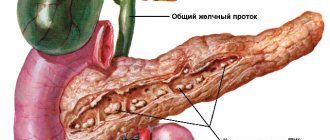
Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder that develops after an infection enters the organ, often as a result of some kind of surgery. It occurs in acute and chronic form, worst of all if stones form.
Attacks are fraught with improper treatment of gallstone disease or neglect of therapy. The first alarm bell is a pain in the right side. This dangerous disease affects both adults and children, but, according to statistics, women are primarily affected by it.
An attack in the form of biliary colic occurs suddenly and requires urgent medical attention, without which everything can end very sadly. The most common causes of attacks: overeating, alcohol consumption, inflammation.
Causes of acute cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis begins to actively develop when an obstruction occurs in the path of bile outflow from the gallbladder. E. coli is often the culprit of the pathology. Staphylococci and other bacteria are also dangerous. Their entry into the gallbladder is accompanied by severe pain.
An attack of illness can occur due to the following reasons and conditions:
- improper diet, snacks on the run, dry food;
- abuse of fatty and spicy foods, fast food, sweets, carbonated drinks, alcoholic drinks;
- inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity;
- fasting, strict mono-diets;
- pressure on the abdomen (for example, the wrong size jeans belt cutting into the flesh);
- developmental anomaly or bending of the gallbladder;
- deformation, compression, displacement of ducts due to injury, tumor, inflammation of nearby organs;
- stones inside the bubble;
- lack of physical activity;
- overweight;
- stress, nervous exhaustion, depression;
- disruptions in the functioning of the biliary tract;
- atherosclerosis;
- pancreatitis;
- diabetes;
- viral hepatitis.
Watch a video about acute cholecystitis:
Possible complications
Stones are the most dangerous for cholecystitis. They are formed as a result of stagnation of bile, which is caused by poor nutrition with excessive production of bile secretion, or mechanical obstacles - congenital deformation, inflammation of neighboring organs and other factors.
If the stone is thrown out of the bladder into the duct, a complete blockage occurs. A moving stone can damage the walls. Then the contents of the gallbladder enter directly into the abdominal cavity. The result is peritonitis or sepsis. In severe form, death is possible.
Symptoms
Characteristic signs of an attack:
- sharp, ever-increasing pain in the right side under the ribs, radiating to the shoulder, shoulder blade and lower back on the right side;
- belching, nausea, vomiting with bile and blood;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- chills, fever;
- bloating;
- lemon-yellow skin tone, whites of the eyes;
- darkening of urine;
- bowel dysfunction;
- tachycardia;
- lethargy, drowsiness.
When palpating the right side, the pain worsens. If the patient gets worse, his temperature and pulse jump even more. After an attack of vomiting, the expected relief does not come.
The most dangerous attack is calculous cholecystitis, which occurs when stones are moved. When the bile ducts are blocked, a person begins to suffer from severe biliary colic. This condition is fraught with death.
If the migration of stones disrupts the integrity of the walls of the gallbladder, then its contents, along with the infection, will enter the abdominal cavity. The most likely outcome will be peritonitis.
In this case, the patient’s condition will worsen significantly, he will become very pale and weakened, the pain will become unbearable, and the pressure will drop sharply. With such symptoms, self-medication is not only useless, but also dangerous. You need to call an ambulance as soon as possible.
How to understand that an attack has begun
When your health suddenly deteriorates, it is not always easy to determine whether it is an attack of cholecystitis or another disease. The main signs that the gallbladder is reminiscent of itself:
- nausea, vomiting without relief;
- bitterness in the mouth, dry tongue, with a white coating;
- pain under the right lower rib, radiating to the shoulder and back;
- general weakness, sweating, nervousness;
- the temperature may rise to 37-38 degrees;
- liver enlargement;
- drop in blood pressure;
- increased heart rate is proportional to the deterioration of the condition;
- yellowness of the skin.
A festive feast can easily provoke acute cholecystitis. Alcohol, fatty, spicy foods, and sweets put a lot of stress on the gall bladder. If he has already been weakened by improper nutrition, then he will not be able to cope with such a volume of work.
In this regard, it is important to analyze your diet over the past few days. Then the cause of cholecystitis will quickly become obvious.
But other reasons also lead to an attack:
- congenital deformation of the gallbladder or its ducts, preventing the full removal of bile;
- entry of microbes into the organ;
- overeating or, conversely, long-term adherence to strict diets;
- stone formation;
- throwing of pancreatic secretion into the bile duct;
- liver diseases;
- passive lifestyle.
An attack of acute cholecystitis often appears against the background of sluggish chronic inflammation of the gallbladder. In this case, the attack may not have pronounced acute symptoms. However, this situation requires mandatory diagnosis and proper treatment.
Diagnosis of exacerbation
Before making a diagnosis, the doctor does an initial examination to detect visible signs of the disease. Listens to the patient’s complaints, prescribes a number of tests and examinations:
- Bile analysis makes it possible to determine the causative agent of infection.
- Blood tests look for symptoms consistent with liver disease.
- An ultrasound of the abdominal organs is necessary to detect stones and symptoms of the inflammatory process.
- Cholegraphy (x-ray of the gallbladder and bile ducts) shows the cause of inflammation. This examination is contraindicated for pregnant women.
Causes of an attack of cholecystitis
Among the causes of cholecystitis, it is worth highlighting the following:
- cholelithiasis (GSD),
- stagnation of bile in the bladder,
- infections affecting the ducts
- stomach diseases that provoke active growth and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms,
- eating disorder, eating junk food,
- blockage of blood vessels,
- sedentary lifestyle.
Frequently encountered etiological factors should be placed in a separate category. Not least of all is increased pressure in the bile ducts. Hypertension can be caused by reasons such as:
- sphincter spasm,
- formation of choleliths,
- stenosis or blockage of the bile ducts.
According to statistics, 90% of diagnosed cases of acute cholecystitis are the result of malfunctions of the digestive system.
As for cholelithiasis, choleliths over time injure the mucous membrane of the bladder and ducts, contributing to impaired motility. Large stones often block the lumen of the bile duct, resulting in an inflammatory process.
Statistics say that the symptoms of an attack of cholecystitis appear more often in women, and there are objective reasons for this:
- the gallbladder is compressed by the expanding uterus during pregnancy,
- the production of certain hormones, in particular progesterone, negatively affects the general condition of the female body,
- passion for frequent radical diets provokes a decrease in the contractility of the gallbladder.
First aid
At the first symptoms of exacerbation of cholecystitis, it is better not to endure the pain, but to immediately call a doctor at home. It is unlikely that you will be able to relieve the attack on your own, but you can still do something before the local therapist arrives:
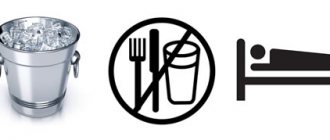
- Provide the patient with bed rest and rest (put him in a horizontal position).
- Apply a cold compress to the liver area.
- Do not give food or drink: if surgery is required, it is dangerous to administer anesthesia with a full stomach due to the likelihood of aspiration pneumonia. This complication is often fatal.
- If you feel nauseous, you can drink a small amount of mint tea.
In case of an acute attack, only urgent hospitalization will help. If the x-ray does not reveal stones in the gall bladder, then after the pain has been relieved, the patient will be allowed to go home for treatment. If stones are present, the question of surgical intervention will arise.
First aid for an attack of cholecystitis at home
Such a dangerous condition as an attack of cholecystitis requires emergency assistance to the patient. Therefore, in the event of an exacerbation of the disease, it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance, and before the doctor arrives, try to relieve the pain syndrome at home. You can do this as follows:
- Lay the victim horizontally.
- Apply something cold (such as frozen food) to your stomach.
- Give the patient antispasmodic drugs: they will help eliminate pain.
- Tea with mint or still mineral water will help relieve nausea.
- If vomiting occurs, you should definitely drink mineral water.
If cholecystitis has entered the chronic stage, then discomfort appears periodically, as the body’s reaction to a violation of the diet, consumption of spicy, salty, smoked and fatty foods, as well as alcoholic beverages. The duration of the attack does not exceed one hour and is accompanied by a dull arching pain.
To stop an attack, in this case it is enough to take antispasmodics and painkillers.
In order not to blur the clinical picture, you should not give the patient narcotic painkillers or analgesics, otherwise the doctor may make an incorrect diagnosis during examination. In addition, during an acute attack of cholecystitis, it is strictly prohibited:
- drink alcoholic drinks,
- take medications that the doctor did not prescribe,
- apply hot compresses or heating pads to the stomach,
- give the victim an enema.
After stopping the attack, the doctor adjusts the treatment, adding drugs that can prevent relapses of the disease. If it is appropriate, the doctor may prescribe medications that help dissolve stones (Ursosan, Ursofalk).
What is forbidden to do during an attack
Sometimes, out of ignorance, relatives or the patient himself cause harm instead of helping. To avoid such a situation, you should remember what not to do:
- Take analgesics, otherwise the clinical picture of the disease will be distorted. Due to painkillers, you can “miss” a perforation of the gallbladder wall, requiring immediate surgical intervention.
- Apply a hot heating pad to the sore spot: heating will aggravate the inflammation and increase the risk of purulent complications.
- Use choleretic pharmaceuticals and medicinal herbs.
- Give an enema.
Therapy
Having determined the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes infusion, antibacterial and analgesic therapy. If breathing is impaired, provides oxygen through a nasal catheter.
Organizes daily monitoring of blood pressure, pulse, and urination adequacy. Further therapy depends on the severity of the disease.
Traditional methods
In acute cholecystitis, doctors do everything possible to preserve the gallbladder and treat it with medication. It is removed only if the stones have blocked the bile duct. However, with the help of endoscopy, in many cases it is possible to remove stones while preserving the gallbladder.
The operation begins with a small puncture in the abdomen, and then the surgeon removes the stones using laparoscopy. What is happening inside the patient’s abdominal cavity is monitored on the monitor of a special device.
In less serious cases, doctors first prescribe injections (clarophan, cephobid, cefazolin, gentamicin), then oral antibiotics: amoxiclav, amoxicillin.
For acute pain and disruption of the gallbladder - injections of No-shpa, Papaverine. In the hospital, an attack of acute cholecystitis is usually relieved within 3 days. It takes about 12 days to completely get rid of the characteristic signs of the disease and eliminate the inflammatory process.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine can be used to treat such a serious disease only with the approval of a doctor.
To prevent the formation of gallstones, drink a decoction of Solyanka Kholmovoy: 1 tbsp. l. dry raw materials pour 1 tbsp. hot water. Boil for 10 minutes, cool, filter and take 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day before meals.
In autumn they are treated with red rowan juice. To obtain it, ripe berries are pounded in a mortar, and then the resulting pulp is filtered through cheesecloth. The drink is consumed at 0.5 tbsp. 3 times a day half an hour before meals. The course of treatment can be continued until the rowan fruiting ends.
Another recipe: dry plantain leaves, chop them, take 1 tbsp. l. raw materials and pour a glass of boiling water. Leave covered for 40 minutes, strain and drink in small sips for an hour. And so once a day. The duration of the course is a week.
Watch the video to see what exercises are good for your gallbladder:
Diet
In case of an acute attack of cholecystitis, you should not eat at all for the first three days. Drinks allowed include warm non-carbonated mineral water and green tea with mint leaves. After fasting, the diet consists of:
- weak broths;
- puree soups;
- pureed food;
- well-cooked porridge with a viscous consistency.
You need to eat little, but often: every 3 hours. Food can be eaten steamed, boiled and baked, but in no case fried or stewed. When you return home, it is recommended to cook using a double boiler or multicooker. You should not eat foods that are too cold (below 15°C) or hot (above 50°C).
Coarse fiber is dangerous for a fragile stomach during this period; bran, alcoholic beverages, buckwheat, fatty meat and fish, mushrooms, nuts, seeds, fruit peels, strong coffee and black tea, baked goods, herbs (parsley, dill, spinach) are excluded from the diet. and many vegetables:
- broccoli;
- peas and other legumes;
- zucchini;
- potato;
- onion;
- carrot;
- cucumbers;
- radish;
- radish;
- beet;
- Bell pepper;
- green beans;
- tomatoes;
- pumpkin;
- cauliflower.
When the condition improves, the doctor will allow you to drink non-acidic juices (diluted with warm water 1:1), compotes, fruit drinks, weak tea with rosehip, high-quality green tea.
It is recommended to switch to steamed omelettes, salads with olive oil, boiled lean meat (can be put through a blender or cut into small pieces), boiled cod, navaga, pollock and other dietary fish, viscous porridges, fermented milk products with a small percentage of fat content.
Among sweets, preference is given to dietary oatmeal cookies without additives (preferably not store-bought). Butter dough, alcohol, smoked meats, pickles, fatty foods, marinades, ketchups, mayonnaise, and seasonings are still on the black list.
Prevention and prognosis
Primary prevention consists of a number of measures to prevent the formation of gallstones. This is facilitated by a properly selected diet. The patient is recommended to lead an active lifestyle, jogging, yoga - to the best of his ability, but regularly.
If you have gallstone disease, it is dangerous to go on strict diets: sudden weight loss can cause migration of stones and gallbladder dysfunction. To reduce the risk of an attack, the attending physician may suggest surgery while the disease is not yet in the acute stage.
With proper and timely treatment of cholecystitis, the prognosis is positive. Even after removal of the gallbladder, the liver does not stop producing bile, but sometimes postcholecystectomy syndrome develops. Initially, after surgery, patients often experience soft, frequent stools, but for most they soon return to normal.
In the acute form of the disease, as well as in emergency surgery, the prospects are much worse. If you do not seek medical help at all, you can die due to extremely serious complications.