Why does a child have heartburn?
The main causes of heartburn in children:
- An unlimited amount of simple carbohydrates in the diet (buns and sweet pastries, potatoes, pasta, fruits and honey), consumption of sweet carbonated drinks, spicy and fatty foods, constant overeating is a direct path to gastrointestinal pathologies.
- Wearing tight clothing that puts pressure on the abdominal area can also contribute to discomfort in the esophagus.
- Some neurological disorders .
- Acute gastritis is a disease in which the gastric mucosa is damaged due to poor nutrition. The child also feels pain after eating, heaviness in the stomach and belching.
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Food allergies.
- Scoliosis (causes heartburn due to excess pressure on the walls of the stomach by neighboring organs due to incorrect posture).
- Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the esophagus , or esophagitis. Heartburn is most typical for the dyspeptic form of this disease. Esophagitis also manifests itself as a burning sensation in the esophagus and belching, often involuntary and loud. Symptoms peak within an hour and a half after eating.
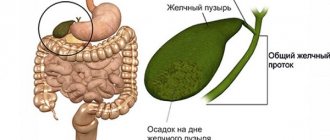
- Hernia in the esophageal opening of the diaphragm . This disease is quite common in children. Its occurrence is due to the fact that part of the stomach moves upward through the esophageal opening to the chest cavity. The cause of the hernia is the failure of the diaphragm and the lack of rigid fixation.
- Malfunction of the cardinal sphincter . The cardinal sphincter is a muscle located at the border of the esophagus and stomach. After food passes from the esophagus into the stomach, this muscle closes the lumen. Insufficiency of sphincter function may be associated with a congenital defect, poor nutrition (frequent consumption of foods that irritate the gastric mucosa: chocolate, spicy seasonings, etc.).
- Reflux gastritis , or chemical gastritis. This disease can develop if a child takes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, potassium and iron supplements for a long time. Reflux gastritis can also manifest itself as a feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium (“in the pit of the stomach”), nausea after eating.
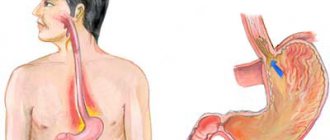
Up to 4 months, about 50% of children are susceptible to acid reflux - the backflow of acid from the stomach into the esophagus. This is due to the immaturity of the digestive tract and causes heartburn.
In children over 5 years old, acid reflux occurs for other reasons:
- eating junk food - chocolate, fried foods, sugar, carbonated drinks;
- incomplete closure of the esophageal sphincter;
- improper diet;
- binge eating;
- habit of eating a lot before bed;
- excessive physical activity;
- tight clothes;
- obesity;
- frequent lifting and bending of the body;
- some drugs, for example Aspirin, Ibuprofen;
- stress.
In adolescents, these reasons are added to: smoking and first attempts at alcohol.
Typical symptoms of heartburn in children
In young children, diagnosis is complicated by the fact that the baby cannot talk about his condition. The main signs that a child is suffering from heartburn are:
- irritability and tearfulness after eating;
- arching of the back;
- gases;
- suffocation (the child does not have enough air);
- dry mouth;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea;
- unpleasant belching. Source: N.V. Lyarskaya Modern aspects of the etiology, pathogenesis and clinic of gastroesophageal reflux disease in children // Bulletin of VSMU, 2008, vol. 7, no. 2
If you observe similar symptoms in your child, you should report them to your doctor.
Therapy
Treatment of heartburn in children can take a long time if the discomfort is caused by a disease of the gastrointestinal tract.
The most important treatment against heartburn is diet. Since this is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to ease the work of the digestive system. When eating heavy food, a large amount of gastric juice is produced, which must digest all the contents of the stomach, but due to the load, malfunctions can occur, which affect the formation of a burning sensation.
It is necessary to remove a large number of sweet, fatty, sour and spicy foods from the diet. It is forbidden to give your baby carbonated drinks.
In addition to diet, your doctor may prescribe medications. In some cases, the use of traditional medicine methods is allowed.
If a baby develops heartburn, parents will need to follow certain rules:
- Feeding should only be done at an inclination of 45-60 degrees, this will ensure unhindered passage of food into the stomach.
- During night sleep, the child should lie so that the head is 10 centimeters higher than the body.
- It is necessary to add mixtures that contain a high content of gluten or another thickener to the diet.
For older children you should:
- Remove ice cream, pepper, garlic, and fatty meat from your diet.
- Reduce consumption of chocolate and baked goods.
- Introduce more cereals, lean fish and meat into your diet.
- Give your child fermented milk products with a low fat content every day.
- Feed 5-6 times a day, in small portions.
- The last meal should be no later than an hour and a half before bedtime.
- After eating, it is necessary to reduce physical activity to a minimum for about 30 minutes.
- Dress your child only in comfortable clothes that do not cause discomfort.
A large number of drugs are used as drug therapy, which are divided by age categories. Thus, children aged 12 and older can take Nexium and Rebeprzol, Almagel and Gelustil.
For children from 3 years of age, Iberogast is produced - a herbal preparation.
In particularly severe cases, surgery may be required. During the operation, the lower valve of the esophagus is strengthened.
Traditional medicine methods
The use of traditional medicine is allowed only with the permission of a doctor, because they can only worsen the situation. The most common recipes are:
- the use of crushed walnuts, which should be given a teaspoon per day. Nuts are an excellent means of prevention against disease;
- tincture of bitter wormwood is prepared as follows: 1/3 spoon of wormwood is poured into a glass of hot water and infused for 24 hours. The prepared liquid should be given to the child throughout the day, in small portions;
- by mixing a large spoonful of apple cider vinegar and half a glass of warm water, you can relieve your child of the burning sensation;
- A spoonful of sunflower oil is also considered an excellent remedy against heartburn.
Thus, heartburn is an unpleasant disease that will cause great discomfort not only to the child, but also to his parents. If you do not treat this disease in time, complications may arise: Barrett's esophagus and posthemorrhagic anemia. It is necessary to carefully monitor your child’s behavior and, at the first suspicion of the development of the disease, take him to a specialist for a full diagnosis.
What to do to diagnose the disease?
It is necessary to find the cause, that is, the disease that causes heartburn. To do this, you need to contact a pediatric gastroenterologist with your child, who will examine the patient, interview him for complaints, and collect an anamnesis of the disease. Already from the results of the first consultation, you can understand a lot and prescribe initial therapy. The following types of diagnostics may be recommended:
- FGDS, during which a biopsy of a suspicious area of the mucous membrane can be done. Fibrogastroduodenoscopy allows you to determine the acidity of gastric juice and test for Helicobacter Pilori.
- X-ray of the stomach and esophagus - if it is impossible to do FGDS. A less informative method, but it can detect narrowing of the esophagus and hiatal hernia.
- Esophageal manometry - makes it possible to determine the peristalsis of the esophagus and the work of the sphincters.
- Daily pH-metry of the esophagus - measurement of pH levels in various parts of the stomach, duodenum and esophagus. It is carried out if there is a suspicion of a disease accompanied by a change in acidity levels. Allows you to determine treatment tactics for gastritis, ulcers, duodenitis, etc. Source: P.L. Shcherbakov, A.N. Zablodsky Gastroesophageal reflux disease of children: the role of endoscopy Experimental and clinical gastroenterology, 2014, issue 101, No. 1, pp. 66-73
Diagnostics
At times, it is difficult to clearly diagnose heartburn in young children because they cannot clearly identify their symptoms. At most, a small child will say that his stomach hurts in the upper part.
If your child is showing any symptoms of heartburn or acid reflux, start by visiting your pediatrician. You can contact a gastroenterology specialist. Testing for heartburn caused by acid reflux will depend on the child's age.
- X-ray of the intestines with barium. After the child drinks a chalky liquid containing contrast material (barium), an X-ray of the esophagus, stomach and part of the intestines will be taken;
- endoscopy. With the child under general anesthesia, a small flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) is inserted through the mouth into the esophagus and stomach. This will allow the doctor to look at these areas and take a tissue sample (biopsy) if necessary;
- esophageal pH probe. The doctor inserts a thin, flexible tube through the child's nose and into the esophagus to check the level of acid in the esophagus;
- study of the work of peristalsis. After the child drinks milk containing a specific radioactive material, the doctor uses a camera to monitor the movement of the substance through the digestive tract.
Methods for treating heartburn in children
Parents first of all think about what they can give their child for heartburn in order to quickly relieve the symptoms. However, therapy is more complicated. It includes taking medications, diet, and lifestyle changes.
Drug treatment
If the problem cannot be solved by diet and proper eating habits, the doctor may prescribe the following to the child:
- antacids – acid neutralizers;
- drugs that reduce the production of gastric juice;
- agents that stimulate the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter;
- Prokinetics – drugs to normalize the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract.
Diet
The simplest home remedies are:
- to drink a lot of water;
- drink a glass of cold milk;
- eat cold food and even ice cream.
You need to eat fractionally - 4-5 times a day in small portions. From the child’s menu you need to exclude everything that provokes heartburn:
- fatty, fried, sour, smoked;
- sauces, hot seasonings;
- soda, strong tea and coffee;
- chocolate;
- tomatoes and citrus fruits;
- citrus fruit juices;
- onion;
- sour cream, cottage cheese;
- yeast baked goods.
The following will be useful: lean boiled meat, porridge, steamed vegetables, low-fat dairy products, bananas, apples, rice and oatmeal, potatoes, cabbage, fish and poultry, eggs, white bread, mineral water.
Food can be baked, boiled or steamed.
Some nutrition rules
- After feeding, the baby should be kept in an upright position for about 30 minutes.
- Leafy vegetables and milk help well.
- You need to eat often and in small portions.
- After eating, do not lie down for 30-45 minutes.
- Sleep on a high pillow.
- Don’t overeat, don’t eat in a hurry and “on the go.”
- Chew your food well.
Appearance in pregnant women
During pregnancy, women may experience heartburn attacks at different times. If a burning sensation occurs in the early stages, the reason lies in hormonal changes in the body and changes in taste preferences, which are often quite unexpected. If the burning sensation appears in the later stages, this process is caused by compression of the internal organs by the growing fetus. At the same time, the level of the hormone progesterone increases, which relaxes the muscles to prepare the body for childbirth.
The main reason for heartburn in pregnant women is the physiology during this period. The burning sensation occurs due to the reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus, which enters through a loosely closed flap valve. If the sphincter is tightly closed, high intra-abdominal pressure will be created, which will adversely affect the growth of the uterus
But a pregnant woman should be treated for heartburn carefully, preferably with herbal preparations. Folk remedies are more suitable
What is the danger of the disease without treatment - the main complications
The main danger is the disease that caused heartburn. He definitely needs to be found and cured. And reflux itself is dangerous, since with prolonged exposure to acid on the esophagus, esophagitis, an inflammatory disease, can develop. A chronic inflammatory process can cause mucosal degeneration and cancer.
Erosion and peptic ulcers may form, which lead to bleeding. In some cases, narrowing of the esophagus (scar strictures) appears, which does not allow food to be taken normally - it is difficult to swallow.
Complications
Increased acidity, heartburn, reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus leads to pathological processes in the digestive organs, oral cavity, lungs, and respiratory organs.
- Gastritis;
- Gatroduodenitis;
- Reflux esophagitis;
- Bulbit;
- Barrett's esophagus;
- Intestinal inflammation;
- Dry cough;
- Caries;
- Inflammation of the gums;
- Esophageal strictures;
- Cancer;
- Hiccups;
- Hoarseness of voice;
- Tonsillitis;
- Glossitis.
Ignoring heartburn results in hiccups, nausea, stomach pain, vomiting, bloating, diarrhea or constipation.
Preventive measures
The child must change lifestyle and eating habits:
- do not lie down after eating, do not bend over;
- sleep on a high pillow;
- do not wear tight clothes, belts, corsets;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- lose weight;
- do not overeat;
- eat warm food, not hot or too cold;
- do not overeat at night - the last meal should be 3-4 hours before bedtime;
- give up spicy, fried, fatty foods, marinades, sour vegetables and fruits;
- do not drink strong tea, coffee, fruit drinks, sour juices;
- do not take medications that cause heartburn.
Sources:
- N.V. Lyarskaya. Modern aspects of the etiology, pathogenesis and clinic of gastroesophageal reflux disease in children // Bulletin of VSMU, 2008, vol. 7, no. 2.
- P.L. Shcherbakov, A.N. Zablodsky. Gastroesophageal reflux disease of children: the role of endoscopy // Experimental and clinical gastroenterology, 2014, issue 101, No. 1, pp. 66-73.
Vostrikova Ekaterina Borisovna Clinic
Author of the article
Vostrikova Ekaterina Borisovna
Specialty: gastroenterologist
Experience: 13 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment
Treatment of heartburn in children includes several methods. First, you need to organize your daily routine so that you have full sleep at night and short sleep at lunchtime.
Nutrition is important for a baby’s health, and only well-chosen foods can be easily digested and not cause discomfort. Therefore, the child’s menu should not contain a lot of sweet, spicy, fried, sour and fatty foods. You should not drink carbonated drinks. Medicines and traditional medicine help.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment with a gastroenterologist, therapeutic and diagnostic, primary, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Consultation with prescription of a treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound of the abdominal organs | 2900 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the retroperitoneal space (and retroperitoneal lymph nodes) | 1400 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the gallbladder | 1400 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound of the abdominal organs | 2900 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the liver | 1600 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the spleen | 1600 rub. |
| Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection (HELPIL test) | 1200 rub. |
| Colonoscopy | 5050 rub. |
| Biopsy during endoscopic examination (1 biopsy) | 1000 rub. |
| Body composition assessment - bioimpedance analysis | 2150 rub. |
| Body composition assessment - repeated (bioimpedance analysis) | 1750 rub. |
| Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EFGDS) | 3050 rub. |
Symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease in infants
GER is very common in the first year of life. If GER symptoms worsen or do not go away after 18 months, take your child to the doctor.
The above symptoms, in addition to heartburn, can be caused by other diseases. If your child experiences any of these, you should see a doctor.
- Coughing up or vomiting;
- The child does not grow or gain weight;
- Refusal to feed or problems feeding;
- Irritability or fussiness during or after feeding;
- Arching your back or other movements during or after feeding;
- Regurgitation or bloody vomiting;
- Breathing problems;
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Recurrent pneumonia and other respiratory diseases;
- Apnea or blue skin (so-called cyanosis, cyanosis);
- cough or wheezing;
- Hoarseness;
- Anxious sleep;
- Excessive baby crying.