What it is?
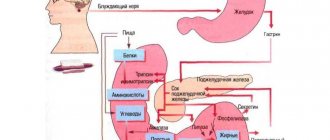
Belching is an unexplained release of air, sometimes with a small amount of stomach contents, through the mouth. This action does not always manifest as pathology. An individual’s stomach is not a hermetically sealed organ and normally contains up to one and a half liters of air inside it, which ensures normal internal pressure. There are two ways to remove air from the stomach, through:
- intestines - exits the anus, partially absorbed by the intestinal walls;
- esophagus - belching occurs.
When a fairly large amount of food enters the stomach, some of the air comes out of it. This picture is quite natural and indicates normal gastrointestinal motility. If a 3-year-old child burps after eating, when he has had a heavy lunch, several times with air, then this is normal. In addition, reflux:
- activates the production of gastric juice;
- promotes normal digestion of food;
- protects against stretching of the stomach wall.
Sometimes belching becomes frequent and painful, the reasons for which are determined by the doctor.
Belching, regurgitation and vomiting
All three processes differ from each other at the physiological level. Wherein:
- Belching - excess air comes out of the stomach through the mouth due to swallowing it during meals or when consuming a significant amount of food.
- Regurgitation is the expulsion of food from the stomach and esophagus without any effort. The child often does not develop negative emotions.
- Vomiting occurs when the abdominal muscles tense, the child turns pale, the heart rate increases, and the temperature of the extremities decreases.
Is it possible to help a child cope with burping and reflux?
There are two things to pay attention to: how you feed your baby and what exactly.
1. What to feed:
If you have started complementary feeding with baby food, pay attention to the portions. Small portions are digested faster, and smaller amounts of food reduce the likelihood of heartburn. It is worth consulting with your pediatrician which mixture is suitable for your child; it is possible that the doctor will recommend anti-reflux mixtures. It is worth remembering that the prescription of anti-reflux mixtures should be preceded by identifying the causes of regurgitation, so the mother needs to be very attentive to her child.1
2. How to feed:
- Feed your baby slowly and try to hold him at a 45-60 degree angle, which helps prevent reflux
- Let your baby release excess air while feeding
- Do not feed your baby just before bedtime, and do not put your baby in the crib immediately after feeding2
- Make sure the diaper or wrap is not too tight for the baby
Causes of air belching in children aged 3 years
The causes of air reflux in three-year-old children can be completely different. They arise from:
- Large amounts of food taken during meals.
- Drinking drinks containing gas.
- Fatty foods, legumes, garlic, onions.
- Wearing tight clothing and tight belts to prevent the stomach from expanding after eating.
- Talking while eating.
- Intense physical activity, when there is a sharp displacement of the contents of the stomach and some of the air comes out.
- Burping of air in a 3-year-old child often occurs due to rapid swallowing and poor chewing.
- Emotional overexcitement.
- Nervous shock.
- Frequent inhalations in the treatment of diseases of the oropharynx.
- Diseases of chronic tonsillitis, runny nose. When breathing is difficult, a large amount of air is also swallowed through the nose.
- Problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract with strong salivation.
- Dental diseases.
Parents need to be very attentive to their child’s behavior and try to notice everything that happens to him, so as not to miss serious complications.
Associated symptoms
Involuntary release of gases through the mouth may be a sign of an acute or chronic disease. In order not to miss the development of pathology, you need to know what accompanying symptoms indicate the seriousness of the situation:
- If, with constant belching, the child is bothered by pain in the chest, on the left, where the heart is located, problems with the cardiovascular system are possible.
- Belching with diarrhea, fever, or after vomiting indicates food poisoning or the presence of a rotavirus infection in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Nausea and heartburn, as additional symptoms in a child, indicate stomach problems: gastritis, ulcers or esophagitis.
- The simultaneous appearance of belching and gases in the intestines is a sign of fermentation in the gastrointestinal tract, evidence of disturbed intestinal microflora.
- Oral release of gases and coughing in a child are symptoms of respiratory diseases.
- Belching and bitterness in the mouth indicate diseases of the biliary tract.
If you notice additional symptoms, do not delay your visit to the doctor! Timely treatment will help quickly restore the baby’s health.
Why does burping have different tastes and smells?
Let us focus on the causes of belching in a 3-year-old child, which has a rotten smell, as well as a bitter and sour taste:
- The most unpleasant symptom is considered to be a putrid odor when belching. This means that a fermentation process is taking place in the stomach, caused by the bacteria in it. Low acidity of gastric juice is not able to overcome them. This situation occurs with atrophic gastritis, when the tissue of the gastric mucosa is damaged and the number of glands that produce gastric juice decreases.
- Bitter taste. It most often arises from the content of bile in the esophagus. Bile is produced in the liver and through special ducts; it enters the duodenum to digest food. With some disorders of the digestive organs, a reverse flow of bile is observed, and it, overcoming the resistance of the sphincter, is thrown into the stomach and esophagus. The cause of belching in children can be physical activity after eating, pancreatitis, overeating, blockage of the bile ducts and taking certain medications.
- Sour taste. Appears when gastric juice refluxes into the esophagus. This is possible with stomach ulcers and gastritis.
Infants under 1 year
After the birth of a child, during the first 6-7 months, regurgitation is considered normal and indicates the normal functioning of the body. But by 8 months, a healthy child experiences belching less and less often.
Regurgitation after eating occurs for the following reasons:
- The baby was overfed.
- The child was suddenly picked up after eating, played with, or placed on his stomach. Due to the fact that the baby was in a horizontal position during feeding, and was abruptly transferred to a vertical position, as a result, the sphincters of the digestive tract do not have time to close and belching appears.
- The baby has digestive problems.
- The formula is not suitable for the child.
- Incorrect attachment of the baby to the breast during feeding, due to which gases accumulate in the intestines and do not pass away naturally.
- Intestinal obstruction. This is a pathological condition that requires emergency care. It is characterized by belching green or brown food.
- Infectious diseases in which the child regurgitates undigested food debris. In addition, the baby becomes capricious, his temperature rises, and his skin turns pale.
In addition, belching in a child under one year old may be due to incompletely formed sphincters and the nervous system.
Usually, the process of belching in children of the first year of life is considered the norm, during which the child’s stomach is freed from excess food, air comes out, having entered the baby’s body with food or strong crying, and intestinal motility is normalized.
But if belching is frequent, then it irritates the mucous membrane of the esophagus and negatively affects the condition of the oral cavity. To prevent this, you must follow the following recommendations:
- 30 minutes before the next feeding, place the baby on his stomach;
- during feeding, you need to gently massage the belly in the navel area clockwise so that the air that enters the digestive tract leaves the body through the intestines;
- After feeding, the baby must be kept in an upright position for a quarter of an hour;
- Lightly stroking the child's back facilitates the passage of gases and air.
If, after regurgitation, the child experiences vomiting mixed with blood, this may indicate a ruptured blood vessel and the baby should be immediately shown to a specialist. Sometimes belching is accompanied by pain, crying, refusal to eat, and sleep disturbances. If these symptoms appear, you should consult a neurologist and gastroenterologist.
Stomach pain and belching of air
When swallowing, a slight rush of air occurs into the stomach, normalizing the pressure inside it. Then the excess is gradually released through the mouth in small portions. But if belching is accompanied by pain in the solar plexus area, this indicates pathological changes in the diaphragm. Frequent air reflux after eating and pain can occur due to the formation of a hernia. The lower section of the esophagus passes through the diaphragm, therefore, when food moves, due to a violation of the sphincters, gastric juice is thrown into the esophagus, causing not only frequent belching of air in the child, but also:
- burning in the throat;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- erratic heart rhythm.
Sometimes stomach pain is not at all related to the functioning of the digestive organs. Some nervous and cardiovascular ailments also cause belching of air after eating. Factors that provoke the release of gas include:
- cardiospasm;
- neurosis;
- failure: vascular or cardiac.
All of the above disorders of the child’s body require immediate treatment.
What causes air to leave the stomach?
All causes of regurgitation are divided into physiological and functional. In some children, nervous breakdowns affect the frequency of belching. In everyday life, the development of aerophagia is promoted by:
- binge eating;
- increased mobility after eating;
- conversations and nervous atmosphere at the table;
- incorrect combination of foods (for example, if fruits were eaten after animal proteins).
Why does my child burp frequently? Regular episodes of aerophagia indicate stooped posture or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- gastritis;
- hepatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- dysbacteriosis;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- hiatal hernia;
- intestinal damage by helminthic infestations.
Belching of air in children occurs due to eating on the go, dry snacks, and conversations during meals. At the age of 3–4 years, kids are in a hurry to start playing. Active behavior after eating promotes the release of air through the mouth. Other culprits of empty aerophagia are carbonated drinks, protein foods and dishes with legumes. Additionally, they cause increased gas formation.
Upon reaching 5–6 years of age, the child matures, and the belching changes in origin. It appears as a result of an inflammatory process that affects the esophageal mucosa due to the reflux of gastric contents (diagnosis - reflux esophagitis or GERD).
When a child burps sourly at intervals of 30 minutes after eating, it is most likely due to an enzymatic deficiency. Enzymes cannot cope with food processing, which leads to fermentation processes and accelerated gas circulation. If aerophagia with an unpleasant taste is released immediately after eating, the condition indicates incomplete closure of the valve between the esophagus and the lower tract.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Attentive parents will always notice disturbances in the child’s gastrointestinal tract. Problems may be accompanied not only by the release of gases accumulated in the stomach through the mouth, but also by abdominal pain, and possibly diarrhea. Frequent belching in a 3-year-old child occurs as a result of various pathological conditions:
- A hernia located in the esophageal opening of the diaphragm. In this case, part of the stomach and esophagus is displaced into the chest cavity. Due to disruption of the sphincters, acidic contents from the stomach are thrown into the esophagus, causing reflux and heartburn.
- Pancreatitis in both acute and chronic forms. Inflammation of the pancreas leads to a malfunction in its functioning. Food stagnates in the intestines, fermentation begins with increased formation of gases exiting through the mouth.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease. When it occurs, stomach contents regularly reflux into the esophagus. This factor provokes heartburn and belching after eating in a 3-year-old child.
- Ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or stomach. In addition to belching and heartburn, a sick child often experiences hunger and night pain in the stomach, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
- Neoplasms of malignant and benign nature. Tumors in the gastrointestinal tract compress organs, increasing pressure, which leads to the appearance of reflux.
If frequent belching occurs in a child, it is necessary to examine him to diagnose the disease and prescribe therapy.
Main causes
The reasons for a child's belching after eating can be physiological and pathological.
Physiological:
- Binge eating.
- Incorrect body position and talking while eating.
- Consumption of fast food, carbonated drinks, chewing gum. Having a large amount of protein products in the diet.
- Mixing incompatible products: meat - fruits, meat - legumes, fruits - nuts, fish - milk.
- Tight clothes. Compression of the abdominal organs causes excess gases and food to be pushed out of the stomach.
- Stress. They lead to spasms of the abdominal muscles, slow down or increase peristalsis of the stomach and intestines. This contributes to indigestion and the appearance of belching, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
Sometimes involuntary release of gases from the stomach can become a symptom of diseases:
- gastrointestinal tract: achalasia cardia, esophagitis, gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, duodenitis, inflammation of the pylorus, pancreatitis;
Less common:
- ENT organs: sore throat, chronic tonsillitis;
- nervous, cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- neoplasms of various nature.
Important! If your child's frequent belching is accompanied by a foul odor, has an unpleasant taste or a strange color, you should consult a doctor and find out the cause of the symptom.
Belching rotten eggs in a child
Belching rotten eggs can be caused by low-quality products containing sulfur. This category includes products that contain protein: meat, fish, eggs, milk, vegetables, cereals. Belching is usually accompanied by diarrhea. Disruption of the digestive system can lead to dehydration, so urgent measures must be taken. Severe belching in a 3-year-old child, which has the smell of rotten eggs, occurs with the following diseases:
- Salmonellosis is one of the most well-known causes of burps that smell like rotten eggs. The disease is accompanied by a sharp rise in temperature, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. The disease is infectious, so treatment of the child must be started immediately.
- Poisoning - ranks second after salmonellosis in the frequency of occurrence of belching with the smell of rotten eggs. The disease is accompanied by diarrhea, intoxication, and vomiting.
- Inflammation of the pancreas - a lack of enzymes inhibits the process of digesting food, and its fermentation begins.
- Inflammatory process of the gastric mucosa - microflora is disrupted.
- Poor nutrition – overeating meat and fatty foods. To belching are added symptoms of intoxication associated with its fermentation.
- Lack of bile – delays the digestion of food.
- Individual intolerance to foods - they are not digested, causing fermentation and related symptoms.
The list of factors that provoke belching of rotten eggs can be continued. Here are the most common cases where hydrogen sulfide is produced.
Treatment with medications
Before prescribing treatment, you need to determine what caused the belching. The following tests can help make a diagnosis:
- general analysis of urine and feces;
- blood biochemistry;
- respiratory tract examination;
- FGDS;
- pH-metry;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- colonoscopy;
- computer and magnetic resonance therapy;
- gastrobiopsy.
After the child has been examined and the cause of the belching has been determined, the doctor will, if necessary, select an individual treatment plan.
With increased acidity, children from birth can take Phosphalugel, which is available in a gel for oral administration. It can be given when belching is associated with the following pathologies:
- gastrointestinal ulcer;
- gastritis with normal or high acidity;
- GREB;
- diaphragmatic hernia.
Phosphalugel should not be given to a child if he has been diagnosed with kidney dysfunction and intolerance to the composition of the medication. It should be taken with caution in case of liver cirrhosis and heart failure.
Taking Phosphalugel can cause constipation.
In case of increased gas formation, Espumisan is recommended, which can be taken in the form of an emulsion and drops from birth, and in capsules it is allowed from 6 years. The drug is contraindicated in case of allergies to its composition or intestinal obstruction. Drops and emulsion are prohibited if you are intolerant to fruit sugar.
From birth, with increased gas formation, you can take Smecta, which has an adsorbing effect. The drug binds viruses, bacteria and toxins on its surface.
Read: If there is blood in the stool: causes in children and adults
Smecta should not be taken if there is intestinal obstruction or if its composition is tolerated. It should be given with caution to a child who has frequent constipation. Taking Smecta may cause allergies, bloating, constipation, and vomiting.
The following drugs can restore intestinal microflora:
- Hilak forte. The medicine is available in drops, which are contraindicated in case of allergies to their composition, impaired absorption of glucose and galactose, lactose intolerance, lactase and isomaltase deficiency. The medication may cause allergies, stomach upset, and constipation. Hilak Forte has no age restrictions; it can be given before or after meals. The drops should be diluted with a small amount of liquid, but not with milk.
- Bifiform. The drug is available in capsules, which can be used for intestinal dysbiosis and indigestion of various origins. Bifiform should not be taken if you are intolerant to its composition, in which case it can cause allergies.
For pancreatitis and other pathologies, when enzyme deficiency is observed, enzymes, for example, Creon, can be prescribed. The medicine is available in capsules that contain microspheres. It has no age restrictions. Creon should not be given if you are intolerant of its active and auxiliary components.
The medication may cause the following adverse reactions:
- abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, indigestion, constipation, flatulence;
- stenosis of the ileum, cecum and colon;
- allergy, which manifests itself as itching, urticaria, anaphylaxis.
If the child is overly excitable, you can give valerian and motherwort.
If belching occurs with the smell of rotten eggs, diet, exercise, and taking enzyme preparations are recommended. To remove decomposition products, you can give your child adsorbents, for example, Polysorb MP.
Recommended video:
It is produced in powder from which a suspension is prepared; it is contraindicated in case of exacerbation of peptic ulcer, bleeding from the digestive tract, intestinal atony, hypersensitivity to the composition of the medication.
Polysorb MP can cause allergies, constipation, dyspeptic disorders, and impaired absorption of vitamins and calcium. Sometimes belching that smells like hydrogen sulfide may require surgery.
Belching food in a 3 year old child
Many children do not get used to kindergarten well and have a hard time with the adaptation period. The baby is nervous, which contributes to spasmodic muscle contractions. After eating, he sometimes burps air, and more often undigested food, and vomiting is also possible. Over time, the child gets used to the living conditions in the kindergarten, and the stressful state goes away. After this, as a rule, colds begin. A weak immune system cannot cope with the invasion of pathogens. The baby has a sore throat and a runny nose.
He does not breathe through his nose, and when breathing through his mouth, an excess amount of air accumulates in the stomach and the child burps air. A large concentration of children in the kindergarten and failure to observe proper hygiene contributes to infection with helminths, which cause allergic reactions, coughing and belching. In addition, serious gastrointestinal pathologies occur, one of the clinical manifestations of which is belching.
Children of primary preschool age
In a child under 5 years of age, the digestive system is developing. The gradual introduction of new products and the reaction to them is reflected in the operation of the tract. The appearance of belching, especially after a year, tells parents about problems in the gastrointestinal tract that deserve special attention.
Infants
The release of air along with milk through the esophagus in the opposite direction in infants occurs due to the not fully strengthened nervous system and the peculiarities of the digestive system. Causes of belching:
- Binge eating. The main food product for a child up to 6 months is mother's milk, but not all women are able to breastfeed. Mixtures come to the rescue. Incorrect calculation of portions leads to overeating of the child, regurgitation of excess residues occurs. To prevent the phenomenon, it is necessary to reduce the dose of baby food until the condition normalizes.
- Accumulation of a large amount of gas in the baby's stomach. The body’s inability to remove them through the anus due to improper application to the mother’s breast. If the cause occurs frequently, injury to the narrowing passage of the esophagus may occur due to the pressure of accumulated gases on the stomach and intestines.
- Sudden change of position. When a baby is abruptly transferred from a supine feeding position to a standing one, the esophageal sphincter does not have time to close and belching appears. Before feeding, let the baby lie on his tummy for a few minutes. This will allow the intestines to get rid of excess air naturally.
- Artificial mixture. In a bottle-fed newborn, belching indicates intolerance to one of the nutritional components. Consultation with a pediatrician will help resolve the situation. When feeding, it is undesirable to change the baby’s position; this can provoke a new strong release of air.
- Intestinal obstruction is an extremely dangerous rare pathology. Symptoms: belching food that is brown or green in color. Emergency medical attention required.
- Presence of infection. The baby is capricious, regurgitates undigested breast milk, has a body temperature and pale skin. You should consult a doctor for a diagnosis and treatment.
- Frail nervous system, unformed esophageal sphincter.
Any belching in a child leads to a consultation with a pediatrician. Only a specialist will be able to correctly determine the cause and prescribe adequate treatment.
Children 1-2 years old
A one-year-old baby's diet is more varied than a one-year-old baby's diet. The menu includes fruits, vegetables, and sweets. Particularly loving mothers give their children chocolate and ice cream to try. Gradually, breastfeeding fades into the background and the amount of mother's milk decreases. A new stress occurs for the baby’s digestive system, including the need to rebuild. Again, malfunctions in the internal organs responsible for digesting food lead to belching and abdominal pain.
New products are introduced gradually, giving the body the opportunity to get used to it and produce the necessary enzymes for absorption. If parents notice a negative reaction to an ingredient, they should stop taking it for a while or replace it with a similar one. It is too early to offer chocolate, cake and ice cream at this age. The glucose necessary for the body is found in fruits, berries and honey, subject to tolerance.
The activity of a one-year-old baby is not in dispute. Constantly on the move, crawling, exploring the world around him. This can cause belching, especially if the activity occurs while the food has not been digested.
If for newborns the removal of gases and air through the mouth is considered a natural and common occurrence, for a child older than one year, the appearance of belching immediately after eating indicates improper functioning of the digestive system and difficulties with breathing. Contacting a specialist and examining the child’s body are necessary actions for parents.
Children 2-5 years old
Most children go to kindergarten at 2-3 years old. The first period of adaptation is difficult for a child: the mother is not around, there are strangers around. The baby cries, which causes spasmodic muscle contractions, and the passage between the esophagus and stomach contracts. This leads to belching (air or undigested food). Gradually the child calms down and the unpleasant sensation disappears.
The stressful situations don't end there. While in kindergarten, a child often suffers from colds and viral infections. The baby’s immune system is not yet ready to fight a large flow of viruses and pathogens. A cold is accompanied by a stuffy nose and a red, sore throat. Breathing becomes difficult, causing the muscles of the lower esophagus to contract. Allergies also contribute to the appearance of belching.
Worms begin to appear in children's bodies due to the inability of the fragile immune system to resist them. It is easy to become infected with parasites through animals. Helminths spread throughout the body. By affecting intestinal function, they lead to allergies, coughing and belching.
In children over two years of age, the digestive system has developed; belching is not a good sign. Parents should consult a doctor and be examined for diseases: gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, worms, scoliosis, neurosis, etc.
Reasons why you should not run to the hospital and prescribe medications: tight clothing, drinking too much liquid, bending over, and physical activity immediately after eating.
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky
Belching - the involuntary release of accumulated air in the stomach through the mouth - can occur in a child up to ten times a day. Reflux without odor or other unpleasant symptoms is normal and beneficial. It helps strengthen the motility of the digestive organs, relieves the child of excess gases that stretch the stomach and cause pain. Belching accompanied by other symptoms, nausea, abdominal pain, bad breath, indicates problems with the functioning of the digestive system. If a child has belching at the age of 3, Dr. Komarovsky advises parents to take the following actions:
- Adjust your diet: avoid overeating, eat often and in small portions.
- Teach your child to chew food thoroughly. Without developing such a skill in childhood, an individual will have problems with the gastrointestinal tract as an adult.
- Remove unhealthy foods from the menu: carbonated drinks, snacks.
- Maintain a rest and wakefulness routine.
- After eating, a short break is necessary before outdoor games.
- Physical activity and daily walks are required.
- Maintain a calm environment in the house so that the child can completely relax.
If following the above tips does not solve the problem, then medical help is needed.
Belching and vomiting
Frequent belching in a 3-year-old child, heartburn, and then vomiting may indicate disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. The same symptoms indicate a child’s nervous state and stress. In addition, the following situations are possible:
- The disorder is caused by overeating. Belching and vomiting are accompanied by painful sensations in the abdominal area.
- Increased acidity. Vomit consists of a liquid with a sour odor and a slight admixture of food matter.
- Failure of the evacuation-motor function of the stomach. Vomit has a sour or rotten taste.
All cases require medical attention. A vomiting reaction can lead to dehydration of a child's body.
What to do in such cases?
The most important thing is not to panic, and to calm down for yourself and your child. Assess the situation with a sober look, and think about why this or that trouble occurred. Your further actions depend on your correct position.
If vomiting is accompanied by a rise in temperature, uncontrollable vomiting, diarrhea, loss of consciousness, cold extremities, severe pallor, the presence of blood in the vomit, call the Ambulance Service immediately.
Other cases, such as frequent attacks of heartburn, belching, and nausea require mandatory consultation with a doctor.
Belching that occurs constantly
Why does a 3 year old child burp? There are many reasons for this phenomenon, as noted earlier. But if it constantly torments the child, then this is most likely due to indigestion, when gases are produced in excess quantities during the digestion of food. This is possible in the following cases:
- The child washes down food with plenty of water. As a result, he swallows a lot of air and chews it poorly.
- Low or high stomach acidity. In the first case, the child is tormented by belching, which has a putrid sulfuric taste, and in the second, a sour or bitter taste. In addition, heartburn, nausea and stomach pain appear.
- Gastritis occurs at any age and even in a child as young as 3 years old. Constant belching with a putrid, rotten smell is one of the symptoms of this disease. It is accompanied by aching or sharp pain in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite and rapid satiety.
If persistent reflux with odors is detected in a child, an urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary; the diseases can be very serious.
Hiccups and belching
Hiccups are a failure of external respiration associated with involuntary contraction of the diaphragm and simultaneous closure of the epiglottis. In most cases it occurs suddenly. Hiccups appear in a child when:
- emotional stress;
- hypothermia;
- overeating.
It is rarely considered a symptom of pathologies. Belching, on the contrary, never occurs suddenly. Its appearance is associated with food intake, and is provoked by various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Hiccups, accompanied by belching, are most often a symptom of some disease associated with poor nutrition and nervous shock. And hiccups and belching in a 3-year-old child are often signs of overeating or eating dry food.
Sour belching in a child
A child may experience sour belching:
- Immediately after eating. The reason is incomplete closure of the valve between the esophagus and the gastrointestinal tract. Gastric juice is thrown into the esophagus.
- After half an hour, there may be a lack of enzymes for digesting food, the fermentation process begins and acidic gases are released. The problem is related to problems with the pancreas.
- One hundred and twenty minutes after eating. The presumptive diagnosis is gastritis with increased acidity of gastric juice.
To eliminate belching in a 3-year-old child, first of all, the cause of acid reflux is determined. In this case, you cannot do without a doctor’s prescription, but parents also need to be attentive to their child and choose suitable products for him in order to eliminate the unwanted symptom.
Belching and gas in babies
Reflux and gases occur in babies at any age. When the digestion process is disrupted, increased release of gases occurs. And their increased formation and reflux occur when consuming large amounts of fiber and swallowing air during meals. To eliminate the problem, it is necessary to change the child’s diet. Eliminate foods that contain a lot of carbohydrates:
- all types of cabbage;
- peas, beans, beans;
- carbonated drinks;
- some fruits (apples, pears, peaches).
To get rid of belching it is recommended:
- do not engage in outdoor games immediately after eating;
- eat slowly and in small portions;
- don't talk while eating.
If the condition does not improve after the measures taken and pain appears in the abdominal area, then you should consult a gastroenterologist.
Belching treatment methods
Treatment of any disease, including belching in children, begins with diagnosis, during which the causes of the ailment are identified. In addition, even before a diagnosis is made, a diet is prescribed. It is advisable for parents to remove foods that cause bloating, as well as carbonated drinks, from the diet, reduce single servings and switch to 5 or 6 meals a day. After diagnostics have been carried out and an accurate diagnosis has been established, appropriate therapy is carried out. Treatment is used depending on the type of belching:
- Air - eliminated by simply following a diet and correct behavior of the child while eating.
- With a sour or bitter taste, indicating excessive secretion of gastric juice, they are treated with alkalizing agents, which will be prescribed by the attending doctor.
- Belching of food in a 3-year-old child with the smell of rotten eggs, indicating gastrointestinal diseases (stomach ulcers, gastritis, intestinal microflora disorders), is eliminated by therapy using a therapeutic diet, enzymes, and gymnastics. In extreme cases, surgical treatment is resorted to.
- An unpleasant, rotten odor and bitter taste are treated with medications recommended by a gastroenterologist, additionally using therapeutic exercises and dietary nutrition.
- Those that appear before meals are eliminated by using the missing lactobacilli, which normalize the disturbed intestinal flora.
- Accompanying heartburn can be eliminated with proper nutrition, avoiding overeating. For more serious causes (pancreatitis, gastritis, cholecystitis), complex treatment is prescribed by a gastroenterologist.
All therapy is carried out strictly under the supervision of the treating doctor.
Treatment
To get rid of belching, you need to establish the root cause and eliminate the influence of negative factors. Infants are advised to have frequent meals and abdominal massage. Children under 2 years of age should be gradually introduced to new foods and have colds treated professionally. From the moment a child enters society, more serious health problems begin - worms, colds, neuroses. Actions are symptomatic.
Treatment of belching in older children includes:
- regular checks for worms;
- proper nutrition;
- adherence to food intake;
- avoiding stress and nervous tension.
As for eliminating the root cause, which most often is a disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, they take folk remedies or pharmaceutical drugs. Antacids are indicated - they coat the walls of the esophagus and stomach, protect against irritation, improve digestion, reduce acidity, and relieve pain.
The drugs are produced in the form of capsules, lozenges, and suspensions. Drugs are indicated for normalizing the functioning of the nervous system and relieving muscle spasms - tincture of valerian, motherwort, glod. To normalize intestinal function, take probiotics - Laktiale, Laktovit, Turbiotic, Hilak Forte, Bifidumbacterin. To reduce gas formation, Smecta, Kolikid, Espumisan, and Activated Carbon are prescribed. In any case, you should drink large quantities of still mineral water.