Why does diarrhea occur?
Diarrhea in a one-year-old child is caused by various factors and phenomena.
Poor nutrition
An incorrectly formulated diet can lead to digestive disorders, in particular diarrhea. Most often, diarrhea in a child aged 1 year is caused by the following dietary flaws:
- consumption of age-inappropriate foods;
- binge eating;
- excessively carbohydrate foods;
- excess foods containing large amounts of fat.
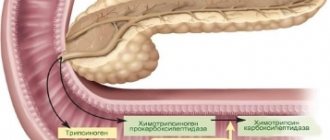
As a result, the child’s gastrointestinal tract experiences relative enzyme deficiency. Partially digested foods enter the lower intestine, where the fermentation process begins. Irritated intestinal walls provoke the development of diarrhea.
Infection
Infectious lesions are the most common cause of loose stool in one-year-old children. Trouble can be caused by the following diseases:
- Acute intestinal infection. The causative agents of infection are Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Staphylococcus aureus, etc.
- Dysentery. The disease is caused by bacteria of the genus Shigella.
- Rotavirus infection. This infectious disease is often called “stomach flu”, but rotaviruses have nothing to do with influenza viruses.
The baby’s immunity to an intestinal infection is short-term and weak, so re-infection and relapses of diarrhea are possible.
A child can become infected with these infections in several ways:
- eating foods containing microorganisms and parasites;
- drinking untreated water and raw (not heat-treated) dairy products;
- insufficient adherence to personal hygiene rules.
Serious illnesses
Tender age does not protect a baby from serious diseases. On the contrary, a child’s body and immunity are much weaker compared to adults. As a result, dangerous diseases can lead to loose stools in a child:
- Hartnup's disease;
- inflammation of the wall of the digestive tract;
- hyperthyroidism;
- diverticulosis;
- intussusception;
- lactase deficiency;
- cystic fibrosis;
- celiac disease, etc.
Other reasons
Sometimes diarrhea in a one-year-old child is a consequence of other factors, for example:
- Taking antibiotics. The stool becomes liquid as a result of an imbalance in the intestinal flora after taking medications. This reaction occurs both when the baby himself and his mother take antibiotics, if the baby is still breastfed.
- Stress. Constant, prolonged nervous disorders and overexertion lead to diarrhea against a background of fear and negative emotions.
- Food allergies.
- Breastfeeding. If a breastfed baby has diarrhea, it may be a reaction to breast milk. It can be too thin, greasy, or contain laxatives due to the mother’s failure to follow a special diet.
- Colds. A rather rare cause of diarrhea in a one-year-old child, however, such cases also occur in medical practice.
Peculiarities of child digestion and causes of diarrhea
Before determining what to give a 5-year-old child for diarrhea, you need to understand what triggered this condition and act on the root cause. Eliminating the symptom will not bring long-term effect.
At 5 years old, a child’s diet is already close to that of an adult. He can eat any adult food, but his stomach still does not accept fatty, heavy foods well. Its excess leads to the release of bile, which irritates the stomach, causing diarrhea and nausea.
The glands located on the gastric mucosa develop gradually. At 5 years of age, the ability to digest food is still reduced, so overeating and heavy foods should be avoided.
Depending on the causes, there are several types of diarrhea: neurogenic, drug-induced, infectious, etc. Each type requires its own treatment. The most common causes of loose stool in a preschooler are:
- Infectious diseases. Immunity only develops by the age of 4–5 years, so young children are especially susceptible to various viral or bacterial infections. If the baby is not accustomed to hygiene, forgets to wash his hands and fruits before eating, parasite eggs, salmonella and other pathogens enter the body. Without specific treatment, they rarely go away on their own and lead to various complications.
- Taking medications. Loose stools appear after taking antibiotics that disrupt the intestinal microflora, drugs that are not suitable for age, or when you are individually intolerant to one of the components. You must carefully read the instructions and consult your pediatrician before starting to take medications.
- Lack of enzymes. Digestive enzymes help break down food and make it easier to move through the intestines. The lack of these elements leads to indigestion, constipation and diarrhea, nausea, and flatulence.
- Intoxication with harmful substances. Poisonous chemicals, such as mercury or arsenic, cause diarrhea. Symptoms of poisoning are supplemented by laryngeal spasms, swelling, and severe abdominal pain. In this case, urgent medical attention is required.
- Stress. Young children tend to perceive situations more acutely. Problems and conflicts cause severe stress, which provokes disturbances in peristalsis. Fear, nervous tension, and prolonged excitement lead to diarrhea.
If a 5-year-old child has diarrhea without fever, the reason often lies in indigestion and poor diet. Intestinal problems can be caused by a lack of vitamins, an unbalanced or monotonous diet.
Associated symptoms
Liquid feces in children aged 1 year are to some extent normal, indicating the absence of serious pathologies in the body. However, there are often cases when the baby’s stool not only becomes frequent and liquid, but also begins to change color, and impurities can be found in the contents.
Depending on the causes of occurrence, the consistency and color of stool can vary significantly:
- White. White, loose stool in a one-year-old child is a serious cause for concern. At the age of 1-1.5 years, such a symptom may indicate liver dysfunction.
- Watery. Mucous, excessively liquid (almost the consistency of water) stool is a typical symptom of intestinal infections, overeating, and intolerance to cow's milk. The child’s general condition does not suffer, but such diarrhea quickly leads to dehydration.
- Green or orange flakes. The appearance of impurities in feces is typical for salmonellosis and coli infection. Often accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
- Green. Green stool with an unpleasant, pungent odor, weakness, high temperature, the baby’s complaints of headache, crying, and vomiting are also direct signs of an infectious lesion in the baby.
- Bloody. Blood-stained stool indicates a bacterial infection. Greenish lumps and red streaks indicate dysentery.
- Foamy. Foamy stool in a child aged 1 year is often a consequence of lactose deficiency, dysbiosis or celiac disease.
- Black. Black stool in a one-year-old baby can be a warning sign of internal bleeding or drug abuse (for example, activated charcoal or bismuth).
A child's liquid, yellow stool is relatively normal. However, even this shade may indicate deeper health problems, especially if the following symptoms accompany diarrhea:
- abdominal pain;
- lethargy;
- headache;
- itching in the anus;
- lack of appetite;
- poor sleep;
- elevated temperature;
- vomit;
- nausea.
Medicines to treat diarrhea
Traditional methods help when abdominal pain and diarrhea are not associated with viral infections. In serious cases, you cannot do without consulting a pediatrician. Only a doctor has sufficient qualifications to select medications. Medicines to eliminate diarrhea are divided into types:
- Probiotics (cope with intestinal disorders, used to eliminate side effects after antibiotics). Popular products: Linex, Lactiale, Bifiform.
- Enterosorbents (combine and remove sources of toxins from the body). Pediatricians prescribe medications: Smecta, Enterosgel.
When taking it, do not forget about the dosage and carefully read the recipe. You are not allowed to choose the course of antibiotics yourself.
It will be useful for parents to watch the video on the topic - how to stop diarrhea in a child:
Your humble servant will be very happy if you rate the article:
Forms and types of diarrhea
Diarrhea that occurs in one-year-old children includes several varieties. Classification is based on the causes of the symptom and the pattern of its development. Regardless of the type of diarrhea, it can take two forms:
- Chronic. Loose stools and other symptoms of diarrhea persist for a long time, up to several weeks.
- Spicy. This form can be completely eliminated (often without contacting a pediatrician) within 2-3 days.
Depending on the reasons
When the criterion for dividing diarrhea is the cause of its origin, experts distinguish the following types:
- Dyspeptic. Secretory insufficiency of the liver, small intestine, stomach or pancreas leads to the development of dyspeptic diarrhea in a child.
- Infectious. The cause is any infectious disease: dysentery, salmonellosis, foodborne illnesses, viruses, amoebiasis. Until a child is 2 years old, in winter he may often experience infectious diarrhea. The incubation period is several days. The disease begins with vomiting, continues with diarrhea, and ultimately ends with fever, muscle pain and headache. The average duration is a week.
- Medication. It is the result of suppression of intestinal flora and dysbacteriosis by antibiotics (less commonly, other drugs).
- Nutritional. In this case, digestive disorder occurs as a result of prolonged disruption of the diet. Risk factors for the development are a monotonous diet poor in vitamins, as well as food allergies to foods.
- Neurogenic. The causes are stress, fear, anxiety, anxiety, and depression.
- Toxic. Develops as a result of kidney failure or poisoning (most often with arsenic or mercury).
According to the flow mechanism
Depending on the type of flow, diarrhea occurs:
- Hypokinetic. The stool is liquid, mushy, and has a foul odor. Bowel movements are quite frequent, but in small quantities. Develops as a result of a reduced rate of movement of food through the intestines.
- Hyperkinetic. Feces are not abundant, liquid, mushy. It occurs due to the opposite reason - the increased speed of food movement through the digestive system.
- Hypersecretory. It is characterized by copious, watery bowel movements. Hypersecretory diarrhea is a consequence of increased secretion of salts and water into the intestines.
- Hyperexudative. Feces have a watery consistency, with admixtures of blood and mucus. Formed when liquid penetrates into the pre-inflamed intestine.
- Osmolar. Copious, fatty, stool with remnants of undigested food. Develops with reduced absorption of salts and water by the intestines.
Causes of prolonged diarrhea in children
The diagnosis of “prolonged diarrhea” is made if a child has a defecation disorder for 3 weeks or more and the number of bowel movements per day reaches 4 or more times.
Reasons for this condition:
- Errors in the diet - for infants when introducing complementary foods, switching from breastfeeding to formula, replacing formula. In older children, the cause of diarrhea is an excess of sweets, refined foods, and semi-finished products.
- Lack of hygiene skills - it is enough not to wash your hands after a walk or playing in the sandbox for episodes of intestinal upset to appear with regularity.
- Enzymatic immaturity - develops in babies in the first year of life. It manifests itself as a deficiency of lactase, which breaks down milk sugar.
- Dysbacteriosis is the result of long-term treatment with antibacterial drugs, antibiotics, and poor diet.
- Intestinal infections - the penetration of pathogenic flora leads to long-term defecation disorders in the child. A typical example is rotavirus infection.
- Other factors: going to kindergarten, school, changing your usual place of residence, climate.
Regardless of the causes of prolonged diarrhea, treatment should be started as soon as possible. Otherwise, complications may develop, treatment in a hospital setting, and problems with the gastrointestinal tract in the future.
Danger of diarrhea in a child
With diarrhea, fluid leaks into the intestinal lumen and the absorption of water and salts is impaired. Watery, large and frequent stools lead to dehydration when all body tissues lose much-needed moisture and the blood begins to thicken. The younger the child, the greater the danger this condition poses to him.
There are 3 degrees of dehydration :
- With the first, the child urinates less often, his tears gradually disappear when he cries, and the mucous membranes of the oral cavity become dry.
- With the second, the baby experiences lethargy, drowsiness, the skin becomes flabby and dry, and the eyes become sunken.
- The third degree leads to unconsciousness. If the child has not urinated for over 8 hours, dehydration has most likely developed to this degree.
Dehydration leads to disruption of the functioning of all organs and systems. The most serious complication of diarrhea is the development of kidney failure, damage to the heart and brain.
Parents must monitor changes in the quantity or consistency of stool. If the stool contains glassy mucus, blood, or green or bright yellow inclusions, you should show the child to the pediatrician as soon as possible.
The greater the list of symptoms that accompany diarrhea, the greater the danger diarrhea poses to the child. It is not so much the diarrhea itself that is dangerous, but the causes of its occurrence and possible consequences.
Treatment of diarrhea for various types of diarrhea
Proper treatment of diarrhea mainly depends on:
- causes of diarrhea;
- the presence of concomitant symptoms complicating the course of the disease;
- age of the child - in a one-month-old baby, dehydration occurs much faster than in a one-year-old baby.
Therefore, parents need to know how to treat their baby, what medicine can be given on their own, how to stop progressive dehydration and what not to do if diarrhea develops.
Indications for immediate contact with a specialist are:
- frequent urge to defecate, more than 8-10 times a day, with the release of copious, watery, foul-smelling feces in a child up to one year old and after;
- the occurrence, along with diarrhea, of one or more concomitant pathological symptoms - vomiting, fever, abdominal pain, severe lethargy and weakness, blood in the stool or its darkening, the presence of mucus or green matter;
- the appearance and progression of symptoms of dehydration in the baby - dry lips, mouth and mucous membranes, greed when drinking fluids, anxiety or, conversely, lethargy, progressive weakness and drowsiness, sunken eyes, decreased number of urinations, urine becomes dark.
Prolonged or severe diarrhea often leads to dehydration, exhaustion, hypovitaminosis and persistent changes in the functioning of all organs and systems of the body.
Mild and short-term diarrhea caused by non-infectious or non-inflammatory causes, with the correct treatment tactics, timely correction and elimination of the cause, quickly moves into the stage of normalization of stool.
Treatments for mild diarrhea depending on the cause:
- treatment of diarrhea caused by dietary disorders - normalization of nutrition, compliance with the rules for introducing complementary foods and replacing adapted milk formula. Gradually, disturbances in the digestive tract will be eliminated on their own. In case of prolonged diarrhea, it is additionally necessary to give the baby a drink to eliminate the lack of fluid and salts;
- in case of allergic reactions to certain foods and/or intolerance to certain substances, the baby needs a special diet, gluten-free or lactose-free, and complete elimination from the diet of all foods that can cause allergies;
- if adverse reactions develop after using various medications in the form of diarrhea, it is necessary to immediately discontinue the medicine, if diarrhea continues, give the baby a sorbent (Enterosgel, Polysorb, white coal) and seek advice from your doctor;
- if diarrhea in a child has developed as a result of irrational use of antibiotics, it is necessary to take a stool test for dysbacteriosis and, based on its results, correct the positive intestinal microflora with probiotics and prebiotics under the control of repeated tests;
- neurogenic and psychogenic diarrhea completely disappear when the stress factor is eliminated and the child’s psycho-emotional state is normalized.
Treatment of diarrhea of infectious origin (viral and bacterial etiology) in infants is carried out in a hospital setting and is aimed at:
- elimination of the infectious agent: antiviral and antibacterial therapy;
- relief of pathological symptoms such as vomiting, fever, lethargy, pain - antipyretics, antiemetics, drugs that reduce pain and flatulence;
- elimination of intoxication: enterosorbents, feeding the baby with saline solutions or intravenous administration of colloid and crystalloid solutions in case of severe dehydration and intoxication;
- enzyme preparations to improve digestion.
It must be remembered that taking Imodium and Loperamide, drugs that reduce intestinal motility, is contraindicated for young children.
First aid
If your child has severe diarrhea, calling a doctor at home is mandatory. Before the ambulance arrives, you can help the child by slightly alleviating the symptoms. A small patient should be given glucose-saline solutions to drink. To do this, drugs such as Oralit or Regidron are dissolved in a liter of water (boiled and cooled). Give the child the resulting drink, giving it small sips.
Parents should know that they should not give their baby anti-diarrhea medications intended for adults. Adequate treatment is prescribed exclusively by a qualified medical professional.
Prevention of intestinal disorders in children
To avoid intestinal difficulties, it is important to follow simple rules. First of all, you need to teach children to wash their hands after walking and before eating. Adults should thoroughly wash vegetables and fruits and cook meat and fish.
Babies under one year old explore the world around them with great interest, while tasting rattles, toys and everything that comes to hand. Parents should regularly wash toys and carry out wet cleaning in places where the baby plays. It is necessary to exercise constant control over the little one.
Children aged 6 are already old enough to understand what adults say. It is worth explaining that you cannot drink water from reservoirs while swimming during the summer holidays, as well as tap water.
If diarrhea occurs frequently for no apparent reason and does not go away for a long time, and you cannot cure it on your own, you should consult a doctor and inform him about the diarrhea. The doctor may prescribe an examination of the gastrointestinal tract, identifying pathologies accompanied by an unpleasant symptom.
Diagnostics
Making a true diagnosis of what is causing the diarrhea begins in the pediatrician's office. This is the doctor who will be the first to listen to the parents’ concerns, examine the baby and refer him for the first tests. In the future, consultation may be required from specialized specialists: infectious disease specialist, nephrologist, hepatologist, etc.
In order to establish a diagnosis, a small patient is sent for an examination, including:
- stool analysis to detect helminths and dysbacteriosis;
- blood tests - general (mandatory) and biochemical (to identify specific diseases);
- bacterial culture of feces and vomit (if any);
- coprogram;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- X-ray;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
The choice of diagnostic techniques depends on the condition of the child, the nature of his bowel movements and the suspected causes of the digestive disorder.
Based on all the data received, the therapist (or other specialized doctor) will select the appropriate treatment for this particular case.
Treatment of diarrhea in a one-year-old child
Complete therapy for diarrhea in one-year-old children should be comprehensive. For treatment, not only medications are used to eliminate the symptoms, but also a strict diet, which the baby must follow for another 3-4 days after recovery in order to consolidate the results obtained.
Child's diet
The diet of a one-year-old child with diarrhea differs significantly from the diet of a healthy one. Small but frequent meals and thorough chewing of food are recommended for small patients. At the same time, animal fats and carbohydrates should be significantly limited. A balanced diet for diarrhea is the most important aspect of treatment.
The diet of a child with diarrhea should consist of:
- fermented milk products, for example, freshly prepared calcined or unleavened pureed cottage cheese;
- tea, especially green;
- lean and non-wiry varieties of meat and poultry: veal, beef, turkey in the form of cutlets boiled in water;
- low-fat varieties of fish, boiled in water or steam;
- pureed porridges in water - rice, oatmeal, buckwheat;
- wheat bread made from premium flour;
- diluted fruit juices from berries and fruits, except grapes, plums, apricots;
- soups based on low-fat weak fish and meat broth with the addition of mucous decoctions of cereals (barley, semolina, rice), boiled and pureed meat, steamed dumplings, meatballs, egg flakes;
- boiled meat soufflé;
- soft-boiled eggs or in the form of a steam omelet.
The following should be completely excluded :
- dishes with added spices;
- rich, fatty soups and borscht;
- nuts;
- fresh fruits and vegetables;
- salinity;
- bakery products (except for bread made from premium flour);
- whole milk and other dairy products.
Mother's nutrition while breastfeeding
If a one-year-old child has diarrhea, the diet is indicated not only for the patient, but also for his nursing mother (if the baby is still breastfeeding):
- Completely eliminate fatty, spicy, salty, fried foods from the daily menu.
- Foods rich in fiber that enhance peristalsis or irritate the gastrointestinal tract, in particular, dairy products, prunes, beets, plums, legumes, freshly squeezed juices, rich broths, sweets, cakes and chocolate, should be removed from the diet.
- Dishes with a low fiber content, boiled, baked or steamed should be on the menu as much as possible. The more rice, potatoes, pasta and noodles, crackers, and pear crackers in your diet, the better.
Drugs
The content of drug therapy directly depends on the cause of diarrhea in the child. In different cases, a small patient may be advised to take medications for different purposes:
- Maintain water-salt balance. The first thing a child can be given for diarrhea is any saline solution, for example, Glucosan, Regidron, Oralit, Gastrolit, Citroglycosolan, Enterodes. A glucose solution is used for the same purpose.
- Remove the heat. If the baby has not only a digestive problem, but also a fever, antipyretic drugs, for example, Paracetamol, are prescribed.
- Remove toxins. For this purpose, sorbents are prescribed. As a rule, these are activated carbon, Smecta, Polysorb, Polyphepan, Enterosgel, Neosmectin.
- Eliminate loose stools. Sometimes taking medications aimed directly at eliminating the symptom, that is, normalizing stool, may be indicated. Calcium carbonate, Bismuth, Diarol, Tanalbin have proven themselves quite well.
- Get rid of dysbacteriosis. In case of dysbacteriosis, anti-diarrhea drugs are prescribed to normalize the intestinal microflora: Acipol, Bifiform, Colibacterin, Bifikol, Linex, etc.
- Destroy intestinal infection. To cure diarrhea in a baby caused by intestinal infections, doctors prescribe antibiotics. Most often these are Nevigramon, Furazolidone, Ercefuril, Ceftazidime.
- Normalize the functioning of internal organs. Enzyme therapy in children is carried out using drugs such as Festal, Pancreatin, Panzinorm forte, Mezim forte, etc.
- Relieve spasm. To relieve excessive pain in the baby, the therapist may prescribe Papaverine, Spasmomen or Drotaverine.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine is not able to cope with diarrhea in a one-year-old child effectively without causing harm. However, with the permission of the treating pediatrician and in combination with the prescribed therapy, “grandmother’s” remedies can speed up the baby’s recovery. The following recipes deserve particular popularity:
- White flour. Place 1-2 tablespoons of white flour in a hot, clean frying pan and, stirring constantly, fry until caramel-colored. Pour 1 tablespoon of the resulting mixture with a glass of boiling water and stir thoroughly until the consistency of thick sour cream. Give your baby half a glass at a time. The recipe does not have a pleasant taste, but the mixture can be sweetened and fed like porridge.
- St. John's wort. Brew 10 grams of dry St. John's wort herb in 1 glass of boiling water, let it brew. Give your child 1 tablespoon 3 times a day after meals.
- Potato starch. Dissolve 1 teaspoon of potato starch in 1 tablespoon of cold boiled water. Give the child something to drink once.
- Blueberry. Take 30 grams of dried blueberries and brew in a glass of boiling water for 2 hours. Give the child a quarter glass of the resulting infusion 4 times a day.
- Vegetable mix. Take one potato, carrot and onion. Boil the peeled vegetables for 30-60 minutes. Remove the onion and lightly mash the remaining vegetables so that small pieces remain. Add a little salt. Give this soup to the baby first with a spoon, and later in normal portions. The recipe will gradually renew the disturbed intestinal microflora.
- Baked apples. This is a tasty, pleasant and healthy way to relieve your baby of diarrhea. Give oven-baked fruits one at a time every hour.
- Bird cherry. Place 5-7 berries in a glass of boiling water and leave for about an hour. Then heat the drink until warm and give it to the child in small portions each time before meals.
Hygiene
If a one-year-old child has diarrhea, increased attention should be paid to hygiene, especially the area around the anus. Frequent bowel movements make her irritated, redness and itching appear, and the baby himself is sensitive to attempts to touch the skin. To prevent this irritation from occurring, you need to wash your baby more often or wipe the area around the anus with damp hypoallergenic wipes. You should also not neglect baby cream and baby powder that dries out the skin.
Adults caring for a one-year-old child with diarrhea are also strongly recommended to adhere to the following rules of increased hygiene:
- You should wash your hands with soap more often after hygiene procedures, before feeding, and taking medications.
- Wash children's underwear separately from adults' underwear. Bed and underwear are treated with a hot iron.
- In the room where the child is located, regularly ventilate and wet clean with disinfectants.
- Wash your baby’s toys every day with specialized soap, and regularly pour boiling water over his dishes during illness.
- Limit contacts with strangers, do not attend various events with large crowds of people with him.
The baby’s immunity during and after diarrhea is reduced, and the body is not able to provide an adequate response to additional sources of infection.
Medicines for diarrhea for a 1 year old child
All medications are prescribed in accordance with the individual and age characteristics of the small patient. Dosages and frequency of administration are prescribed by doctors.
Antibacterial drugs
Antibacterial drugs are the main treatment for diarrhea caused by intestinal infections. They must be taken with great care, since not all medications can be used at this age.
The most commonly prescribed intestinal antiseptic is furazolidone. But you shouldn’t give it unless the cause of the baby’s diarrhea is cleared up. Nifuroxazide is easier to use, since it is available immediately in the finished syrup form.
If the disease is caused by rotavirus, enterovirus, adenovirus infection or other viral agents, then antiviral immunomodulators are prescribed in complex therapy.
The drugs are Arbidol for children, Interferons. Arbidol is contained in capsules. It will be difficult for 1-year-old children to swallow it, so the contents of the capsules are poured onto a spoon and diluted with water to form a suspension. The baby can easily swallow it.
Interferons are available in the form of rectal suppositories.
Intestinal sorbents
The next step is to take intestinal sorbents; a huge amount of them is released. The most common and cheapest is activated carbon, sold in pharmacies in tablet form.
It is difficult for a child to take them; the mother herself crushes each tablet, crushes it and adds it to some water so that the baby drinks the solution from the papilla.
Activated carbon contains granules that bind toxic substances to the intestinal mucosa and remove them, and has strengthening properties.
Polysorb is a modern and newer sorbent, more expensive than coal. The advantage is that it is sold immediately in powder form for ease of administration to children.
Depending on weight and age, it is diluted with boiled water and given to drink several times a day; it has a larger adsorption surface and removes more toxins. Helps cope with intoxication and dehydration, tastes good.
A very convenient form of using sorbents is gels and pastes, these include Neosmectin, Enterosgel and Sorbitol. Such substances can be spread on a cookie or simply poured into the baby’s mouth, then given some water to drink.
The action is not inferior to solid sorbents, they are not absorbed into the bloodstream, and are excreted from the body along with feces. Helps cope with intoxication and allergic reactions.
Polyphepan has a mixed effect and is recommended for use from the first days of life. It is an adsorbent, antidiarrheal, and antibacterial drug.
The release form is a ready-made suspension, it is easy to use, has proven itself, and is highly effective.
Restoration of water and electrolyte balance
If the patient is not hospitalized, but is being treated at home, the mother needs to desolder him herself. This should be done gradually, in small portions; you can give 1 teaspoon of water every 10 minutes.
The liquid should be clean, boiled, at room temperature, excluding juices completely. In order to restore salt balance and electrolyte balance, special means are prescribed.
Rehydron is recommended for use from 6 months of age. Available in powder form for preparing a solution. Indicated for diseases with diarrhea and vomiting, it treats well dehydration of 1-2 degrees.
Hydrovit is used in children from the first days of life. Sold in powdery consistency. Diluted with water. It has proven itself as an antidiarrheal and antipyretic agent. Fights intoxication.
Reosolan. It can be taken by the youngest patients. Also available in powder form. Contraindicated in children with diabetes and impaired renal function.
Prebiotics and probiotics
Preparations for restoring normal microflora, this includes prebiotics and probiotics.
Prebiotics are substances that contain components for the growth of beneficial bacteria in the intestines. These include Normobact, Hilak Forte, Acipol, all of which are allowed from childhood.
Probiotics are medicines containing ready-made beneficial bacteria. Linex forte and Enterol are allowed for children; they are available in capsules.
Their contents must be poured out and dissolved in water. They have a fixing effect, actively restore microflora, and promote stable digestion.
Prevention
To protect the baby from such an unpleasant phenomenon as diarrhea, responsible parents must adhere to preventive rules. To avoid loose stools (and the diseases that cause them), it is recommended:
- Maintain hygiene. Teach your child the rules of hygiene from an early age. In addition, parents are also required to adhere to hygiene rules. Washing your hands after walking, playing with animals, using the toilet, and before every meal is the direct responsibility of responsible mothers and fathers. Bathing in public places is an unaffordable luxury for a one-year-old child.
- Be careful with products. Eggs, milk, fish, and meat that the baby eats should be subjected to heat treatment. Before eating, vegetables, fruits, and berries should be thoroughly washed. In addition, it is important to monitor the freshness and quality of purchased products.
- Monitor the child’s proper nutrition. There should be as little fried and pickled foods in the diet of a one-year-old child. It is better to bake, stew, boil or steam all foods. Only bottled, purified and boiled water is allowed to be given to the child to drink.
- Follow the rules of breastfeeding. The baby's mother must adhere to a diet during lactation. In addition, the formula for artificial feeding must be of exceptional quality.
- Provide comfort. A one-year-old child urgently needs not only physically comfortable living conditions, but also psycho-emotional ones. The task of parents is to create a cozy atmosphere that eliminates stress.
Diarrhea in a child aged 1 year is caused by many factors: from the wrong product to a serious infection. Only a doctor can correctly diagnose the cause of diarrhea and select the necessary treatment. Therefore, if your baby has loose stools for more than 2 days, you should definitely seek qualified medical help.
Previous post Why does diarrhea with mucus occur and how to treat it?
Next entry How to cook and drink jelly with diarrhea?
Chronic diarrhea syndrome in children
The chronic form of diarrhea in a child is long-term intestinal dysfunction that develops due to non-infectious causes. Its duration varies.
There are 2 groups of reasons for this condition:
- organic - due to impaired absorption of nutrients, dysfunction of other organs of the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas;
- functional – the inability to break down and assimilate certain foods. In childhood, intolerance to milk, dairy products, and gluten is more common.
In early childhood, 80% of cases of prolonged diarrhea occur due to functional disorders. This is due to the predominance of dairy products in the diet. Such diarrhea may be a consequence of the immaturity of the nervous system.
Presumable diagnosis for various periods of diarrhea:
- If a child’s diarrhea does not go away within 5 days, the doctor will assume an exacerbation of a chronic disease, an imbalance of intestinal flora.
- If defecation disturbance lasts more than a week, teething can be assumed in a child of the first year of life. In older children, there is a lack of B vitamins.
- Diarrhea that lasts 10 days is a symptom of Crohn's syndrome, intestinal cancer, colitis, and malabsorption of nutrients.
All these pathologies have additional symptoms. They are accompanied by nausea, inclusions of mucus, blood, undigested pieces of food in the stool, manifestations of intoxication and general weakness, the smell of acetone.
If diarrhea lasts for several days or additional symptoms appear, then you need to consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination.