower abdomen and are associated with problems in the genital organs: the ureter is blocked by a stone or a ball of roundworms does not pass through the intestines. But mainly the pain is associated with a suddenly interrupted pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy, or myomatous node.
Miscarriage
If during pregnancy a woman experiences pain of a cramping nature, what is happening indicates a miscarriage. Before this, there is a nagging pain radiating to the sacrum and bleeding. The increasing intensity of symptoms is the peeling of the fertilized egg. Urgent hospitalization is required. If the patient seeks help in time, it is possible to continue the pregnancy.
A miscarriage is dangerous for a woman due to heavy bleeding. After spontaneous termination of pregnancy, it is necessary to remove the remains of the fertilized egg so as not to provoke blood poisoning and the occurrence of inflammatory and purulent processes.
Hospitalization is necessary to save the patient’s health and life.
Ectopic pregnancy
Inconsistent, recurring pain in the lower abdomen in women may indicate an ectopic pregnancy. This occurs when the fertilized egg, for some reason, does not reach the uterus, but attaches to the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube.
Complicated pregnancy
In the latter case, normal fetal development is impossible. A woman may have a pipe rupture. The situation requires immediate surgical intervention; there is a fight for the patient’s life.
The tube may not rupture, but the fertilized egg continues to be expelled from the body. This process can take not one day, but weeks. The muscles of the fallopian tube contract, causing it to peel off and move toward the exit of the ectopic miscarriage. The process is felt as cramping pain and blood discharge appears from the vagina.
Tubal abortion is dangerous due to the unpredictability of the situation. At any moment, the wall of the fallopian tube can burst. Internal bleeding accompanying the disease can lead to massive blood loss.
What to take if there is pain in the heart area?
Sometimes a person, for some reason, cannot seek medical help, then it is necessary to take pre-medical measures himself. There are some rules and recommendations about this.
If you have angina pectoris, a person should also take Nitroglycerin before the doctors arrive. Hospitalization is required, as the disease can lead to myocardial infarction.
What to do if a symptom arises from problems with the gastrointestinal tract? Often, pain in the heart area occurs after eating, especially if it is fatty, spicy foods. Characteristic features of this pain: bursting, burning, more felt in the epigastric region. Burning pain in the heart area is most often recorded. Another important feature is that along with this pain there should be no shortness of breath, general weakness and increased sweating. In this case, drugs such as Rennie, Gestal, and Almagel will be effective. You also need to drink medicinal alkaline water.
For pain in the chest, which has a clear localization, and its intensity increases if a person changes body position, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be taken. These are Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide. Analgesics may also be effective in this case.
If pain in the heart occurs as a result of psycho-emotional stress, then it can be removed with the help of sedatives. Valerian, peony, motherwort, and Corvalol will help.
For pain that occurs at elevated body temperature, antipyretic drugs will be effective. They also affect the rheological properties of the blood and are painkillers. Such medications may be Paracetamol, Aspirin.
Treatment
The method of fighting is different for different diseases. The only thing that remains unchanged is the method of providing first aid, on which saving a life sometimes depends.
First aid
First of all, it is necessary to provide peace to a person suffering from cramping pain. Lie in a position that is comfortable for him: on his side or back. If possible, find out the cause of the discomfort. Severe pain can be relieved with antispasmodics: No-spa, Drotaverine.
If the patient has lost consciousness, it is necessary to prevent vomit from entering the throat and block breathing. To do this, the person lies on his side. If the pulse and heartbeat have disappeared, it is time to perform artificial ventilation and chest compressions. Wait for the ambulance to arrive.
Medications
No-shpa and Drotaverine are prescribed to relieve spasmodic pain.
If the symptoms are caused by obstruction or weak peristalsis of the digestive organs, then drugs are prescribed that help normalize motor function and enzyme production: Ranitidine, Omeprazole.
Folk remedies
Treatment and prevention of abdominal pain is carried out using complex measures: homeopathy, herbal medicine and reflexology.
- Mint tea. Mint is a natural sedative. It has a gentle effect on the human nervous system. Prepare as follows: pour three teaspoons into a glass of hot water. After half an hour, the product is ready for use. Drink diluted with water.
- Infusion of chamomile and immortelle. Helps relax the stomach muscles, relieves inflammation. 2 tbsp. l. the mixture of herbs is poured with a glass of boiling water and infused for 30 minutes. Take before meals three times a day. The course of treatment is 21 days.
- Motherwort juice. To quickly relieve pain, buy motherwort juice at a natural pharmacy. Dilute a teaspoon of liquid in a quarter glass of water and drink. Take the product warm.
Pathologies of the cardiovascular system (CVS)
Pain in the upper abdomen in the middle can be interpreted as a symptom of developing diseases of the chest organs. For example, pain in the epigastrium or, as they say, in the pit of the stomach can be a sign of myocardial infarction, and pain under the ribs on the right side can be a symptom of right-sided pneumonia. Causes of abdominal pain in the rib area include acute and chronic forms of hepatitis, chronic cholecystitis, pancreatitis, acute pneumonia or acute myocardial infarction.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system, which cause pain in the middle of the abdominal cavity, are among the most life-threatening for the patient. This could be, for example, an abdominal aortic aneurysm. This condition is dangerous due to the rupture of the vessel, which will cause severe bleeding into the abdominal cavity. In this case, the patient feels a strong pulsation of the abdominal tissues.
Treatment of intestinal pathologies
Symptoms characteristic of various intestinal pathologies (relevant for both adults and children):
- sharp or dull pain localized in the lower abdomen (can radiate to the first third of the abdominal region);
- nausea, sometimes vomiting, which usually does not bring relief;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- elevated temperature (in the presence of inflammatory processes);
- apathy, refusal to eat, drowsiness, etc.
It is important to understand that such symptoms can indicate both the presence of mild dysbiosis and the presence of more serious pathologies (including intestinal cancer).
Of course, severe diseases have more “impressive” and vivid symptoms, but this is how they begin.
Video:
In order to identify the pathology in time and begin its adequate treatment, you should visit a doctor and under no circumstances begin independent treatment, hoping that the symptoms affecting the quality of life will go away on their own.
As mentioned above, proper treatment of any intestinal pathology involves taking special medications with a different spectrum of action, as well as following a diet that normalizes metabolism in the human body.
This diet implies constant control over nutrition and an almost complete rejection of foods that cause bloating and pain caused by difficulty digesting “heavy” foods.
When should you start following such a diet? Immediately after the disease causing the appearance of unpleasant symptoms is identified.
As part of a therapeutic diet, you should avoid foods rich in complex carbohydrates, which are found in abundance in sugar and sweets, as well as carbonated drinks.
In addition, you need to significantly reduce the consumption of flour, fried and fatty foods, and add foods such as vegetables, fruits and cereals to your diet.
You need to stick to the diet until all the symptoms of the pathological process localized in the body disappear, as well as for some time after complete recovery.
Treatment of pathologies that cause discomfort in the stomach and intestines, in the vast majority of cases, involves taking enzymatic preparations.
The most popular products enriched with these “digestive” components are “Festal”, “Mezim”, “Motilium”, etc.
Treatment for dysbacteriosis also includes special drugs, such as Florin Forte, Linex, Actobacterin, Biobakton, Acylact, etc.
It is worth noting that many of the drugs mentioned in this article can be used not only when the feeling of discomfort in the intestines becomes significant, but also when you simply want to normalize the functioning of your body.
Video: why it hurts in the lower abdomen
Intestinal pain is any pain or discomfort that occurs in the area of this organ.
It is often difficult to isolate pain in a specific internal organ, especially in the abdominal organs, since it has the largest number of them than any other cavity in the human body.
In addition, these organs are in close proximity to each other.
However, the pain, which is located approximately in the abdominal area, is often accompanied by other symptoms that begin within 30 minutes of the onset of pain and can last up to several hours, especially after eating.
The combination of pain with other signs usually indicates problems with this organ.
What is abdominal pain like?
Abdominal pain can occur acutely or worsen over a long period of time. Sometimes it is constant, gradually intensifies, and sometimes it occurs in the form of attacks. Other characteristics worth paying attention to:
- Nature of pain. It can be stabbing, dagger-like (there is a feeling as if a dagger has been stuck into the stomach), burning, dull, aching, and may be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and discomfort in the stomach.
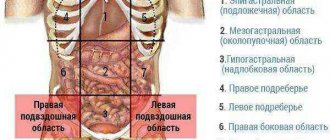
- Localization. Depending on the cause, pain can occur under the rib on the right or left, in the lateral parts of the abdomen, under the sternum (“under the stomach”), below the pubis, in the iliac region, around the navel.
- Provoking factors. Pain may occur or intensify during coughing, after eating fatty foods and alcohol, during stress, or during menstruation.
Factors that lead to improvement
The pain may decrease or go away after taking antacid (reducing the amount of acid in the stomach) medications, changing body position, and following a certain diet.
Associated symptoms
Pain may be accompanied by bloating, belching, heartburn, changes in the frequency, color and consistency of stools, loss of appetite, weight loss and other manifestations.
When contacting a doctor, it is important to describe your sensations and pain characteristics in as much detail as possible. This will help to quickly establish the correct diagnosis.
Therapy and prevention
Medicines such as antacids, simethicone and lactase enzymes help in relieving pain and cramping in the intestines. They can be purchased at any pharmacy.
Prescription medications such as metoclopramide help people with intestinal motility problems. It is necessary to control your diet and diet, limiting the consumption of gas-producing foods.
Simple analgesics or painkillers are often sufficient to treat intestinal or stomach pain.
They are taken until the cause of the pain disappears, for example, in the case of stomach irritation from eating food or drink.
It is necessary to ensure that the analgesics themselves do not irritate the intestines. If the medicine cannot be taken orally, analgesics such as Phenergan can be administered intravenously.
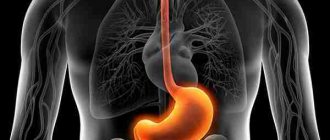
Parietal cells in the stomach create hydrochloric acid to help digest protein in food. The acid is very caustic to denature proteins and begin the digestion process.
Other cells in the stomach create a mucus barrier to protect the intestines itself from acid digestion. When the acid exceeds the protective capacity of the mucus, pain occurs.
Some antacids inhibit the formation of acid. Other antacids neutralize the acid. Once the acid returns to normal levels, the pain usually subsides.
Bacteria such as Helicobacter pylori, Escherichia coli or Clostridium difficile can also cause stomach and abdominal infections.
According to some studies, H pylori causes the protective mucus of the intestines to thin, causing pain from intestinal acids.
Intestinal bacterial infections cause intestinal cramps as the intestines try to flush out the infection.
A variety of broad-spectrum antibiotic medications to treat bacterial infections help relieve pain from these infections.
Sometimes the food consumed is difficult to digest. Food causes bulge in the intestines and stomach. The subsequent spasms are painful. Other conditions, such as gallstones, block the intestinal tract, also causing new cramps.
Muscle relaxants can be used to relax the abdominal muscles and smooth muscles that cause intestinal spasms and stomach pain.
Overall, you can save yourself from all these problems by becoming familiar with the nuances of the digestive system and its functions.
You need to know the strengths and weaknesses of your intestines, its characteristics, know how the intestines or stomach hurt and how often pain is felt at the bottom or top of these organs.
For this purpose, you can consult with a gastroenterologist or nutritionist, who will tell the patient why the intestines hurt, as well as what to do in a given situation.
Diagnostics
Only a clinician can determine the causes of cramping pain in the abdominal area. If such a symptom occurs, you should seek help from a gastroenterologist, because the most often provocateurs are diseases of the digestive system.
Primary diagnosis involves the implementation of a number of manipulations directly by the clinician:
- familiarization with the medical history - to establish the pathological source most characteristic of a person;
- collection and analysis of life history - to confirm the influence of physiological predisposing factors;
- palpation and percussion of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity;
- measuring temperature and pulse, heart rate and blood pressure;
- A detailed interview with the patient will help the doctor to create a complete picture of the course of the pathological condition.
Laboratory diagnostic methods:
- general clinical blood test;
- blood biochemistry;
- coprogram;
- bacterial and immunological tests;
- general urine analysis.
Data from the following instrumental procedures will help accurately diagnose what caused pain in the lower abdomen or other location:
- gastroscopy;
- ultrasonography;
- radiography;
- irrigoscopy;
- colonoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- endoscopic biopsy;
- CT;
- MRI.
Gastroscopy
In addition, the gastroenterologist can refer the patient for consultation with specialists from other fields of medicine:
- endocrinology;
- gynecology;
- neurology;
- oncology;
- pediatrics.