Serous-fibrinous peritonitis is a pathology based on the inflammatory process of the peritoneal layers, accompanied by the accumulation of serous-fibrous exudate in the peritoneal cavity. The disease is characterized by severe pain in the abdominal cavity, tension in the abdominal muscles, nausea, vomiting, upset stool, increased body temperature and deterioration in the general condition of the patient.
Serous peritonitis is an inflammatory process in which serous exudate is observed in the abdominal cavity.
The main cause of the development of all peritonitis is infection of the peritoneal layers as a result of bacterial microorganisms entering the abdominal cavity.
The main reasons for the development of peritonitis are:
- Acute or chronic appendicitis;
- Blunt and penetrating traumatic injury to the abdomen;
- Acute inflammatory processes of the internal female genital organs;
- Perforation in the gastrointestinal tract of ulcerative formations;
- Damage to the intestinal walls or bile ducts.
Among the bacterial microorganisms that can cause the development of peritonitis, both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria are noted. In this regard, the selection of antibacterial therapy becomes significantly more complicated.
Based on the mechanism of pathogenic flora entering the abdominal cavity, peritonitis is divided into two types: primary and secondary.
Primary peritonitis develops when infection spreads from other foci of infection in the body.
Secondary peritonitis is a complication of local diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
At the Yusupov Hospital, patients with serous-fibrinous peritonitis undergo specialized diagnostics, effective treatment and, if necessary, rehabilitation measures. Specialists have extensive clinical experience both in Russia and foreign countries. The Yusupov Hospital is equipped with the latest medical technologies that speed up the patient’s recovery process.
Local serous-fibrinous/serous peritonitis
Local peritonitis is an inflammatory process of the peritoneum, limited to a specific area and localized around the organ that is the cause of the pathological process.
Local serous-fibrinous peritonitis occurs due to the development of adhesions and the ability of the peritoneum to limit the inflammatory process. Most often, local serous peritonitis is closely associated with an acute disease of one or another abdominal organ (stomach, duodenum, gallbladder, segment of the small or large intestine, pelvic organs, kidneys). The main reason for the development of such peritonitis is perforation due to peptic ulcer of a hollow organ (stomach, duodenum, ulcerative colitis, gangrenous appendicitis, etc.). Local inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity occur much more easily than generalized peritonitis; in some cases, patients even remain able to work. However, even with this course of the disease, untimely diagnosis and treatment can lead to a destructive process and the formation of abscesses in the abdominal cavity.
Prevention
Purulent peritonitis can be avoided by observing the following rules:
- do not delay the treatment of diseases that can lead to serious complications (appendicitis, stomach ulcers, pancreatitis, etc.);
- get 50%-60% of all energy per day from fruits, vegetables and other foods rich in vitamins and chemical elements;
- give up unhealthy foods (fast food, sweet carbonated drinks, etc.);
- avoid body hypothermia;
- avoid stress;
- do not take medications without consulting a doctor;
- get enough sleep, don’t forget to rest after work;
- Wash fruits, vegetables, berries and hands thoroughly before eating.
Clinical picture
To make a diagnosis, the doctor needs to collect a detailed history of the disease. Most often, patients with serous-fibrinous peritonitis report the following complaints:
- Abdominal pain, the localization of which depends on the source of inflammation;
- Nausea;
- Vomiting (possibly mixed with bile and contents of the large intestine);
- Suffering face;
- Pale skin;
- Cold sweat;
- Immobility;
- Forced position of the body (on the back or on the side with the legs brought to the stomach);
- Increased body temperature;
- Drop in blood pressure;
- Impaired consciousness (as the patient’s condition progresses);
- Pointed facial features;
- Yellowish tint of the skin and mucous membranes;
- Bloating.
How does pathology manifest itself?
Inflammation of the peritoneum is characterized by a variety of symptoms. The clinical picture of the disease depends on the severity of the pathology. Typically the following symptoms are identified:
- bloating;
- abdominal hardness;
- state of shock;
- weakness;
- chills;
- feverish condition;
- increased sweat production;
- nausea;
- vomit.
Particular attention is paid to older people. In them, inflammation of the abdominal cavity often has atypical, erased symptoms. All manifestations are conditionally combined into several groups.
The nature of the pain
This sign is present regardless of how exactly the inflammation of the peritoneum develops. The localization of pain, as well as their nature, are determined by the primary pathology. If a person’s stomach is affected by an ulcer, or the duodenum has undergone similar changes, then the painful sensations have a sharp “dagger” character. Against this background, the patient often loses consciousness from pain.
With strangulation intestinal obstruction, pain occurs suddenly. The patient's condition is approaching shock. The pain syndrome is expressed most clearly at the very beginning of the development of the pathological process. Its intensification is provoked by even minor movements. When the primary focus is located in the upper abdomen, the pain radiates to the sternum or in the area:
- supraclavicular zone;
- backs;
- shoulder blades.
Features of dyspeptic syndrome
With the development of dyspeptic syndrome against the background of peritonitis, a person becomes very sick, then begins to vomit. Constipation alternates with diarrhea. Gases are retained, which causes severe discomfort in the lower abdomen. The patient's appetite decreases, and sometimes a false urge to defecate appears. The tension in the abdominal wall that occurs in the area of primary inflammation gradually spreads to the entire abdomen. The person's condition deteriorates sharply.
Irritation of the abdominal cavity reflexively provokes nausea and vomiting. As the pathology progresses, symptoms such as intestinal failure and weakened peristalsis appear. If the inflammatory focus is in the pelvis, the process of urination is disrupted, and the person suffers from repeated diarrhea. Such symptoms are observed with gangrenous appendicitis.
Further, signs of inflammatory-intoxication syndrome appear. There is an increase in temperature to 38 C, ESR accelerates, breathing and pulse become more frequent.
Features of peritoneal syndrome
The facial features of a patient with peritoneal syndrome become pointed. The face takes on an earthy tint. As the pathology progresses, the patient's skin becomes cyanotic in color. Against the background of severe pain, the patient's forehead becomes covered with large drops of sweat.
During an examination of the abdomen, the doctor determines the mobility of the abdominal wall. The patient's abdomen may not take part in the breathing process at all. Sometimes a change in its shape is observed. Often during palpation the hardness of the anterior abdominal wall is revealed.
Diagnostics
Making a diagnosis of serous fibrinous peritonitis is associated with certain difficulties, so this process should only be carried out by a qualified doctor. At the Yusupov Hospital, specialists every day encounter various emergency conditions that require immediate diagnosis and treatment. The hospital has innovative equipment that is successfully used for diagnostic purposes to obtain results as quickly as possible.
After collecting anamnestic data, to complete the examination, doctors use:
- Palpation and auscultation to determine the characteristic symptoms of the disease. When listening to bowel sounds, it is due to the accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity. Noises are usually weakened or completely absent.
- X-ray examination of the abdominal organs. A characteristic sign of a subphrenic ulcer is the presence of a layer of air. A specific symptom of “cups” is with intestinal obstruction.
Diagnosis of peritonitis
In addition to the data obtained during the examination, to diagnose peritonitis, doctors prescribe laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Clinical blood test: shows nonspecific signs of inflammation - increased number of leukocytes, accelerated ESR. The leukocyte index of intoxication is above 4 (in the terminal stage it can reach 12).
- An ultrasound of the abdominal cavity shows the presence of liquid and gas in it.
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity: in addition to fluid and gas, you can see signs of intestinal paresis (horizontal levels of fluid in the intestinal loops with accumulations of gas above them - the so-called Kloiber Cups).
- Blood biochemistry shows changes characteristic of multiple organ failure. If possible, a blood procalcitonin test is prescribed, an elevated level of which is characteristic of peritonitis and sepsis.
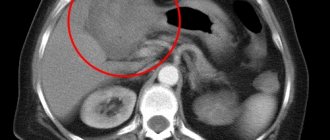
- If technically possible, a computed tomography scan is prescribed, which allows you to clearly visualize the condition of the abdominal cavity.
In unclear cases, doctors may go for diagnostic laparoscopy - an endoscopic examination of the abdominal cavity - or laparotomy - an open operation.
X-ray for peritonitis: dilated intestinal loops
Treatment
The only truly effective treatment for this pathology is surgery, which is most often performed through wide laparotomy. For local serous peritonitis, it is possible to perform laparoscopic (minimally invasive) surgery. The purpose of the operation is to detect and eliminate the cause of the disease (removal of the appendix in case of appendicitis, suturing of a stomach ulcer, etc.) and to carry out high-quality sanitation of the abdominal cavity.
Rational antibacterial therapy is carried out by intravenous or intramuscular administration of medications in various combinations, thus affecting a wide range of bacterial microorganisms.
An important stage of treatment is infusion detoxification therapy, as well as the prescription of immunomodulators. In especially severe cases, it is important to use hemosorption, hemodialysis and other detoxification methods.
The prognosis for detecting local peritonitis is relatively favorable; this pathology responds well to conservative and surgical treatment with timely diagnosis. The mortality rate in this process is quite low, in severe forms it does not exceed 17%. Preventive measures include timely identification and treatment of pathologies that could lead to this condition.
The Yusupov Hospital brings together specialists from various fields who have achieved significant success in their work. It is these doctors who take an active part in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with serous fibrinous peritonitis. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital use modern technical innovations in their work to obtain the best results. Close cooperation with European colleagues allows the hospital to remain a leading medical institution in the Russian Federation. Pleasant communication with the medical staff will brighten up your stay in the hospital, and a rich rehabilitation program will allow you to return to your previous lifestyle in a short time. You can make an appointment or consultation with a specialist at the Yusupov Hospital by phone.
Treatment after surgery
Peritonitis after surgery requires special treatment. It involves taking medications that destroy pathogenic microflora, restore the activity of the gastrointestinal tract and normalize the immune system.
The patient is also prescribed a diet that he must adhere to for a week. Peritonitis in children is treated in the same way as in adults.
Drug treatment
The following types of medications are prescribed:
- antibiotics. Penicillin-Teva, benzylpenicillin, ceftriaxone, gentamicin and others;
- diuretics, the active ingredients of which are Indapamide (trade name - "Arifon"), Spironolactone ("Veroshpiron"), Torasemide ("Trigrim");
- means aimed at removing toxic substances from the body. These include “Calcium gluconate”, “Splenin”, “Unitiol”, etc.;
- infusion solutions (“Hemodez”, “Gelatinol”, “Reopoliglyukin”);
- blood products – “Albumin” (5% and 20% solutions), “protein”, “fibrinogen”;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Ketoprofen, Arcoxia, Indomethacin;
- anti-vomiting agents. Contains ondansetron (Emeset), domperidone (Motilium);
- drugs aimed at preventing the development of intestinal paresis. These are "Neostigmine", "Physostigmine".