Types of diarrhea
Watery. The watery structure of stool indicates a bacterial, viral or toxic lesion. At the initial stages, no other symptoms appear, but as it develops, an allergic reaction to food, jumps in blood pressure (both down and up), dysbacteriosis, lack of vitamins and stress instability occur. If it is watery, it is forbidden to eat sweet, dairy and salty foods. You should not eat vegetables and fruits raw.
Bloody. This species is characterized by the presence of bloody clots in the feces. The cause may be infection with various types of pathogenic microorganisms, as well as the presence of serous diseases.
Based on the mechanism of development, diarrhea after eating can be of the following types:
- the invasive type develops against the background of infection of the gastrointestinal tract;
- osmotic diarrhea occurs due to enzymatic deficiency (the mechanism of water absorption by the intestines is disrupted);
- motor – appears against the background of severe intoxication of the body (intestinal walls contract too intensely);
- secretory - indicates inflammatory processes in which an excessive amount of mucous exudate and fluid is produced in the intestines.
If you do not seek qualified help in a timely manner, any type of diarrhea becomes chronic.
Diarrhea after fried foods, why diarrhea appeared after fried and fatty foods
Fried foods contain a huge amount of fats that take a long time to digest. At the same time, the liver receives a large load, and it does not have time to produce the required amount of bile acids. The pancreas also suffers from this, as it does not have time to produce many pancreatic enzymes. Eating fried foods for a long time will result in the gastrointestinal tract being unable to digest the food. Fried foods are higher in calories. If you abuse it, then over time you may develop diseases of the heart and its blood vessels and become overweight. Also, as a result of the frying process, oil releases chemicals that have a large number of harmful properties. They irritate the walls of the stomach, damaging its mucous membrane. As a result, diarrhea is guaranteed.
Causes of occurrence in adults and children
Diarrhea can occur at any age, even immediately after birth. Diarrhea after eating occurs due to increased bowel activity. This condition develops for a variety of reasons - both ordinary stress and serious illnesses.
Poisoning and infection most often occur in childhood, since due to their young age the child is not able to observe the rules of hygiene and distinguish fresh foods from spoiled ones.
Food poisoning
Food poisoning is possible due to spoilage and poor quality. Poisoning also occurs against the background of infection by bacteria, which, after entering the body, quickly multiply and release waste products that are localized in the blood fluid. Pathogens penetrate through dirty hands, which a person uses to eat or prepare food that has not undergone heat treatment.
Food poisoning is accompanied by the following specific symptoms:
- fever;
- chronic fatigue;
- headache;
- increased sweat production.
When poisoning reaches an advanced stage, more severe symptoms occur:
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- increased heart rate and pulse;
- blood is found in feces and vomit;
- severe pain in the abdominal area;
- the patient begins to delirium.
Pancreatitis
With pancreatitis, the pancreas becomes inflamed, after which it stops producing enough of the required amount of enzymes. Against this background, carbohydrates, proteins and fats are not broken down, which is why peristalsis accelerates. Diarrhea occurs approximately 30-90 minutes after eating.
Feces are characterized by an unpleasant pungent odor, mushy consistency, and a gray tint. The peculiarity is the presence of fatty particles. Symptoms: girdling pain in the upper abdomen, flatulence.
Irritable bowel syndrome
This disease is characterized by a psychosomatic cause - stress, anxiety, quarrels, heightened emotions, etc. Due to disorders in the nervous system, the intestines do not function properly. But there may be other causes of irritable bowel syndrome: lack of exercise, PMS, etc.
How it manifests itself:
- mucous structure of feces;
- Symptoms appear exclusively during wakefulness.
Acute intestinal infections
Infection with bacteria and viruses of various etiologies through food and water. Against this background, inflammatory processes occur, the mucous membranes are damaged, peristalsis accelerates and the absorption process is disrupted. Special features:
- diarrhea occurs after every meal;
- the presence of purulent and bloody exudate;
- severe pain syndrome.
Dysbacteriosis
With dysbacteriosis, the microflora in the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted. Most often it occurs while taking certain groups of drugs and with poor diet. How to recognize:
- frequent change from diarrhea to constipation;
- unpleasant odor of feces and from the oral cavity.
Enteritis
This disease includes a series of inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the small intestine. It appears as follows:
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- nausea.
Feature – symptoms worsen after 12 noon. This is a period of active work of the digestive system.
Colitis
With colitis, the large intestine is affected, as a result of which food is not digested, and carbohydrates, fats and proteins are absorbed very poorly. Specific symptoms:
- immediately after eating there is pain in the abdomen;
- there is blood or pus in the stool;
- liquid structure.
Helminthiasis
When worms enter the body, the gastrointestinal tract organs cease to function normally. This is due to the fact that helminths eat all the beneficial substances. Additional signs:
- lethargy;
- itching near the anus and inside the anus;
- an irresistible desire to eat sweets;
- salivation during sleep;
- teeth grinding at night;
- peeling of the skin.
Other reasons
Also, diarrhea immediately after eating occurs for the following reasons:
- Diseases of the gallbladder and liver disrupt the digestion process, as fats are not broken down. Specific signs are yellowness of the skin and whites of the eyes, darkening of the urine, and white stool.
- Food allergies, in other words – intestinal asthma. After consuming foods to which the body is hypersensitive, diarrhea occurs after eating, which is accompanied by a skin rash.
- Diabetes mellitus and thyroid disorders.
- Enzyme deficiency occurs due to a disruption in the process of their synthesis.
- Taking certain groups of drugs.
Types of diarrhea that appears immediately after eating
To accurately determine what type of disease causes diarrhea, you should pay attention to the characteristics of feces. It matters what color and consistency the stool has, as well as how often diarrhea occurs immediately after eating in an adult.
Types of chair:
- Fatty, sticky stools interspersed with fat . Indicates impaired digestion of food, liver dysfunction. At the same time, it can pull and hurt in the right side.
- Watery, frequent stools. As a rule, green in color, with an unpleasant pungent odor, foamy. Develops during bacterial and viral infections. Can lead to rapid dehydration.
- Pasty stool with pus and bloody streaks . It can develop with the growth of tumors in the rectum, dysfunction of the large intestine.
- White liquid stool . Such diarrhea develops due to overeating, poisoning, excessive alcohol consumption, and stress. In this case, nausea and vomiting appear, and the patient may complain that his stomach hurts.
- Black stool, tarry . May appear in diseases of the stomach accompanied by internal bleeding.
- Foamy yellow stool . Occurs due to dysbacteriosis and intestinal infections. At the same time, pain in the lower abdomen and headaches appear.
With gallbladder diseases, diarrhea and nausea can be replaced by prolonged constipation. Patients with such pathologies complain of a bitter taste in the mouth, suffer from heartburn and abdominal pain.
Associated symptoms
Concomitant symptoms of diarrhea after eating depend on the cause of its occurrence, but there are also general symptoms that indicate a pathological etiology of origin:
- weakness;
- heartburn;
- nausea and sometimes vomiting;
- belching (may be sour or rotten-tasting);
- pain in the stomach and head;
- dizziness;
- feeling of heaviness and bloating;
- decrease or, conversely, increase in appetite.
Why is diarrhea immediately after eating dangerous?
Diarrhea washes away minerals and trace elements, so the following problems arise:
- bowel irritation;
- hypovolemia;
- pathological disorder of microflora;
- anal fissures and subsequently hemorrhoids;
- ulcers and fistulas in the anus and rectum;
- hidden hunger syndrome, which leads to unnatural thinness (anorexia);
- diaper rash in the perianal folds;
- infection of the body;
- dehydration leading to death.
The main causes of diarrhea after eating
Proper nutrition is the key to a healthy intestine.
If frequent loose stools are observed immediately after eating, this indicates functional disorders in the intestines: the food bolus quickly moves through the gastrointestinal tract, while the food is not properly digested and absorbed.
There may be several reasons for this condition:
- Disorders of the nervous system. This condition is known as “bear sickness” or irritable bowel syndrome. The patient may encounter it during a period of prolonged stress; for example, the syndrome may occur in students during a session. Neurogenic diarrhea is usually only part of a complex of symptoms; prolonged stress can lead to vegetative-vascular dystonia and various neuroses.
- Infectious intestinal lesions. This is a more drastic, but possible reason: the body seeks to empty the intestines of food that it considers dangerous. To eliminate a painful condition, it is necessary to cope with its cause using medicinal methods.
- Dysbacteriosis. This is a disorder of the intestinal microflora, which can develop after long-term use of antibiotics or a violation of the diet. If the body is unable to digest food, it tends to get rid of it, which can lead to diarrhea.
Read: Diarrhea during pregnancy: treatment of a dangerous condition
Intestinal upset can also result from eating unusual or spoiled food. In this case, it lasts no more than 1-2 days, and if the process does not stop, you should consult a doctor.
Diarrhea not only brings discomfort and interferes with everyday life: frequent loose stools lead to dehydration and the leaching of essential microelements such as magnesium and potassium. It is especially dangerous for children, so young patients need to be taken to a doctor as quickly as possible.
When should you see a doctor?
Few people go to the hospital with diarrhea, mistakenly believing that the problem can be resolved on their own. In fact, you need to contact a specialist in the following situations:
- with a frequency of bowel movements more than 5-7 times a day;
- if loose stools do not go away for a long time (5-7 days);
- watery and mucous structure;
- the presence of purulent and blood particles;
- increased body temperature;
- lack of results after taking medications;
- nausea and vomiting.
Diagnostic methods
A qualified doctor will always help with treatment.
How to determine when it's time to see a specialist? First of all, you need to pay attention to the nature of the disease. If there is no pus or blood in the stool, this indicates the absence of serious intestinal damage.
If it has a greasy appearance and a strong unpleasant odor, this is a sign of the presence of fat in the stool, that is, the digestion of food is not completed. The doctor will ask the patient in detail about the frequency of bowel movements, the appearance of urges at night, and the diet.
Signs of infection will include fever, bloating, nausea, and deterioration in general health. If an intestinal infection is suspected, the doctor may suggest hospital treatment to prevent infection of others.
A series of tests will be prescribed to confirm or deny the presence of infection. Much more often, the cause of constant diarrhea is a nervous disorder, thus the body reacts to prolonged overexertion.
In this case, the urge is observed in the morning immediately after breakfast and in the afternoon after meals, and at night the patient sleeps peacefully, without feeling any discomfort. Blood and stool tests do not reveal any signs of infection or other bowel problems.
The most effective treatment method in this case will be to eliminate the cause of stress: as soon as the state of the nervous system normalizes, all somatic manifestations of nervous disorders will go away by themselves.
Read: Yellow diarrhea in a child: causes, symptoms and treatment of pathology
However, the diagnosis of “neurogenic diarrhea” can be made only after all studies confirming the absence of dysbacteriosis and infectious diseases. It is quite difficult to diagnose this condition in children: they are often embarrassed to talk about the problem, and problems with studying or communicating with peers can lead to severe manifestations of a nervous disorder.
Diagnostics and necessary tests
During the initial visit to the clinic, the therapist collects anamnesis. That is, he asks the patient about accompanying symptoms, the nature of diarrhea, past and present diseases. The doctor visually feels the abdominal area, measures the pulse rate and blood pressure. Next he will refer you for diagnostic measures:
- Blood sampling for a general examination, which will reveal hormonal imbalance and the inflammatory process.
- Submission of stool for laboratory examination for the level of leukocytes, mucus and other inclusions. The epithelium, fatty acids, the presence of helminths, viruses, and bacteria are studied.
If it is discovered that the cause lies in serious diseases, an additional instrumental examination and blood collection for biochemical analysis are carried out.
Treatment of single and chronic diarrhea
Diarrhea can develop into a chronic stage, when a person suffers from diarrhea constantly. In this case, the therapy is slightly different from the methods of treating single manifestations of loose stools.
Single diarrhea:
- taking sorbents;
- a gentle diet for a week;
- hydrating preparations (restore water and salt balance).
Chronic form:
- sorbents and hydrating agents;
- antidiarrheal drugs;
- sedative medications;
- anthelmintic drugs;
- probiotics;
- strict diet and water intake.
Medicines
Drug therapy is mandatory - it must be aimed at achieving several goals:
- To normalize the water-salt balance, hydrating agents – Regidron – are prescribed.
- To remove toxic deposits and other harmful substances from the body, sorbents are needed: Enterosgel, activated carbon.
- Antidiarrheal medications will help stop loose stools: Imodium, Lopedium.
- If the cause lies in a bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed. The specific drug is selected primarily by the attending physician.
- In case of helminthic infection, antiparasitic therapy will be needed: Dekaris, Pirantel.
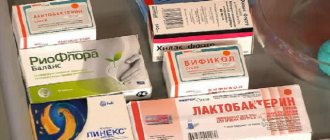
- To restore the microflora, you will have to take enzyme medications: Bifiform, Linex.
- Since prolonged diarrhea often disrupts the psycho-emotional background, sedatives are prescribed: Novo-Passit, Lotusonic, motherwort or valerian tincture. This group is also needed for neurotic type of diarrhea.
Nutrition
If you experience diarrhea after eating, you should immediately think about changing your diet. Use a menu that will reduce the burden on the gastrointestinal system. Basic adjustment rules:
- You should eat food in small portions.
- The interval between doses is 4 hours.
- Don't eat solid foods. It should be semi-liquid.
- Be sure to keep food warm.
- Avoid fried, fatty, salty, sweet, spicy, smoked foods. Remove seasonings completely; they irritate the intestinal mucosa.
- Avoid eating foods that cause gas and fermentation. These are cabbage, radishes, beans, confectionery and butter products. Eat apples only when baked.
- After eating, drink a cup of strong tea.
- Replace bread with crackers.
Water mode
If you have diarrhea, you must stay hydrated. To avoid dehydration, you should drink plenty of fluids. If you have not found any medications at home that will stop diarrhea, use the following recipe. The solution is taken after using the toilet. Heat the water (up to 40°), add salt (a teaspoon), 0.5 tsp. soda and 3 tsp. Sahara. Mix and take 200 ml.
In addition, you can drink mineral water - Narzan, Borjomi, Essentuki. Consumption of tea, jelly or decoctions of medicinal herbs is allowed. The minimum amount of water is 2-3 liters.
Prohibited drinks:
- sparkling sweet water;
- alcohol;
- kvass;
- juices (grape, tomato, pineapple, peach);
- cocoa, coffee, milk and green tea.
Folk remedies
To treat bouts of diarrhea, you don't have to take only medications. Additionally, you can use folk recipes:
- Boil rice in plenty of water. Pour the remaining liquid into a glass. Add 10 grams of chopped ginger. Take during regular attacks of diarrhea.
- A decoction of oak bark and St. John's wort. 2 tsp. Brew each component in 200 ml of “steep” boiling water. Time to insist. Strain. Dosage: 50 ml three times a day.
- Blueberry jelly. Rub fresh berries through a fine sieve. Pour in 400 ml of water. Put on fire and cook for 20 minutes. Then add a tablespoon of starch. Mix thoroughly so that no lumps form. Cook for another 3 minutes and cool. Drink 5 times a day, 0.5 cups.
- Bird cherry. Pour a glass of “steep” boiling water into a container, where you should first add a tablespoon of the dried component. Cook in a steam bath for no more than 20 minutes. After this, the broth is cooled and filtered. Take 1/4 cup 3 times a day.
- Finely chop the pomegranate peel. Place it in boiling water (400 ml). Leave for 25 minutes. Take a tablespoon on an empty stomach.
Treatment
If diarrhea occurs once, it is enough to carry out therapy aimed at detoxifying the body.
A diet that includes eating bland food will also help normalize your health. Taking Regidron will restore the water-salt balance that was disturbed by diarrhea.
If diarrhea occurs repeatedly after eating, more thorough treatment is necessary. Depending on the reasons, they prescribe:
- Anthelmintic drugs (Dekaris).
- Sorbents (Enterosgel).
- Sedatives (Novo-Passit).
- Hydrotaring agents (Regidron).
- Drugs aimed at normalizing intestinal function (Bifiform).
A prerequisite is compliance with the diet. For diarrhea, you need to eat soups that are prepared in low-fat broth, drink enough liquid (water, dried fruit decoction, tea).
Eating should be regular, at intervals of several hours.
Sample menu for a person suffering from diarrhea and poisoning:
- Breakfast : boiled fish with rice porridge, rosehip infusion.
- Second meal : a cup of tea and a baked apple.
- Lunch : rice soup (can be with meatballs) and compote.
- Afternoon snack : jelly.
- Dinner : buckwheat porridge with chicken meatballs, herbal tea.
Important! A proven remedy for treating diarrhea is rice water.
Before each meal, you need to drink half a glass of the broth that remains after cooking rice cereal. If you have diarrhea you should avoid taking :
- dairy products;
- confectionery products;
- legumes;
- pickles;
- citrus fruits;
- fatty foods (meat, butter, lard);
- alcohol and soda.
The above products irritate the intestinal mucosa and contribute to the occurrence of gases and fermentation in the body.
Diarrhea after eating that lasts more than two days requires consulting a doctor.
Preventive measures
A large percentage of the likelihood of diarrhea increases in the summer. To prevent this from happening, you should follow the following preventive rules:
- Wash your hands as often as possible before eating. Also after visiting any crowded places. If it is not possible to use soap, purchase special antibacterial agents (sprayers).
- Wash food under water. It is advisable to pour boiling water over them.
- Don't buy ready-made meals sold on the street. If you come to the beach, refrain from buying food (pies, corn, etc.).
- Store perishable foods strictly in the refrigerator.
- Keep an eye on the expiration date.
- Before placing store-bought eggs in the refrigerator, they must be washed to remove any remaining chicken feces.
- When preparing food, make sure it is cooked or cooked through.
- Observe the proximity of products. Do not place raw foods next to prepared foods, especially those with mayonnaise or sour cream.
- Don't drink tap water. Consume quality liquid.
- Wash kitchen utensils under hot water using detergents. Also rinse thoroughly under running water.
If you notice diarrhea immediately after eating, which does not go away for a long time, go to the clinic immediately. This will allow you to timely identify the cause and quickly get rid of the problem. Modern medicine will allow you to do this in the shortest possible time.
Previous entry How to take Furazolidone for diarrhea?
Next entry How to deal with diarrhea due to nervousness and why is it dangerous?
Traditional and medicinal methods of treating functional diarrhea
It is better not to interfere with the cleansing of the body at the first disorder.
What to do if an unpleasant condition takes you by surprise, and the problem has to be solved immediately? There are a number of folk remedies that will help eliminate symptoms of diarrhea and have a beneficial effect on intestinal health:
- A decoction of oak bark can be used for treatment. It is brewed with boiling water; you can take a glass of the decoction immediately after eating. You can use it twice a day, for example, morning and evening. Usually, a few doses are enough to cope with intestinal dysfunction.
- A simple recipe against diarrhea: regular buckwheat porridge without salt. You need to eat a few spoons of porridge on an empty stomach, and there will be no further problems with diarrhea.
- The following remedy can be used against diarrhea in children: you need to grind one nutmeg, then the resulting powder is dissolved in a glass of milk. The mixture should be given one teaspoon at a time and should be taken every 4 hours.
- Strong tea, acorn decoction and some other folk remedies also have strengthening properties. Among them is an extreme recipe: a teaspoon of salt is dissolved in 100 g of vodka. The product should be taken immediately after meals.
If possible, you should first consult a doctor: diarrhea is one of the body’s defense reactions, and with its help the intestines are cleansed of toxic substances. If this process is interfered with, serious intoxication is possible: diarrhea may be caused by infection or poisoning.
If an intestinal disorder occurs for the first time, it is recommended not to interfere with the cleansing process by providing the patient with warm, generous fluids to prevent dehydration. Taking activated carbon will help, in addition, therapeutic fasting is necessary.
Read: Should you be concerned about frequent bowel movements in a child?
Since the food is not properly digested anyway, eating it repeatedly is like throwing coal into a firebox. Fasting with plenty of fluids is recommended for about 24 hours. If diarrhea is constantly observed at approximately the same time, the patient is not bothered by night urges, but they occur immediately after meals, most likely we are talking about a neurological disorder, and it is advisable to eliminate its cause as quickly as possible.
During periods of stress, the doctor may prescribe sedatives, and in case of prolonged neuroses and severe stress, antidepressants. Diarrhea in this case is only one of the manifestations of the disease, and complex treatment of the nervous system will be required.
You will learn how to treat diarrhea from the video:
Read along with this article:
- Imodium - indications for use - treatment of diarrhea
- Intestinal spasms - causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
- Diarrhea and pregnancy, causes of diarrhea
- Intestinal dysfunction: causes and treatment of the disease, as well as...
- Feeling of nausea, its types and causes
- Symptoms and treatment: intestinal adhesions
- Popular anti-diarrhea remedies
- Mucus in a child's stool - why it might appear
- Loose stools in a 2-year-old child: how to treat, is there a risk of complications?