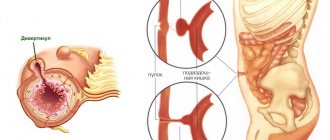
All organs in the human body have a certain arrangement. The digestive system is no exception - any change in the location of organs in it leads to deterioration in health.
One of the possible pathological conditions is intestinal prolapse. In this situation, the intestinal loops are located below the required level. Such an anomaly entails a change in the location of other abdominal organs, which leads to disruption of their function.
Prolapse of the intestine: symptoms and treatment is the topic of this article.
Omission
Main causes of pathology
Intestinal prolapse is a disease that appears during fetal development or throughout life. In modern medicine, the diagnosis has its own code according to ICD 10 - K63.4 - enteroptosis.
During life, such a disorder is formed against the background of improper body composition. In other cases, pathology occurs as a consequence of a number of factors that reduce the tone of the abdominal muscles and weakening of the ligaments that support the intestines. The conditions that contribute to the occurrence of the disease are:
- abdominal surgery,
- unhealthy diet, preference for fatty, fried foods,
- difficult labor, negative consequences or dangerous complications after childbirth,
- pronounced excess weight,
- several pregnancies in a row, in this case the likelihood of a decrease in muscle strength increases, the uterus puts a lot of pressure on the intestines,
- hypodynamia, that is, a sedentary lifestyle, ignoring physical activity, a sedentary lifestyle,
- a strict diet that involves rapid weight loss,
- mechanical effect on the organs of the digestive system,
- severe diseases of the respiratory system: pleurisy or emphysema - such pathologies occasionally lead to prolapse of internal organs,
- Gastrointestinal diseases: colitis, inflammation in the gallbladder, hemorrhoids, dolichosigma,
- heavy physical labor, intense strength training, weight lifting.
Causes of development
The success of further therapy largely depends on identifying the cause. Symptomatic treatment does not provide long-term results and can lead to relapse.
Treatment methods
There are different treatment options available for colon cancer. The doctor chooses the optimal tactics, depending on the stage of the malignant tumor, its location, the general condition of the patient, the presence of certain complications, and concomitant diseases. They perform surgical interventions, use different types of antitumor drugs, and conduct courses of radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy for malignant tumors of the colon can have different goals:
- Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is given before surgery to shrink the tumor and make it easier to remove.
- Adjuvant chemotherapy is given after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- as the main treatment method for advanced stages of cancer for palliative purposes.
For malignant neoplasms of the colon, different types of chemotherapy drugs are used: capecitabine, 5-fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, irinotecan, trifluridine/tipiracil (combination drug). Most often, two or more drugs are used simultaneously, this helps to increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Targeted drugs have a more targeted effect compared to classical chemotherapy drugs: they are aimed at specific target molecules that help cancer cells multiply uncontrollably and maintain their vital functions. Most often, two groups of targeted drugs are used for malignant intestinal tumors:
- VEGF inhibitors are substances that cancer cells use to stimulate angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels). This group includes: Ziv-aflibercept (Zaltrap), Ramucirumab (Ciramza), Bevacizumab (Avastin). They are used for advanced colon cancer, administered intravenously every 2 or 3 weeks, usually combined with chemotherapy.
- Inhibitors of EGFR , a receptor protein that is found on the surface of cancer cells and causes them to multiply uncontrollably. This group includes drugs such as Cetuximab (Erbitux), Panitumumab (Vectibix). EGFR inhibitors are administered intravenously once a week or every other week.
In some cases, drugs from the group of checkpoint inhibitors . They block molecules that prevent the immune system from recognizing and attacking cancer cells. This group of drugs includes: Pembrolizumab (Keytruda), Nivolumab (Opdivo), Ipilimumab (Yervoy). They are usually used for inoperable, metastatic cancer, when chemotherapy is ineffective if there is a relapse.
In order to figure out which drugs will be effective in a particular patient, you need to understand what properties cancer cells have, what mutations have occurred in them, and due to what substances they have acquired the ability to reproduce uncontrollably. Molecular genetic analysis helps with this - compiling a “molecular portrait” of cancer. Thanks to our cooperation with leading foreign laboratories, such a study can be performed at the European Clinic. We know how to increase the effectiveness of antitumor treatment and what to do if it stops helping.
Surgery
In some cases (stage 0, cancer in situ; sometimes stage I), colon cancer can be removed during a colonoscopy. Unfortunately, this opportunity is rarely available. Most often, you have to perform a colectomy - partial or complete removal of the colon. The extent of surgical intervention depends on the location and size of the tumor. Typically, at least 12 nearby lymph nodes are removed at the same time. The remaining ends of the intestine are sewn together and an anastomosis .
Colectomy can be performed openly (through an incision) or laparoscopically (through punctures in the abdominal wall).
Sometimes the anastomosis cannot be performed immediately. In such cases, a temporary colostomy or ileostomy - a section of the colon or ileum is sutured to the skin and an opening is created for the passage of stool. The stoma is subsequently closed.
If the tumor blocks the intestinal lumen and cannot be removed, a permanent colostomy is performed. Intestinal patency can be restored using a stent - a metal frame in the form of a hollow cylinder with a mesh wall. Such operations are called palliative : they are not aimed at removing cancer, but at combating symptoms and improving the patient’s condition.
Surgeons at the European Clinic perform various types of radical and palliative interventions. The specialists in our endoscopy department have extensive experience in installing stents in the intestine, bile ducts and other hollow organs. The Department of Interventional Surgery performs radiofrequency ablation and chemoembolization for liver metastases.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy may be given before ( neoadjuvant ), after ( adjuvant ) colon surgery, or as the primary treatment for metastatic cancer to control symptoms.
When radiation therapy is combined with chemotherapy, the treatment is called chemoradiotherapy .
Symptoms of bowel prolapse
As a rule, when the disease is detected, prolapse of the rectum or various parts of the large intestine (colon) is diagnosed. The disease occurs in both adults and children. In a child, prolapse is a congenital anomaly.
The pathology has a fairly clear clinical picture. The list of symptoms includes:
Pain in the peritoneum
Gender characteristics are also distinguished: in men the number of urges to urinate increases, women are characterized by increased pain during menstrual periods.
In the absence or improper treatment, the pathology quickly progresses, the symptoms become more pronounced, and there is a risk of complications.
Symptoms
Manifestations of colonoptosis can be very roughly divided into local and general.
Local signs
These are all the symptoms associated with a violation of the movement of the food bolus:
- bloating caused by interruption of food passage;
- flatulence or excessive gas production;
- constipation that cannot be treated with conventional remedies;
- abdominal pain, somewhat relieved in a horizontal position;
- urinary disorders and even inflammation of the urinary organs due to compression.
Be sure to read: What is anoscopy and how is it performed?
Bloating and constipation impair digestion of food, and patients may lose weight due to refusal to eat. Concomitant inflammation of the digestive canal is common.
General signs
These are signs of fecal intoxication due to untimely removal of decay products, as well as disturbances in other organs:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- headache;
- weakness;
- decreased appetite and mood;
- phlebeurysm;
- haemorrhoids;
- menstrual irregularities in women and prostatitis in men.
What should be examined if a disease is suspected?
Intestinal prolapse can occur in any part of this organ, so during the examination it is necessary to examine all sections.
- Colon. If the disease affects this area, then in medicine the pathology is called “coloptosis” or “colonoptosis”. The rectum, cecum, colon, and sigmoid colon are areas that can be affected by disease in the large intestine.
- Small intestine: jejunum, ileum and duodenum. This disease is several times less common than colon prolapse.
In addition, there are concomitant pathologies - gastroptosis, prolapse of the stomach.
Important! In the absence of qualified treatment, rectal prolapse may occur and intestinal function may be impaired.
Diagnosis of the disease in patients
The patient may suspect organ prolapse based on the presence of the symptoms described above. But only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis after collecting all complaints and prescribing laboratory procedures. When visiting a therapist or gastroenterologist, a preliminary diagnosis will be made after an in-person examination.
Such control is as follows:
- the patient is diagnosed with a saggy belly even if he has normal weight;
- having placed the patient on the couch, the doctor notices clear beats in his abdominal aorta, which indicates retraction of the intestine in the upper part of its base;
- if the doctor slightly pulls the abdominal cavity upward, the pain in the digestive tract completely disappears or weakens;
- the patient is accompanied by prolonged pain, which may intensify after physical activity and after eating food;
- when palpating the peritoneal area, the doctor determines a clear displacement of the gastric pylorus and feels a bulge in this area.
After an in-person examination, the manipulations described in the table are prescribed.
Table 1. Diagnostic methods
| Diagnostics | Its essence | How do they do it? |
| Gastric juice analysis | Determines the amount of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. When problems arise, reduced acidity is observed. | On an empty stomach, using a soft pipe of 4-5 mm. It is left for 1-2 hours directly in the stomach and taken every 15-20 minutes. The probe can be inserted through the mouth or nose if the gag reflex is severe. |
| Irrigoscopy | This is done to determine the degree of intestinal displacement and to identify any violations that have occurred due to this. | The patient is injected with contrast through the rectum and a photo is taken in a position on his side, lying on his stomach. At the end, a double contrast is made using the previously introduced substance and air to identify ulcers and neoplasms. |
| Colonoscopy | It is used to assess possible disorders and the current state of the mucosa, to determine the intestinal lumen and to collect material for biopsy. | The patient lies on his left side with his legs crossed. The doctor lubricates the patient's anal area and inserts an endoscope, slowly moving it along the intestines to assess his condition. |
Attention! If a patient has contraindications to colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy is used to assess bowel function.
What diagnostic methods are used?
One of the important stages in making a diagnosis is conducting diagnostic studies.
At the first appointment, the doctor collects anamnesis and clarifies the identified symptoms. Based on the data obtained, he prescribes subsequent diagnostic procedures.
When detecting bowel prolapse, the following is used:
Ultrasound
When conducting diagnostics, you can determine the extent to which the organ has descended and whether there are any changes in the abdominal cavity. Only after this stage can effective therapy be developed.
It is important to note that making such a diagnosis on your own is impossible. The therapeutic prognosis depends on the timeliness of seeking help.
Treatment of dolichosigma
After identifying the pathology, the patient is registered with a gastroenterologist, who prescribes a diet according to the examination indications and drug treatment. In case of acute manifestations of symptoms, the doctor may prescribe treatment in a hospital.
What is the treatment?
During drug treatment, the specialist prescribes the following drugs to the patient:
- Prozerin (injection);
- Dibazol (two-week courses with breaks of 1-2 months);
- B vitamins;
- Preparations aimed at improving intestinal microflora;
- Antispasmodic drugs to relieve pain;
- Abdominal massage courses.
After completing a course of medication, the patient is recommended to undergo additional rehabilitation treatment in a sanatorium, but this treatment option has a positive effect only in the early stages of the development of the pathology; in cases of progressive disease, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Surgical intervention for the formation of intestinal loops
Indications for surgery are based on the patient’s condition, as well as on the findings of the study of the course of the disease.
Surgery is prescribed to the patient only for persistent constipation that lasts more than a month, as well as in cases of progress in increasing the intestinal lumen and when conduction damage is detected at the neuromuscular level.
In cases where there is no positive reaction to medications, when the intoxication process threatens the patient’s life, this is also an indication for surgical intervention.
Patients with dolichosigma must adhere to all the instructions of the attending physician: the prescribed drug therapy and diet aimed at eliminating the possible causes of the disease and treating the patient.
Treatment course in the fight against pathology
Intestinal coloptosis: symptoms and treatment is a relevant topic for many, since most often the disease affects the large intestine. However, regardless of where exactly the violation occurred, the treatment complex has an identical focus and principles.
Treatment of the disease involves the use of surgery only when conservative therapy does not bring the desired result. Surgery may be prescribed if there is a disruption in blood flow and intestinal obstruction develops.
Taking medications
In most cases, treatment involves a combination of several mandatory areas: special gymnastics, normalization of the diet, taking medications, physiotherapeutic procedures and the use of a bandage.
Treatment
Conservative and surgical methods are used, their combination is determined by the doctor.
Conservative treatment
The main task is to restore motor skills and normalize the movement of food, eliminate bloating and constipation. For this purpose, diet, medications, bandages, and physical therapy are used.
Diet
Products that enhance peristalsis are used:
- containing a lot of fiber or dietary fiber - bran bread, raw vegetables and fruits, legumes, nuts, coarse cereals (barley, barley);
- containing organic acids - lactic acid, naturally pickled vegetables, sour juices and fruit drinks;
- sweet dishes;
- meat of old animals containing a large amount of connective tissue;
- carbonated drinks;
- dishes served cold - okroshka, beetroot soup, aspic, ice cream - which stimulate peristalsis due to temperature.
Be sure to read:
Rectum: sections, structure, functions and diagnosis of the organ
Food should be large in volume, but low in calories. It is useful to eat dishes of contrasting temperatures. Losing body weight and regularly filling the intestines with rough foods helps eliminate constipation.
Medicines
Laxatives are used only as prescribed by a doctor for a short course.
They cannot be used often, as addiction to them quickly develops. Anti-inflammatory agents, enveloping agents, and digestive enzymes may sometimes be used. To improve motor skills, Prozerin is used, a cholinomimetic that improves neuromuscular transmission. After an intramuscular injection, the intestines “come to life” and the condition improves significantly. However, injections must be repeated periodically.
Bandage
This is a medical product whose purpose is to support the abdominal organs. The bandage is an elastic belt, which is selected individually according to size. You need to put it on in bed before getting up, wear it throughout the day, and take it off before going to bed while lying down.
The bandage is most effective for stretching the muscles and white line of the abdomen, which happens after pregnancy and sudden weight loss.
Physiotherapy
Physical exercises are aimed at strengthening the anterior abdominal wall. The movements are something like this:
- from a lying position on your back with a bolster placed under your lower back, lift your straight legs alternately and then together;
- "bike";
- pull your legs bent at the knees towards your stomach and turn your torso left and right;
- from a position on all fours - leaning on your hands, raise your pelvis as high as possible and stand there for several minutes.
Folk remedies
Use decoctions and infusions to reduce flatulence and constipation. The following are used:
- infusion of yarrow and wormwood (pour 2 tablespoons of the mixture with a glass of boiling water, keep in a water bath for 5 minutes, strain, filter, dilute with a glass of boiled water, drink 1-2 tablespoons before meals three times a day);
- dill water - mix cumin, dill and fennel (seeds) in equal parts, pour 1 tablespoon of the mixture with a glass of boiling water, leave for 2 hours, drink 1 sip during the day, drink the entire volume per day).
Be sure to read:
Main symptoms of appendicitis
Surgery
Used in extreme cases, the operation is abdominal and very complex. Its essence is to suture intestinal loops to weakened ligaments with a non-absorbable thread. The complexity of the operation is that there is no guarantee of a return to health - adhesions may form at the site of the threads, and the ligaments may weaken even more.
Due to the large number of complications, surgical treatment is used less and less.
Bandage as a method of therapy
An effective remedy that helps achieve pronounced and quick results. The bandage is used in the treatment of prolapse not only of the intestines, but also of other abdominal organs. Thanks to the bandage, the abdominal muscle is toned, keeping the organs in an anatomically correct position.
The bandage does not interfere in any way with living, doing everyday household chores, or working, since it is selected individually for each patient. However, there is a risk that after removal the organs will prolapse again, so the bandage requires long-term wearing. This direction allows you to avoid transition to the chronic stage.
Bandage
What is dangerous and how does colonoptosis manifest itself?
The development of colonoptosis in the body can lead to the following pathological conditions:
- development of pollakiuria;
- manifestation of enuresis;
- excessive flatulence;
- chronic types of constipation;
- uterine fibroids;
- disruptions in menstrual cycles;
- prostate adenomas;
- problematic pregnancy;
- state of infertility;
- different forms of hemorrhoids;
- varicose veins.
In the early stages of its development, this pathology is practically devoid of symptoms, so identifying it becomes very problematic, especially if a person practically does not visit hospitals and does not suffer from diseases of the digestive system.
With more advanced forms of intestinal prolapse, people complain of:
- frequent bloating;
- excessive manifestations of flatulence;
- private and prolonged constipation;
- aching nature of pain in the pelvis.
Based on the existing manifestations, you should immediately visit a doctor. The clinic will carefully study the existing symptoms, and appropriate treatment will be prescribed.
By the way, it is advisable to treat such a problem under the supervision of an experienced doctor, bypassing the spontaneous use of certain drugs and procedures. You can resort to a folk remedy for getting rid of intestinal problems, but you should first consult a doctor.
Use of physical therapy
Therapeutic physical education helps to strengthen the muscles of the abdominal cavity: transverse, external, oblique and rectus, prevent the development of the disease, and speed up recovery. The treatment complex is selected by the doctor, based on the characteristics of the physique and the nature of the disease.
A popular and effective exercise: lying on a flat surface, arms parallel to the body, and legs performing a movement simulating scissors.
“Cat” - this exercise involves being on 4 points: knees, elbows. The pelvis slowly arches, then returns to its original position. All actions are performed slowly and smoothly.
Therapy using non-traditional methods
Traditional medicine is also used in the treatment of the disease.
Important! Before using traditional methods, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
One of the effective recipes. 10 g of crushed buckthorn bark is poured into 0.3 liters of boiling water. After which the infusion is boiled for 15 minutes, cooled and filtered. An equal amount of water is added to the broth. Then take 100 ml after waking up and before going to bed.
This method allows you to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and eliminate constipation.
Dolichocolon
The choice of therapeutic tactics is made taking into account the clinical form of the disease. For patients with asymptomatic dolichocolon, primary prevention of constipation is recommended - regular physical activity, eating a well-balanced diet and enough water, and not suppressing the urge to defecate. If the transit of feces is disrupted, drug therapy, changes in lifestyle and nutrition, and withdrawal of medications that cause constipation are indicated. To restore the evacuation function of the large intestine, the following are used:
- Means to increase stool volume
. Due to the active binding of liquid by plant and microcrystalline preparations, the intestinal contents soften. The mucous components of medications absorb toxins, preventing their absorption. The increased volume of soft feces activates intestinal peristalsis, which simplifies and speeds up bowel movements. - Osmotic laxatives
. With the help of salt preparations, indigestible carbohydrates (prebiotics) and polyethylene glycol derivatives, it is possible to increase the osmotic pressure in the intestinal lumen and stimulate hydration processes. When fluid enters from the plasma, the intestinal contents soften, which, combined with an increase in the volume of feces, causes defecation. - Prokinetics
. To enhance the motility of the large intestine, herbal remedies, serotonergic agents and myotropic regulators of the contractile activity of smooth muscle fibers are used. The laxative effect of prokinetic drugs is associated with neurohumoral effects. Strengthening the peristalsis of the intestinal wall allows you to accelerate the movement of feces through the elongated intestine.
For persistent constipation, it is justified to supplement therapy with dietary fiber, contact laxatives in the form of suppositories and enemas. Selective antispasmodics and non-narcotic analgesics are indicated for patients with severe pain. Antifoam agents are used to reduce bloating. Drug treatment of dolichocolon is combined with physiotherapeutic techniques - acupuncture, laser therapy and electrical stimulation of the intestines.
In therapeutically resistant forms of the disease with a significant deterioration in the quality of life, surgical methods are recommended for patients - subtotal resection of the large intestine, colectomy with the creation of an ileorectal anastomosis. Surgical treatment of complicated forms of dolichocolon is carried out according to the principles of operating patients with strangulation intestinal obstruction. In case of intestinal volvulus while maintaining the viability of the intestinal wall, endoscopic or laparotomic detorsion is performed; in case of persistent disruption of the blood supply, resection is performed.
Preventive measures
Anatomical characteristics cannot be changed by any person. However, there are several general recommendations that can reduce the risk of developing bowel prolapse. Secondary prevention is especially relevant in the first year after treatment.
Compliance with such recommendations will minimize the risk of developing pathology.