Noncalculous cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder wall with a recurrent course and further impairment of its function.
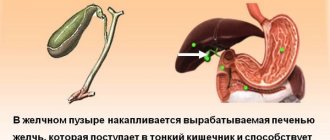
The gallbladder is an important component of the digestive system. It serves as a reservoir for bile, which is produced by the liver, and at the right time releases it into the intestines.
Non-calculous simply means that gallstones have not yet formed. But the insidiousness of this disease is that over time, gallstones can still form, but the process will not manifest itself in any way. By the way, abroad, chronic non-calculous cholecystitis is not considered a separate disease - it is considered as one of the stages of the formation of cholesterol stones.
Symptoms of occurrence
In the clinic, pain syndrome predominates, which occurs in the right hypochondrium, less often in the epigastric region. The pain radiates to the right shoulder blade, collarbone, shoulder joint, is aching in nature, and continues for many hours, days, sometimes weeks. Often, against this background, acute cramping pain occurs due to exacerbation of inflammation in the gallbladder.
The occurrence of pain and its intensification is often associated with a violation of diet, physical stress, cooling, and intercurrent infection. An exacerbation of a painful attack is usually accompanied by increased body temperature, nausea, vomiting, belching, diarrhea or alternating diarrhea and constipation, bloating, and a feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
Vomiting is an optional symptom of chronic acalculous cholecystitis and, along with other dyspeptic disorders (nausea, bitter belching or constant bitter taste in the mouth), can be associated not only with the underlying disease, but also with concomitant pathology - gastritis, pancreatitis, periduodenitis, hepatitis.
Often an admixture of bile is found in the vomit, and it turns green or yellow-green.
Lethargy, irritability, and sleep disturbances are observed. A transient icteric coloration of the sclera and skin can be observed due to difficulty in the outflow of bile due to the accumulation of mucus, epithelium or parasites (in particular, Giardia) in the common bile duct.
When palpating the abdomen in patients with chronic cholecystitis, the following symptoms are determined.
- Kehr's symptom - in the area of the projection of the gallbladder, located at the intersection of the outer edge of the right rectus abdominis muscle with the edge of the false ribs, pain appears on deep palpation during inspiration.
- The Grekov-Ortner-Rashba symptom is pain when tapping the edge of the hand along the right costal arch.
- Murphy's sign is a careful, gentle insertion of the hand into the gallbladder area, and with a deep breath, the palpating hand causes sharp pain.
- Mussi's symptom is pain when pressing on the phrenic nerve between the legs of the sternocleidomastoid muscle on the right.
Hardware methods for diagnosing cholecystitis
To make a correct diagnosis and clarify the classification of cholecystitis, hardware diagnostics are performed.
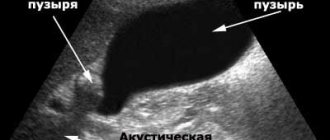
This is the main diagnostic method, in medical language called cholecystometry. If ultrasound is performed by a highly qualified specialist, then other methods may not be needed at all.
Ultrasound of the liver and gall bladder Ultrasound can reveal in the shortest possible time:
- Pathological enlargement of the gallbladder;
- Deformation of the walls, thickening, destructive changes in organ tissue;
- Violations of motor and evacuation functions associated with the movement and delivery of bile to the digestive organs;
- Structural anomalies;
- Heterogeneity of the contents of the gallbladder;
- The presence of stones in the organ and ducts.
Cholecystometry is performed on an empty stomach. It is recommended to follow a diet 2-3 days before the examination. It is necessary to exclude carbohydrate foods and foods that increase gas formation (baked goods, rye bread, fresh cabbage, legumes).
Normally, the gallbladder should be pear-shaped with clear boundaries. With cholecystitis, thickening of the walls is always observed.
Important!
For the prevention and treatment of liver diseases, our readers successfully use an effective remedy...
Cholecystitis is clinically similar to other pathologies. To establish the cause of the pathological condition, differential diagnosis is carried out.
Usually they try to exclude the following diseases:
- Appendicitis in acute form. Inflammation of the appendix is not characterized by pain in the right hypochondrium, repeated vomiting of bile, pain on the right side of the sternum and under the scapula;
- Ulcer. With perforation of the walls of the stomach and duodenum, acute pain is observed, localized in the right central part. They are associated with perforation of the walls and leakage of gastric juice outside the organs;
- Pyelonephritis. Accompanied by renal colic and acute pain in the lower back. The pain may radiate to the hip and groin. This disease is characterized by the presence of blood in the urine;
- Pancreatitis. During an exacerbation, there is acute pain on the left, obvious signs of intoxication: nausea, vomiting, deterioration in general health. Pancreatitis can be diagnosed accurately and quickly in a hospital setting.
Clinical signs help differentiate cholecystitis from other diseases, but the main evidence will be the results of laboratory and instrumental studies.
Differential diagnosis of cholecystitis can also be carried out with other diseases:
- Ulcerative colitis;
- Chronic gastritis in the acute phase;
- Worm infestation;
- Duodenitis.
A natural remedy has been found that causes aversion to alcohol!
Elena Malysheva: “Surely you know that until recently the only effective means of combating alcohol addiction was...”
For diseases of the liver and bile ducts, duodenal intubation is used as a diagnostic method. An irritating drug is introduced into the body by injection or inhalation. It stimulates the contractile function of the gallbladder and relaxes the sphincter.
Methods for diagnosing bile:
- Microscopy. The disease is indicated by the presence of leukocytes, epithelial cells, and cholesterol inclusions in the bile;
- Biochemistry of bile. Cholecystitis is indicated by increased levels of immunoglobulins (immune response to inflammation), proteins, alkaline phosphatase, as well as low concentrations of bilirubin.
Gastroduodenoscopy
Using endoscopic devices, the inner surface of the duodenum and stomach is examined. The cause of inflammation and blockage of the ducts is identified. A flexible optical instrument with a lighted tip is inserted directly into the esophagus. On examination, you can also see incarceration and localized tumors.
Gastroduodenoscopy is necessary for the following symptoms:
- Pain in the abdomen;
- Weight loss;
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Vomit;
- Frequent manifestations of heartburn;
- Anemia;
- Problems with stool.
Endosonography
Endoscopic ultrasound examination is a combined type, in which an ultrasound probe is inserted into the esophagus, stomach, and intestines and allows one to obtain high-quality images of the internal surface of organs. The procedure can be combined with a fine-needle biopsy.
Many of our readers actively use the well-known method based on natural ingredients, discovered by Elena Malysheva, to treat the liver...
Using endosonography, diagnostics is carried out in the following organs:
- Gallbladder. Pathologies of the exit sections of the bile ducts are identified;
- Pancreas. Pancreatitis is diagnosed in the acute and chronic phase;
- The stomach and esophagus for the presence of varicose changes, characteristic of some liver diseases.
Endoscope with ultrasound sensor Using radionuclide testing, diseases of the biliary system, which include the liver, gallbladder, pancreas and stomach, are diagnosed. Intravenous administration of radiopharmaceuticals is undertaken.
After the radioisotope is distributed throughout the tissues, the radiologist takes several sequential images using a gamma machine. In this way, the functioning of organs is assessed, the condition of tissues and blood vessels is recorded, and pathological formations are detected.
In terms of information content, the method is inferior to ultrasound examination. It is carried out only when it is necessary to comprehensively assess the condition of the liver, pancreas and gall bladder. Using tomography, acute cholecystitis with parenchymal changes is diagnosed.
Shock wave lithotripsy may be needed as a conservative treatment. In some cases, surgical removal of the gallbladder is performed.
Judging by the fact that you are reading these lines now, victory in the fight against liver diseases is not yet on your side...
Have you already thought about surgery? This is understandable, because the liver is a very important organ, and its proper functioning is the key to health and well-being. Nausea and vomiting, a yellowish tint to the skin, bitterness in the mouth and unpleasant odor, dark urine and diarrhea... All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand.
Course of the disease in adults
Inflammation of the gallbladder tissue can appear at any age and occur in acute or chronic form. This disease is one of the most common, if we take into account the digestive organs. In addition, this disease often begins to develop in people who are overweight or suffer from gallstone disease.
Although in thin people, inflammation of the gallbladder is also not uncommon. Cholecystitis in adults can be a complication of cholelithiasis, although there is also an acalculous form of the disease. According to statistics, a young body (up to 20 years) is less susceptible to the formation of gallstones when compared, for example, with older people.
The older a person is, the greater the likelihood that the diagnostician will detect stones due to cholecystitis already at the first ultrasound.
How to treat non-calculous cholecystitis
Treatment of noncalculous cholecystitis in adults will depend on the symptoms of the disease. Acalculous cholecystitis in the acute stage is treated conservatively using various medications. Drug therapy is complex; the treatment regimen may include:
- Antispasmodics that help relax the bile ducts - “Papaverine”, “No-shpa”, “Atropine”.
- Analgesics that relieve painful colic - “Sedalgin”, “Baralgin”, “Ketonal”.
- Antibiotics - Erythromycin, Rifampicin, Ampicillin.
- Antiemetic drugs - Motilium, Ondansetron, Cerucal.
- Enzymes that help activate the motility of the digestive tract - Festal, Creon, Mezim Forte.
- Choleretic drugs - “Cyqualon”, “Cholenzim”, “Hologon”, “Nicodin”.
- Probiotics for the restoration of beneficial intestinal microorganisms - “Enterol”, “Bifiform”, “Linex”, “Bifidumbacterin”.
In addition to taking medications, the patient is recommended to stay in bed and avoid eating for several days. When non-calculous cholecystitis passes through the acute phase, electrophoresis and mud applications are used. If the bile duct becomes suppurated or blocked, the organ is removed.
If serious complications develop or drug treatment fails, surgery is performed. Two types of surgical intervention are used: classical surgery and laparoscopy.
Video on the topic:
The disadvantage of the first method is the long recovery period. Laparoscopy is performed using a more gentle method and recovery after it does not last long.
Traditional methods of treatment
In addition to drug treatment, it is also allowed to use folk remedies to treat the disease.
It is good to regularly use decoctions of the following choleretic herbs - yarrow, marshmallow, buckthorn, tansy.
Herbal remedies are gentle and have few side effects. Traditional medicine helps to liquefy stagnant bile and activate its outflow. In addition, they suppress infections and relieve non-calculous inflammatory processes.
Traditional methods of treatment are allowed to be used only after the end of the acute stage and with the permission of a doctor.
The most popular are infusions of corn silk, parsley, and immortelle flowers. They are drunk warm, half a glass 3 times a day before meals. To prepare, pour 8-10 g of herb with boiling water (1 glass) and infuse.
Diet for non-calculous cholecystitis
Fatty, sweet, fried, pickled, and spicy foods are excluded from the diet. Prohibited: soda, cold food, alcoholic drinks, baked goods, egg yolks, raw fruits and vegetables, nuts.
Dishes are consumed only warm; the preferred type of heat treatment is baking, boiling, steaming. To restore and stabilize the functionality of the gallbladder, it is recommended to eat melons, watermelons, pumpkin, beets, carrots, sweet peppers, rowan, dried fruits, and chicory.
Liquid porridges, soups, jellies are recommended. Gradually pureed meat, fish, vegetable, dairy and fruit dishes are added to the diet.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, the doctor may expand the diet during the diet or, conversely, reduce it slightly.
Course of the disease in children
If a child is diagnosed with cholecystitis, the disease is treated by a pediatrician and pediatric gastroenterologist. It is important to seek medical help as soon as possible to eliminate the risk of developing any complications.
Inflammation of the digestive system is common in children today. Cholecystitis in children and adolescents can be acute or chronic. The disease rarely affects one organ, in this case the gallbladder, because most often with such an inflammatory process the entire biliary tract system is affected.
Children are often diagnosed with hepato- and angiocholecystitis, as well as cholecystocholangitis. Purulent forms of the disease are extremely rare. As a rule, a chronic form of inflammation is discovered in childhood, which occurs with remissions and exacerbations.
Protea, cocci and E. coli can provoke the development of inflammation in the gallbladder and its ducts. In order for chronic cholecystitis to develop, conditions favorable for this fact must be created in the child’s body, for example, helminthic infestation.
The causes of the development of the disease are conventionally divided into microbial and parasitic, and cholecystitis can be associated with other problems: tonsillitis, tonsillitis, appendicitis or even influenza. An inflammatory disease of the gallbladder may also appear due to poor nutrition, if, for example, a child’s diet constantly contains food high in carbohydrates and fats.
If a child is diagnosed with cholecystitis, the symptoms may differ slightly from the symptoms of the disease in adults. Children most often complain of a bitter taste in the mouth, unstable stools, nausea and lack of appetite. Abdominal pain can be paroxysmal and disturb from several minutes to 4-5 hours.
Treatment of cholecystitis in adults
In order to treat acute and chronic acalculous cholecystitis, medications, traditional medicine methods are prescribed, and surgical intervention is performed. Outside of exacerbation, in the absence of symptoms of non-calculous cholecystitis, treatment with physiotherapeutic methods is indicated. Treatment with drugs includes painkillers, antispasmodics, and agents that improve the flow of bile.
- Antispasmodics are used to relieve acute pain and spasms. These are No-Shpa, Analgin, Platyfillin, Papaverine.
- In case of severe, prolonged pain and the presence of signs of inflammation in the tests, it is recommended to use broad-spectrum antibiotics: Erythromycin, Cefantral, Ampicillin.
- To eliminate signs of intoxication (vomiting, nausea), Hemodesa is prescribed intravenously.
- Enzymes will help normalize digestion. This is Festal, Mezim Forte.
- To increase bile secretion, Allohol, Cholenztm, Ursohol are used.
- Cholekinetics have a choleretic effect: Holagol, Urolesan N.
- For giardiasis, take Furazolidone.
- Vitamins B and C are included in complex therapy. During an exacerbation, the patient is advised to remain in bed, table No. 5.
Treatment
Timely diagnosis and proper treatment will help avoid serious consequences of the disease. Acute cholecystitis may require hospitalization. Outpatient treatment should be continued under the supervision of a specialist, periodically examined and tested. For chronic cholecystitis, examination is recommended at least once a year. To prevent relapses, the patient must follow a diet and take medications. The drugs must be prescribed by a gastroenterologist. If symptoms occur, you should consult your doctor.
Treatment of cholecystitis in pregnant women
There is a standard treatment regimen for cholecystitis during pregnancy, which includes diet, taking mild choleretic drugs and the use of folk recipes. There are conservative and surgical methods of therapy:
- The first group includes treatment of cholecystitis with home remedies, homeopathic methods and medications.
- The second method involves performing an operation, which is extremely undesirable during pregnancy.
One of the most important stages in the treatment of cholecystitis is compliance with the diet and rules of nutrition. A girl should not overload herself physically, but also not eliminate activity completely, because this is important for the proper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and the secretion of bile. Diet is the main method of not only effective treatment, but also prevention.
It is necessary to adhere to the following recommendations for the treatment of cholecystitis during pregnancy:
- exclude salty, fried, spicy foods from the diet;
- completely give up alcohol (which is important during pregnancy even without signs of cholecystitis);
- eat small portions 5 times a day;
- reduce or completely eliminate animal fats;
- your diet should include egg yolks, butter,
olive oil in small quantities.
Treatment of cholecystitis in children
Treatment of cholecystitis in children can be carried out with surgical or conservative methods. In the first case, the organ is completely removed, after which the body completely adapts to the new regime within a few months.
Indications for surgical intervention may include large stones in the organ cavity, frequent relapses and abnormalities in the structure of the gallbladder that impede the outflow of fluid. The recovery period after surgery is carried out by analogy with standard conservative treatment of cholecystitis:
- a gentle diet with a predominance of boiled and steamed pureed vegetables, lean meats and fish, as well as dairy products;
- bed rest - physical activity can be restored over time;
- antibiotics to kill bacterial infections;
- antispasmodics for pain relief;
- specific agents against parasites (according to indications);
- choleretic medications - you can replace tablets with herbal preparations;
- hepatoprotectors - drugs to protect the liver.
Causes of the disease
Non-calculous cholecystitis most often develops due to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the gallbladder, which enter the organ cavity through the bloodstream, after which they provoke inflammatory reactions. The initial foci of infection may be other organs: kidneys, bronchi, lungs. The causative agents are most often staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, less often Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Proteus. The risk of infection of the gallbladder is present when bile stagnates and its outflow is impaired.
The trigger for the development of acalculous cholecystitis can be:
- congenital or acquired deformities of the gallbladder or ducts;
- prolapse of abdominal organs;
- pregnancy (the result of compression of the walls of the gallbladder by the uterus);
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- parasitic infections;
- disturbance of intestinal motility;
- gallbladder dyskinesia;
- gastritis;
- diabetes;
- physical inactivity;
- excessive consumption of spicy, salty and fatty foods;
- alcohol abuse;
- passion for diets and fasting;
- decreased immunity;
- abdominal injuries.
Almost all of the above factors not only can lead to stagnation of bile, but also reduce the body’s protective functions, which makes the body defenseless against various pathogenic bacteria.