Increased stomach acidity has a negative effect on digestive processes and the condition of the gastrointestinal tract, causing discomfort. Accompanies some diseases of the digestive system, including gastritis and peptic ulcers.
Increased stomach acid causes discomfort
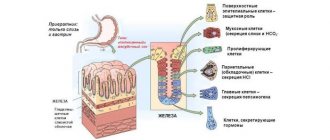
The acidity of the stomach, i.e., the pH of gastric juice, is determined by the concentration of hydrochloric acid contained in it, produced by parietal cells. Hydrochloric acid is necessary for the normal digestion process. Its main functions:
- imparts antibacterial properties to gastric juice;
- activates the action of digestive enzymes of gastric juice;
- denatures proteins and also promotes their swelling;
- stimulates the secretory activity of the pancreas;
- regulates the evacuation function of the stomach.
Causes
The most common cause of increased stomach acidity is a nutritional factor, i.e., improper, irrational nutrition. Spicy, salty, fatty foods, and alcoholic drinks have an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa, as a result of which the parietal cells begin to secrete hydrochloric acid in greater quantities than required. The nutritional factor also includes too rapid absorption of food. In this case, a poorly chewed bolus of food enters the stomach, not sufficiently moistened with saliva, containing too large particles. To digest it, a larger amount of gastric juice is required, and therefore hydrochloric acid, which leads to increased acid production, and therefore to an increase in the acidity of gastric juice.
The most common cause of high stomach acidity is poor diet.
An increased concentration of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice can cause damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
Other causes of increased stomach acidity may include:
- Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and/or corticosteroids , as they have an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa.
- Chronic stress. In itself, it does not have a negative effect on the state of the digestive system, however, being in a depressed state, a person stops eating properly, often smokes, drinks alcohol, which negatively affects the gastric mucosa.
- Smoking. Nicotine has a stimulating effect on parietal cells, resulting in an increase in stomach acidity.
- Infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. This is a unique microorganism that can survive in an acidic environment. Once in the stomach, bacteria produce urease, which has an irritating effect on its walls. In an effort to destroy these bacteria, stomach cells intensively synthesize hydrochloric acid and pepsin.
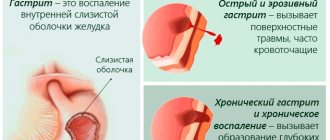
Harm
When it deviates upward, the intestinal mucosa becomes thinner, as the acid helps to corrode the lining. This leads to various pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
If the acidity of gastric juice deviates to a lesser extent, then the balance of beneficial and pathogenic microflora is disturbed, and doctors diagnose viral or fungal pathologies.
Symptoms of high stomach acidity
The main symptoms of increased stomach acidity are epigastric pain and heartburn. The pain is nagging, aching and dull in nature, in most cases it occurs 1.5-2 hours after eating. Heartburn develops as a result of gastric juice entering the esophagus. Often its appearance is provoked by eating foods that increase stomach acidity:
- orange or tomato juice;
- spicy and/or fatty foods;
- smoked meats;
- some types of mineral water.
Heartburn is the main symptom of increased stomach acidity.
Other symptoms of high stomach acidity include:
- nausea, and in some cases vomiting, occurring 15-20 minutes after eating;
- belching sour;
- constipation;
- flatulence;
- frequent intestinal colic;
- the appearance of a white-gray coating on the tongue.
Symptoms
Increased or decreased acidity of the stomach manifests itself with characteristic symptoms. This is the body’s signal about the development of diseases. Determining the acidity of the stomach independently begins with studying the clinical manifestations.
Decrease in pH
A decrease in pH is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Belching with an unpleasant, putrid odor.
- Bloating.
- Severe pain, discomfort in the abdominal area.
- Diarrhea followed by constipation.
Secondary signs include:
- The skin becomes dry.
- Brittle nails.
- Irritation and rash on the skin.
- Cuperosis.
- Apathy.
- Weight loss.
- Decreased hemoglobin in blood plasma.
Raising pH
Increasing the norm is a problem that leads to serious complications. Due to the increased content of hydrochloric acid, the intestinal walls are constantly irritated, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Heartburn after eating.
- Taste of iron.
- Belching after eating.
- Pain in the stomach area.
- Bloating.
- Problems with bowel movements.
- Pain after using pharmacological drugs.
Increased stomach acidity is also manifested by secondary symptoms:
- Loss of appetite.
- Indifference to life.
- Discomfort.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- The act of defecation is difficult.
If the patient is not bothered by the above clinical manifestations, then the indicators are at the normal level. If any symptoms appear, you will have to consult a specialist to diagnose the pathology and clarify the question of how to normalize the acidity of the stomach.
Diagnostics
To determine the acidity of gastric juice in clinical practice, the following methods are used:
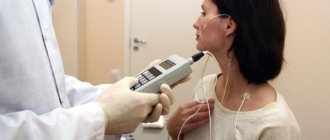
- Intragastric pH-metry. Using a special device, the acidity of the stomach is determined in its various parts. The method allows for both short-term and daily pH measurements.
- Fractional intubation of the stomach. The procedure is performed on an empty stomach. A thick probe is inserted into the patient's stomach through the mouth, and then the gastric contents are sucked out using a Janet syringe at certain intervals. This technique allows you to evaluate the characteristics of the secretory function of the stomach, as well as carry out a laboratory study of gastric juice with determination of its pH. However, fractional intubation cannot provide accurate results, since gastric juice is mixed from different zones, and in addition, the probe itself irritates the gastric mucosa. Normally, the content of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice should be 0.4–0.5%.
- Gastrotest, or acidotest. Before the study begins, the patient completely empties the bladder, after which he takes special medications orally. After a certain period of time, the patient urinates again and the acidity of the gastric juice is assessed based on the degree of staining of the urine. The method is imperfect, so it is rarely used today.
Intraventricular pH testing helps determine stomach acidity
You can detect increased acidity of gastric juice at home. To do this, you should drink a glass of freshly squeezed apple juice on an empty stomach, which does not contain any additives. If after some time a burning sensation appears behind the sternum, a feeling of heaviness or pain in the epigastric region, then the acidity is most likely increased.
Increased stomach acidity accompanies some diseases of the digestive system, including gastritis and peptic ulcers.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine recipes have long proven themselves. There are enough recipes that help restore balance:
- Herbs. Tinctures, decoctions, drops, for example, calamus and wormwood have a positive effect.
- You need to eat a little honey in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Heartburn is relieved with baking soda diluted in warm water.
- Crushed eggshells, ground into powder, are taken orally over a course of several days. After therapy, relief occurs and attacks stop.
- Potatoes help not only restore the balance of acid content, but also reduce inflammatory reactions on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract. To prepare, you need to take 6 medium-sized potatoes, grate them and squeeze out the juice. Take half of the resulting juice on an empty stomach. Why is it recommended to lie down for 20-40 minutes. The course of therapy is 7-8 days.
- Carrot juice helps combat high acidity; preparation is similar to the potato recipe.
- Dill or flax seeds help restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. They will have to be taken several times a day, always in a course.
Interesting! What are the causes of nausea and vomiting of gastric juice?
Important! Review and adjustment of nutrition are measures that will help relieve clinical manifestations. But they cannot completely get rid of the disease. The patient will have to see a doctor to confirm the diagnosis.
The specialist will prescribe a treatment regimen for complete cure. Will give recommendations: stomach acidity, how to determine it at home to identify pathology at the initial stage of development.
Treatment of high stomach acidity
Drug treatment of high gastric acidity is carried out with drugs from the following pharmacological groups:
- proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole, Pantoprozole, Nolpaza) – reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid by the parietal cells of the stomach by blocking H+/K+-ATPase;
- H2-histamine receptor blockers (Ranitidine, Cimetidine) – block histamine receptors, thereby reducing the secretion of hydrochloric acid and pepsin;
- antacids (Phosphalugel, Almagel, Rennie, Gastal) – neutralize hydrochloric acid in gastric juice, thereby eliminating heartburn, pain and discomfort;
- M1-cholinergic receptor blockers, which have a predominant effect on stomach receptors (Gastrocepin) - inhibit the secretion of pepsin and hydrochloric acid, have a gastroprotective effect;
- antibacterial drugs - therapy for helicobacteriosis.
To prevent relapses, it is extremely important to adhere to proper nutrition for a long time, or even better, for life.
In case of severe pain, antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpa), as well as local anesthetics orally (novocaine solution, tablets with anesthesin) are prescribed.
Omeprazole and other proton pump inhibitors help reduce acid secretion
Some patients take a solution of baking soda orally to eliminate symptoms of increased stomach acidity. Soda enters into a neutralization reaction with hydrochloric acid, as a result of which pain in the abdominal area and heartburn quickly disappear. But such treatment of increased stomach acidity subsequently leads to even greater secretion of hydrochloric acid by parietal cells. As a result of a chemical reaction between baking soda and hydrochloric acid, table salt and carbonic acid are formed, which is an unstable chemical compound that easily breaks down into water and carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide irritates the gastric mucosa, thereby causing increased secretion of hydrochloric acid. As a result, there is an even greater increase in stomach acidity. This phenomenon in medicine is called “acid rebound”.
Diet for high stomach acidity
Modern pharmacological treatment of high stomach acidity allows you to quickly eliminate the patient’s complaints and improve his condition. However, in most cases, after some time, patients again begin to suffer from epigastric pain and heartburn. To prevent relapses, it is extremely important to adhere to proper nutrition for a long time, or even better, for life. The basic rules of the diet for high stomach acidity are:
- eating 5-6 times a day in small portions (so-called fractional meals);
- providing mechanical and chemical sparing of the stomach;
- a diet completely balanced in the content of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, as well as vitamins and microelements.
For increased stomach acidity, diet No. 1 according to Pevzner is recommended
For patients suffering from diseases accompanied by high acidity of gastric juice, diet No. 1 according to Pevzner has been developed, corresponding to the listed principles. During a period of sharp exacerbation of the disease, patients are prescribed diet No. 1a for 6-8 days: dishes are prepared only by stewing or boiling, they are pureed and served warm, foods that can irritate the gastric mucosa and increase the secretion of hydrochloric acid are excluded:
- raw vegetables, berries and fruits;
- alcohol, carbonated drinks, strong tea, cocoa, coffee;
- chocolate;
- herbs, spices, sauces;
- fermented milk products (including cheese);
- bakery products.
Spicy, salty, fatty foods, and alcoholic drinks have an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa, which can result in increased stomach acidity.
During the period of mild exacerbation, as well as when the intensity of clinical manifestations of exacerbation decreases, diet No. 1 is recommended. With it, dishes are prepared by stewing, boiling, steaming and baking in the oven (without forming a crust). Well-cooked meat or fish can be served in portions; all other dishes should have a mushy consistency. The diet limits foods that have a stimulating effect on the gastric mucosa, such as broths. Completely excluded:
- herbs and spices;
- chocolate, ice cream;
- sour and unripe berries, fruits;
- cabbage, onions, turnips, rutabaga, cucumbers, radishes, sorrel, spinach;
- mushrooms;
- legumes;
- marinades and pickles;
- corn, pearl barley, barley, millet cereals;
- fried or hard-boiled eggs;
- sharp and salty cheeses;
- fatty fish;
- fatty meats;
- fresh and/or rye bread.
Features of the symptom complex
Given the nuances of the symptoms, one can only suspect how exactly the pH values have changed. This is not enough to start treatment, but it is enough to correct your diet.
Excessively acidic environment
Increased acidity may be indicated by frequent and intense belching after eating, or a burning sensation in the chest. Irritation is manifested by weakness of the esophageal sphincter and regular reflux of gastric contents into its lumen. The patient suffers from heartburn.
When chyme enters the duodenum, irritation is also observed here. A person is bothered by pain in the intestines. With increased load on the digestive glands, pain can radiate to the right and left. Digestive disorders are manifested by a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the abdomen. Nausea and vomiting may occur. After it, the patient feels a sour or bitter taste in the mouth, a burning sensation in the throat.
Contrary to popular belief, heartburn does not always signal increased acidity. A pH above 3.5 indicates low acidity, but reflux also feels like heartburn.
Low acidity in the stomach
It manifests itself as regular heaviness in the upper abdomen after eating, since the speed and quality of food digestion is impaired. Due to putrefactive processes, bad breath is observed (the characteristic smell of rotting or rotten eggs). The feeling of nausea increases and ends with vomiting. The patient suffers from flatulence and persistent constipation. Undigested food particles are present in the stool, and the smell becomes putrid. Spasms are regularly felt in different areas of the abdomen. Due to the development of opportunistic microflora, manifestations of dysbacteriosis occur - frequent diarrhea. A whitish-gray or yellowish coating appears on the tongue, which indicates the activation of fungi.
What to do
At the stage of symptoms, the patient cannot take medications. To use any drugs, you need good reasons - accurate information about the level of acidity and the condition of the gastric mucosa. Before visiting the hospital, a person can make dietary adjustments to temporarily relieve symptoms.
If there are signs of increased acidity, it is necessary to abandon all stimulants of hydrochloric acid production:
- spices;
- soda;
- salty, sour foods;
- fruit juices;
- sour fruits;
- fermented milk products.
Enveloping porridges (boiled rice, oatmeal, wheat cereals) contribute to alkalization of the environment. Your diet should include more vegetables with a neutral taste (cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkin). It is better to refuse fresh white and black bread.
If you have symptoms of decreased acidity, you should not eat acidic foods. You can increase the amount of fermented milk products, fruits and vegetables with a sour taste (citrus fruits, berries, tomatoes, bell peppers) in your diet. When acidity decreases, it is important to ensure normal digestion. You should eat fractionally - often and in small portions. It is important to regulate your drinking regime - drink 1.5 liters of clean water per day. Drink a glass of water 40 minutes before meals and an hour after.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of high stomach acidity should be based, first of all, on the organization of proper, balanced nutrition:
- eating small portions of food;
- chewing food thoroughly;
- inclusion in the diet of foods rich in plant fibers, vitamins, microelements, and protein;
- limiting fatty and spicy foods;
- refusal to eat fast food, snacks, so-called junk food;
- giving up alcoholic beverages and smoking.
Equally important in the prevention of high stomach acidity is the correct lifestyle:
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- regular exercise;
- compliance with the optimal work and rest regime.
It is also necessary to promptly treat infectious diseases, since they can lead to disruption of the secretory activity of cells in the gastric mucosa.
Possible consequences and complications
Excessive content of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice is dangerous for the development of severe complications that are difficult to treat. The entry of aggressive gastric contents into the lumen of the esophagus is not only accompanied by the unpleasant sensation of heartburn, but also causes damage to its mucous membrane. Long-term gastroesophageal reflux is the main cause of the formation of an esophageal ulcer, and its subsequent possible degeneration into a malignant tumor.
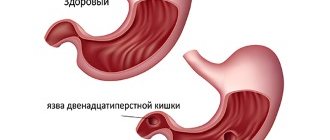
A complication of increased stomach acidity can be an esophageal ulcer.
An increased concentration of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice can cause damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract. Initially, such damage is superficial and is called erosion. Subsequently, the defect spreads deeper, which leads to the formation of ulcers of the stomach and duodenum. This is a serious disease that requires long-term systematic treatment. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications:
- ulcer malignancy;
- internal bleeding;
- perforation (perforation) of the ulcer;
- stenosis of the pylorus of the stomach and/or duodenum with obstruction;
- peritonitis.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Low acidity
How do you know if your stomach acidity is high or low? Insufficient production of hydrochloric acid is a sign of pathological conditions in the body associated with metabolic disorders. Hormonal imbalance and atrophic processes affect the decrease in acid production in the stomach. To increase acidity to a normal value, the underlying disease should be treated. It is almost impossible to eliminate this problem symptomatically. Some relief can be achieved with diet and herbal teas. The cause of low acidity is identified during an instrumental examination.