Pancreatitis: development of the disease
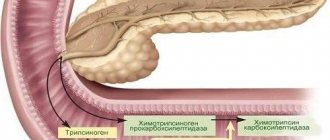
The main function of the pancreas is the production of enzymes that actively process food and break down many substances. The gland produces pancreatic juice, which contains its enzymes in an inactive form. They are activated in the duodenum. If their outflow is disrupted for any reason, enzyme activation occurs in the tissues of the gland itself: self-destruction of the organ begins. The inflammation that develops causes:
- replacement of functioning cells with adipose or connective tissue;
- in acute cases - massive necrosis (death) of organ cells.
Clinically, acute or chronic pancreatitis in the acute stage is characterized by a sharp attack of girdle pain that accompanies the process of destruction of cells in the gland. A similar clinical picture is observed with reactive pancreatitis. It occurs if the gallbladder or other organ of the digestive system becomes aggravated. Existing cholecystitis is a disease that most often causes a reactive process in the pancreas. Its manifestations resemble an attack of acute pancreatitis.
The pain begins in the left side and is girdling in nature, intensifying when lying down and after eating or drinking alcohol.
In addition to intense pain, the disease is accompanied by: nausea;
- indomitable vomiting that does not bring relief;
- diarrhea (oily stool with undigested food residue);
- high temperature.
Medical care for pancreatitis
An acute attack of pancreatitis is a life-threatening condition. The patient needs urgent treatment. It is urgent to call an ambulance. When an attack has developed, the use of non-narcotic analgesics and antispasmodics is ineffective in severe cases; treatment is carried out in the surgical department.
Before the doctor arrives, you should not give an anesthetic injection, so as not to blur the clinical picture. The injection of any antispasmodic is allowed, its name can be anything.
It will help provide minor pain relief for a short period of time before the doctor appears. It is necessary to create absolute rest in order to eliminate stress on the diseased organ. Apply cold to the abdomen (for example, a heating pad with ice), which will help reduce the inflammatory process and reduce the intensity of pain by reducing swelling.
All appointments are made by a gastroenterologist or therapist. Treatment of acute or chronic pancreatitis in the acute stage is carried out in a hospital setting. In case of acute pancreatitis, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital where there is a surgical department and an emergency department. This is associated with a severe course of the disease and complications, including death, if assistance is not provided in a timely manner. Complications of pancreatitis include, in addition to acute pancreatic necrosis:
- diabetes;
- pancreas cancer.
Analgesic
Despite their effectiveness and immediate relief of symptoms, narcotic analgesics are used in extreme cases and only in a hospital setting, as they cause unwanted complications and side effects (withdrawal syndrome and addiction).
The mechanism of action of analgesics is the inhibition of pain receptors and the release of enkephalins and endorphins.
The group of narcotic analgesics includes the following:
- Promedol and Fentanyl have a strong analgesic effect and are used for acute pancreatitis.
- Tramadol is considered a non-narcotic opioid analgesic. However, the drug belongs to the list of potent substances of the Standing Committee for Drug Control of the Ministry of Health and is available only with a doctor’s prescription with two seals. Tramadol has a mixed mechanism of action, affects the spinal cord and instantly relieves symptoms.
The drug, which is called Morphine, blocks pain, but is strictly prohibited for pancreatitis, since it can aggravate the situation by causing spasm of the smooth muscles of the pancreatic ducts and gallbladder.
Non-narcotic analgesics for injection
The following drugs belong to this group:
- Baralgin is one of the most effective analgesics. In a matter of minutes, it relieves the patient from spasms of muscle fibers, inflammatory processes and elevated body temperature.
- Maxigan - has a similar effect on the patient’s body.
- Mivalgan is similar in characteristics to previous drugs, but is prohibited for use by patients with agranulocytosis.
- Nospaz is an antispasmodic and analgesic. The drug cannot be prescribed to patients with bronchial asthma and a tendency to allergic reactions.
- Sandostatin - inhibits the degree of pancreatic secretion and prevents the secretion of pancreatic juice. Often an injection with this drug is used after surgery.
- Contrical is available in the form of a lyophilisate for solution and is used to prevent pancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis.
Pancreatitis in the acute stage can be accompanied by severe pain in the pancreas. To relieve pain, the treating gastroenterologist prescribes injections to the patient for pancreatitis. Antispasmodics help cope well with the manifestations of pain.
Antispasmodic spectrum injections
If the condition can be normalized without surgical intervention, the further treatment process is carried out in a gastroenterological or therapeutic department. Several groups of drugs with different mechanisms of action are used to restore pancreatic function. Among them are antispasmodics, which can be injected intramuscularly into both the shoulder and buttock:
- papaverine;
- drotaverine (No-shpa);
- atropine.
They have a myotropic effect (expand the lumen of blood vessels, improving blood circulation) and relieve spasm of smooth muscles.
Papaverine is a drug that has the name of its main active ingredient. Refers to potent antispasmodics. Available in various pharmacological forms, one of them is a 2% solution for injection. It is administered intramuscularly, but it can be taken intravenously as part of a complex lytic mixture. To effectively relieve pain, a drip method of administering such solutions is used. The mechanism of action is based on:
- to normalize the outflow of bile and pancreatic juice;
- to reduce pressure inside the affected organ.
There are contraindications:
- glaucoma;
- atrioventricular block (one of the types of heart rhythm disturbances);
- arterial hypotension;
- liver pathology;
- individual intolerance.
Not recommended:
- pregnant women;
- women during lactation;
- children under 1 year of age.
This drug can be prescribed to them individually for special indications only by a doctor due to side effects:
- allergic reactions;
- rhythm disturbances;
- decreased blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- sudden sweating;
- eosinophilia in the blood count (usually with a pronounced allergic component).
When prescribing a drug, carefully study the instructions. It is used individually, taking into account all existing concomitant diseases.
Analgesics
Analgesics are used to relieve moderate pain. Gives a good effect:
- Analgin;
- Baralgin;
- Acytomifene.
As a rule, their use is combined with drugs that have a different mechanism of action.
Baralgin is used in the acute period of the disease by injection and is a typical representative of this group.
Renders:
- analgesic effect;
- antispasmodic;
- hypothermic (reduces elevated body temperature).
It easily penetrates the blood-brain barrier (BBB), therefore it is prohibited for use in pregnant and lactating women.
Prescribed and supervised by a doctor. It is not recommended to use medications on your own to relieve pain.
Anti-inflammatory
Injections of anti-inflammatory drugs for pancreatitis have the following therapeutic effect:
- eliminate inflammatory processes;
- cope with mild to moderate pain (for severe pain, these drugs are ineffective);
- at elevated temperatures they lower it, but do not affect the normal temperature.
There are many anti-inflammatory drugs available, but not all of them are used for pancreatitis. Most often, doctors prescribe medications based on diclofenac.
These medications have a strong anti-inflammatory effect and can relieve the patient of pain. Administered intramuscularly.
Ketorolac is another anti-inflammatory drug prescribed for pancreatitis by injection. This remedy has a strong analgesic effect, reduces temperature, and eliminates inflammation. Ketorolac negatively affects the digestive tract, so it is used with caution.
Injections with solutions of Ketoprofen, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, and Aspirin effectively fight inflammation.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are part of complex treatment for acute pancreatitis. They are prescribed infrequently, in severe cases, when there is a threat of complications and involvement of other organs of the digestive system (gallbladder, intestines) in the acute inflammatory process. Broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are used, the purpose of their use is to prevent the development of:
- sepsis;
- peritonitis;
- retroperitoneal phlegmon;
- abscess of the head of the pancreas.
Also prescribed for treatment
- pancreatic necrosis;
- cholangitis;
- hypomotor dyskinesia of the gallbladder with stasis of bile or with existing stones in it;
- in the presence of multiple pancreatic cysts.
Antibiotics for complications of pancreatitis
They are used if, with all the treatment measures being carried out, against the background of the use of antispasmodics, painkillers, anti-enzyme drugs, the pain symptom intensifies.
As a rule, this is observed in acute pancreatitis. In the abdominal cavity, effusion with biologically active substances produced by the body in response to inflammation accumulates, which leads to peritonitis. The intestinal microflora joins the process. The pancreas can become even more inflamed, and its destruction accelerates.
In 70% of cases the disease is fatal. It is important to start antibiotic therapy on time. And do not miss the moment when complications begin to develop. As soon as the pain begins to get worse, a drug from one of the groups is prescribed:
- macrolides (Klacid, Azithromycin);
- cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime, Cefaperazone);
- protected aminopenicillins (Sulbactam);
- aminoglycosides (Amicocin);
- tetracyclines (Doxycycline).
Most often, when complications begin, they are administered in the form of injections (intravenously or intramuscularly). They begin to work almost immediately after the injection.
Antibiotics for chronic pancreatitis
The prescription of antibiotics during exacerbation of a chronic process is justified in the development of peripancreatitis - when the process involves tissues of organs adjacent to the pancreas (indication is, for example, cholecystitis or cholangitis). In such cases, they must treat inflammation and help the body fight complications.
Any antibacterial drugs, even the latest generations, have contraindications and a number of side effects. Therefore, only the doctor decides what injections are given for pancreatitis. The dose and duration of treatment are selected taking into account the severity of the condition and existing concomitant diseases. Typically the duration of therapy is 14 days. You cannot treat yourself with antibiotics.
What is the difference between tablets and injections?
| Characteristic | Injections | Pills |
| 1.amount of drug use per day | 1 time | 1-3 times |
| 2.dose of the main substance (medicine) | 100 mg in 2 ml (1 ampoule) | 125 mg per 1 tablet. |
| dose of the main substance (veterinary drug) | 50 or 100 mg in 2 ml (1 ampoule) | 50 or 125 mg per 1 tablet. |
| 3.soreness (unpleasant taste) | expressed when injected into the muscle | tasteless |
| 4. when it starts to work | 30 min | from several hours to several days |
| 5.action time | 1-3 hours (depending on the method of administration) | 4-5 hours |
| 6.period of elimination from the body | up to 3 hours | 5 o'clock |
| 7.course of treatment | from 5 to 14 days | from 5 days to 3 months |
| 8.approximate cost of 1 minimum package | 500 rub. | 300 rub. |
ul
Why does pain occur?
Pain is the main manifestation of acute pancreatic pathology.
It is caused by the same reasons as the exacerbation itself:
- non-compliance with the prescribed diet - overeating or consuming prohibited foods;
- drinking alcoholic beverages;
- nervous stress;
- pathologies of other organs of the digestive system in the acute stage - for example, inflammation of the gallbladder or gastritis;
- poisoning by food, drugs or chemical fumes.
Usually pain makes itself felt half an hour after consuming an inappropriate product. It is this period of time that is required for the secretory function of the pancreas to be activated after food enters the stomach. If the food is heavy and indigestible, the pancreas is under great stress, and its inflammation begins. In this case, swelling of the pancreas develops, blood flow to the organ increases, as a result of which the pressure inside it increases and pain occurs.
Pain is also caused by:
- narrowing of the pancreatic ducts;
- degenerative tissue changes;
- hypoxia - insufficient oxygen supply to the organ;
- disorders of the blood supply to the pancreas.
Extensive tissue damage leads to the development of pancreatic necrosis. If the lobules of the pancreas become necrotic (it is in them that pancreatic juice is produced), it is poured into the peritoneal cavity. This also causes severe pain; the patient is in a very serious condition and cannot think of anything else but how to relieve the pain of pancreatitis by any means.
Pain in the chronic form of pancreatitis has a slightly different development mechanism. The inflammatory process is not as acute as during an attack, irritation of the pancreas is insignificant. But those tissues that were damaged during the exacerbation period are scarred, and dense connective tissues are formed in their place instead of glandular ones. They put pressure on the surrounding vessels, nerve endings and internal organs. Therefore, the patient may complain of constant, aching pain in the hypochondrium, sometimes radiating to the right or left side, to the back between the shoulder blades.
ul
What to do in case of acute pain
If the patient has had an attack of acute pancreatitis for the first time, the pain occurs suddenly and rapidly increases.
Typically, such a situation finds a person at work, at home or at a party. You can numb the inflamed pancreas with improvised means before arrival.
But at the same time, it is important to know what you can and cannot do, so as not to harm the patient even more:
- The patient should take a sitting or semi-sitting position, slightly tilting the body forward. It is better not to lie on your back - this will increase the pain.
- Under no circumstances should you take medications containing enzymes, as many people do for abdominal pain after a feast and libations. On the contrary, now you need to slow down the production of enzymes.
- Do not stimulate vomiting if you are worried about nausea, belching and retching, using potassium permanganate and other solutions.
- Do not eat - some try to drink jelly, broth or eat a portion of viscous porridge, but now is not the time to do this. It is only allowed to drink still mineral alkaline water in small sips and small portions.
- Try not to take analgesics and other painkillers, as this will make diagnosis more difficult. The only thing you can try to relieve pain in acute pancreatitis before the ambulance arrives is tablets or injections of Drotaverine and Papaverine.
As a rule, the patient is hospitalized; this is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis and provide emergency assistance if bleeding occurs or severe damage to other organs is detected.
ul
Medicines for pain in acute pancreatitis
How to relieve pain both with pancreatitis in general and with its specific forms will be determined by the doctor, taking into account the patient’s condition. Painkillers are usually used in the form of injections, since due to vomiting and diarrhea that accompany exacerbation of pancreatitis in almost all cases, tablets and capsules do not have time to dissolve and be absorbed.
For moderate pain, a combination of analgesics and antispasmodics is administered - Drotaverine and Baralgin or Papaverine and Analgin, etc.
If these drugs do not help, narcotic painkillers are used:
- Tramadol;
- Promedol;
- Omnosexual
Ketanov is not a narcotic drug, but is a potent, effective pain reliever, which is why it is often used as an alternative remedy. Sometimes a blockade is carried out with Novocaine. These two drugs (unlike narcotic drugs) can be purchased at a pharmacy without a doctor's prescription.
But this does not mean that you can use them yourself without a doctor’s prescription, even with severe pain.
During an exacerbation of pancreatitis, the patient needs complete rest - physical, emotional. After pain relief for pancreatitis has been administered, an ice pack is placed on the abdomen. This helps relieve swelling of the pancreas, which also helps reduce pain. But it is not recommended to do this at home: hypothermia can cause vasospasm and worsen the patient’s condition.
Comprehensive drug therapy aimed at:
- to restore water-salt metabolism;
- to suppress enzyme secretion;
- to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms.
As the inflammatory process stops and the functions of the pancreas are restored, the pain will become weaker and weaker.
ul
How to eliminate pain from chronic pancreatitis
When pain occurs in a chronic form of the disease, only a doctor should select the means to eliminate it. Pain-relieving drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory or analgesics, as well as drugs that eliminate the cause of pain, are prescribed.
Typically this is:
- NSAIDs - Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Nimesil.
- Antispasmodics and analgesics - Baralgin, Analgin, No-shpa.
- Inhibitors of pancreatic juice production - they allow you to relieve the pancreas when it is inflamed. These are Gordox, Kontriven, Kontrikal.
- Products containing the hormone somatostatin - this substance suppresses the secretory ability of the pancreas and partially relieves pain.
- Enzyme preparations - stimulate digestion and support the pancreas, these include Mezim, Creon, Festal, Pancreatin.
- Antihistamines and diuretics - relieve tissue swelling during inflammation of the digestive organs, these are Furosemide, Triampur, Suprastin, Diphenhydramine, Pipolfen.
Following a diet, breathing exercises, and folk remedies will help you cope with pain and prevent new attacks.
But these methods only help with minor pain during remission.
If the patient's condition worsens despite the measures taken, an ambulance should be called immediately.
ul
Injections for the pancreas in the treatment of pancreatitis
In case of severe exacerbations or an acute process accompanied by the release of a large number of enzymes, anti-enzyme drugs are used in the form of intravenous drips:
- Gordox - 500 thousand units each;
- Contrikal - 200 thousand units each.
The daily dose is 1 million units and 400 thousand units, respectively. They prevent the destructive action of proteolytic enzymes. It is recommended to install IVs only in a hospital setting.
Kvamatel (active ingredient - famotidine) is a widely used H2-histamine receptor blocker. Histamine provokes increased production of gastric juice, thereby further exacerbating the inflammatory process. Kvamatel (a third-generation drug that blocks histamine H2 receptors) ensures functional rest of pancreatic cells:
- indirectly reduces the synthesis of proteolytic enzymes;
- stimulates the development of connective tissue at the site of necrosis.
Treatment begins with intravenous drip and is carried out in a hospital setting.
Dalargin is an antiulcer drug, but is also used in the treatment of pancreatitis:
- suppresses enzyme production;
- restores damaged gland tissue;
- replaces necrotic areas with full-fledged cells.
The medicine is prescribed as injections for inflammation of the pancreas intramuscularly or intravenously.
Sandostatin (Octreotide) is used to relieve pain in chronic or acute pancreatitis. Acts on the secretion of the pancreas, inhibiting it. The drug is not for home use. Prescribed by a doctor for injection use in a hospital setting as part of a comprehensive treatment. It is enough to give several injections against pancreatitis so that the level of amylase in the blood decreases to normal. Used by surgeons for acute pancreatitis.
Normalization of blood circulation in the affected organ is facilitated by trental and solcoseryl in small doses (2 ml) when administered jointly intravenously. This is necessary in the early stages of treatment of acute inflammation of the pancreas to enhance the effect of drugs from other groups.