What is bloating?
Bloating (flatulence) is an accumulation of gases in the intestines due to indigestion. This process is most often accompanied by bloating, an increase in the volume of the abdomen and an unpleasant feeling of distension from the inside.
Without a doubt, we have all experienced this to one degree or another and know very well what inconvenience this illness can cause. The intestines filled with gases create a feeling of a full stomach, and the colic caused by this brings a lot of trouble, making us feel uncomfortable.
Flatulence also occurs in healthy people, but most often it is a manifestation of other, more serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Gases in the intestines can accumulate due to pathologies such as:
- chronic pancreatitis – the body lacks the enzymes produced by the pancreas and, as a result, bloating appears after eating any type of food.
- irritable bowel syndrome – there is a violation of the motor function of the intestines, bloating in this case is accompanied by pain,
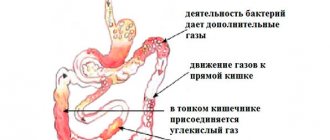
- dysbacteriosis – the balance of microflora is disturbed, and harmful microorganisms begin to produce gases (methane, hydrogen sulfide, ammonia),
- lactose intolerance – the body of adults often lacks enzymes that facilitate the absorption of lactose (milk sugar),
- intestinal obstruction - the passage of gases may be difficult due to the development of a tumor or polyps.
It is possible to temporarily get rid of bloating at home, but it is better to find the root cause of the disease together with your doctor. Remember that traditional medicine is not a substitute for primary therapy, but only an addition to it.
Diagnostics
If heaviness and bloating accompany a person regardless of what food he eats, this is a reason to go to the doctor and undergo an examination. The three most effective ways to identify the cause are:
- Palpation - determines the degree of abdominal pain, and also allows the doctor to assess the condition of the internal organs, identifying their pathological increase in size.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs - using a special device, it is possible to assess the performance of all organs of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as suggest all possible causes of gas formation.
- Gastroscopy of the stomach - using a probe, you can assess the state of the microflora in the stomach, as well as identify its various pathologies.
When conducting research, the patient is interviewed, determining his diet, the nature of the pain, its frequency and dependence on various external stimuli (after prolonged sitting, during physical activity).
Causes of bloating
Diet as the main cause of bloating
- Very often, excessive consumption of various types of carbonated drinks leads to excessive accumulation of gases in the esophagus. Usually, such bloating goes away without causing any particular inconvenience, since gases in a healthy person are quickly absorbed by the intestinal walls or eliminated physiologically.
- It is also possible for air to enter the stomach in large portions while eating. Therefore, you should not rush while eating food.
- Remember that some foods, consumed in large quantities, cause a fermentation reaction and, as a result, gas formation. To avoid undesirable consequences, you should moderate your consumption of sweets and baked goods, brown bread, beans, potatoes and other foods containing large amounts of easily digestible carbohydrates, fiber or starch.
- Another reason for the accumulation of gases is the mixing of foods that should be eaten separately from each other. This is especially true for fruits, which should be eaten either an hour before the main meal, or no earlier than 2 hours after a meal.
Sometimes the cause of bloating can be an attempt to get rid of heartburn by drinking soda, since it neutralizes the acidic environment of gastric juice and provokes increased gas formation.
Celiac disease
Bloating is also the main symptom of a rare disease called celiac disease. According to statistics, in Russia 1 person out of 1000 suffers from celiac disease. With celiac disease, gluten is not completely broken down, forming toxic substances that damage the inner surface of the intestine. It is treated exclusively with a gluten-free diet, or by constantly taking enzyme preparations that will help break down gluten.
Read more: What is celiac disease?
How and with what to treat?
Increased gas formation, which provokes bloating and discomfort extending to the right hypochondrium, is treated depending on what caused the problem. It is the causes that are the key factor in treatment. Its main task is to neutralize the negative effects of the root cause, as well as to establish peristalsis and the digestion process.
Drug therapy
This includes groups of medications that can normalize digestion, as well as painlessly remove accumulated gases:
- Antispasmodics: Spazgan, Spazmalgon, Baralgin, No-Shpa - these drugs are prescribed when there is a strong spasm in the abdomen. The average price of these drugs is about 140 rubles. There are contraindications, so it is better to consult a doctor before starting use.
- Pancreatin is a natural enzyme in the body that can speed up the digestion process. Its price is no more than 12 rubles. It is approved for use even in childhood, but has other contraindications.
- Smecta - envelops the walls of the stomach and intestines, eliminating pathogenic microflora and carefully removing gases. It has no contraindications, the price depends on the form of release.
- Espumisan and other medications that contain Simethicone, an active substance that can collapse gas bubbles, removing their surface tension, resulting in gases being eliminated naturally. Used from the first days of life. It is most popular among newborns who have to endure colic.
- Hilak and Hilak-Forte - drops help relieve swelling of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as relieve bloating. The drug contains a large number of microelements, thanks to which peristalsis is restored and normalized.
- Prebiotics: Linex, Lactiale, Bifiform, Bifilife - populate the intestines with beneficial bacteria that are able to independently cope with dysbiosis, restoring the natural balance.
Diet
Patients are offered a gentle diet, which contains the simplest dishes that do not require increased enzyme production. Useful products are considered:
- low fat lactic acid products;
- vegetable stew;
- steamed cutlets and lean meats: chicken, rabbit, turkey;
- boiled and baked fish.
It is also important to ensure plenty of fluids, which include tea, dried fruit compote and apples.
It is important to eat small portions, but at least 5-6 times a day. Food should be warm, but not hot. In the first 5-6 days, it is recommended to grind all dishes to a puree state, which will facilitate digestion.
It is better to avoid the following foods, as they place increased stress on the digestive tract and also contribute to the production of gases:
- sweet carbonated drinks and confectionery;
- bread;
- kefir;
- canned food;
- fatty meats;
- pickles and marinades;
- hot spices, sauces, mayonnaise.
You should also exclude fresh juices and limit your intake of fresh fruits and vegetables, preferring stewed counterparts.
Folk remedies
Simple decoctions of medicinal herbs will help get rid of discomfort in the stomach:
- chamomile – has bactericidal properties;
- sage – neutralizes pathogenic microflora in the intestines;
- oak bark – normalizes intestinal motility;
- St. John's wort – enhances gastric secretion;
- fennel or dill seeds - promote rapid removal of gases;
- mint – removes spasms.
Decoctions are prepared according to the instructions indicated on the package. Before you start taking it, it is better to consult a specialist, since there may be contraindications in specific situations.
Replacement therapy
In case of increased gas formation and bloating in the abdomen, replacement therapy can be used, when those substances are introduced into the body, the synthesis of which is impossible under natural conditions. This includes two drugs:
- Pancreatin is a pancreatic enzyme used for pancreatitis.
- Prebiotics – normalize intestinal microflora in case of chronic dysbacteriosis.
Symptoms of bloating
Most often, bloating is not an independent disease, but only a symptom of other, more serious diseases of the digestive system.
Excessive formation of gases in the intestines is possible with chronic pancreatitis, a disease in which the body lacks enzymes produced by the pancreas. In this case, bloating usually occurs after eating, regardless of its composition.
Flatulence can also be caused by irritable bowel syndrome. In this case, the motor function of an anatomically healthy intestine is disrupted, and bloating is accompanied by abdominal pain, and in some cases also diarrhea or constipation.
The cause of bloating may be intestinal obstruction caused by a tumor or polyps. In this case, the passage of gases from the intestines becomes difficult and leads to flatulence.
Excessive gas formation may be a consequence of intestinal dysbiosis. Due to a decrease in the protective properties of the body, microflora is disrupted in the large intestine. Harmful microbes that enter there produce gases in large quantities (mainly ammonia, methane and hydrogen sulfide). This process leads to bloating, accompanied by a foul odor.
Also, flatulence often accompanies individual lactose intolerance - a condition in which the body lacks enzymes that allow a person to digest dairy products.
Bloating and abdominal pain. The pain is usually short-term but painful. The discomfort goes away when the gas passes through the intestines. Pain can occur at various points in the abdominal cavity and, passing through the intestines, change location. If you experience prolonged and intense pain over a long period of time, this may be a signal that the cause is not bloating, but some more serious illness.
Heaviness in the abdomen with belching and heartburn
The combination of a feeling of heaviness with belching is quite often observed in different conditions. Most often, in this way the body reports the consumption of low-quality products. Additional nausea and pain in the right side may indicate diseases of the pancreas. Sour belching sometimes warns of the presence of pancreatitis, gastritis or dyspepsia.
Flatulence, stomach heaviness and belching of air indicate a violation of the diet. Air belching is associated with the appearance of an air bubble inside the intestine, which puts pressure on the intestinal walls. When the sphincter between the stomach and esophagus opens, air enters through the esophagus into the oral cavity, forming a belch. The cause of the phenomenon is poorly chewed food, eating on the go or at fast food establishments, and consuming large amounts of carbonated drinks.
The occurrence of heartburn is also often determined by the quality of nutrition. Such unpleasant symptoms are sometimes caused by overly sour, fatty or sweet foods. The symptoms most clearly appear against the background of increased acidity of gastric juice. Therefore, when these signs are combined, the likelihood of gastritis should be checked.
The appearance of nausea and vomiting.
When chronic heaviness in the stomach is accompanied by nausea, several reasons can be suspected. The safest reason is overeating, especially after a long forced fast. Nausea can also occur as a result of irritation of the mucous membrane by aggressive foods (spicy, fatty, fried foods). The most obvious symptoms appear in acute food poisoning. Among the pathological causes, it is necessary to mention the high probability of developing gastritis, pancreatitis or cholecystitis. In other words, if you have chronic intestinal heaviness with nausea, you should consult a doctor.
A characteristic sign of acute poisoning is the addition of vomiting. In this case, diarrhea and pain in the stomach area are also observed. A late, heavy dinner leads to vomiting syndrome after heaviness in the abdomen and flatulence, if during the day there was a quick meal in small quantities. In the case when such a regimen becomes a habit, one can expect the appearance of functional digestive disorders, leading to the chronic nature of the manifestations in question.
Bloating after eating
In most cases, flatulence is associated with poor diet. In a healthy person, bloating can be caused by accidentally swallowing a large portion of air with food, or by drinking highly carbonated drinks. Also, unpleasant sensations can occur if a particular food is poorly absorbed by the body. Therefore, instead of being digested, it begins to form gases.
Another cause of bloating may be dairy foods. To digest this type of food, the enzyme lactose is needed. If there is insufficient quantity, milk and similar products can cause discomfort. The cause may also be products made from coarse fiber or starch, for example, seeds, cabbage, potatoes, nuts, oats. If flatulence occurs frequently, such products should be excluded. And, if you consume them, you should remember that these types of products must be chewed very carefully, otherwise discomfort may occur.
What to do if you have bloating?
One day after bloating, you should give your intestines a rest. You should only eat boiled rice and wash it down with herbal teas. Subsequently, you should reconsider your diet. For meat, you should give preference to chicken, turkey and veal, and for cereals, rice. Milk should be replaced with fermented milk products (cheese, yoghurt). You need to drink teas made from mint, St. John's wort and chamomile. It is good to add spices and herbs to dishes that reduce gas formation: ginger, cumin, cardamom, parsley, dill, fennel.
To understand which specific foods cause bloating, you should focus on your feelings. Monitor the sensations you experience while taking a particular product and draw conclusions. Medical intervention, in most cases, is limited to taking enzyme preparations. And if infection or bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract is suspected, antibiotics are prescribed.