Focal atrophic gastritis is considered a dangerous pathological change in the gastric mucosa under the influence of the inflammatory process. When the disease occurs, the glands that synthesize acid and gastric juice die. Therefore, it is necessary to know, when faced with a focal form of pathology, what it is. Atrophic gastritis is called focal, affecting only a few areas of the gastric mucosa.
Forms of atrophic gastritis
There are several classifications of the disease. According to the intensity of symptoms, chronic and acute forms of pathology are distinguished. When a lesion is detected in the antrum of the stomach, antral gastritis is registered; when several foci of mucosal atrophy are diagnosed, focal gastritis is registered.
Focal
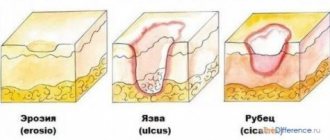
Gastritis with focal atrophy has a second name - subatrophic, it is the initial form of the disease, characterized by alternating affected areas of the mucosa and epithelial hyperplasia.
With the development of pathology, healthy areas of the epithelium and secretory cells strive to compensate for the work of damaged glands, which provokes an imbalance in the acid balance in the stomach. Focal atrophic gastritis is recorded in the lower parts of the stomach.
Antral
Atrophic antral gastritis is diagnosed in the antrum of the stomach. Pathomorphological changes contribute to the formation of scars on the mucous membrane of the organ. The disease provokes damage to the outlet of the stomach, which disrupts the process of moving food masses further through the digestive system.
Damage to the mucous membrane leads to a pronounced change in the acid balance in gastric juice. The symptoms of the disease coincide with a number of other pathologies of the stomach, therefore, in the case when atrophic gastritis affects the stomach in the antrum, high-quality diagnostics are necessary to make the necessary differentiation.
What happens if you don't get treatment?
With timely and complete treatment, the consequences of antral atrophic gastritis can be completely avoided . But it should be understood that complete restoration of the structure of the mucous membrane in severe atrophy requires a long time, and in some cases is impossible.
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilievna
Practicing gastroenterologist
Vitamin deficiency or anemia can often develop as a result of the disease. Atrophic gastritis can cause improper functioning of other internal organs. In advanced cases, atrophic gastritis of the antrum transforms into cancer (malignant tumor) of the stomach.
On our website: Chronic superficial gastritis - symptoms, treatment, diet
Clinical manifestations
With focal atrophic gastritis, the patient's appetite decreases, which gradually leads to a decrease in body weight. Pain syndrome in the epigastric region does not occur in all patients, so with this disorder it is necessary to focus on the occurrence of frequent attacks of nausea or vomiting. Malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract cause increased gas formation, heartburn, and belching.
Often, reduced immunity does not allow the body to resist attacks from various infections, which leads to the development of diarrhea. The results of urine and blood tests can also reveal changes.
Exchange disorders
Atrophy of the mucous membrane, changes in the acidity of gastric juice disrupt the functioning of the stomach, which provokes the appearance of a constant feeling of heaviness in the abdomen and changes in blood composition. Laboratory tests can reveal a deficiency of essential microelements and vitamins, hemoglobin.
With further development of the disease, the condition of the patient’s nails and hair worsens, and the skin becomes pale.
General changes in the body
Intoxication caused by disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system causes not only a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood, but also persistent headaches and hypotension. The acute course of the pathology can provoke an exacerbation of other chronic diseases, including pancreatitis, cholecystitis.
People complain of the appearance of a dense white coating on the tongue, a rotting smell that cannot be eliminated with toothpaste or mouth fresheners.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of atrophic antrum gastritis is not much different from the diagnosis of other chronic forms of gastritis and includes several stages.
- Clinical diagnosis. Collecting anamnesis, examining the patient, drawing up a plan for instrumental examination.
- Laboratory diagnostics . General blood and urine analysis, blood test for immunological parameters, stool test for helicobacteriosis.
- Respiratory diagnostics is one of the ways to identify the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Using a special device, the concentration of ammonia in the patient’s exhaled air is assessed.
- Intragastric pH-metry - determination of the state of the glands and the acidity of gastric juice.
- Endoscopic diagnosis with mandatory biopsy sampling. It is carried out to assess the condition of the mucous membrane and identify the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
- Ultrasound of internal organs . Used to identify concomitant diseases of the digestive tract.
Therapy
Differentiation of symptoms and treatment of the disease should only be performed by a doctor. Therapy requires an integrated approach, including the prescription of drugs to normalize the acidity of gastric juice, relieve pain, and suppress the activity of pathogenic microflora.
The choice of treatment method and necessary medications depends on the severity of the pathology, the cause of its occurrence, and localization.
Principles of treatment
In most cases, conservative therapy is used, including the complex use of medications, traditional medicine, and diet. The chronic form of the pathology allows taking pharmaceuticals prescribed by the attending physician at home. The acute course of the disease may require hospitalization with the prescription of therapy, which requires constant monitoring by a doctor.
Surgical intervention for atrophic gastritis of the stomach is necessary only if local necrosis is detected. Therapy involves removing pockets of dead tissue and prescribing medications to prevent further atrophy of the gastric mucosa. Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting, the patient must adhere to a strict diet.
Eradication
The basis of treatment is the suppression of the pathogenic activity of the causative agent of the disease, including Helicobacter pylori. Taking antimicrobial medications often provokes an imbalance in the intestinal microflora. Therefore, getting rid of the infectious component of the pathology is carried out by simultaneous administration of:
- Metronidazole and Amoxicillin. Antibacterial and antiprotozoal agents affect pathogenic microflora, but can also suppress the number of bacteria necessary for the body.
- Immunomodulators, vitamin complexes, probiotics. Medicines from these groups are necessary to restore healthy intestinal microflora. It is possible to stimulate the production of gastric juice with rosehip decoction or syrup, which is additionally an immunomodulator.
Substitution treatment
Restoring the natural acidity of gastric juice helps prevent further damage to the gastric mucosa and normalize the functioning of the organ. Taking medications that improve the secretion of hydrochloric acid helps to cope with this problem. In addition to stimulating the work of the gastric glands, medications containing enzymes are also prescribed to reduce the load on the digestive organs. Popular representatives of the group are Pepsidil and Abdomin.
The gradual restoration of the mucous membrane also requires eliminating the deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body, which is ensured by taking appropriate vitamin complexes. The choice of medications is carried out only by a doctor, focusing on the results of laboratory and instrumental examination of the patient, information on the presence of concomitant pathologies.
In severe forms of the disease, Pancreatin, Creon or Festal may be additionally prescribed, which improves the quality breakdown of food, which is necessary for the absorption of substances necessary for the body that come with it.
Anesthesia
Painkillers are not a mandatory component of complex therapy; they are prescribed only when pain occurs. In most cases, the patient is recommended to use antispasmodics, for example No-shpa, or anticholinergics (Platifillin).
Symptoms of antral gastritis
The initial stage is most often hidden. Heartburn, heaviness in the stomach, and bloating may occur.
In the chronic stage, nausea, hunger pain in the stomach or a couple of hours after eating, constipation or diarrhea are added.
During a visual examination, the doctor may notice a coated tongue, bad breath, and soreness in the epigastric region on the left.
This disease affects the general condition in the form of negative manifestations: weakness, apathy, heart pain, hypotension. In pregnant women with a previous history of gastritis, toxicosis may increase. An indirect sign of the disease in newborns is frequent regurgitation.
Symptoms often resemble gastric ulcers, so a careful differential diagnosis is necessary.
Weight loss occurs only with the development of a deep inflammatory process in the later stages.
In order to combine the signs, symptoms and treatment for superficial antral gastritis, it is necessary to conduct a number of additional studies to confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis (FGDS, obtaining histological data with identification of the pathogen).
Proper nutrition
Diet for focal atrophic gastritis is an obligatory part of complex therapy. There are standard recommendations, indicated by a serial number. When treating gastritis, the patient is recommended to adhere to nutritional rules in accordance with:
- With diet No. 2. The patient is allowed to eat only baked, stewed or boiled foods in a warm form. To stimulate the production of hydrochloric acid, it is necessary to avoid irritating effects on the walls of the stomach, so it is important to avoid eating cold or hot foods or eating large amounts of food at one time. The basis of the diet is vegetables and fruits, which can be varied with lean fish. Avoid eating marinades, smoked meats and fatty foods.
- With diet No. 1. It is used to reduce reflex excitability of the stomach walls and restore the mucous membrane. This diet can be used in case of exacerbation of pain. All dishes must be stewed or boiled, they are consumed in a semi-liquid or liquid state. Baked foods included in the list of permitted foods can be consumed after the acute condition has been relieved. With this diet, it is necessary to minimize the amount of cereals and bread in the diet.
- With diet No. 4. Dishes prepared from products in accordance with this list help prevent further development of the inflammatory process and restore stomach function. Meals should be taken in small portions at least every 3 hours. The menu should expand gradually to help a person return to their usual eating routine.
Treatment
Superficial gastritis of the antrum is a disease that is easy to cure with the right treatment regimen.
The easiest option is treatment in the early stages of the disease, when symptoms are just beginning to appear and the inflammatory process has not affected the deeper layers. But since a person experiences discomfort and pain at the stage of chronic inflammation, the therapy becomes more intense.
Treatment of superficial antrum gastritis must be entrusted to a specialist who will prescribe medications and select a diet.
An effective combination of medications, traditional methods, diet and further recovery with the help of exercise therapy (electrophoresis, mud therapy and paraffin therapy).
Often drug treatment is combined with traditional methods.
Medication
The treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor is based on the following:
- Antispasmodics (No-shpa, Spazgan, Buscopan) to relieve pain symptoms.
- Antibiotics if Helicobacter bacteria are detected (clarithromycin, tetracycline, ampicillin).
- Enveloping agents (De-Nol, Phosphalugel).
- Antacids to reduce stomach acidity (Omeprazole, Gaviscon).
- Means for restoring the microflora of the stomach and intestines (Bion-3, Bifidumbacterin, Primadophilus).
- B vitamins.
Folk remedies
Traditional recipes are often used to treat antral gastritis. Their combination with drug treatment under the supervision of a doctor is especially successful.
It is recommended to consume infusions of chamomile, linden, burdock root, calamus root, flax seeds, 0.5 cups warm, 3 times a day.
Well restores the inflamed gastric mucosa by consuming:
- potato and cabbage juice (half a glass half an hour before meals for 10 days);
- fresh aloe juice (1 tsp half an hour before meals for a month);
- sea buckthorn oil (1 tsp 2 times a day, morning and evening before meals for a month);
- propolis tincture (20 drops in half a glass of water 20 minutes before meals).