In patients with oncology of organs that have contact with the peritoneum, the likelihood of abdominal ascites occurring is quite high.
What is ascites in essence? It is a complication of various diseases when a lot of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity. The possibility of abdominal ascites occurring in patients with oncology is about 10%.
Remember! The complication of ascites in diagnosed oncology further complicates cancer treatment and worsens the prognosis of the disease.
Leading clinics in Israel
Assuta
Israel, Tel Aviv
Ikhilov
Israel, Tel Aviv
Hadassah
Israel, Jerusalem
What tumors are accompanied by ascites
Fluid accumulation in the abdomen occurs in nearly half of episodes of ovarian cancer in women. Also, cases of abdominal ascites (edema of the abdomen) can occur with neoplasms in:
- Rectum (colorectal cancer);
- Large intestine;
- Mammary glands;
- Liver;
- Stomach and pancreas (also pancreatitis);
- Pelvic organs.
The result of the appearance of ascites complications is a clear deterioration in the functioning of the heart and lungs, cardiac and respiratory failure occurs, and this accelerates death.
Remember! When diagnosing ovarian cancer, the risk of developing dropsy reaches 40% of cases, and 50% of women with such a diagnosis and the presence of a cancerous tumor die from ascites.
Both women and men can develop complications in the form of ascites, it all depends on the presence of the underlying cancer.
Why does fluid accumulate with ascites?
Remember! In more than half of the cases (75%), patients diagnosed with ascites have liver cirrhosis.
This disease creates the largest number of factors that provoke the occurrence of ascites.
These factors include an increase in hydrostatic pressure in the vessels under the influence of stagnation in the venous and lymphatic systems, a decrease in oncotic pressure in the blood (due to liver damage), and a decrease in the level of albumin fraction. Also another provoking factor is hyperfunction of the epithelium of the abdominal cavity (this occurs when the tumor affects the layers of the peritoneum). The development and growth of cancer cells causes nonspecific inflammation. This is how ascites gradually begins, damage to the peritoneal layers by cancer cells provokes the formation of carcinomatosis. In case of uterine and ovarian cancer (especially after stage 3), the role of contamination with cancer cells is great, and the complication of ascites greatly aggravates the general condition of the patient, so that they can die from ascites of the abdominal cavity.
Also, compression of the liver by a tumor can lead to an increase in venous pressure, at which the water component of the blood is discharged and collected in the abdominal cavity.
Since poisoning by waste products of malignant neoplasms can cause a lack of oxygen (air), the kidneys react to this by reducing filtration, and this leads to the fact that the pituitary hormone begins to retain sodium and water.
Also, the provoking causes of dropsy in oncology can be an anatomical feature of the structure of the body, in which the close fit of the folds of the peritoneum, coupled with the abundance of blood and lymphatic vessels, causes the rapid spread of cancer cells to neighboring tissues.
In addition, there is also chylous ascites, which can occur with abdominal lymphoma. It is characterized by the removal of lymph and emulsified fats, which penetrate the intestines and abdominal cavity.
Disease and oncology
Any disease in the field of oncology disrupts the functions of many organs, not just the one in which the lesion develops. Various complications that arise from such diseases significantly worsen the situation and the general condition of the patient. Ascites is one of these complications, with the development of which the volume of the abdomen can literally increase several times.
In the presence of oncological processes, the probability of ascites occurring reaches 10%, but such a complication does not occur with all cancers.
In most cases, abdominal ascites develops in the presence of:
- Stomach or colon cancer;
- Colorectal cancer;
- Pancreatic cancer;
- Malignant lesions of the ovaries or mammary glands.
When fluid accumulates in a large volume, the pressure inside the peritoneum increases greatly, and the diaphragm moves into the chest cavity. As a result, a violation of the anatomical location of internal organs occurs, which cannot but affect their functioning. First of all, with such a displacement, a disruption of blood circulation, heart and lung function occurs. If ascites is massive and persists for a long time without taking any measures to eliminate it, this causes significant protein losses in the body.
Considering all the changes that occur in the body when ascites appears, this condition creates significant complications of the underlying disease, adding to it respiratory and heart failure, as well as metabolic disorders.
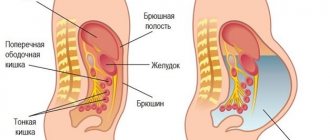
In a healthy person, the amount of ascitic fluid is very small. This fluid is always contained in the peritoneal cavity, since it is necessary to provide internal organs with free working movement and prevent them from sticking together. It is the presence of this fluid that ensures the free movement of intestinal loops, preventing their sticking and friction. The body has complete control over the processes of producing and absorbing fluid.
similar articles Diagnostics Why an X-ray of the abdominal organs is performed
3 036 0
Liver and pancreas Forecast for life with liver cirrhosis in the stage of decompensation
935 0
Liver and pancreas Symptoms of alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver and life prognosis
91 0
In oncology, the barrier, secretory and resorptive functions of the peritoneal layers are disrupted, as a result of which either intensive fluid production begins or its absorption stops. Thus, the liquid begins to fill the entire space of the peritoneum, stretching it and increasing the volume of the abdomen. In each case, the volume of pathological fluid is different, and in especially severe cases it can exceed 25 liters.
In case of oncological diseases, cancer cells can enter the peritoneal cavity, where they settle on the parietal and visceral layers, increasing the accumulation of fluid. But due to damage to the peritoneal space by cancer cells, in most cases carcinomatosis occurs and quickly develops.
In the presence of ovarian cancer, the probability of the appearance of ascites reaches approximately 40%, while in half of the cases of development of this complication, women die, and death occurs precisely because of the appearance of ascites.
The appearance of ascites in cancer significantly worsens not only the general condition of the patient and the course of the underlying disease. As a rule, patients who develop such a complication due to cancer die soon.
Many, of course, are interested in this sad question: how long do people live with abdominal ascites? If timely measures are taken, approximately 50% of people with this disease live for about 2 years. But if a person, along with abdominal ascites, has renal failure, hypotension, metastases, for example, in large quantities in the liver, and the patient’s age is more than 50–60 years, then the prognosis worsens significantly.
Symptoms of ascites
In patients with cancer, the development of ascites can occur in just a few weeks or a couple of months. Patients may experience symptoms of a large amount of fluid accumulating in the abdomen. The main symptoms that may be felt are:
- Shortness of breath even at rest, especially lying down;
- A feeling of heaviness in the stomach of a bursting nature;
- Mild pain in the abdominal area;
- Heartburn (nausea, vomiting);
- Belching after eating.
All these signs are associated with disruption of the peristalsis of the esophagus, intestines, and reflux of acid from the stomach into the esophagus.
Sometimes patients may complain of arrhythmia attacks. You can also distinguish swelling with dropsy by such obvious signs as an enlarged abdomen, which, when standing, falls down with a protrusion of the navel, and dilated veins and striae (white stripes of stretched skin) may appear on stretched skin. Accumulated fluid in the abdomen makes it difficult to bend over. When lying down, the expanding belly spreads out to the sides. If ascites is a complication of liver disease, then you can see the characteristic “jellyfish head” symptom - dense dilated veins around the navel.
There are frequent cases of identifying young women with advanced malignant ovarian tumor (carcinoma), who were confident in their pregnancy due to the cessation of menstruation.
The accumulated fluid in the abdomen puts pressure on the tumor, causing it to collapse. The spread of metastases through the veins and heart failure is expressed by a heavy outflow of blood to the heart, which is fraught with swelling of various parts of the body (legs, external genitalia).
All such symptoms do not form in isolation; the symptoms of a malignant neoplasm remain in the main place. But ascites also needs to be treated, since with its appearance the main one becomes even more dangerous due to the occurrence of other complications and ascites poses a mortal danger to humans.
Symptoms of pathology
The course of ascites caused by cancerous tumors develops for a long time, the process lasts for weeks and months. In this case, the first signs of an increasing nature are observed, associated with the pressure of the diaphragm on the upper organs and disruption of the functioning of the intestine:
- heaviness in the stomach, flatulence;
- belching after eating;
- aching pain in the abdomen;
- shortness of breath even in a lying position;
- heartburn, nausea, vomiting;
- cardiac arrhythmia.
The main symptom is considered to be a slowly and disproportionately increasing volume of the abdomen; in a standing position, its drooping and protrusion of the navel are noticeable. A person cannot bend over and tie his shoelaces.
If ascites has caused liver cancer, the patient will develop a network of veins on the abdomen in the navel area, known as the “head of the jellyfish”.
With cysts and ovarian cancer, women stop menstruation. Given the slow growth of the abdomen, many people mistake the condition for pregnancy, which leads to late diagnosis of the disease. After ascites, oncology is diagnosed.
The patient also experiences swelling of the feet, legs and genitals as a result of metastasis of the venous system, its blockage and lack of blood flow to the heart. All described symptoms are secondary. The main ones are provided by the primary pathology - oncology, while dropsy also requires treatment to prevent serious complications.
Stages of ascites
Regardless of the reasons for its appearance, the course of the disease itself has three stages, which are typical for people with cancer:
- The transient stage is characterized by the fact that the patient only feels bloating, and the amount of accumulated fluid is no more than 400 ml;
- The moderate stage is characterized by the fact that the volume of fluid accumulated in the abdominal cavity can be up to 5 liters, all the described symptoms may appear, and complications may develop;
- Intense stage - ascites accumulates more than 20 liters of fluid and is considered resistant. It is not possible to treat this stage with diuretics; the functioning of the heart and breathing may be impaired, and it needs to be pumped out.
Pathogenesis
Normally, in the absence of any diseases, a small amount of fluid is constantly present in the abdominal cavity, but it does not accumulate, but is absorbed through the peritoneum. With the development of pathological conditions, more free fluid is formed, and the possibilities of its absorption are reduced. The more fluid accumulates during dropsy, the more the surrounding organs and tissues are compressed and the disease itself worsens.
Thus, with cirrhosis, the liver increases in volume due to the death of the cells of which it consists and the appearance of fibrous tissue. The enlarged organ compresses the portal vein and the blood cannot circulate normally; water, unable to find a way out, begins to sweat through the venous wall into the abdominal cavity. The accumulated liquid puts even more pressure on the vessel and a vicious circle arises. Protein deficiency, which occurs as a result of a violation of the protein-forming function of the liver and a decrease in oncotic pressure (which retains water in the bloodstream), aggravates the process.
A weak heart muscle cannot pump the entire volume of circulating blood, and congestion occurs in the vessels. As a result of increased pressure, water leaves the blood vessels and ascites forms.
In kidney disease, water escapes through the wall of blood vessels due to an increase in arterial pressure and a decrease in oncotic (created by blood proteins) pressure.
In case of malignant neoplasms, the mechanisms of the appearance of excess fluid in the abdomen can be different, from compression of the great vessels by the tumor to protein deficiency.
The progression of the disease is associated with violations of the basic functions of the peritoneum (protection, absorption of fluid and its release, barrier to harmful substances), which also affects the functioning of the lymphatic system.
Ascites in ovarian cancer
The most severe consequences of ovarian cancer arise precisely because of dropsy.
Death is likely in more than half of cases. The formation of ascites in ovarian cancer occurs in the last stages of cancer, when metastases have spread to the abdominal cavity and liver. Fluid accumulating in the abdominal cavity increases the size of the ovarian tumor, and this can result in rupture (burst) of the ovary and release of exudate into the abdominal cavity. A complication in the form of ascites in ovarian cancer leads to swelling of the lower abdomen and genital area, then the swelling can spread to the legs.
At first, the accumulation of fluid does not manifest itself in any way on how you feel, but then severe pain may appear, which can be perceived as attacks of appendicitis. The sooner ascites is diagnosed and fluid removal (pumping) from the cavity begins, the higher the chances of a good outcome in treating the underlying disease and getting rid of ascites. The cause of frequent mortality in women with ovarian cancer is ascites (a complication of the disease, and not the disease itself).
What is ascites?
Ascites (also popularly called “edema of the abdomen”) is a manifestation of the body’s adaptation to severe pathological disorders (most often these disorders are associated with liver dysfunction). The main manifestation of ascites is the accumulation of liquid effusion in the abdominal cavity (up to 25 liters).
Main signs of pathology:
- enlarged abdomen with uniform bloating;
- skin tension with the appearance of a characteristic shine;
- the appearance of stretch marks on the lateral surfaces of the abdominal wall (white stripes);
- dilation of the saphenous veins in the abdominal wall (typical of increased pressure in the portal vein);
- umbilical hernia with protrusion of the navel;
- dyspnea (especially when the patient takes a lying position);
- bowel dysfunction;
- dysuria;
- edema (as a consequence of cardiac decompensation).
Liver cirrhosis is the most common etiological factor of “abdominal hydrops”. Cirrhosis is a liver disease characterized by the appearance of connective tissue instead of parenchymal liver tissue. Accordingly, the liver loses its functions, which leads to associated disorders (including ascites). Living with cirrhosis for 10 years or more means running the risk of developing dropsy in half the cases. How long people with ascites and liver cirrhosis live depends on several factors.
Complications after ascites
If the underlying disease is quite severe, then the appearance of ascites only aggravates the condition and reduces the chances of recovery. The risk of fatal complications increases more. These include:
- Intestinal obstruction;
- Hemorrhoidal bleeding;
- Bacterial peritonitis (the appearance of infection causes acute inflammation of the peritoneum);
- The appearance of a hernia (in the navel, in the groin, with pinching);
- Hydrothorax (with acute respiratory failure), etc.
All of these conditions can develop suddenly or gradually, but they present additional challenges when treating the patient.
Possible complications and consequences
Lack of treatment for ascites caused by cancer leads to rapid deterioration of the condition. Against the background of an increase in the amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity, bacterial peritonitis, intestinal obstruction, cardiac and respiratory failure develop.
Patients experience the formation of hernias in the groin, navel and abdominal line. Increases the risk of pinching. Also, bloating as a result of ascites causes bleeding and prolapse of the rectum through the anus.
Exudate begins to accumulate between the pleural layers, which leads to acute respiratory failure.
Complications with ascites develop suddenly and lead to a significant deterioration of the condition. They most often cause death. This is why treatment should not be delayed.
Diagnosis of ascites
Ascites, as a complication, is expected in advance during cancer.
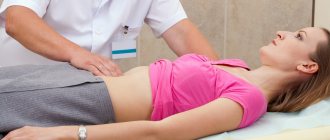
The attending physician periodically weighs the patient. An increase in body weight with obvious weight loss in the arms, legs, and body should raise suspicion of the presence of hidden edema. A test can determine the presence of water in the abdominal cavity. To do this, make a pushing movement with your hand on one side of the abdomen, while the second hand should feel the wave in the opposite side. This test is confirmed by additional research:
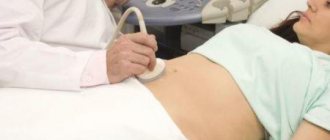
- Ultrasound. It makes it possible to detect the presence of free fluid in the abdominal cavity, and at the same time helps to monitor changes in the internal organs;
- Radiography and tomography. It detects fluid when the body position changes;
- Laparocentesis. This procedure consists of puncturing the anterior abdominal wall in order to pump out fluid for laboratory analysis and to remove it from the cavity. The procedure is both diagnostic and therapeutic.
Diagnosis of ascites in cancer abroad
When examining a patient, the presence of ascites can be determined by a simple test - changing body position. Using percussion (tapping), the doctor determines the level where the sound becomes dull. In a vertical position of the body, this will be the horizontal level in the lower abdomen; in a position on the side, it shifts accordingly.
The very presence of ascites is determined by ultrasound or computed tomography. To determine the cause of ascites, magnetic resonance and positron emission tomography and scintigraphy are performed to accurately determine the location of the tumor and its metastases. Such examinations are the basis for treating metastases abroad.
The portal vein system is examined using duplex ultrasound technology, and if necessary, angiography and lymphography are performed. Laparocentesis is also performed - a puncture of the abdominal cavity with fluid taken for examination. Laparocentesis is also therapeutic - the fluid is evacuated partially or completely, temporarily alleviating the patient’s condition.
A full laboratory study is also carried out, including immunological, molecular genetic tests, and determination of tumor markers in the blood.
Diseases associated with ascites
Sometimes, if the tumor or metastases affect the liver or biliary tract, the patient may develop jaundice. AST and ALT increase, and bilirubin levels can reach several hundred units. Outwardly, such a patient is easy to identify - he has yellow sclera of the eyes and skin. With this variant of the disease, the patient also receives intoxication of the body. Glucose droppers and the use of various sorbents help solve this problem. Instead of ineffective activated carbon, it is better to take Polysorb or Enterosgel. A good effect is also obtained from the use of membrane plasmaphoresis.
Treatment
Chemotherapy treatment
The use of a drug such as chemotherapy is acceptable, since it makes it possible to reduce the complications of ascites, which is caused by the generalization of the tumor process.
Treatment of ascites with diuretics
When recommending the use of diuretics (diuretics), do not overdo it. In case of cancer, doctors recommend drinking more fluids to remove decay products of tumor cells from the body. Ascites imposes restrictions on the use of large volumes of water for drinking, plus diuretics are prescribed, which can also increase the intoxication of the body with decay products of cancerous tumors. Therefore, it is considered possible to reduce body weight by 0.5 kg per day while taking diuretics. It does this by removing water through urine when you go to the toilet.
The prescription of a specific diuretic drug and dosage remain under the control of the doctor. You cannot change the drug yourself and create your own medication regimen. The combination of “Veroshpiron”, “Diacarb” and “Furosemide” is considered the most effective.
“Veroshpiron” is a potassium-sparing agent; it contains an adrenal hormone (spironolactone), which helps get rid of excess fluid without losing potassium. The effect of the medicine begins 2-5 days after the start of treatment, and the residual effect of the medicine continues three days after stopping the medicine.
"Diacarb" refers to targeted drugs. It is especially recommended for the prevention of cerebral edema, but is not as effective in the process of urine output. The medicine begins to work 2 hours after you start using the medicine. The medicine works by blocking the enzyme carbonic anhydrase in the tissues of the kidneys and brain.
Furosemide (Lasix) is classified as a loop diuretic. Its work is based on blocking the reabsorption of sodium and chlorine in the tubule and loop of Henle (the excretory apparatus of the kidneys), but at the same time it removes potassium.
Would you like to receive an estimate for treatment?
*Only upon receipt of data on the patient’s disease, a representative of the clinic will be able to calculate an accurate estimate for treatment.
Surgical method for treating ascites
The most common method of treating ascites is laparocentesis (puncture of the abdominal cavity). This method is considered surgical, although it is also fully mastered by therapists in specialized departments.
The technique is as follows. With the patient sitting on a chair, the abdomen around the navel is treated with iodine. Next, novocaine (for anesthesia) is injected into a place located 2 cm below the navel and a puncture is made in the abdominal wall with a trocar (special instrument). A tube is attached and fluid is pumped out of the abdominal cavity by gravity. About ten liters of liquid are removed at a time. Against the backdrop of a shrinking abdomen, the sheets are tightened to prevent collapse. If it is not possible to immediately remove a large volume of liquid, then insert a drainage tube until next time. The water pumping procedure can be repeated for several days in a row.
The main condition for carrying out such a procedure is sterility, since there is a high chance of getting infection of the peritoneum and peritonitis.
The laparocentesis (abdominal paracentesis) procedure is excluded if:
- Severe flatulence;
- Removal of a hernia during the recovery period;
- Adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity.
The following palliative surgical interventions are also possible:
- Peritoneovenous shunting. It lies in the fact that the abdominal cavity is connected to the superior vena cava; through this tube, when the patient breathes, the liquid goes into the venous bed;
- Omentohepatophrenopexy. This method consists of excision of the fused anterior abdominal wall and omentum and suturing it to the diaphragm or liver (if the omentum does not allow laparocentesis);
- Deperitonization. This involves excision of areas of the peritoneum in order to provide additional routes for fluid removal.
The use of folk remedies in the treatment of ascites
To treat this complication, folk remedies are also used, which should reduce ascites in cancer. Traditional medicine does not approve of such treatment methods, since many cancer patients, having started treatment with traditional methods, abandon the main treatment. But this method makes sense when real results from classical treatment methods are not observed. Here are some plants that, according to traditional healers, can help with this type of disease:
- Calamus (root);
- Astragalus membranaceus;
- Clefthoof (root);
- Prince of Siberia;
- Spurge;
- Marsh cinquefoil.
But doctors, nevertheless, can recommend, in addition to basic medications and drinking at home, diuretic infusions from herbs growing in central Russia:
- Birch buds (as well as birch sap);
- Calendula (flowers);
- Linden (flowers);
- St. John's wort;
- Oregano;
- Thyme;
- Milk thistle;
- Mint;
- Motherwort;
- Melissa;
- Sage.
But it is recommended to use herbal infusions with the permission of a doctor and under his supervision and only in conjunction with the main treatment.
Problems encountered in the treatment of ascites
First of all, treatment of ascites should consist of suppressing the growth of cancer cells in the peritoneum. In this case, it is possible to restore the fluid absorption function. But in fact, chemotherapy only helps to reduce ascites if the tumors are localized in the intestines, and if the tumors are located in the liver, stomach, ovaries or uterus, no results are observed.
The optimal option remains to control the accumulation and excretion of fluid along with food and also take diuretics (diuretics). It also makes sense to follow a diet that requires salt-free nutrition (with your doctor’s permission, you can add salt to the food on your plate). It is recommended to exclude fatty, spicy foods and fried foods from the diet. The volume of liquid allowed for consumption should be calculated based on diuresis (volume of urine excreted per day). The food must contain foods that sufficiently provide the body with protein and potassium. The following products contain these substances:
- Lean boiled meat and fish;
- Oatmeal;
- Potatoes (baked);
- Cottage cheese, kefir;
- Carrots, spinach;
- Compote of dried fruits (raisins and dried apricots).
When consuming all these products, it is also necessary to consider the possibility of their use for the underlying disease.
Features of treatment of ascites in Israel
Surgical treatment of ascites
Operations for ascites in Israel are palliative, that is, they do not cure the underlying disease, but create conditions for the outflow of fluid from the abdomen. These operations are performed under anesthesia, in cases of the third stage of ascites, refractory ascites, giant ascites, when it is necessary to remove a large amount of fluid during puncture - more than 7-8 liters, but in cases where the patient’s condition allows it.
These are so-called drainage operations, in which an artificial path is created for fluid to exit the abdominal cavity.
Examples of such operations are:
- omento-hepato-phrenopexy , in which the omentum (omento) is sutured to the surface of the liver (hepato) and diaphragm (phrenopexy), creating two additional pathways for fluid outflow;
- deperitonization of the walls of the abdominal cavity - in several places of the abdominal wall the peritoneal cover is removed, through which the liquid seeps into other tissues and is gradually absorbed;
- peritoneal-venous shunting , in which a shunt is installed - a drainage tube connecting the abdominal cavity with the superior vena cava. The tube is passed through a tunnel under the skin and inserted into the jugular vein (in the neck), from there it is advanced into the superior vena cava. During inhalation, the diaphragm lowers, intra-abdominal pressure increases, and fluid enters the tube. There is no reverse flow because the tube is equipped with a valve. This is a rather complex but effective operation.
Features of treatment of ascites with liver metastases
When the cause of ascites is metastases to the liver, along with complex treatment, if possible, their removal by radiosurgical method (gamma knife, Novalis, etc.) is used. The method of selective chemotherapy is also used - the introduction of chemotherapy into the hepatic artery through a catheter. Selective radiotherapy (SIRT) is carried out using a similar method - a solution containing radioisotopes is administered.
Prognosis for ascites
Fluid in the abdominal cavity against the background of developing oncology is a very bad sign. It contains many cancer cells, which means that there is a high probability that the cancer will affect the entire peritoneum and spread throughout the body.
Often, along with this disease, pleurisy (fluid accumulation in the lungs) can develop; this is also a very bad sign, which increases the patient’s risk of death.
The overall survival rate of people diagnosed with ascites in the presence of cancer is disappointing. Half of patients with this diagnosis survive only two years. The final outcome is slightly less or more than this period - it depends on the nature of the cancer, the patient’s response to treatment, and the presence of chronic diseases.
If ascites is diagnosed in the initial stage, treatment is much more effective and it is completely curable. Therefore, it is advisable to provide for earlier diagnosis of complications during cancer therapy.
Therapy methods
Treatment of ascites in oncology is carried out regardless of the stage of its development. This condition reduces the effectiveness of cancer therapy and worsens the prognosis for the patient.
If there is a slight increase in the amount of fluid in the abdomen, the patient is prescribed a special diet. Nutrition for ascites implies a maximum reduction in salt. The diet of a sick person should contain foods rich in protein and potassium. Dietary food implies the presence in the menu of boiled lean meat, fish, baked potatoes, cottage cheese, spinach, carrots, and dried fruit compote.
If there is a large amount of fluid in the abdomen, diuretics (Veroshpiron, Diakarb) are prescribed. The dose and regimen of medications is calculated individually, taking into account the patient’s condition. During the course of treatment, it is assumed that no more than 500 ml of fluid will leave the patient’s body during the day. Otherwise, the likelihood of increasing signs of intoxication of the body increases.
With a rapid increase in the volume of fluid in the abdominal cavity, drug treatment is ineffective. In this case, a special operation is indicated - laparocentesis. To remove excess fluid, under local anesthesia, a puncture is made in the abdominal wall just below the navel, after which it is pumped out by gravity. In one procedure you can get rid of 10 liters of water. If the volume of fluid is greater, laparocentesis is repeated after a few days.
Some experts advise treating ascites using folk remedies. Doctors allow the use of diuretic medicinal herbs - milk thistle, birch buds, sage, oregano and others. But these plants should be used with caution after consultation with a specialist.