All infants burp after feeding. Belching in newborns is a natural physiological manifestation that does not require treatment. However, it is important for parents to know the limits beyond which physiological belching becomes a pathology. The body of toddlers in the first months of life has not yet formed, it is sensitive and vulnerable. The only source of growth and development is nutrition, and disruptions in the digestive system can cause harm to the newborn. After reading this article, you will know if there is cause for concern.
What is burping
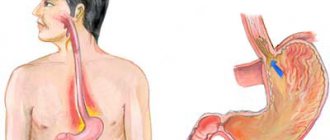
In adults, this is the release of gases from the esophagus accompanied by sound. Sometimes the air traps some food or stomach acid. For gases to escape, the stomach must contract and the esophageal sphincter must open. The cause of belching in adults is excessive gas formation in the stomach. Belching in infants has a similar physiological meaning - freeing the stomach from excess gases, but their nature is different.
During sucking, the infant swallows air, which causes the baby to burp. In infants, the organs of the gastrointestinal tract are still developing and have age-related characteristics: a short esophagus and weak cardiac sphincter muscles. At the slightest pressure on the walls of the stomach, its muscles contract to get rid of the excess and the baby burps.
Belching in infants and its types
In healthy children, the body gets rid of excess food only occasionally. If the problem bothers you frequently or is systematic, then parents need to take action as soon as possible. In particular, rotten belching occurs due to putrefactive processes in the stomach. They can be caused by insufficient gastric juice. Such a problem cannot be identified without additional diagnostics.
In addition, one should distinguish between the following types of belching:
- Sour. Occurs due to tumors and peptic ulcers.
- Gorky. This type is characteristic of cholecystitis, as well as intussusception.
- By air. It only appears in babies if they are not properly latched to the breast or do not eat bottle food well.
Causes of regurgitation
There are always reasons why a newborn burps after feeding. The main one is the entry of air into the stomach during sucking. In breastfed infants, excessive swallowing of air causes improper attachment to the breast. In newborns fed artificial formula, the cause is incorrect position of the bottle.
Secondary causes of regurgitation:
- overfeeding;
- physical activity after meals;
- clothing that puts pressure on the tummy or tight swaddling;
- screaming and crying, which causes excess air to enter the stomach;
- flatulence.
The main cause of belching in babies is swallowing air.
Prevention
The basis for preventing the occurrence of an unpleasant symptom is proper feeding, carried out on time. If the baby does not cry before eating, it means that air ingress will be minimized.
Tummy massage
Before eating, place the baby on his tummy 30 minutes before eating. The action allows the accumulated gases to escape and not provoke bloating. Light stroking without pressure will help. The massage is performed using a warm towel. Dry heat helps the intestinal tract relax and allow air to escape easily through the anus.
Body position
The cause of burping is often due to improper positioning of the body during feeding. To prevent air accumulation, the baby should eat while in a semi-sitting position.
Positive points if the body is positioned correctly:
- The nutrient fluid does not linger in the esophagus and immediately enters the stomach.
- The incoming air does not accumulate at the bottom, but immediately exits upward.
- The air escapes much easier.
- The bottle with artificial formula is positioned vertically in relation to the baby, there is no air in the nipple.
Mixtures
A properly selected mixture will help normal digestion of food. There will be no disturbances or accompanying symptoms. If there is additional food in the diet, the moment of belching is discussed with the doctor.
Amount of food
Belching can occur from overeating. It is worth reducing the amount of food while increasing the frequency of meals. This will allow the stomach to cope with the incoming food and be free to accept the next portion. Absorption will be better, and belching will no longer bother both the baby and the parents.
After meal
Do not rush to put your baby to bed immediately after feeding. Try to hold it slightly in your hands in an upright position so that the accumulated air can move away naturally and not cause discomfort.
Source
Is overfeeding to blame?
In many articles, one of the reasons for burping in infants after eating is overeating, in which more food enters the baby’s stomach than its volume. Breastfeeding experts say that overfeeding occurs exclusively when using artificial formula. Some mothers, in an effort to better feed their newborn, exceed the recommended amount of nutrition. Others make a hole in the nipple that is too large, and the baby’s stomach cannot cope with the strength and speed of the incoming flow.
Overeating is impossible when breastfeeding. The baby independently chooses the time and amount of milk consumed. Feeding with breast milk is a natural physiological process that is regulated by nature. There is no need to interfere with it, set a diet and limit the time of sucking.
How to prevent spitting up milk
Although belching in a newborn is a natural physiological process, parents have the power to control the amount of milk regurgitated. After eating, you cannot immediately put the baby in the crib - you need to hold him in a “column” for 10 minutes, pressing his tummy to you. This is necessary so that the air plug comes out of the stomach. When the body is in an upright position, little milk or formula comes out with it. After each meal, the baby must wait for the burp of air. This will avoid a large volume of regurgitated milk.
Never place your newborn on his back after eating. In this position, he may choke on regurgitated milk and suffocate.
Sometimes a newborn does not burp after eating because he does not always swallow a lot of air. If the mother follows the feeding technique and the baby is calm, he does not swallow air and there is no regurgitation. Hold the newborn upright, watch him, if nothing bothers him, then parents don’t need to think about how to induce a burp.
Try to place your baby's tummy on a hard surface before each meal. This will help the gases escape before he eats.
Basic techniques to prevent regurgitation:
- compliance with feeding techniques;
- vertical position of the newborn after eating;
- placing on tummy before feeding.
Putting these simple rules into practice will help reduce the amount of milk belched in newborns.
What to do if a child chokes on a burp
It often happens that a woman produces a lot of milk right in the process of feeding her child, so the child burps and choke.
In order to avoid this phenomenon, experts advise the mother to take an almost supine position and place the baby on her chest. It is not advisable to tilt too much!
In the case when the baby choked, the mother should turn him with his back to her, put her hand on the baby’s tummy, tilt the child forward and gently pat him on the back.
Such actions help the baby spit out the milk and bring his breathing back to normal.
Consultations with a pediatrician should not be ignored when a child often hiccups and exhibits symptoms of improper digestion.
Feeding technique
Following feeding techniques allows you to minimize the amount of air the baby swallows. When the air plug is small, it comes out easily and painlessly, without causing excessive regurgitation of milk. During feeding, the newborn's head should be positioned above the stomach. In this position, it is easier for the baby to make sucking movements, he strains less, milk enters the stomach faster and less air is swallowed.
You should not start feeding when your newborn is crying a lot. In this state, he will swallow air and burp profusely. Try to calm him down, hold him close to you with your tummy and stroke his back. Also try not to delay the meal time - when the baby is very hungry, he sucks greedily, avidly, swallowing more air.
If the mother of a newborn is breastfeeding, proper attachment to the breast will ensure a small burp after feeding. The baby should grasp part of the areola with his lips along with the nipple - such a tight fit will block the access of air.
When bottle-feeding, the mother must monitor the position of the body and the bottle. The newborn's head should be raised, the bottle should be held at an angle with the bottom up, and the nipple should be completely filled with mixture. In this way, you can reduce the amount of air you swallow and reduce the amount of regurgitated mixture.
Basic techniques for proper feeding technique:
- calm state of the baby;
- elevated position of the newborn's head;
- tightly grasping the mother's nipple with the lips;
- lack of air in the nipple.
Follow the correct feeding technique to prevent excessive regurgitation.
Physiological norms of belching
Belching that occurs in newborns after feeding is not a disease and does not require treatment if it meets physiological standards:
- Frequency: after each feeding.
- Volume – up to 2 tablespoons.
- White color.
- The smell is of fresh milk or formula.
If the newborn feels well, does not cry, and is gaining weight, then parents have no reason to worry. As the baby grows and the gastrointestinal tract matures, the frequency of regurgitation will decrease. As a rule, by 7-8 months, children stop burping.
Physiological belching is not a disease and does not require treatment.
When should your baby be shown to a doctor?
There are certain reasons why young mothers should understand that the baby needs to be examined. These include weight loss, severe irritability, tearfulness, problems with sleep and eating, and excessive regurgitation.
In the case when the belching after eating becomes yellow and has an unpleasant aroma, one can suspect the presence of some pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract in newborns.
For example, these:
- Pyloric stenosis is a congenital pathology characterized by a narrowed area of the stomach. This can lead to the baby spitting up a lot, hiccupping and not gaining weight.
- Hiatal hernia.
- Dysfunction of the central nervous system, manifested due to difficult childbirth, difficult pregnancy or congenital defects. The baby cries a lot and sweats a lot. He has colic in the intestines, belching and bloating.
- Infectious pathologies. For example, meningitis, characterized by an inflammatory process in the brain, or hepatitis.
- Heredity.
- Kidney pathologies are common causes of belching and digestive disorders.
- Food poisoning also causes belching with an unpleasant odor and a yellow color. In addition, there may be blood inclusions in the mass.
In any case, parents should not self-medicate, because belching after eating may indicate serious health problems for the baby. It’s better to play it safe several times and consult a doctor.
Signs of abnormal regurgitation
If parents think that the baby is regurgitating a lot of milk, they can do a comparative test. To do this, pour 2 tablespoons of water onto the diaper next to the regurgitated milk and compare the size of the spots.
Profuse belching in newborns, when milk flows like a fountain from the mouth, and regurgitation continues between feedings, is pathological and requires the attention of a doctor. Pathological regurgitation does not depend on the type of feeding: breast or artificial. Its causes are problems with the nervous system and gastrointestinal tract (developmental anomalies, enzyme deficiency, etc.).
The danger of excessive belching is that the newborn does not receive enough nutrition, grows poorly and gains weight, and the body becomes weaker and more vulnerable to disease. All this has a negative impact on the development of the child.
If, based on the results of the examination, no pathologies of the development of the gastrointestinal tract are identified in the newborn, anti-reflux mixtures are introduced into the diet. They contain thickeners that increase the viscosity of the mixture. This consistency keeps the mixture in the stomach during the release of the air lock. Mothers of newborns who are breastfed should not give it up. Mother's milk should still form the basis of nutrition, and anti-reflux formulas are replaced at several feedings.
If a newborn has pathological regurgitation, consultation with a pediatrician is necessary.
Baby burping after feeding
Organization of a children's room
Some parents prefer to put their baby to bed for the first months of his life in his bedroom - either in a crib, or in a cradle, or in his own bed. Others believe that the child should live in the nursery from birth. Let’s not argue who is right: there are so many people, so many opinions, each family chooses what is suitable for it personally. But one way or another, the room in which the newborn baby is located must meet certain requirements.
First of all, the air temperature in winter should not fall below 21-22 degrees, and in summer it should not exceed 27-28 degrees. The second important condition is this: even if the climate in the room is maintained by air conditioning, it must be ventilated frequently to keep the air fresh.
If space allows, it is advisable to place a cabinet or table in the room for changing the baby: then mom and dad will have less back pain when changing the baby. Otherwise, changing diapers will have to be done on the wide parental bed (but not on the sofa in the living room, since there is not enough space there and the baby is more likely to roll onto the floor).
In principle, up to 3 months the baby will be more comfortable in a cradle or a removable cradle from a stroller. Cradles are available for rent at many baby goods stores, where parents purchase a trousseau for the baby. When choosing a permanent crib, be sure to check that it meets Israeli safety standards, considered one of the strictest in the world. It is better to install the crib near the inner wall of the house. If you have to place it against an external wall, make sure that the distance between the wall and the crib is at least 20 cm. A fleecy rug on the wall is undesirable, as it is an excellent dust collector, and therefore a potential source of allergens and microbes.
Check that the mattress on the crib fits snugly against its sides on all sides. And don’t forget to raise the side of the bed, even if your baby still seems completely helpless. Early development specialists advise placing bright pictures in the crib, at a distance of about 30 cm from the newborn’s eyes. But you don’t need to put a pillow or a folded diaper on the baby yet - support for his head will only interfere, not to mention the threat of suffocation. In winter, your baby will need a warm blanket or envelope. In summer, a light sheet or thin diaper is enough.
A little advice: some babies sleep better swaddled the old fashioned way, because sometimes the baby wakes himself up with chaotic hand movements in his sleep.
Daily baby care
Feeding
Without going into details of the choice (breastfeeding or formula feeding), we will consider only some general issues of feeding a newborn. Many parents are confused when they are told that the best indicator of whether the baby is getting enough food is a calm and contented child. Not every baby behaves calmly, even when he is completely full. He may be bothered by abdominal pain, discomfort and much, much more. Therefore, you should focus on the number of soiled diapers: a normally nourished child soils diapers at least 5-6 times a day. The above applies to babies born after the 37th week of pregnancy weighing more than three kilograms. For premature or very young babies, the indicators are different and you should consult a specialist about them.
Contrary to popular belief, breastfed babies do not need extra fluids. Mother's milk is already 90% water. But if the baby wets diapers less than 5 times a day, and his urine is dark and has a strong odor, you should offer him water (up to 50 ml per day) in between feedings. It is still advisable not to give water to a child until two months of age. But the most important thing is that no matter how much you want to give your baby something to drink, do not be tempted to add a little sugar, juice or syrup to the water. Before you know it, your smart child will become addicted to sweetened drinks. And this is harmful both to the child’s health and appetite. If you want to give your child herbal tea, make sure first that its composition does not include sugar of any kind - fruit, grape, and so on.
What young parents are most concerned about is usually weight gain: the better the child gains weight, the better (in their opinion) they cope with their responsibilities. On average, it is expected that in the first two weeks the baby should regain the weight with which it was born. After this, the minimum weight gain is 120 g per week. Some manage to gain weight by one and a half kilograms per month, others barely gain 500 g - both are within normal limits. After three months, the rate of weight gain will decrease slightly. In addition, babies fed breast milk are usually slimmer than those fed formula. The norms in the Tipat Halav consultation are designed for artificial people, and therefore are not the ultimate truth. In principle, by six months the baby should double its birth weight, and by one year it should triple it. It is clear that if a child was born weighing 3 kg, at six months or a year he will weigh much less than his peer who was born weighing 3.8 kg.
When to call a doctor
This is necessary when the baby, due to excessive regurgitation, loses weight, sleeps poorly, cries often, and refuses to eat. If a baby's belching has yellow or green impurities, traces of blood, a strong unpleasant odor, disturbances in the functioning of the digestive organs are possible. Sometimes the release of the air plug causes pain to the newborn - he gags, coughs and cries.
Alarming symptoms that require consulting a doctor:
- repeated refusal of the newborn to eat;
- lag in weight gain;
- regurgitation not related to nutrition;
- pain during the release of the airlock;
- abnormal volume or color of regurgitation;
- decreased urine volume;
- belching, turning into vomiting.
In case of viral and infectious diseases, belching may be accompanied by vomiting, have a greenish tint due to bile, the newborn’s temperature rises, and he refuses to eat.
If your newborn burps within normal limits, is happy, and is gaining weight well, you have no reason to worry. Any deviations in the baby’s behavior, weight loss, changes in the color and volume of belching are reasons to consult a doctor.