Pangastritis is a type of gastritis that has a chronic course of the disease. The inclusion of junk food in the diet and the abuse of bad habits affect the thinning of the walls of the gastric mucosa. The inflammatory process affects the entire surface of the digestive organ. Untimely treatment of pangastritis leads to the development of ulcers and malignant tumors.
Pangastrit
Pangastritis is one of the forms of inflammatory damage to the stomach. Another pathology is called widespread, or extensive, chronic gastritis. This is the focus of this is a packed -to -thelerts of the use of the work, which is revealed to the same time - the time, the time, is, the ANTPALENDOM )
Pangastritis - what is it? This is not an independent diagnosis, but a characteristic of the spread of pathological processes in the stomach, which affect all 3 parts of the organ: fundus (located next to the esophagus), body (central part) and antrum (next to the duodenum). It can be superficial, with high or low acidity.
Pangastritis is one of the forms of inflammatory damage to the stomach. Another pathology is called widespread, or extensive, chronic gastritis
This pathology is quite rare, and its treatment will be more difficult than with ordinary, albeit chronic, gastritis.
Classification
It is customary to classify the disease according to several clinical criteria. Based on the cause, degree and nature of gastric damage.
Taking into account the etiological factors, the following types of gastritis are distinguished:
- A type. An autoimmune chronic form in which the lesion covers only the body of the stomach.
- In type Helicobacter form. There are no immune disorders, endoscopy reveals the antral type of gastritis, the test for H. Pylori is positive.
- C type The chemical-toxic form is formed due to the effects of various toxic substances on the lining of the stomach.
- Mixed variety. Characterized by a combination of several forms.
Taking into account the secretion function, it happens:
- increased secretory function;
- normal secretory function;
- decreased secretory function.
Based on the nature of the spread of inflammatory effects, the following are distinguished:
- focal pangastritis;
- diffuse.
According to the degree of damage and depth, pangastritis is:
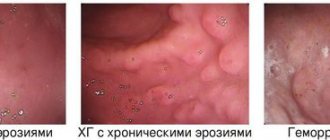
- Superficial (non-atrophic, erythematous). The mildest form of the disease. The lesion affects only the upper layer of the mucosa. It responds well to treatment and does not cause complications.
- Erosive. Defects are observed in the mucous membrane, but the pathology does not affect muscle tissue.
- Atrophic. A severe form that causes replacement of areas of the mucous membrane with connective tissue. This may be multifocal gastritis, when atrophy affects the entire stomach or individual areas of the organ.
- Hypertrophic gastritis. It is characterized by thickening of the mucous membrane with tissue deformation, which leads to the appearance of cysts and adenomas.
The following gradation is a collective one, which includes other forms of the pathological process:
- Follicular or lymphoid. A special type of disease that is characterized by the presence of follicles - formations in the stomach that appear during the accumulation of lymphocytes. In most cases, it occurs when the stomach is damaged by infection or against the background of chronic inflammation.
- Autoimmune. Occurs due to the presence of autoimmune diseases.
- Hyperplastic. Areas of mucosal atrophy are combined with hyperplasia.
Chronic non-atrophic gastritis responds best to therapeutic measures and does not cause irreversible consequences if the disease is treated. This is the first stage of the pathology, when the inflammatory process covers only the superficial layer of the stomach lining.
Pangastritis causes of development
Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, NSAIDs, is a common cause of pangastritis. Other risk factors include tobacco products, alcohol, certain recreational drugs, large doses of vitamin or mineral supplements, chronic stress, frequent vomiting, radiation during cancer treatment, and bacterial infection caused by H. pylori. Stress gastritis or pangastritis can be the result of injury, illness, burns or surgery.
Doctors identify a number of risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing inflammation in the digestive system. These include:
- improper diet – frequent consumption of fried, fatty, salty foods, addiction to fast food;
- non-compliance with food intake – rare and large portions, snacks “on the run”, dry drinks;
- food poisoning due to expired products and some chemical substances that accidentally got into the food;
- carrying out drug therapy with anti-inflammatory drugs - non-steroidal and steroidal drugs;
- strong stress, emotional instability of the patient;
- abuse of alcoholic drinks and smoking.
Pangastritis can be the result of other diseases or disorders. Bile reflux forces bile, a fluid secreted by the liver to aid digestion, back into the stomach. Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and celiac disease may present as pangastritis. Autoimmune diseases cause pangastritis when immune cells attack healthy stomach tissue.
The combined influence of risk factors increases the likelihood of pangastritis.
Reasons why gastritis develops
Among the reasons why superficial inflammation may occur are the following:
- stressful situations - the blood supply to the mucous membrane is disrupted, the production of hydrochloric acid increases, which leads to inflammation;
- long-term use of medications - hormones, NSAIDs, antibiotics (increase stomach acidity);
- malnutrition;
- consumption of hot and cold foods (irritate the mucous membranes, which causes inflammation);
- heredity (if there were relatives in the family with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the person is at risk);
- metabolic disorders (increases acidity);
- fungal, viral and bacterial infection (irritates the mucous membrane, causing an inflammatory process);
- smoking, alcohol abuse (ethanol and nicotine destroy mucosal cells).
The main risk factor is poor nutrition. Many people, under the pressure of an intense lifestyle, simply do not have time to have breakfast, and do not forget to smoke a cigarette on an empty stomach. Use:
GALINA SAVINA: “How easy it is to cure gastritis at home in 1 month. A proven method is to write down the recipe. » Read more >>
- fatty foods;
- salty dishes;
- smoking;
- hot seasonings.
Leads to severe stomach irritation. With such a rhythm of life and poor nutrition, gastritis develops. Moreover, the disease is getting younger every year. If previously the pathology was diagnosed in only 20% of the population, today the numbers have tripled. The disease is diagnosed in many adolescents aged 14-15 years.
Pangastritis species
Extensive damage to the stomach has an unfavorable effect on the patient’s condition, which leads to the appearance of a characteristic clinical picture of gastritis. Therefore, patients should know everything about chronic pangastritis - what it is and how to suspect that they have the disease.
We found out what pangastritis is. In the development of pangastritis, a number of factors are important that worsen the condition of the gastric mucosa. The main cause of inflammation in the stomach is considered to be the influence of specific microorganisms - Helicobacter. They penetrate the mucous membrane of the organ and cause the development of a local inflammatory process. The active influence of microbes leads to disruption of stomach acidity and the appearance of symptoms of pangastritis.
The depth of damage to the mucous membrane is directly related to the severity of the disease. There are 5 types of degree of damage to the surface of the stomach:
- superficial pangastritis (exudative, erythematous) – minor damage to the lining of the stomach;
- chronic pangastritis – absence of cicatricial deformations of the organ mucosa, reduction in the secretion of gastric juice due to damage to the glandular membrane;
- erosive pangastritis - the presence of wounds, cicatricial deformations on the surface of the mucosa;
- atrophic pangastritis – damage to the connective tissue of the stomach and intestines as a result of cell death due to insufficient production of necessary enzymes;
- hypertrophic pangastritis – the appearance of cysts, tumors of various types, adenomas.
Forms of pangastritis
Doctors offer several classifications of pangastritis. Based on the origin of the disease, they are divided into:
- The bacterial form is the most common type of disease associated with the presence of Helicobacter in the stomach.
- The autoimmune form is a pathology that occurs due to a change in the immune response to mucosal cells.
- The chemical form is a disease that appears as a result of damage to the stomach by chemicals (medicines, alcohol).
- Mixed form is a disease based on a combination of several factors listed above.
Depending on the nature of the changes in the mucous membrane of the organ, hypertrophic and atrophic pangastritis are distinguished. The atrophic form of the disease is characterized by the death of stomach cells and the disappearance of glandular cells that produce digestive enzymes.
A less common form is the hypertrophic type of the disease. Many patients know nothing about non-atrophic pangastritis - what it is and what changes are characteristic of it. The hypertrophic type of the disease is characterized by the appearance of growths formed from mucosal cells. These can be cysts, adenomas, benign tumors. Chronic non-atrophic pangastritis has a less favorable prognosis for the patient's health.
Superficial pangastritis is
Superficial pangastritis is usually less active than other forms. Therefore, when it is detected, only drugs that have a protective effect on the stomach are prescribed:
Depending on changes in acidity for gastritis, different groups of drugs are used. In case of high acidity, antacid
, which include
Maalox
,
Gaviscon
,
Gastrogel
,
Almagel
. Low acidity requires the administration of enzymes - pepsin, salpepsin, as well as abomin and potassium gluconate.
Superficial pangastritis usually occurs less actively than other forms.
Proper nutrition of the patient is of great importance during treatment. The diet must comply with the following rules:
- You need to eat in small portions many times a day (fractional meals).
- It is necessary to eat softened or minced foods to reduce the load on the digestive system.
- Food can only be boiled or baked; fried foods are strictly prohibited.
- Too spicy, fatty foods, carbonated water, alcohol, and coffee are completely excluded from the diet.
Without following a diet, the likelihood of improvement in the patient's condition is significantly reduced.
Treatment of pathology
In the early stages, it is possible to completely get rid of such pathology as erythematous gastritis. Treatment is carried out using various methods. Among them:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- visiting resorts and sanatoriums.
But the main thing during treatment and in subsequent life is diet. Only by following simple nutritional rules will it be possible to prevent complications and the transition of inflammation to a chronic form.
Treatment with medications depends on what caused the inflammation. If this is an infection, then the following are prescribed:
- antibacterial;
- antiviral;
- antifungal;
- antiparasitic drugs.
Pangastritis symptoms
Pangastritis is a chronic form of the disease. The onset of symptoms occurs suddenly. Intermittent disturbing signs lead to the patient’s frivolous attitude towards the disease, and as a result – to serious complications.
The main symptoms signaling an inflammatory process in the stomach are:
- severe pain in the upper part of the epigastrium;
- loss of appetite;
- increased gas formation;
- heartburn, sour belching;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- urge to feel sick;
- severe dizziness;
- weakness in the body;
- pale complexion;
- white coating on the tongue.
Each type of pangastritis has individual symptomatic signs.
The forms of the disease differ in the intensity of the pain syndrome: inflammation with foci of atrophy is characterized by moderate pain, erosive - severe, atrophic - dull. Burning spasms indicate a severe stage of development of pangastritis, manifested in the form of blood in the stool and elevated body temperature.
Hemorrhagic inflammation accompanied by internal bleeding is characterized by unstable blood pressure, rapid pulse, and tarry stools. Mild forms of the disease may occur without obvious symptomatic signs.
Treatment
To treat erythematous gastritis, drug therapy is used, including astringents, antacids, and inhibitors. The drugs gastrofarm and gastrocepin are prescribed, which have a beneficial effect on the mucous membrane, helping the epithelium during regeneration. A drug called de-nol is released, which has a detrimental effect on Helicobacter bacteria, although the drug is not an antibiotic.
If the disease is superficial, there is no need to take medications, you just need to follow the rules.
Recommendations
- Small meals to avoid heaviness in the stomach. You need to eat in small portions, maintaining an interval between meals of at least three hours.
- Do not consume foods that can injure the gastric epithelium.
- Introduce porridge and broth into your diet, drink jelly, and eat jelly as a treat.
- Avoid drinking coffee and black tea during treatment and instead drink plenty of water, including herbal tea.
- Avoid drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking tobacco, which cause irreparable harm to the body.
Diet therapy is considered an important, main part of the treatment of erythematous gastritis. It is recommended to pay attention to the patient’s nutrition, adjust the menu, and include in the list exclusively gentle products that have a beneficial effect on the inner walls of the stomach. Cross off the list of dishes that irritate the mucous membranes.
Traditional methods of treatment
For the treatment of erythematous-exudative gastropathy, decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs are widely used. They can be consumed on their own, as an additive to regular tea. Herbal infusions and decoctions are prepared based on the level of acidity in the gastric environment. For low acidity, cabbage juice helps well; for high acidity, with symptoms of heartburn, birch bark is suitable. A tincture is prepared from it.
You cannot self-medicate; herbal medicine must be discussed with your doctor. This is a serious disease that requires increased attention and control to avoid complications.
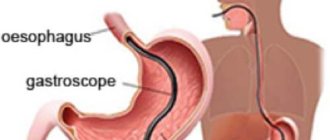
In particularly complex cases of the disease, surgical intervention is provided, used in the absence of results from drug treatment of the disease. Basically, gastric resection is performed, which is characterized by the least trauma and minimal incisions of the stomach tissue. The operation is performed through a special tube passing through the esophagus into the stomach. Thus, when using the necessary medical instruments, the affected parts of the gastric mucosa are carefully removed.
Pangastritis consequences
With pangastritis, the development of gastroduodenitis is possible.
Widespread chronic damage to the stomach poses a danger to the patient's health. With pangastritis, the following complications may develop:
- Gastroduodenitis
or
colitis
- spread of the inflammatory process to the small intestine; - Peptic ulcer
– the formation of erosions and ulcers at the site of inflammation; - Duodenal-gastric reflux
is the reflux of contents from the intestines into the stomach, as a result of which the acidity of gastric contents decreases and the digestion process is disrupted; - In severe cases - stomach cancer
, which can occur with the atrophic form of gastritis.
The listed conditions pose a great threat to the life and health of the patient, which is why it is so important to promptly begin treatment for pangastritis when the first symptoms of the disease are detected.
Diagnostics
When the first symptomatic signs are detected, a visual examination and palpation of the patient by a gastroenterologist is performed. To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory tests and examination are prescribed. Diagnosis of pangastritis includes:
- analysis of feces, urine, blood (general, biochemical);
- biopsy;
- conducting a breath test;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- endoscopy;
- X-ray of the stomach;
- fibrogastroscopy.
Laboratory tests are prescribed to detect bacteria and infectious diseases in the body. Examinations make it possible to identify the nature, severity, and spread of the inflammatory process, and determine the presence of cicatricial deformities and erosions. After the appointment and diagnostic measures have been carried out, treatment is prescribed.
Pangastritis: when to see a doctor
People with pangastritis should seek emergency care if chest pain begins suddenly, gets worse, or spreads to the back, neck, shoulders, or arms. Severe abdominal pain that moves to the lower right side of the abdomen and frequent vomiting are also emergencies.
Other symptoms that require immediate medical attention include difficulty breathing or swallowing, confusion, fast heartbeat, extreme sleepiness or difficulty waking up, fainting, and blood in the vomit or stool. Blood in the stool looks black and tarry, and blood in the vomit looks like coffee grounds.
Types of gastritis
Before talking about the types of gastritis, it would be logical to understand what this disease is. As mentioned earlier, gastritis can be both acute and chronic. In any case, this disease is associated with changes in the mucosa, which are dystrophic-inflammatory in nature.
The most serious and destructive effect of gastritis is on the secretory function of the stomach lining
The stomach is the first to suffer from the fast pace of modern life, since most of us snack during the day almost on the run or at work. Also, deformation of the pituitary layer is provoked by disruption of the daily routine, torn sleep and frequent stress.
Acute gastritis
This type of gastritis is caused by a one-time negative impact of external irritants. This can be either a side effect from taking certain potent medications, or a consequence of ingestion of low-quality food or products that have expired.
In addition, acute gastritis can develop as a background disease during acute infections, as well as due to disruption of normal metabolism
Acute gastritis is usually divided into the following types:
- catarrhal gastritis, otherwise called simple or banal;
- fibrinous gastritis (alternative name – diphtheria);
- gastritis is corrosive, also known as toxic-chemical or necrotic;
- phlegmonous gastritis.
Each of the varieties develops depending on the ingestion of certain unwanted irritants into the stomach, while the severity and irreversibility of the consequences for human health from these types of acute gastritis is ranked from least to greatest. With catarrhal gastritis, doctors talk about poor diet or ordinary food poisoning. Fibrinous gastritis refers to the ingestion of sublimate or caustic acids into the stomach. Corrosive gastritis is provoked by salts of heavy metals, as well as alkaline and acidic concentrates. The most severe form of acute gastritis - phlegmonous - is a reaction to complications associated with stomach cancer or peptic ulcer.
Chronic gastritis
There are several classifications of chronic gastritis. The first of them is called the Houston one and describes the forms of chronic gastritis according to the types of influences that lead to the disease. The second is based on the locational principle and takes as a basis the areas of the stomach in which chronic gastritis develops.
Table 1. Classifications and forms of chronic gastritis
It is important to understand that any form of chronic gastritis from the Houston classification can result in extensive damage, which is what pangastritis is meant. Moreover, in most countries of Europe and America, doctors extremely rarely diagnose a patient with “chronic gastritis”. As a rule, a specialist pays attention to the symptoms and uses the term “functional dyspepsia.” At the same time, Japanese doctors are increasingly resorting to a combined diagnosis, combining dyspepsia with gastritis.
The variability of such views and concepts is clear evidence of the reliability of recent research data, according to which almost every second inhabitant of our planet suffers from gastritis in one form or another.
Pangastritis diet
However, therapy is not limited to just taking medications. The first step is to establish the nutrition process and follow a diet. Patients with pangastritis must adhere to the following rules:
- Meals should be fractional and occur at regular intervals, ideally every 4 hours . Food should be warm and free of solid particles, as they can further injure the damaged mucous membrane. You should eat slowly, chewing your food thoroughly and washing it down with a small amount of water to facilitate digestion and absorption.
- fast food, semi-finished products, fried, oiled, fatty and spicy dishes . You should avoid eating baked goods and fresh white bread, products containing dyes and preservatives. Tea, coffee, carbonated drinks and alcohol are prohibited.
- Preference is given to low-fat boiled or steamed dishes, baked vegetables, liquid slippery porridges, dietary soups and broths . In each individual case, the diet is prescribed by a doctor; all changes in nutrition must be consistent with him.
You should also establish a daily routine, take light walks, try to spend as much time as possible in the fresh air, and don’t get nervous. This will strengthen the body's defenses, which will have a positive effect on the condition of the stomach as well.
It is advisable to eat often, but in small portions. Of course, you should avoid stimulants such as coffee, alcohol and cigarettes, and certain medications such as aspirin and other NSAIDs. It is necessary to exclude too spicy dishes. Symptoms of the disease are worsened by carbonated drinks. And in the case of autoimmune inflammation of the gastric mucosa, you need to take vitamin B 12 by injection (once a month) to avoid anemia and its complications. In some cases, partial or complete removal of the diseased organ may be necessary.
Methods of therapy
Pangastritis can be cured by using medications, traditional methods and following a special diet.
Medications
Taking medications helps reduce pain, neutralize the level of hydrochloric acid, and remove bacteria and harmful microorganisms. Such drugs include:
- painkillers, antispasmodics;
- antacid drugs;
- antibiotics;
- inhibitors;
- enzyme agents.
At the discretion of the doctor, hormonal drugs, as well as products containing azelaic acid, can be prescribed.
ethnoscience
To prevent the disease, you can use folk recipes. Herbal infusions and decoctions have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and healing effects. For inflammation in the stomach, he recommends drinking potato or celery juice on an empty stomach throughout the day before meals.
Sea buckthorn oil or wheat germ have a positive effect on damaged mucous membranes.
Diet
Proper nutrition for pangastritis is the key to a positive prognosis in the treatment of the disease. The diet includes:
- fractional meals - regular meals in small portions;
- chewing food thoroughly;
- exclusion of spicy, fried, smoked, salty foods, sweets, coffee, carbonated drinks;
- eating boiled, steamed food;
- giving up alcohol and tobacco.
Inflammation of the gastric mucosa is a common disease. Timely treatment for initial symptomatic signs leads to complete recovery. Advanced stages of the disease can develop into malignant cancer tumors.
A healthy and balanced diet, giving up bad habits, regular visits to the doctor, and getting tested are the basis for preventing pangastritis.
We recommend: How to drink cabbage juice correctly for gastritis?
Pangastritis treatment
Proton pump inhibitors are used not only in the treatment of gastritis and peptic ulcers, but also for the prevention of stomach diseases.
In most cases, pangastritis can be successfully treated. In the case of frequent viral inflammation of the stomach, healing most often occurs spontaneously (after several days). If a Helicobacter Pylori infection is detected, antibiotic treatment is used along with drugs from the group of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). The bacterial eradication therapy regimen is carried out together with antibiotics. It should be remembered that in no case should you change or stop such treatment yourself: then the development of strains of bacteria that are resistant to standard antibiotics is possible.
Proton pump inhibitors are used not only in the treatment of gastritis and peptic ulcers, but also for the prevention of stomach diseases, for example, in people constantly taking anti-inflammatory drugs. When the cause of pangastritis is the excessive use of NSAIDs, the first recommendation should be the possibility of replacing them with safer substances (such as paracetamol). When this is not possible (for example, when treating joint degeneration or other rheumatic diseases), a drug that inhibits the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach (Omeprazole, Pantoprazole, Lansoprazole) should be used.
In case of reflux of bile into the stomach from the gallbladder, the doctor may include drugs with azelaic acid in the treatment. Treatment must be supplemented with a proper diet. Following a diet for chronic gastritis is important because it relieves signs of inflammation, reduces irritation of the mucous membrane, promotes the healing of ulcers and prevents further atrophy of the glands in the mucosa. You should consume easily digestible, cooked and low-fat foods. Avoid fried foods that cause bloating. In addition, very hot foods can irritate the stomach lining.
Pangastritis is the most complex type of gastritis; its treatment will be more complex and lengthy compared to the focal form. In this case, the patient will need iron restraint, since following a strict diet can take a long time, and failures will lead to an inevitable aggravation.
To never know what pangastritis is, you need to be responsible about your lifestyle and diet. This will help keep your stomach healthy for many years.
Forms of the disease
Pangastritis belongs to the group of political sciences and is born under the influence of a complex of exogenous and endogenous causes. The probability of transformation of the initial stage into a chronic stage in the working population increases with age. Development takes a long time and sometimes unnoticed. For a clearer analysis, let’s consider all stages and types of education.
Stages of disease development
If not stopped, the disease develops according to a certain scenario. Slight damage to the gastric mucosa, accompanied by minor digestive defects, leads to catarrhal superficial gastritis. This mild form of the disease is completely curable.
The chronic stage is characterized by deformation of the glandular membrane. Erosion of the mucous membrane has not yet been observed, but the production of gastric juice has already been reduced. Lack of enzymes causes discomfort during digestion of food.
Atrophic gastritis with intestinal type restructuring develops in patients with low acidity. This is a chronic disease with digestive pathology. Reduced production of enzymes provokes the death of glandular cells. They are replaced by a layer of intestinal epithelium. The digestive organ is replaced.
Hypertrophic gastritis refers to serious damage to the stomach, reaching the muscle tissue. The walls of the digestive organ change, becoming overgrown with folds, cysts, benign tumors, and adenomas. The diameter of the tumor can be up to 3 centimeters. The person experiences severe pain, accompanied by nausea and diarrhea.
Forms of chronic gastritis
According to etiological characteristics, pangastritis is divided into types:
- Autoimmune. Gastritis is hereditary and is extremely rare. Mostly in old age. Caused by insufficient production of immunoglobulin by the immune system. As a result, antibodies are formed that destroy the cells of the stomach glands. Damage to the glands leads to a sharp decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid and the amount of vitamin B12 absorption.
- Bacterial. The most common type of disease. It is formed due to the proliferation of bacteria Helicobacter pylori. This spiral-shaped bacterium has adapted to life in acidic conditions by producing a special enzyme - a hydrochloric acid neutralizer. The bacterium releases toxins that promote dissolution of the membrane. As a result of its vital activity, food enzymes penetrate deeper, corroding the mucous membrane.
Appearance of gastritis - Chemical. The walls of the stomach are deformed under the influence of incompatible drugs, bile or alcohol.
- Mixed pangastritis is characterized by a combination of several of the above groups.
Pangastritis forecast
The gastric mucosa rarely returns to a completely normal and healthy state after chronic pangastritis. Severe mucosal changes or the presence of precancerous lesions may require annual monitoring with upper endoscopy. Pernicious anemia with pangastritis is not always reversible. It develops due to a lack of a certain substance in the stomach that is necessary for the digestion and absorption of vitamin B12. If pernicious anemia persists after treatment for pangastritis, regular B12 injections may help manage symptoms.
Sources
https://gastritunet.online/bolezni-zheludka/gastrit/vidy/pangastrit.html
https://gb5 kem.ru/zheludok/pangastrit-chto-eto-takoe-simptomy-lechenie-i-profilaktika.html
https://dverisvm.ru/zhivot/pangastrit-prichiny-razvitiya-zabolevaniya-osobennosti-techeniya.html
https://jktblog.ru/zabolevaniya-zhkt/gastrit/pangastrit.html
https://g b5kem.ru/zheludok/pangastrit-chto-eto-takoe-simptomy-lechenie-i-profilaktika.html
Complications
The main cause of complications is the chronic form of the disease. If signs of chronic gastritis appear, but the patient does not consult a doctor, the following complications may occur:
- anemia;
- atrophic gastritis;
- leptic ulcers;
- benign or malignant tumors on the mucosa.
The only way to restore health is to promptly consult a qualified doctor who will give recommendations on how to treat gastritis. Taking pills for gastritis on your own is not recommended, so as not to provoke an exacerbation of the disease and its transition to a severe form. The likelihood of complications depends on what patients with chronic gastritis eat.
Prevention and treatment of pangastritis
As preventive measures that can protect the stomach of a person of any age from gastritis in general and pangastritis in particular, experts suggest giving up basic bad habits (such as smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages). Also an important aspect of the prevention of stomach diseases is a healthy and moderate diet, with an emphasis on reducing fried foods and fatty foods in the daily diet. Regular medical examinations by specialized specialists will help monitor the condition of the mucous membrane and, if necessary, begin treatment for pangastritis at the earliest stage.
Gastritis is one of those ailments that are easier to prevent than to treat.
If the disease has already been diagnosed, the dietary requirements become more stringent. You will have to completely give up spicy, fatty, fried or smoked foods, as well as alcohol of any strength, coffee, sweets and any colored soda. The patient's diet includes dishes prepared in the oven and steamed, and hard vegetables, as well as all types of fish and meat, must be chopped using a blender or meat grinder before consumption. All types of fast food, smoking and products that stimulate the fermentation process - primarily black bread and grapes - are subject to the strictest moratorium.
You will have to give up fast food
The diet of a patient with pangastritis becomes strictly regulated and fractional. Small portions of food should be consumed strictly according to a schedule consisting of equal periods of time. An exception is made only for periods allocated for night sleep. Nutritionists consider five or six meals a day optimal.
Medication for pangastritis is indicated by the use of so-called PPIs, or proton pump inhibitors. Under this collective name, medications are known whose main purpose is to suppress the production of hydrochloric acid by the mucous membrane. In this way, normalization of the acidity of gastric juice is achieved. Among the most commonly prescribed drugs are Lansoprazole and Omeprazole.
Also, during the period of exacerbation of painful sensations, doctors advise the use of antispasmodics (No-shpa, Papaverine) and antacids that coat the walls of the stomach and provide protection from the destructive effects of gastric juice. It could be “Rennie”, “Almagel” or, for example, “Phosphalugel”.
Folk recipes for combating damage to the mucous membrane consist of introducing chamomile infusions, cabbage juice, rosehip decoction and flax seeds into the diet. True, it is important to understand that these “secrets” should first be discussed with doctors, since some of the above products are suitable for patients with pangastritis with insufficient secretory function, while other dishes will be indicated for moderate or strong secretion.
The best results in the treatment and relief of exacerbations of pangastritis are achieved with a competent combination of medication, diet and maximum distance from sources of constant stress.
Video - Gastritis, heartburn, ulcer. How to and how NOT to treat the stomach
Symptoms of gastritis
Chronic superficial gastritis develops gradually. Symptoms appear unexpectedly. A person suffering from the disease feels discomfort mainly after eating; the rest of the time there is no pain. Such inconstancy leads to neglect and to an advanced stage of the disease. Knowing the symptoms, there is a chance to prevent the development of the disease at an early stage.
The main signs of gastritis:
- Pain in the upper abdomen and left side.
- Lack of appetite.
- Flatulence.
- Heartburn.
- Nausea.
- Dizziness.
- Belching.
- Weakness.
- Acidic taste in the mouth.
- Pallor.
- Change in color of the mucous membrane of the tongue.
Preventive measures
The patient will need to pay special attention to further prevention of relapse. To do this, you must follow all the recommendations of your doctor and avoid any situations in which an exacerbation of pangastritis could develop again.
What to do for prevention:
- normalize your diet, give up junk food and unhealthy drinks;
- do not take medications without consulting a doctor;
- treat concomitant diseases;
- on an empty stomach, drink a glass of pure water or mineral water without gas;
- Eat a tablespoon of vegetable oil a day before meals;
- drink weak green tea or herbal infusions;
- Also, a good preventive measure would be to consume 1 spoon of aloe juice daily;
- visit a gastroenterologist at least 2 times a year;
- do not drink alcohol, do not smoke.
Gastritis does not disappear on its own, so a person must make every effort to prevent its reappearance. If you follow all doctor's prescriptions, lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right, the disease will never return again.