Common forms of dysfunction
Gallbladder dysfunction occurs in 2 variants:
- dyskinesia of the hypokinetic type - the contractility of the organ is reduced, bile constantly flows into the duodenum;
- dyskinesia of the hyperkinetic type - the motility of the gallbladder is accelerated, bile enters the duodenum intermittently.
From this position, gallbladder dysfunction is divided into primary and secondary. The primary form of the disease occurs against the background of a violation of neurohumoral regulation. The secondary form develops mainly as a result of other diseases of the digestive tract.
Dysfunction can occur in hyperkinetic (with increased tone, bile does not constantly enter the duodenum) and hypokinetic (decreased tone) types. It is important to pay attention to the symptoms of dysfunction in a timely manner in order to undergo modern research as soon as possible, make an accurate diagnosis and begin treatment.
How dangerous is the disease?
If the disease is not treated in adults, complications may occur. Most often, inflammatory process and cholelithiasis develop with JVP.
Violation of the tone and motility of the gallbladder leads to stagnation of secretions in the biliary tract and reflux - the release of bile into the stomach and esophagus. When an infection occurs, inflammation occurs, which is accompanied by acute symptoms - fever, paroxysmal pain, vomiting of bile contents.
Another dangerous pathology is cholelithiasis - cholelithiasis.
Stones form in the bladder and bile ducts due to stagnant processes and changes in the chemical composition of the secretion. Stones can block the ducts, leading to obstructive jaundice. This condition requires surgical treatment.
Causes of the disease
The reasons leading to impaired motility of the gallbladder are often associated with anatomical features - constrictions in the organ cavity and kinks cause congestion. Other factors include the following:
- hereditary predisposition;
- frequent diets, poor nutrition;
- taking hormonal contraceptives;
- overweight;
- violation of diet, long intervals between meals;
- hormonal imbalances in the body;
- abuse of junk food (smoked, salty, spicy);
- the presence of worms in the body;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- diseases of the nervous system.
Gallbladder diseases
Dyskinesia
Dyskinesia is a disorder of varying degrees of motility of the gallbladder and the bile ducts extending from it. It develops according to the hypertonic type ( hypermotor ) or the hypotonic type ( hypomotor ). The main causes of dyskinesia:
- autonomic disorders;
- pathologies of the development of the gallbladder and ducts;
- pathologies and dysfunction of other organs.
The symptoms of the disease are as follows: pain and bursting sensations in the area of the right hypochondrium, aggravated by palpation of this area and after eating spicy, fried and mostly fatty foods, heaviness under the ribs in the right side, bitterness and a metallic taste, nausea - sometimes with vomiting, enlarged liver, bad breath.
Damage to the bile ducts directly is not corrected; the person’s condition is corrected by diet and taking individually selected choleretic drugs. In cases of other causes of dyskinesia, drug correction of the underlying and concomitant diseases is carried out.
Cholelithiasis
Gallstone disease or, as it is also called, cholelithiasis. This is the formation of stones (sand and various types of stones) in the cavity of the gallbladder. Large stones can reach the size of a walnut and deform the walls of the gallbladder, disrupting its functioning and causing unpleasant and painful sensations.
The symptoms of the disease are mild. Usually sand and small stones do not bother the patient and do not injure the organ itself. In general, if the stones are not bothersome, it is recommended to monitor the patient without any intervention.
However, when the ducts are blocked, severe stabbing pain occurs. If the pain does not go away on its own or after taking a painkiller, it means that the duct is tightly clogged and urgent medical attention is required. If help is not provided in time, the duct will rupture and peritonitis will begin.
Gallstones in the gallbladder are crushed by ultrasound and dissolved with the help of medications and long-known folk remedies. Sand and dissolved stones enter the small intestine in the form of clots, and are excreted naturally from there.
But more reliable and radical is abdominal surgery to remove stones from a diseased organ and its ducts. If the gallbladder is filled with large (more than one and a half centimeters) stones, as a result of which its shape has changed, the walls have stretched, motility and the ability to accumulate and secrete bile have been impaired, then it will have to be removed.
For the entire duration of treatment and in the future, to prevent the formation of stones, it is necessary to strictly follow a hypocholesterol diet. The diet involves the strict exclusion of “bad” cholesterol from the diet and the extreme reduction of “good” cholesterol.
Symptoms of gallstone disease are:
- non-localizable or slight heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- sharply arising and self-subsiding pain in the same area (often provoked by heavy intake of heavy fatty and / or fried foods);
- when the ducts are blocked or damaged and the mechanism of bile inflow and outflow is disrupted, jaundice develops (yellowing of the skin and sclera), and there is a high risk of liver damage.
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is an inflammatory disease characterized by:
- damage to the mucous membrane and walls of the gallbladder,
- formation of stones in it (optional),
- motor-tonic disturbances of the entire biliary system.
Cholecystitis rarely occurs on its own; much more often it develops against the background of hepatitis of any type, pancreatitis, gastritis.
The most common causative agent of cholecystitis is bacteria (strepto- and staphylococci, Escherichia coli). Less commonly, it is provoked by helminthic infestation , fungi and viruses (most often hepatitis). Rarely, cholecystitis is toxic or allergic in nature.
The prerequisites for cholecystitis are: stagnation of produced bile in the ducts, dyskinesia of the biliary system, endocrine disorders, pregnancy, prolapse of internal organs, rare meals. The trigger for triggering inflammation is excessive consumption of fatty foods, alcohol, and the acute phase of inflammatory diseases of other internal organs.
Symptoms of cholecystitis are aching pain on the right, in the hypochondrium, radiating to the right shoulder, under the right shoulder blade, less often to the neck on the right side. After eating, especially acute or fatty food, the pain changes character and becomes sharp, stabbing. There is a constant metallic and/or bitter taste in the mouth.
Abnormal bowel movements, nausea, flatulence, and belching are often observed. On the part of the nervous system, sleep disturbances and irritability are noted. On palpation, the location of the gallbladder is hypersensitive.
The prognosis of the disease is favorable. Decreased ability to work and deterioration in well-being are observed only during an exacerbation and are quickly eliminated. Often cholecystitis provokes cholelithiasis.
Postcholecystectomy syndrome
Postcholecystectomy syndrome is a complex of manifestations observed after cholecystectomy or other surgical interventions on it. The syndrome manifests itself in the form of impaired motility of the small intestine and sphincter of Oddi . The condition does not have a list of internationally recognized symptoms, so it is described very loosely.
Basically, the symptoms described are common to all diseases of the biliary system: pain and heaviness on the right side under the ribs, bitter belching, deterioration after a heavy meal, increased sweating, rapid heartbeat.
Tumor diseases, including cancer
Any cancer is a tumor consisting of rapidly and chaotically dividing cells. The gallbladder is rarely susceptible to tumor diseases, especially cancer, but it should not be discounted. The first symptoms of cancer:
- causeless weight loss;
- lethargy; drowsiness;
- depressed state of mind;
- irritability; tearfulness;
- excessive fatigue.
A little later, problems with stool begin, nausea, vomiting, heaviness, bloating, pain in the right side, the temperature remains elevated without signs of an infectious or inflammatory disease.
The causes of the disease are cholelithiasis that went unnoticed or remained without adequate treatment and chronic diseases of the digestive system that have not been treated for a long time. Treatment consists of taking painkillers and drugs to crush and dissolve stones, as well as a strict diet.
If there is no result, repeated surgery is performed.
Symptoms of dysfunction
The main symptoms of gallbladder dysfunction can be confused with exacerbation of other chronic gastrointestinal diseases. The main feature of the course of the disease is periodically occurring pain in the right hypochondrium, which lasts 5-10 minutes. Usually people do not pay attention to this, attributing discomfort to overwork or dietary errors.
The following factors can trigger pain:
- physical fatigue;
- eating unhealthy foods rich in fats and simple carbohydrates;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- prolonged exposure to stress.
Dysfunction is accompanied by cramping, sharp or aching pain, tenderness of the gallbladder during palpation, and general malaise. A person may become weakly active and irritable immediately after a heavy meal, when discomfort appears.
With dysfunction, frequent loose stools, regular nausea, a bitter taste in the mouth, and general weakness appear. During the interictal period, satisfactory health remains, but short-term spastic pains and moderate spasms occur regularly.
The pain syndrome may be constant. There are complaints of increased gas formation, unstable stools, and frequent belching. Due to the development of cholestasis and changes in the size of the gallbladder, the liver enlarges and becomes painful when palpated.
What is the difference between hypomotor and hypermotor dyskinesia?
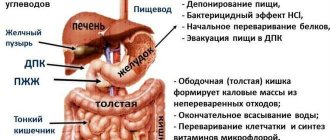
Bile is a special liquid that is produced in the liver. Bile secretion improves the absorption of fats and activates the movement of the food bolus through the intestines. Before entering the intestines, bile passes through a complex path through the biliary tract.
With dyskinesia of the gallbladder, a violation of contractile function occurs, which occurs for a number of reasons (often against the background of parallel pathologies)
With biliary dyskinesia, problems arise with the excretion of bile. Experts distinguish two main forms of the disease: hyperkinetic and hypomotor. First, let's talk about the hyperkinetic type. In this case, the tone of the organ is increased; it contracts too quickly and strongly. Along with this, the sphincters do not open enough.
This leads to severe pain in the right hypochondrium. In some cases, the pain attack can be short-lived, and sometimes it lasts for an hour. Stress and anxiety can trigger a new attack. During critical days, the tone of the gallbladder is increased, so in women the exacerbation of the disease is associated with the menstrual cycle.
If the hypertensive form of dyskinesia most often affects young people and adolescents, then hypotonic type gallbladder disease is more common in older people. In this case, the pain lasts longer, but is mild in nature. The aching pain can last for days.
Now let's talk about the symptoms of the hyperkinetic form:
Pain in the right hypochondrium in front after eating
- pain syndrome in the form of colic. Intense pain in the right hypochondrium occurs after stress or dietary errors. Usually the painful outbreak lasts about half an hour and occurs several times a day. The pain radiates to the back, arm, shoulder blade and even to the heart area, which is why the disease may be confused with an attack of angina;
- loss of appetite due to a spasmodic and excessively contracted gallbladder;
- weight loss due to poor breakdown of food and insufficient absorption of nutrients;
- attack of nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- disorders of the autonomic nervous system: hypertension, sweating, weakness, tachycardia, headache.
With hypokinetic biliary dyskinesia (HBD), a more pronounced clinical picture is observed. In addition to pain, nausea and vomiting, belching, bitterness in the mouth, bloating, obesity and more appear.
In both forms of JVP, yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes is observed. This is due to a violation of the outflow of bile secretions. Along with this, the feces become discolored and the urine becomes dark. Also, when bile flows back, a white or yellowish coating appears on the tongue.
With hypotonic biliary dyskinesia, symptoms from the ANS are observed: dizziness, headache, tachycardia
Diagnosis of dysfunction
Which doctor should I contact?
If you suspect the development of dysfunction, you must contact a therapist, hepatologist as soon as possible and undergo a comprehensive examination. The child should be additionally examined by a pediatric gastroenterologist. To make an accurate diagnosis and determine the form of the disease, specialists prescribe laboratory and instrumental tests.
Which examination to take?
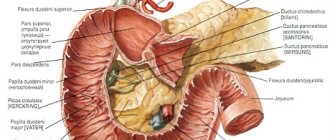
The main method of examination is ultrasound. During an ultrasound examination, it is possible to study the anatomy and functional abilities of the gallbladder, which creates bile and regulates its transport to the gastrointestinal tract. The diagnostic results make it possible to evaluate not only the anatomical features, but also to obtain information about the contents of the gallbladder, the patency of its ducts and the ability of tissues to contract.
Ultrasound is performed mainly after a provocative breakfast. The method of duodenal intubation of the duodenum to obtain its contents is much used. The study helps to determine the signs of the inflammatory process, the initial changes in the organ characteristic of the formation of stones.
What tests to take
Additionally, specialists prescribe blood biochemistry and stool testing for the presence of helminths. If necessary, intravenous cholecystography and MRI diagnostics are performed.
Methods for diagnosing diseases
A comprehensive diagnosis will allow a gastroenterologist or hepatologist to establish an accurate diagnosis. Patients are prescribed the most informative diagnostic methods to obtain reliable results. They help not only make a diagnosis, but also create an effective treatment regimen.
Problems with the gallbladder (symptoms will help a gastroenterologist or hepatologist determine the stage of development of pathological processes) require the following examination methods:
| Name | Description |
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) | A diagnostic method that allows you to identify pathological changes in the gallbladder, the formation of stones or the development of an inflammatory process. Tumor, polyps, or abnormal lesions. |
| General blood analysis | The results will help identify the development of the inflammatory process, infection, pancreatitis and other complications that often appear against the background of stones. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | Diagnostic examination methods that allow you to obtain the most accurate image of the gallbladder in order to identify pathological changes or the formation of stones. |
| Computed tomography (CT) | |
| Cholescintigraphy | The examination allows you to evaluate the functioning of the liver and bile ducts and identify their blockage. |
| Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) | A combined instrumental examination method, during which a specialist examines the gallbladder, bile ducts and pancreas. Thanks to the contrast agent, the doctor visually sees all the necessary structures. |
It is important to differentiate diseases or disorders in the gallbladder, since many diseases are accompanied by similar clinical symptoms.
Principles of nutrition
Traditional treatment for dysfunction involves diet. Dietary restrictions prevent relapses of pain and prevent the formation of gallstones.
What to exclude from your diet
The following products are prohibited:
- fried, excessively fatty foods;
- seasonings, pungency;
- sparkling water;
- an abundance of sweets;
- offal in large quantities (liver, kidneys).
What can you eat
People with dysfunction often suffer from dysbiosis. To restore normal intestinal microflora, it is recommended to consume:
- lactic acid products;
- greenery;
- vegetables;
- fruits;
- cereals;
- slimy porridges and soups.
Coarse fibers are a breeding ground for beneficial microorganisms that inhabit the human intestine. Additionally, it will be necessary to take medications with probiotic cultures.
Diet
It is better to eat smaller meals, avoiding overeating. It is advisable to eliminate or significantly reduce the amount of simple carbohydrates found in sweets and baked goods. It is recommended to replace sugar with honey (1-3 teaspoons per day). The diet must include cereals that contain complex carbohydrates that enrich the body with nutrients and the necessary energy.
Principles of treatment
When choosing treatment for gallbladder dysfunction, the doctor is guided by the results of diagnosis, general examination and the functioning of other digestive organs. Specialists must fight not only the symptoms of the disease, but also act directly on the cause of its development - a violation of the neurohumoral mechanisms of bile formation.
Principles of dysfunction treatment:
- early seeking of medical help, compliance with all doctor’s prescriptions;
- creating a calm psychological environment;
- strict adherence to the diet, exclusion from the diet of prohibited dishes and foods that can provoke a painful attack, progression of the inflammatory process;
- an integrated approach, including medication, physiotherapy, diet, and a measured lifestyle.
In case of nervous disorders and hyperexcitability, psychotherapists should work with the patient, who will correct the detected disorders and be able to find a connection between the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, the endocrine system and the mental state.
Often, dysfunction of the gallbladder and biliary tract requires the use of sedatives. Light sedatives relieve hyperexcitability, normalize sleep and increase resistance to stress factors. Experts prefer natural sedatives based on medicinal herbs and extracts.
Antispasmodics are prescribed to relieve pain and spasms. Such drugs can also affect the biliary tract. Physiotherapeutic procedures have proven themselves well, especially relaxing massage of the cervical-collar area. It relieves tension well, restores blood circulation in the neck, improves nutrition of the brain and helps get rid of chronic muscle spasms in the upper half of the body.
Treatment with mineral water
Treatment of gallbladder dysfunction with mineral water is carried out after preliminary consultation with your doctor. But the presence of stones is a contraindication for this procedure.
Heat mineral water without gas to 40°C. Drink 1-2 glasses at once, but in small sips. Lie down in bed on your right side, place a warm heating pad under it. For an hour, continue to drink warmed mineral water in small sips so that the total volume of liquid consumed is 400-500 ml.
If moderate pain appears in the area of the right hypochondrium, you must take any antispasmodic. During the procedure, contractions of the gallbladder occur, bile exits into the duodenum, which eliminates congestion and prevents the formation of stones in the future.
Tubazh
Tubing of the gallbladder in case of dysfunction can be carried out in different ways. Most often, still mineral water is used, to which you need to add a dessert spoon of sorbitol (per glass of liquid) and drink slowly. Then you need to lie on your right side with a heating pad, pulling your legs to your chest. It is recommended to cover yourself with a warm blanket.
Tubage can also be carried out with magnesium. It enhances the choleretic effect of the procedure. In a glass of warm mineral water, you need to dissolve a tablespoon of magnesia powder and drink the composition in small sips.
Before tubage and for several days after it, follow a diet, limiting fatty foods. Fried foods and alcohol should not be consumed. You can read more about the procedure in the article What is tubage and how to carry it out correctly
Breathing exercises
For symptoms of gallbladder dysfunction in adults, breathing exercises can be performed. Its goal is to restore normal blood flow in the epigastric region and motor functions. Do gymnastics in a standing position. Try to inflate your stomach while inhaling and hold in this position for a few seconds. While standing with your hands on your belt, lift your shoulder girdle and head up as you inhale, and as you exhale, slowly return to the starting position.
Herbal treatment
Herbs for symptoms of gallbladder dysfunction should be used with caution so as not to provoke severe spasms and the appearance of colic. Corn silk provides a light and safe choleretic effect. Pour a glass of boiling water over a tablespoon of herb and let stand for 20 minutes. It is better to do this in a thermos. Take the infusion warm in small sips throughout the day.
Also, for gall dysfunction, you can take dandelion root, chamomile, rose hips, and chicory. Herbs can be combined with each other or used separately.
Disease prognosis
With timely initiation of treatment, a professional approach and adherence to diet, the prognosis is favorable. But to prevent complications, it is necessary to regularly visit a gastroenterologist, conduct preventive examinations and ultrasound examinations.
It is also important to follow a diet. This is the only way to prevent frequent relapses of the inflammatory process and avoid the formation of stones, which can lead to the need for surgical interventions.
Gallbladder dysfunction in children
Children with gallbladder dysfunction require constant medical supervision and ultrasound monitoring of the bile secretion organs. It is recommended to ensure visits to specialized children's sanatoriums, where the main emphasis is on restoring impaired functions and preventing further progression of the disease.
What are the main causes of dysfunction in childhood?
- force feeding of children;
- early introduction of complementary foods;
- congenital pathologies;
- childhood neuroses, VSD;
- lack of fiber in children's diets;
- early introduction of children to “adult” food.
Children with dysfunction need to be protected from stress, nervous breakdowns and oppressive loneliness. Even a minor experience can trigger the inflammatory process and provoke another exacerbation.
The prognosis of the disease is greatly influenced by the psycho-emotional situation in the family, at school, and the level of trust between parents and child. With the normalization of the psycho-emotional background and the nature of nutrition, the likelihood that the disease will recede sharply increases closer to adolescence.
We invite you to watch a video about gallbladder dysfunction in children.
Prevention
Gallbladder dysfunction occurs for a long time without pronounced clinical manifestations. Preventive examinations, examinations, and regular biochemical blood tests make it possible to detect deviations from the norm at an early stage and do everything to restore impaired functions.
Always pay attention to the quality of nutrition and limit fatty, fried foods, prohibit children from drinking carbonated drinks and eating unhealthy foods with trans fats, large amounts of simple carbohydrates and chemical additives, and do not violate the principles of therapeutic nutrition yourself.
You may be interested in the following topics: What is tubage and how to do it correctly Useful herbs for the liver and pancreas How to properly clean the gallbladder What is hypotension of the gallbladder and how to treat it correctly
How do gall pathologies manifest?
Almost all diseases of the biliary tract are accompanied by similar symptoms. The difference lies in their combination and intensity of manifestations. Sometimes the syndrome manifests itself with all the signs at once, which is typical for the rapid development of diseases. In some cases, symptoms are isolated and can be ignored by the patient. Such signs indicate a slow progression of irreversible changes in the organ. The main manifestations of gallbladder damage:
- Painful sensations: pulling, aching or sharp, sharp, stabbing. With the development of hepatic colic, the pain is acute and localized in the right hypochondrium. Since the organ is innervated, referred pain rarely occurs. The intensity depends on the degree of inflammation.
- Dyspeptic syndrome. Since bile is involved in the digestive process, disturbances in its outflow affect the state of the gastrointestinal tract. Nausea occurs, sometimes vomiting with bile, heaviness in the abdomen and right hypochondrium. With a lack of bile, constipation occurs, and with excessive production, diarrhea occurs. Bloating and flatulence are often observed.
- Sensations in the oral cavity. Biliary pathologies provoke heartburn, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth (especially at the root of the tongue), and belching of air with an unpleasant odor. These signs are more intense in the morning. With a strong reflux of bile into the stomach and esophagus, a yellowish coating appears on the tongue.
- Jaundice. Jaundice syndrome may indicate chronic bile stagnation. Its intensity varies. Only the mucous membranes (eyes, mouth) or skin throughout the body can turn yellow. With severe jaundice, skin itching and rash occur. The progression of stagnation leads to discoloration of feces (it becomes whitish, “clayey”) and darkening of urine.
Pathologies of the gallbladder affect the condition of the body. This is also noticeable from the results of biochemical and general blood tests, which are prescribed when the patient has complaints consistent with damage to the gallbladder.