Description of the procedure
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) is a technique for endoscopic examination of the upper digestive system
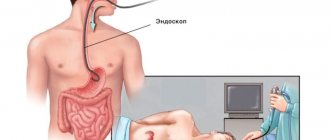
(stomach, duodenum, esophagus). To carry it out, a special probe is used, which is equipped with a miniature camera and a manipulator.
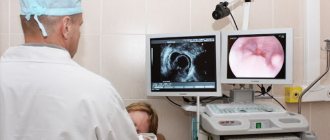
In modern endoscopy, the image is displayed on a special screen. Acidity is also constantly monitored. FGDS usually includes a test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection
.
If necessary (for example, long-term existence of an ulcer, the appearance of neoplasms, chronic inflammatory processes), the examination is supplemented by a tissue biopsy with cytological examination
in a specialized laboratory.
An FGDS certificate is the basis for diagnosing diseases of the stomach, duodenum or esophagus.
It allows you to visualize changes in the mucous membrane that are difficult to see on CT or MRI. It is based on the results of FGDS that one can distinguish gastritis, peptic ulcer or malignant process
.
The study is of particular importance for highly specific rapid diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is prescribed if the patient has the following symptoms:
- aching pain in the upper abdomen, which intensifies after eating or drinking (especially alcoholic or carbonated);
- sensations of discomfort in the epigastrium ;
- the occurrence of nausea, single vomiting;
- burning behind the breastbone or heartburn;
- decreased appetite and subsequent loss of body weight;
- tendency to constipation or diarrhea.
Typically, FGDS is carried out after the patient is examined by a doctor and undergoes basic laboratory tests.
Features of the procedure
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is used not only to diagnose various pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, but also for treatment. The area of intervention becomes clear when the term is deciphered: an endoscope can be used to assess the level of condition of the gastric and duodenal mucosa. During the procedure, you can not only determine deviations in the condition of the mucosa, but also perform a biopsy (sampling a part of the mucosa for further examination).
The technique used is based on the use of an endoscope. This device is a hollow tube with a camera at the end. To perform the procedure, the patient must have certain indications that guide the specialist, taking into account possible adverse reactions.
Indications for use of FGDS:
- Pathology of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) identified during a clinical examination.
- Performing diagnostics for other diseases.
- Control of previous treatment.
Abdominal pain is a reason to get examined
Most often, patients who periodically report stomach pain, nausea, heartburn, belching after eating, and impaired bowel movements are sent for an endoscopic procedure. Oncology and anemia are also indications for FGDS. If internal bleeding from ulcers is suspected, an endoscope can not only identify them, but also treat them. An important aspect of the use of FGDS in practical medicine is the ability to remove foreign bodies from the gastrointestinal tract, which previously got there through accidental or intentional ingestion.
Relative contraindications to endoscopic examination:
- Pathology of the cardiovascular system: acute heart attack and stroke (the restriction is valid for at least 6 months), aortic aneurysm, persistent hypertension turning into crisis.
- Hemophilia or coagulation defects.
- Pathology of the esophagus: burns, scars.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Mental illnesses, especially in the acute stage: are dangerous due to the rapid uncontrolled development of motor reactions, which can lead to accidental injury to the gastrointestinal mucosa by the endoscope.
Mental disorder may become an obstacle to undergoing FGDS
An absolute contraindication to FGDS is the patient's agony. Taking into account the clinical picture and general condition of the patients, the specialist conducting the study must take into account the possible deterioration of the patient’s condition. When performing a diagnosis, the benefit gained for the treatment being performed must be taken into account. Of course, this procedure may cause a certain feeling of pain during its passage, however, given the possible deterioration of the condition in the absence of intervention, you should tune in and prepare as accurately as possible for the manipulations being performed.
Is it painful to have a gastroscopy?
Most patients who have undergone FGDS in the traditional way, if asked to describe their feelings from the procedure, call it unpleasant. To reduce the severity of these sensations, a local anesthetic is used, which is applied to the back wall of the oropharynx.
.
However, it does not always save the patient from discomfort. The most common complaints
from patients:
- nausea;
- a feeling of discomfort in the neck, behind the sternum or in the abdomen;
- increased salivation;
- belching;
- feeling of lack of air;
- panic attacks;
- aching or cutting pain in the neck or abdomen.
Oddly enough, pain syndrome is relatively rare. It is possible in the presence of acute pathology (for example, exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease in young patients), complications (wall perforation) or careless examination, however, swallowing the intestine to check the stomach is unpleasant. The main thing is to behave correctly during the procedure and listen to the doctor’s recommendations.
Does it hurt
Gastroscopy is painful, say only those who are not entirely familiar with all the intricacies of the study.
To prevent discomfort, the specialist performs the following procedures:
- Sprays lidocaine onto the root of the tongue. This drug freezes the pharynx, so there is no gag reflex and pain during the process of inserting the endoscope into the pharynx.
- They may offer gastroscopy in your sleep. In this case, a certain amount of sedative is injected into the patient's vein. This puts him to sleep, and while he sleeps, they conduct research.
- In severe cases, when the contents of the stomach can enter the bronchi, the procedure is performed under anesthesia. You just shouldn’t ask the doctor for such a “favor,” since general anesthesia is a difficult test for the whole body.
- To avoid a gag reflex, gastroscopy can be performed through the nasal passage. To do this, use a tube with a diameter of about six millimeters. But not all clinics can provide this service, as special equipment is required.
During the procedure, it is important to strictly follow the doctor's advice. The specialist will tell you in detail how to breathe and what to do.
During the procedure it is possible:
- strong secretion of saliva. Therefore, you need to take a towel with you that is placed under your chin. You should not swallow saliva;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach. It's not scary. The discomfort will pass as the endoscope advances, and the air will be released by belching;
- vomit. If you do not follow the advice not to eat or drink anything, vomiting may occur.
By following all the doctor’s recommendations, you can undergo a painless examination and obtain accurate information about the state of the gastrointestinal tract. If your health worsens, the doctor will remove the device and reschedule the procedure.
How can I make the procedure easier?
The correct approach to fibrogastroduodenoscopy can significantly improve the patient’s well-being during the procedure. Below are the main recommendations that make FGDS absolutely painless.
Choosing the right doctor
Choosing a qualified doctor with a friendly approach to his patients can significantly reduce anxiety before the procedure, as well as reduce the severity and frequency of side effects.
A good approach from a specialist relieves anxiety and helps the patient relax. This allows the procedure to be carried out without unnecessary trauma (for example, scratching the throat), since the probe advances more easily.
In clinical practice, there are situations when, due to low professionalism, the doctor applies the wrong or insufficient anesthetic . Also, some medical professionals do not explain the essence of the procedure, possible risks, and nuances of patient behavior.
Important The doctor must carefully explain the nuances of preparing for the study, as well as select the most appropriate method of performing the procedure (nasal insertion of a probe, sedation or anesthesia) for a particular patient.
Psychological attitude
Many patients are scared and anxious; they do not know how to withstand a stomach examination. Some people generally cannot tolerate such procedures and do not know what to do or how to pass the FGDS.
It is usually scary to do research due to the lack of reliable information about FGDS, as well as reviews from friends. And if the patient is sure that he will be in pain during the procedure, then the risk of this complaint increases significantly, even if the study went without complications.
It is important to have contact between the doctor and the patient
. This will help make the procedure easier. He must be ready to answer all questions that arise, as well as give truthful and objective information about why FGDS is performed, what its value is and how you can avoid the occurrence of side symptoms.
There is no need to be afraid or ashamed belching, increased salivation or an attack of nausea occurs during the procedure .
These symptoms, to varying degrees of severity, bother most patients, but they are not a sign of the development of complications and quickly disappear after the diagnosis is completed . It is important to remember that medical staff encounter this every day, and therefore, for example, frequent belching does not bother them at all .
Before the procedure begins, the patient is given a small mouthguard that protects the probe from the teeth . In modern clinics, it is selected according to the diameter of the endoscope and the size of the patient’s oral cavity.
The procedure is performed with the patient lying on his side
.
During FGDS, the probe passes through the oral cavity, oropharynx, larynx, esophagus and enters the lumen of the stomach. The doctor examines the condition of the mucous membrane, conducts acidity measurements, as well as a test for Helicobacter pylori infection . If necessary, a biopsy is performed.
Please note: The total duration of the procedure does not exceed 10-15 minutes (if the doctor takes tissue, it can take up to 20-30 minutes).
Phytotherapy or medications tune in correctly to FGDS and eliminate anxiety.
.
The importance of proper preparation
Proper preparation for FGDS can significantly reduce the severity of side symptoms (especially vomiting) and increase information content. Therefore, on the day of the study, the patient should not eat. The last meal should optimally be no later than 10 hours before the test. For 2 hours, limit the intake of drinks - tea, coffee and even plain water.
To increase information content (especially if a Helicobacter pylori infection is suspected), special medication preparation is required.
It is necessary to discontinue medications that may affect the result - antisecretory agents, antacids, antibiotics, Bismuth preparations and some other medications.
Therefore, when prescribing a study, you should always warn the doctor about the presence of concomitant pathologies and medications taken.
Breathing feature
Before starting the procedure, the doctor must explain to the patient how to breathe correctly during FGDS. Breathing should be through the nose
, deep and smooth.
In this case (despite popular belief) there is no need to swallow
while moving the endoscope through the oropharynx and larynx. When you swallow, your larynx contracts, you touch the endoscope, and the doctor advances it. This leads to microtraumas of the throat and after the procedure you may feel that your throat hurts. Also, during the procedure you will feel that you cannot control the situation and panic.
That’s why it’s so important to relax and trust the doctor , breathe calmly, and burp calmly. This way you will not harm your body and will allow you to complete the procedure faster.
Following these recommendations will help the patient to adjust himself, promote calm and prevent sudden movements, therefore reducing the risk of injury and serious side effects.
GENERAL PREPARATION FOR THE PROCEDURE
Gastroscopy is not a particularly painful, but unpleasant procedure. To endure it with minimal discomfort, you should follow a few simple recommendations.
- During the several days preceding FGDS of the stomach, you should adhere to a special diet. From your diet you will need to exclude all those foods that irritate the mucous membrane of the digestive system. These products include marinades, smoked meats and dishes with a high content of spices.
- The day before the procedure, the last meal should be no later than 8 pm. The optimal dinner menu is low-fat dishes: vegetables or unsalted or lightly salted porridge with water.
- Soon after waking up, it is recommended to drink water or weak tea without sugar - this will help cleanse the walls of the stomach.
- It is advisable to refrain from smoking at least a few hours before FGS. The fact is that tobacco smoke irritates the digestive system, as a result of which it begins to more actively secrete mucus, which complicates the examination.
- If possible, you should stop taking blood thinning medications (in particular, aspirin) for a few days before gastroscopy, and on the day of the procedure, stop taking any medications. When performing FGS, there is a risk of injury to the gastric mucosa, and therefore bleeding. And the thicker the blood, the faster this internal bleeding will stop.
- Overly impressionable people are allowed to take mild sedatives (but it is better to consult a doctor first).
The right attitude or how not to be afraid
Gastroenterologists believe that the degree of discomfort during gastroscopy determines the psychological mood. As a result of strong fear and thoughts of “whether it hurts or not to do gastroscopy,” the patient experiences a spasm, which makes it difficult for the device tube to pass through the esophagus. Therefore, the first advice that a gastroenterologist gives after referring a patient for examination is to prepare yourself correctly and be sure that the procedure will be easy and completed successfully.
In order not to be afraid of FGDS, experts advise:
- read literature about painless gastroscopy of the stomach;
- talk with friends and relatives who underwent gastroscopy and can describe what happened;
- learn techniques on how to survive strong anxiety;
- study the instructions on how to behave correctly before, during and after the procedure.
If it is difficult to cope with anxiety and fear on your own, the doctor may prescribe a course of sedatives. They will not bring direct physical relief during FGDS, but they will help facilitate the procedure by eliminating spasm due to fear.
Note! Only a doctor can select medications with a sedative effect! When using medications without authorization, there is a risk of distorting the results of the study, since the drugs can affect the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Methods for painless passage
In the last decade, techniques have begun to be actively used that can significantly reduce discomfort or even painlessly undergo gastroscopy of the stomach:
- Sedation
.
Sedation will help you survive FGDS calmly without fear. The patient is injected intravenously with a drug from the group of benzodiazepines, after which he falls asleep . The procedure is widely carried out and makes it easier to endure unpleasant sensations and painlessly perform FGDS of the stomach for adults and children. A few minutes after completion of the study, the patient wakes up. In an hour he can go home. The risk of side effects is low. - Anesthesia
(general anesthesia).
Used more rarely under the supervision of an anesthesiologist. The patient is given several drugs for pain relief, but mechanical ventilation is not required. Usually performed before planned surgery. -
Capsule endoscopy
.
This is an innovative technique in which the patient does not have to swallow the tube. Instead, it swallows a small capsule-shaped chamber
that travels all the way through the digestive system. The image is recorded and then viewed by a doctor without any problems. Among the disadvantages of capsule endoscopy is the impossibility of a more thorough examination of the changed area of the mucosa, conducting a Helicobacter test or biopsy. Helps those who cannot undergo the standard FGDS procedure.
Insertion of a probe through the nose is also used.
(transnasal technique).
This technique provides a more comfortable FGDS
, since it causes nausea much less often and does not affect hemodynamic parameters (which is important for patients with cardiovascular diseases).
A probe with a significantly smaller diameter is used - 5.4 mm
(standard - 11 mm). When asked whether it is painful to do gastroscopy of the stomach in this way, many patients answer negatively.
Some diseases can be diagnosed using less unpleasant procedures: x-rays of the stomach and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. In this article we have presented all the alternative methods of FGDS.
Recommendations after the procedure
In order for FGDS to pass without unpleasant consequences, it is important to behave correctly after its completion.
Diet
After the examination, you should refrain from eating for half an hour, and if a biopsy or sedation was performed, then about two hours.
The first meal should be light; it is better to eat something simple - porridge, lean meat, dry cookies or hard cheese.
You shouldn't eat a lot. You need to refrain from drinking alcohol.
Peace
On the day of the test, it is important not to overexert yourself physically and emotionally. Some patients feel well after fibrogastroduodenoscopy and are ready to work. Others may feel weak, in which case it is better to rest. It’s good if important things are postponed to another time. It is recommended to sleep after the procedure.
FGDS of the stomach is an informative study that helps doctors diagnose severe pathologies. It is associated with some unpleasant sensations (swallowing a probe), but endoscopy cannot be replaced by other methods, such as ultrasound. You should not refuse FGDS out of fear. The right attitude and preparation will allow you to undergo the examination without any discomfort or consequences.
Possible consequences
After completion of the procedure, patients may have the following complaints:
- aching pain in the epigastrium (upper abdomen), neck or behind the breastbone, which may intensify after swallowing;
- weakness, dizziness , headaches, drowsiness (if drug sedation was used);
- cough (entry of stomach contents into the respiratory tract due to improper preparation of the patient);
- allergic reactions (to anesthetic);
- heartburn or burning sensation;
- increased saliva production ;
- loss of appetite;
- palpitations or increased blood pressure (due to activation of the sympathetic nervous system);
- nausea that gets worse when eating or drinking water.
Important The severity of these complaints greatly depends on the qualifications of the doctor, as well as on the method of conducting the diagnostic procedure.
They usually go away completely within a few hours. Recommendations after the procedure:
- Diet . After completing the FGDS, you cannot eat for another 30 minutes (and if a biopsy or sedation was performed, then 2 hours). The first meal should consist of simple foods and dishes: porridge, lean meat or fish, yesterday's bread, dry cookies, hard cheese, honey.
- Peace. Avoid increased physical and emotional stress during the day. Some people feel completely fine after the procedure and are ready to get back to work. But some people feel quite weak, like after a slight poisoning. If you have the opportunity to schedule your sleep after the procedure, take advantage of it.
Preparatory part
It is recommended that the patient begin preparing for FGS by adjusting the usual menu and daily diet. Diagnostics are carried out in the order specified, when making an appointment with the attending physician. The patient is recommended to switch to lighter and healthier foods one week before fibrogastroduodenoscopy. Preparation consists of eliminating the following foods:
- Fatty sauces, mayonnaise content.
- Hot seasonings, spices.
- Sweet baked goods.
- Pork, lamb, fatty cuts of beef.
- Dishes prepared using various types of mushrooms.
- Fatty dairy and fermented milk foods.
- Legumes, peas.
- From smoked meat, smoked fish, poultry.
- Pickled vegetables.
- All types of nuts. Dishes containing nuts.
- Alcohol-containing drinks of any kind.
During gastroscopy, it is recommended to limit and exclude the following foods from the daily diet:
- All types of bread.
- Caffeinated drinks.
- Sweet foods.
- Raw vegetables and fruits.
- Sausages, semi-finished products.
Previously taken preparatory measures will help to correctly undergo fibrogastroduodenoscopy of the stomach. A good research result and an accurate diagnosis also depend on this.
Before diagnosis, the patient is recommended to exclude meat, fish, baked goods, and cereals prepared from large-grain varieties from the diet.
It is important to remember that in case of surgical intervention on the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, the patient is recommended to stop eating food, starting from the lunch break until the completion of diagnostic measures. More precisely, one day before the proposed examination.
The most beneficial effect on the diagnosis is a previously followed diet menu, which includes poultry meat (breast), lean fish, porridge cooked in water, without additional addition of sugar-containing substances (it is allowed to use natural honey in small quantities), stewed vegetables. It is not recommended to prepare food by frying; instead, you should stick to stewed and boiled dishes. It is allowed to season ready-made food with low-fat sour cream and natural yogurt. Dietary nutrition before the examination is designed taking into account fractional meals, containing an interval of three to four hours between meals.
The next recommendation is to avoid bread, all flour products, and raw foods, including vegetables and fruits, three days before the analysis. For two days, the patient excludes cereals and pasta of all types from his diet. It is allowed to eat food ten or twelve hours before the examination of the stomach and duodenum. The gastrointestinal tract should be in an empty state. Drinking water or weak tea is allowed when calculating two, two and a half hours before the start of the procedure.
Taking medications is allowed for vital indications. Those medicines that support health and the normal condition of a person are allowed. It is recommended that you inform your attending physician about the medications you are using when making an appointment for an FGDS, since a certain group of medications may cause inaccurate diagnosis. A person with an existing disease uses prescribed medications, dissolving, but not swallowing. An unprepared stomach prevents a thorough examination of all parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
The main factor influencing an effective and comfortable examination is the patient’s psycho-emotional preparation for the upcoming events. A good, positive attitude helps to undergo fibrogastroduodenoscopy easier without associated problems. Fear with nervous overstrain during FGDS does not allow swallowing movements, which help the fibrogastroscope to move easily through the larynx.
Correct breathing
“I’m afraid to do a gastroscopy,” doctors hear from their patients every now and then. Is it painful to do FGDS? If you follow the basic recommendations, everything will go as smoothly as possible. To minimize discomfort during endoscopy, do not forget about proper breathing. In modern clinics, each patient undergoes a short instruction, where he is taught how to breathe during gastroscopy.
You need to inhale and exhale only through your nose. Breathing from the throat is painful and can lead to the release of saliva, which enters the respiratory tract and provokes a cough reflex. You should breathe as smoothly and measuredly as possible. Jerky inhalations and exhalations do not allow the gastroscope to be inserted painlessly and correctly, which can cause a rupture of the esophagus.
Pain during the procedure
Most people who delay or do not want to do FGDS are simply not familiar with this procedure. Somewhat less often, fear arises on the basis of a previously suffered unsuccessful experience, which was remembered by unpleasant sensations.
The sensations from performing an FGDS can be described as unpleasant, but generally almost painless.
It should be remembered that the doctor performs the procedure quickly - it usually does not take more than 5-10 minutes. You need to calmly listen to him and follow his instructions. Patients often do not know whether gastroscopy is painful, which is why they refuse such an important study. Nowadays, all diagnostic offices must take this into account. There are the following ways to prevent discomfort:
- First of all, a person must be determined to successfully carry out the procedure. It is also in his power to provide himself with maximum comfort:
- It is worth giving preference to light, loose clothing that prevents compression of fabrics in the décolleté and neck area, and loosen the belt;
- It is advisable to remove lenses and dentures during medical procedures;
- The day before you should stop smoking, even if you really want to;
- Before the manipulation, the patient is irrigated with special sprays (with Lidocaine), in particular the area of the root of the tongue. Because of this, the sensitivity of nerve endings is temporarily reduced, eliminating the appearance of pain or a gag reflex;
- In rare cases, FGDS is allowed to be performed during artificial sleep caused by the administration of sedatives with a hypnotic effect;
- For weakened or seriously ill patients, gastroscopy is performed using general anesthesia. An anesthesiologist is specially called for this purpose;
- If a person refuses additional use of medications or has contraindications for performing FGDS through the oral cavity, he may be offered a transnasal method. But not all specialists have sufficient skills or equipment to do this.
Carrying out gastroscopy under general anesthesia is possible only under strict indications, and not at the request of the person.
There is severe depression of the central nervous system, which in itself is a severe stress for the body, and complications can be life-threatening. For some time after FGDS, a person may experience increased secretion of saliva, abdominal discomfort, nausea or even vomiting. These phenomena are temporary and go away on their own, without requiring the use of additional funds.
Preparation rules
Before referring a patient for testing, a doctor (usually a gastroenterologist) interviews and examines him. Based on the information received, additional recommendations may arise not only for the patient himself, but for the endoscopist. The coordinated work of several specialists allows you to achieve the desired result, as well as avoid many unpleasant moments.
Before FGDS, a person can eat light meals (soups with low-fat broth, boiled meat/fish, stewed vegetables). You cannot eat for 9-10 hours before the procedure, as it is performed only on an empty stomach. Non-carbonated mineral water and weak teas are allowed,
Alcohol and carbonated drinks, fast food, fried, smoked and marinades are also prohibited - such products contain substances that intensify gastric secretion, which can distort the results.
Preparation includes talking with doctors. They need to be told in detail about concomitant diseases, family history and cases of allergic reactions, especially to medications. The attending physician gives recommendations on an individual basis, since each patient has his own characteristics. During FGDS it will not hurt if you strictly follow all the specialist’s instructions. This also minimizes the risk of complications after the procedure.