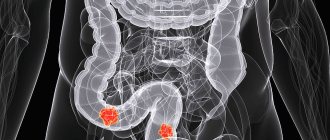
What are metastases
First of all, it is worth understanding what metastases are. This is the name given to secondary neoplasms. They are formed as follows:
- mutated cells are shed from the primary cancer tumor;
- cells begin to “travel” with the flow of lymph and/or blood;
- after some time, atypical cells settle in some organ and give rise to the development of a new malignant neoplasm.
Advice! Considering the fact that mutated cells have the ability to divide, just one cell that splits off from the primary formation can give rise to several new tumors.
The process of metastasis starts from the moment when the body can no longer fight the disease. As a rule, any type of stomach cancer metastasizes at the third stage of development, although individual secondary tumors can be detected at the second stage. With cancer of the stomach, metastases can affect the lymph nodes, as well as various vital organs.
Surgery
Surgical intervention in the first stages often eliminates intestinal obstruction. In addition, patients in the later stages are prescribed palliative surgery to form anastomoses between the unaffected area of the stomach and the intestines. In some cases, the oncologist surgeon sews a special hollow tube into the patient to create the ability to independently pass food. Extription of the stomach at this stage is actually not used, because the cancer cells have already completely spread throughout the body and formed foci of malignant formation in other organs.
The most effective feeding option for the patient is a gastrostomy tube. Local anesthesia is required for this procedure. The main purpose of a gastrostomy is the surgical installation of a hollow tube into the anterior wall of the peritoneum, into which a probe is inserted so that the patient can eat special food mixtures.
The principle of the development of metastases in gastric cancer
Why does a tumor sometimes metastasize a short time after its occurrence, and sometimes the disease lasts for years without starting the process of cancer metastasis? The rate of spread of secondary tumors depends on the following factors:
- degree of differentiation of the primary focus of cancer. The more the mutated cells differ from healthy ones, the more aggressive the course of the disease;
- development stage. At the initial stages of tumor growth, the affected cells are not able to penetrate tissue barriers. However, over time, the body’s resistance decreases and carriers of the disease can freely penetrate the lymph and/or bloodstream;
- The age of the patient also influences this. In young people, all processes occur faster, and the disease progresses faster in them.
The greatest danger of this process is that the affected cells, settled in other organs, are a kind of time bomb. That is, it is unknown when exactly the development of secondary lesions will begin and what exactly will trigger the pathological process.
The disease can recur at any time, including decades after removal of the primary lesion. The most severe case is that sometimes cancer is detected due to the detection of metastases.
In some patients, the initial stages of gastric cancer occur without the appearance of symptoms. And health problems begin to arise due to organ failures that have affected metastases.
During the examination, the primary focus of the disease is also detected. Affected cells can spread throughout the body in three ways:
- With blood flow. Most often, the portal vein, a large vessel that is connected to all organs of the peritoneum, is involved in the process of spread of affected cells.
- With lymph flow. In case of stomach cancer, this is the most common type of “spreading” of cells throughout the body;
- With direct contact. The affected stomach is in contact with other organs of the retroperitoneal space, so the tumor can grow into tissues that are in contact with the primary neoplasm.
Advice! Often, affected cells spread in two, or even all three, ways at once.
How do metastases spread?
The proliferation of secondary tumor cells in cancer patients occurs at different time intervals. The timing depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the type of cancer. These features include:
- Degree of differentiation (oncology as a science distinguishes highly differentiated, moderately differentiated and poorly differentiated forms of tumors). The low-differentiated form is the most aggressive towards humans and thus, in the process of development, metastasizes and spreads throughout the human body faster than other forms.
- Stage of development of the pathological process. The appearance of metastases is characteristic of the third and fourth stages of development of a malignant oncological process. At the first and second stages, the tumor has not yet gained sufficient mass and level of development for cellular structures of atypical shape to separate.
- The primary localization of the tumor affects the geography of distribution of secondary foci.
- Patient's age. The most aggressive growth was observed when gastric cancer was detected in young patients.
The greatest danger to life is the situation when a primary tumor is discovered in connection with the identification of secondary foci of oncological development. This means the onset of at least the third stage of cancer development. This often happens during examinations of liver and lung pathologies.
There are 3 ways of spreading metastases throughout the body:
- Contact. With this path of spread of atypical cellular structures, metastases penetrate into the organs of the abdominal cavity closest to the primary localization. No use of the lymphatic system or bloodstream is required.
- Hematogenous. The process of spread of atypical cellular structures occurs through the portal vein. The mentioned blood vessel supplies all organs of the abdominal cavity.
- Lymphogenic. The third way is the most common among the ways of developing metastasis of the body from the primary localization. Movement throughout the body is carried out thanks to the lymph flow, which passes through the lymph nodes closest to the site of the lesion.
Where can metastases grow in stomach cancer?
When studying the ways of gastric cancer metastasis, one can understand that practically no organ is immune from the entry of affected cells. However, long-term observations have made it possible to find out where gastric cancer metastasizes most often.
Since mutated cells predominantly spread through the lymphatic tract or through the bloodstream, the lymph nodes and organs located next to the primary tumor are the first to suffer. At later stages, the appearance of distant metastases in gastric cancer cannot be ruled out.
According to medical statistics, in case of oncological gastric pathology, the probability of the appearance of foci of secondary neoplasms in organs is as follows:
- most often, multiple metastases are detected in the lymph nodes; this pathology is detected in 45% of patients with metastatic cancer;
- in 30% the liver is affected;
- another 20% have lungs;
- with a five percent probability, distant metastases of stomach cancer may appear, affecting the brain and skeletal system.
Lungs
Gastric cancer pathology metastasizes to the lungs in approximately every fifth case. Secondary tumors appear in lymph nodes located in the subpleural region. Most often, the development of secondary tumors is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the alveoli. The following symptoms are noted:
- often recurrent fever, which can be treated with antibiotics and antipyretics, but develops again after a short time;
- progressive shortness of breath. First, the patient has breathing problems during physical activity, and later it may occur at rest;
- the appearance of a wet cough, the sputum secreted contains blood impurities.
The symptoms are very similar to those that appear when a primary tumor develops in the respiratory system. But sometimes, when metastases appear in the lungs, there are no external appearances for a long time; characteristic symptoms appear when the pleura is involved in the process.
Liver
Metastases to the liver from cancer of the stomach appear quite often. The fact is that the liver and stomach are connected by the portal vein, so the rudiments of a secondary tumor enter the main hematopoietic organ quite quickly.
Several lesions may appear in the liver at once; the prognosis for survival depends on their number and location. At the initial stages, oncological pathology of the stomach with metastases to the liver does not have pronounced specific symptoms, but with the growth of secondary formations the following signs are noted:
- frequent temperature fluctuations; in many patients, low-grade fever persists for a long time, sometimes rising to critically high levels;
- constant aching pain in the right side;
- sudden weight loss, even to the point of exhaustion;
- prostration;
- development of jaundice;
- enlargement of the liver.
Spine
Cases of stomach cancer with metastases to the spine are relatively rare. Secondary tumors in bone tissue occur if the primary lesion in the stomach is removed, and further treatment with chemotherapy or radiation waves is not carried out.
In this case, malignant cells remaining in the lymphatic fluid and blood can trigger the development of metastases in the spine. This pathology manifests itself as follows:
- painful attacks, which many mistake for attacks of radiculitis;
- destruction of the vertebrae in which the secondary tumor is located;
- feeling of numbness in the lower body;
- restriction of mobility, which can result in complete immobility of the limbs.
If detected early, the pathology can be quite successfully treated with therapeutic methods, that is, the use of radiation therapy and chemotherapy. If detected in late stages, the prognosis is poor.
Brain
The most severe complication of gastric cancer is the appearance of metastases in the brain. Such a pathology can only be detected using modern diagnostic methods - MRI. Thanks to this, it became possible to detect a secondary tumor in the early stages.
Single malignant tumors in the brain are easier to treat, but in about half of patients with this pathology, multiple tumors form. Main symptoms:
- frequent headaches, dizziness;
- short-term clouding of consciousness, inability to concentrate on something, memory impairment. In the later stages, there is loss of vision and hearing, complete loss of consciousness, and the development of coma;
- speech disorders;
- decreased sensitivity in the arms and legs, and often this syndrome is observed only on one side of the body. That is, only the right (or, conversely, left) leg and arm suffer;
- paralysis, paresis.
Main symptoms of stage 4 cancer
Doctors note that stage 4 stomach cancer has the following typical symptoms:
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- the appearance of general malaise and weakness in the limbs;
- complete lack of appetite and increased body temperature to high parameters.
Additional symptoms indicating the development of stomach cancer are:
- the appearance of heaviness and bloating, especially these symptoms appear in the patient after eating;
- the presence of pain in the stomach and when swallowing;
- the appearance of severe pain in the lower abdomen. Typically, such pain can radiate to the lumbar region, as well as to the sacrum and perineum. This is due to the appearance of metastases in the nerve fibers of the pelvic floor and the development of the inflammatory process in nearby organs and tissues;
- the presence of various impurities in feces. Such impurities may contain blood, pus, or mucus;
- the appearance of fecal discharge during urination or the appearance of urine from the intestinal cavity. Typically, these signs indicate the appearance of a cancerous tumor in the bladder. As a result, a fistula appears in the area between the intestines and the bladder;
- the presence of a constant feeling of the presence of a foreign object in the intestinal area. This indicates that the neoplasm is large and is felt by the patient;
- the appearance of thick, liquid-like vomit. It usually appears when bleeding develops in the internal organs;
- presence of gastric obstruction. With it, the patient refuses to drink liquids and food. Most often localized in the upper gastrointestinal tract;
- a sharp increase in the size of the stomach. This indicates the appearance of metastases in neighboring organs.
Diagnosis of metastases in stomach cancer
Modern research methods are used to identify malignant foci in the body. It is necessary to identify the extent of metastases throughout the body. Since oncologists often diagnose stomach cancer at the second or even third stage, checking for the presence of secondary lesions is mandatory. The following methods are used:
- Ultrasound. Using the method, lesions can be diagnosed in the liver and abdominal cavity.
- X-ray. Using X-rays, you can identify secondary lesions in the spine, liver, and lungs.
- MRI. Necessary for studying lesions of the brain and bone tissue.
- Puncture. This method helps to find tumors in the bone marrow and skin.
Diagnosis of the disease
For this purpose, the following techniques are used:
1. Questioning the patient to identify individual complaints, as well as family history. 2. Visual examination of the affected area of the gastrointestinal tract using fibrogastroscopy. This procedure involves inserting an optical device into the gastric cavity, which allows you to take the required area of cancer tissue for analysis. 3. Ultrasound and X-ray diagnostics. 4. A biopsy allows you to definitively make or refute the diagnosis, taking histological material as a basis.
Treatment of metastatic stomach cancer
If cancer with metastases is detected, treatment will be aimed at preserving the functions of the affected organ and stabilizing the condition of cancer patients. Unfortunately, at this stage, complete recovery is impossible. But if you follow all the instructions given by the oncologist, it is possible to prolong life or put the patient into remission.
Surgery
For cancer with metastases, surgery is advisable only in some cases. The operation is performed if:
- the primary lesion has not progressed to the stage of inoperable formations;
- no metastases were found in organs that cannot be removed;
- secondary tumors were detected in single quantities.
Most often, the primary lesion is removed with simultaneous removal of a group of nearby lymph nodes.
Chemotherapy
In most cases, chemotherapy is given after surgery to prevent the development of metastases. If secondary lesions are detected, such treatment helps to curb their growth. Chemotherapy drugs are also used when pathology is detected at an inoperable stage, in this case the main goal is to improve well-being.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is aimed at destroying malignant tumor cells and is used to reduce the size of tumors. Radiation therapy is used at any stage of the disease, often in combination with chemotherapy.
Metastases in the lungs
At stages 3-4 of pathology, the list of organs to which gastric cancer metastasizes expands significantly. Lung tissue is quite often involved. In this case, either a single node or several tumors can form. This is manifested by a cough, the appearance of blood in the sputum, and shortness of breath.
Important: often lesions in the lungs are detected earlier than the primary lesion, since the symptoms of their development are more vivid.
Metastases in the lungs may appear before the primary cancer site
It is quite easy to determine this type of complication using radiography. The formations will be clearly visible in the image. Once the diagnosis is made, treatment is prescribed. It consists of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Surgical intervention is prescribed in cases where the formation blocks large bronchi, thereby impairing breathing.
Prognosis for gastric cancer with metastases
The prognosis for gastric cancer with the development of metastases directly depends on the extent of the process. Modern medicine cannot provide a complete cure for the disease, but it can increase life expectancy, significantly improving its quality. Properly prescribed treatment can contain the growth of secondary tumors and prevent the appearance of new lesions.
Cancer is insidious in that it can spread throughout the body, forming secondary tumors in various vital organs. The prognosis for complete recovery in case of widespread metastases is unfavorable, however, with timely treatment, the possibility of prolonging life exists.
Lymph node involvement
As gastric cancer progresses, metastases in the lymph nodes appear quite often. This is determined by palpation. In this case, the nodes located on the neck and in the armpit are the first to suffer. Adrenal nodes are often involved.
When lymph nodes located under the skin are affected, their malignancy can be determined by their increasing size. Later they become painful and take on an irregular shape. This is accompanied by dizziness, weight loss, and anemia.
When lymph nodes are affected, the first manifestations are noticeable on the neck
For stomach cancer with metastases to the lymph nodes, the prognosis is more favorable. But for this you must undergo full treatment, including, first of all, surgery and, secondly, chemotherapy.
How is diagnosis carried out?
To diagnose the disease, an X-ray examination is performed, which will show whether there is a formation in the image.
Cancer metastases can be suspected by the presence of symptoms characteristic of this disease in the patient. To confirm the diagnosis, it is recommended to perform an X-ray examination with the preliminary introduction of a radiopaque substance, which allows for good visualization of the mucous membrane. In addition, magnetic resonance and computed tomography are performed. A biopsy is performed to remove a piece of the tumor to determine the histological type of atypical cells that caused the disease. The patient needs to undergo a general and biochemical blood test.
Active and dormant metastases
Not all metastases necessarily give rise to a new tumor; many of them are capable of freezing and hiding for many years - their activity is suppressed by local immunity. However, under a certain set of circumstances that reduce the body’s defenses, such a silent metastasis can wake up and begin to grow, leading to a relapse of cancer in the patient. This can happen many years after the primary tumor has been successfully treated.
The situation is aggravated by the fact that even with the help of a thorough examination with modern diagnostic methods, microscopic tumor cells that have broken away from the primary tumor and penetrated into distant areas of the body cannot be detected. That is why, even in the case where it was possible to carry out a total resection of the tumor, there can be no confidence that all malignant cells without exception have been removed from the body - and it is for this reason that surgery is supplemented with radiation or chemotherapy. Experience shows that the preventive use of chemotherapy or radiotherapy in the treatment of cancer, even in the absence of confirmed metastases, provides a much more favorable prognosis in the long term. The only exceptions are the very early stages of cancer, when malignant cells have not yet left the primary tumor, in which case it can only be removed.
Treatment
Regardless of the choice of therapy, it will be extremely difficult to fight metastases. In the absence of spread of subsidiary defects beyond the organ, only in half of the cases does surgical intervention have a positive effect. In addition to the main lesion, neighboring healthy tissues are excised.
After surgery, chemotherapy is used to consolidate the results. Often this type of therapy is used to reduce symptoms and increase the patient’s life expectancy. Due to low differentiation, metastases are less susceptible to the influence of powerful drugs.
If only one cancerous lesion is diagnosed, then radiation is used. Radiation rays eliminate tumor activity, slow down the growth and progression of the disease, and prolong life.
Sometimes immunotherapy is given before surgery. Special products strengthen the immune system to better fight the disease.
On this topic
Targeted therapy is considered an accurate and gentle method of treating metastatic cancer. Antitumor drugs are administered to the affected area without affecting healthy tissue structures. Most often, in this case, palliative treatment is required, which allows the patient to live his last days more comfortably.
After therapy, proper rehabilitation is necessary. Particular attention should be paid to nutrition. The diet should consist of fresh fruits, vegetables, lean meat, sea fish, liquid cereals, and dairy products.
Kinds
Lymphatic metastasis occurs when abnormal cells invade the stomach through the lymphatic vessels. Most often, this process occurs with melanoma or sarcoma. These metastases remain in the lymph node for some period, so during surgery the cancerous tumor is removed along with the regional nodes.
A hematogenous complication develops when cellular structures are transferred by blood. Such metastases can cause even minor primary formations. Often, a patient learns a disappointing diagnosis during an examination for a completely different reason.
Contamination occurs when the affected cells affect the abdominal, pleural cavity, pericardium, and cerebrospinal fluid zone of the nervous system. With the help of fluid flow, structures fall on the walls of organs and the surfaces of mucous membranes.
Dormant metastasis is characterized by slow growth. If chemotherapy is not carried out after removal of the primary tumor, then under the influence of stress, hormonal disorders, and decreased immunity, a rapid growth of complications is activated.
Diagnostics
If timely diagnosis is made, the patient's chances of survival increase significantly. Ultrasound examination can detect metastatic changes in the digestive organ, ascites fluid. Using computed tomography, you can obtain accurate data on the location and size of secondary tumors.
A biopsy followed by histological examination will determine the origin of metastasis, thereby confirming the presence of a malignant formation. X-rays will help determine the nature of the pathological process.
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to examine the painful lesion in more detail, and the contrast agent will accurately identify the location of the tumor in the stomach.
Specificity of treatment
Therapy for stomach cancer with metastasis to various organs consists of performing surgery, if possible. The patient also needs symptomatic treatment to eliminate the main symptoms and improve the patient’s overall well-being. In this case, the tumor is removed within healthy tissue. In case of extensive metastasis or endophytic growth of atypical cells, surgery is ineffective. After this, chemotherapy and radiation are indicated, which help slow down the growth of the tumor and prevent its spread throughout the body.
Symptomatic treatment
The patient is advised to take medications to relieve pain, as well as drugs that improve peristalsis and food absorption processes. The use of vitamin-mineral complexes is required. In case of constipation, laxatives are used; diarrhea is an indication for the use of fixative drugs. Substances that have an enveloping effect on the gastric mucosa, such as Omez, are also used. Pancreatin will help improve digestion processes.
Surgery
During surgery, the stomach is completely removed or a gastrectomy is performed.
Metastases in the stomach are an indication for a total gastrectomy or organ removal. In this case, the surgeon leaves a stump of the esophagus, which is inserted directly into the intestine. After surgery, a person becomes disabled and is no longer able to digest food normally, but people who have had surgery live much longer than those who have not had surgery. It is important to remove the tumor within healthy tissue and in one conglomerate.
Radiation and chemotherapy
They are carried out after surgery and are aimed at preventing the spread of atypical cells throughout the body. Most often, for neoplasms in the gastrointestinal tract, the drugs “Fluorouracil”, “Cisplastin”, “Etoposide” and others are used. Radiotherapy is used very rarely, as it is not able to eliminate distant metastases of gastric cancer.
other methods
There are also non-traditional methods of treating cancer. They include the use of aloe juice infusion with cognac. At the same time, it must be kept for at least 3 years and consumed a tablespoon every day before meals. Physiotherapy and therapeutic massage are also used, which improve the general well-being of the patient.
In gastric cancer, metastases primarily affect the lungs and liver.