Constipation with ulcerative colitis may be a consequence of poor nutrition. To normalize the functioning of the intestines, it is necessary, first of all, to review the diet and exclude foods from the risk group: white bread, fatty and fried fish and poultry, peas, rice, semolina, etc. Together with Kroncolitis experts, we will understand how ulcerative colitis is related and constipation, and what else, besides diet, will help stabilize the stool in a short time.
Constipation and diarrhea are constant companions of UC
Due to the inflammatory processes characteristic of autoimmune intestinal diseases, such as ulcerative colitis, the absorption of food in the gastrointestinal tract is difficult. Loose stools are a sign of impaired fluid absorption, constipation is a consequence of narrowing of the intestinal lumen and stagnation of feces.
However, physiological changes due to a chronic disease do not always become the main cause of constipation. Quite often, the culprit is the usual diet.
During a consultation with a patient, any gastroenterologist will warn against including fresh fruits and vegetables in the daily menu. Indeed, with UC, products containing fiber and those that have not been subjected to heat treatment should be treated with extreme caution so as not to provoke disturbances in intestinal motility. However, doctors accompany the recommendations with a clarification: fiber is harmful during an exacerbation, but in moments of remission it is necessary for the intestines to maintain functions.
Usually, patients, even in a stable condition, do not begin to gradually dilute the usual menu by adding fruits and vegetables to it, despite the absence of contraindications to the dosed consumption of cucumbers, tomatoes, apples, etc. The main role in this matter is played by the psychological factor, caused by fear of exacerbation or uncertainty about good health.
What is intestinal colitis with constipation?
Intestinal colitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the colon as a result of drug, infectious, toxic and ischemic effects . Intestinal colitis with constipation is more common, when flatulence, difficult painful stools, false urge to defecate, and increased gas formation come to the fore.
With colitis, a pathological change in the structure of the tissues lining the colon occurs, disrupting the secretory, motor and evacuation functions. Almost a third of colitis occurs as a result of intestinal damage by salmonellosis, dysentery and E. coli, parasites, long-term antibiotic therapy, and dysbacteriosis.
The disease code according to ICD-10 is K52 - intestinal colitis. Depending on the severity and nature of the pathology, it is designated by codes K52.0-K52.9. Nonspecific ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease are not included in the classification of typical colitis, since they are autoimmune in nature.
Classification
The classification of intestinal colitis with constipation involves division according to the nature of its occurrence (infectious, parasitic, toxic, ulcerative-erosive, radiation), according to the nature of the course: acute and chronic.
Classification according to topography and degree of damage to the lining of the colon is key:
- Catarrhal. Superficial damage to the mucous membranes, the initial stage is a consequence of mild food poisoning and infections. Usually, after correcting the diet, it goes away on its own.
- Erosive. Deep inflammation of the intestinal lining with the formation of erosive elements (single or numerous). Damage to the membranes reaches small capillaries, which provokes bleeding.
- Atrophic. The pathological process covers the muscular layers of the submucosal structures, leading to disruption of muscle tone, up to their complete atrophy or excessive tension.
- Fibrinous (otherwise known as pseudomembranous colitis). The formation of a dense mucous film in the area of the lesions is noted. A common cause is infection with clostridia, drug-induced dysbacteriosis.
- Ulcerative (otherwise, nonspecific or undifferentiated). Formation of multiple bleeding wounds and crater-shaped defects.
The classification helps to quickly determine treatment tactics and further management of the patient , and take measures to prevent more serious complications.
Risks and complications
The consequences of colitis are always serious, especially with frequent exacerbations and severe persistent symptoms. Intestinal colitis can lead to the following complications :
- intoxication (poisoning the body with its own feces);
- neoplasms (polyps, tumors);
- malabsorption syndrome;
- pancreatitis;
- abscess (including liver).
Chronic intoxication due to intestinal colitis with constipation in children and adults significantly worsens the quality of life , aggravates the symptoms of the disease, and leads to damage to internal organs and systems.
Chronic constipation with ulcerative colitis: what to do
If a patient complains of chronic constipation due to ulcerative colitis, what to do to improve well-being should be explained by the attending physician. Contacting a specialist is the first step that a patient with UC must take before doing anything. In this article, Kroncolitis provides only generalized thesis recommendations that are usually practiced to improve the condition. Every responsible patient with ulcerative colitis should be aware that self-medication can be harmful to health.
To begin with, we suggest defining what is meant by constipation in UC.
The problem is really relevant if difficulties with bowel movements continue for several days. In this case, you should seek help. One-time and short-term constipation (or difficulty with bowel movements due to excessively hard stool) usually does not require medical intervention. For repeated episodes or prolonged conditions, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
As auxiliary means to reduce the risk of defecation disorders and softening stools in case of an existing problem, it is recommended:
- Increase the amount of water you drink per day.
- Eliminate stress reactions (eat in a calm environment).
- Add oil to food.
- Include fiber (vegetables, fruits) in the menu.
- Eliminate flour (replace with black bread), rice, semolina, potatoes, chocolate and other foods that help harden stool.
Fresh vegetables and fruits are necessary for the intestines to improve peristalsis. When processed, fiber loses most of its beneficial properties. However, there is a condition: vegetables and fruits must be peeled before consumption.
If for some reason you cannot decide on drastic changes in the menu and the presence of “fresh” in it, then you should think about alternative options - bake tomatoes, apples and pears, eat boiled beets, carrots, cook pumpkin, eat steamed prunes .
Oil in the diet can be flaxseed, olive, almond or regular sunflower. In any form, the product helps normalize the consistency of stool. However, heating food using these oils is not recommended.
If a diet for ulcerative colitis with constipation does not help cope with the situation, the doctor prescribes medications. However, it is worth considering that an overabundance of medications reduces the calcium level in the blood and also affects the intestines’ ability to absorb a number of vitamins.
Features of diagnosing intestinal colitis with constipation
Diagnosis of colitis with constipation includes a number of laboratory and instrumental studies . First, a physical examination, palpation of the abdomen and peritoneum, and a digital rectal examination are performed. Next, blood, urine, and stool tests are prescribed to differentiate other possible diseases.
The following studies are considered the “golden” standard for diagnosing colitis::
- irrigoscopy with a contrast agent - X-rays with contrast help to reliably identify lesions and detect tumors at an early stage of development;
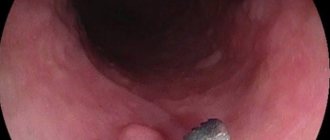
- endoscopy (colonoscopy, ileocolonoscopy) - visual examination of the intestinal walls, the possibility of taking a biopsy.
If necessary, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed . Colitis of the intestine with constipation is differentiated from ordinary constipation caused by malnutrition, decreased evacuation function of the intestine, its peristalsis, Crohn's disease, and nonspecific ulcerative colitis.
Diet for UC with constipation
If you have constipation due to ulcerative colitis, treatment should begin with changing the method and frequency of food. Often the cause of disorders is overeating or irregular eating patterns. It is important to eat often, but in small portions. The standard daily diet for UC consists of 5 meals. In case of exit from remission, treatment table No. 4 according to Pevzner is recommended.
Nutrition for ulcerative colitis of the intestine is specific. The diet mainly consists of protein products. Fresh fiber is excluded during exacerbations, but in the calm phase the intestines are able to digest fruits and vegetables, peeled, and benefit from them.
Constipation in ulcerative colitis is easier to prevent than to cure. In each specific case, the gastroenterologist works with the patient on an individual diet, taking into account the current characteristics of the chronic disease and other nuances.
The diet for ulcerative colitis with constipation is aimed at reducing pathogenic and inflammatory processes in the intestines, restoring digestive functions, improving motility and the production of gastric juice and providing the body with the nutrients necessary for normal functioning.
Causes of intestinal colitis with constipation
The causes of colitis with constipation are reflected in the classification of the disease. The following factors can trigger the pathological mechanism :
- intestinal tract infections;
- inadequate nutrition (violation of the regime, fasting along with overeating, junk food);
- food allergic reactions;
- dysbacteriosis of various nature.
Parasites, antibiotics, chemotherapy or radiation therapy for cancer, dehydration - all this can cause the development of the disease. Colitis is often a consequence of colon surgery.
Note! Congenital causes include autoimmune pathologies, abnormalities in the development and anatomy of the colon, and impaired intestinal absorption.
Basics of diet for ulcerative colitis
The daily calorie content of foods for UC is 2000 kcal. It is difficult to achieve an increase in energy value, because with colitis, the consumption of fats and carbohydrates is reduced, as well as foods that are high in calories, but can irritate the intestinal mucosa and provoke the growth of harmful bacteria and microorganisms that support fermentation processes.
Gastroenterologists insist on frequent but dosed meals. When you overeat, the digestive system experiences overload, and this condition can cause constipation.
List of allowed foods for ulcerative colitis with constipation:
- Soups: fish broths, vegetarian first courses, non-rich meat soups.
- Lean meat: cutlets, meatballs, meatballs.
- Low-fat fish varieties: pollock, pollock, cod, navaga, pike perch, crucian carp, etc.
- Greens: parsley, dill, bay leaf, lettuce.
- Cereals: buckwheat, wheat, pearl barley, barley.
- Vegetables: tomatoes, pumpkin, carrots, zucchini, peas, beets, cauliflower.
- Fruits: apples, raisins, dried apricots, figs.
The list of food products for ulcerative colitis also includes different types of bread. However, flour products made from wheat and rye flour are best consumed dried.
How to deal with constipation due to colitis
First of all, it is important to consult a doctor. Laxatives can be part of the complex treatment of colitis, and the specialist will take into account the type of pathology, severity of symptoms, and general health. The main goal of the course of treatment is to get rid of the cause of constipation - colitis itself. Antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory therapy, including glucocorticoids, and agents to improve recovery processes and mucosal regeneration may be prescribed.
Chronic forms of colitis require the use of intestinal motility regulators, antispasmodics (with caution for prolonged constipation) and other agents.
For emergency assistance, medications can be used that help soften stool and promote bowel movements. Laxatives for colitis with constipation should be selected with caution. One of the approved drugs is the British drug “Fitomucil Norm”. It contains the pulp of plum fruit and the shell of plantain seeds, which are plant fibers. The fibers absorb water and turn into a soft mucous gel, helping to soften and remove stool. The product does not cause increased gas formation, cramps or pain, acts predictably and can be used for a long time. The drug is not addictive.
It should be remembered that if at the time you started taking Fitomucil Norm you had not had a bowel movement for 3 days or more, it is recommended to first cleanse the intestines using a cleansing enema or a suppository with glycerin.
It is worth noting that colitis is accompanied by a change in the balance of intestinal microflora. Thus, when performing bacteriological studies in patients with colitis, the growth of opportunistic flora is detected. And in people over 40 years of age, suffering from alternating constipation and diarrhea, there is a decrease in bifidobacteria and an increase in defective strains of E. coli. Shaposhnikov and Storozhuk studied and found that “in persons over 60 years of age suffering from persistent constipation, there is a sharp decrease in obligate microflora (bifidum and lactobacilli) in the stool with a simultaneous increase in the level of opportunistic microflora” (Shaposhnikov, Storozhuk, 2013, p. 130). Therefore, it may be advisable to prescribe a course of medications to normalize the balance of intestinal microflora: probiotics and prebiotics.
Nutrition and diet during exacerbations of UC
During periods of recovery from remission, a strict diet is recommended, aimed at alleviating the symptoms of UC in the acute phase, and also excluding:
- Bread and bakery products;
- Rich broths;
- Soups containing cereals;
- Smoked meats;
- Marinades;
- Pickles;
- Semi-finished products;
- Products containing artificial additives, flavor enhancers and preservatives;
- Dairy products, including milk;
- Carbonated drinks, black loose leaf tea;
- Legumes;
- Chocolate;
- Fatty fish and meats.
Alcohol, cocoa, eggs, pasta - these products are also excluded from the menu.
In addition, there are restrictions on temperature conditions: dishes must be eaten warm to eliminate the possibility of irritation of the mucous membranes. It is better to take grated foods to protect the intestines from injury.
For UC with constipation, freshly squeezed vegetable and fruit juices, drunk on an empty stomach, relieve the condition. Honey water, sweetened rosehip decoction, foods rich in magnesium and fiber also help stabilize the condition and improve intestinal function.
Treatment of colitis at home
Treatment of acute colitis is quite feasible at home; it begins with fasting for 1-2 days. Give boiled water (tea without sugar with lemon juice) to drink in small portions - 1.5-2 liters per day.
In acute colitis (enteritis, enterocolitis) due to consumption of foods infected with pathogens and/or their toxins, therapy begins with gastric lavage with a warm solution of sodium bicarbonate and the prescription of laxatives.
To create temporary rest of the intestines and restore its normal activity, fasting is prescribed for 1-2 days. For extremely weakened patients, it is recommended to add 1 tablespoon of red wine (per cup of tea) to unsweetened tea. On the second or third day, tea is replaced with an apple diet (up to 1.5 kg of non-acidic apples, 5-6 times in the form of applesauce).
In the following days, the diet is gradually expanded by introducing foods that do not irritate the intestines and do not contribute to the secretion of digestive juices and an increase in its peristalsis:
- oatmeal, rice, semolina porridge with water or low-fat veal meat broth;
- blueberry and blackcurrant jelly;
- strong tea;
- low-fat cottage cheese;
- meat puree or meatballs made from lean meat.
During the period of exacerbation of chronic colitis, pureed cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, honey tea, mucous soups with water made from oatmeal or rice are recommended (you can add meat stew from lean meat). Meat and fish are served boiled and chopped; Allows steamed cutlets, meatballs, dumplings. Rice or, better yet, oatmeal porridge is served as a side dish. You can eat crackers made from wheat flour, stale rolls, jelly and jelly from black rowan and cherry. If fermentative dyspepsia predominates, limit the consumption of carbohydrates (150-200 grams per day).
For chronic enterocolitis with symptoms of protein, vitamin and mineral deficiency, a diet containing a significant amount of protein (130-150 grams), fat (100-110 grams) and a limited number of carbohydrates (up to 400 grams) is recommended - a total energy value of 3500-4000 kcal. This diet includes lean meat and fish, well-cooked and fried, lean cheese, vegetable and mashed potatoes, lean meat soup, mashed porridge, stale white bread, butter (100 grams), rosehip infusion, mashed apples, tea, fruit juices.
Raw vegetables and fruits, beans, prunes, whole milk, brown bread, salty and cold dishes and snacks, ice cream, carbonated drinks are removed from the diet, and cereals and crackers are limited.
In cases where putrefactive dyspepsia predominates in the diet, the protein content is reduced. Allow pureed vegetables and herbs (except cabbage, radish, rutabaga), well-soaked herring.
In cases of dyskinetic constipation, it is recommended to eat foods rich in plant fiber: salads, vinaigrette, prunes, stale black bread, raw vegetables and fruits (apples, beets, carrots).
Fasting days are very effective: apple, kefir, cottage cheese days; They constantly use rosehip infusion.
For another 7-10 days you need to avoid fried meats, vegetables, potatoes, spicy and salty snacks, seasonings, that is, follow diet No. 4. In the case of fermentative dyspepsia, diet No. 4a is used, food is enriched with vitamins, especially vitamin C. For this, a decoction of rose hips and black rowan is used.
Sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated in Morshyn, Truskavets, Mirgorod, Odessa, and health institutions in Transcarpathia. Mineral waters are prescribed individually (depending on the functional state of the intestine).
Herbal remedies against constipation in UC
In addition to pharmaceutical laxatives, herbs such as:
Example of tincture: 6 hours. alder buckthorn, 2 tsp. horsetail and 2 teaspoons of nettle. The ingredients are crushed, 250 ml of hot water is brewed and infused for 8 hours. Afterwards, filter the broth and drink 100 ml before bed.
It is easy to prepare a tincture yourself that will act as a natural laxative without damaging the intestinal wall, but you must first consult a doctor. Self-medication of UC is dangerous due to exacerbations.
Treatment methods
Treatment of chronic colitis with constipation does not differ in childhood, adulthood and old age . The main criterion for choosing a treatment method is the severity of the disease, the degree of threat to health and life when complications occur.
Traditional medicine
Drug treatment is complex, prescribed in accordance with the nature of the disease and symptoms. The main goal is to relieve the root cause, symptoms, and prevent complications.
A typical assignment scheme includes:
- antibiotics for the infectious nature of colitis (antiparasitic - respectively);
- antispasmodics for acute spastic pain;
- choleretic agents when symptoms of gallbladder disease occur;
- enzyme agents to improve the absorption of nutrients.
Constipation is relieved with laxatives on a synthetic or natural basis (Senade, Microlax, Duphalac, Fitolax, Poslabin, Lavacol and other drugs based on macrogol). Additionally, absorbents are prescribed to cleanse the body of toxins (Polysorb, Enterosgel, Florafilter, Smecta).
Note! If the cause of colitis is dysbiosis, be sure to eliminate its cause and prescribe drugs to restore the intestinal microflora (Linex, Acipol, Bifidumbacterin).
Traditional methods and remedies
How else to treat intestinal colitis? Traditional methods of treating colitis in acute cases are not used as monotherapy, but in chronic forms they can provide stable remission of the disease.
Popular recipes:
- Olive or flaxseed oil. It is recommended to drink 1 tbsp on an empty stomach. oil 30 minutes before breakfast, at night 2 tbsp. no earlier than 2 hours after the last meal. The product softens stool and removes it. In addition, the oil envelops and protects from the negative effects of aggressive factors.
- 1 tbsp. bitter wormwood and sage flowers, pour 1 liter of boiling water, leave for 3-4 hours, filter and drink 100 ml after meals several times a day. The course of treatment is 14 days, after which a break of 2-3 weeks is taken.
- Alder infusion. A handful of alder cones is poured into 1 liter of boiling water, simmered over low heat for about 10 minutes, then left for about an hour and taken 100 ml 3-4 times a day. You can prepare an alcoholic decoction: a handful of cones are poured with 0.5 liters of vodka, placed in a dark room and left for 7 days. Single dose - 30 ml of tincture before each meal. To improve the taste, the composition is slightly diluted with water.
- A decoction of buckthorn, senna leaves, anise. 2 tbsp. mixtures of plants are poured with 500 ml of boiling water, infused, and filtered. To prepare a decoction for drinking, pour 100 ml of concentrate and dilute it with 200 ml of warm water. The drug is drunk for 7 days 2 times a day. The drug is not prescribed for acute spastic pain, since senna enhances intestinal motility.
The course of treatment with a laxative decoction must be supplemented with absorbents and probiotics to prevent intestinal dysbiosis. Additionally, vitamin complexes are prescribed.
Diet
An important condition for successful recovery is nutritional correction . The main goal is to minimize the traumatic factor during the digestion of food, reduce food aggression and digestive load.
excluded from the diet:
- fatty, fried, salty, spicy;
- alcohol;
- fresh baked goods, confectionery baked goods;
- spices, seasonings, industrial sauces;
- fresh vegetables and fruits (in the acute stage, especially gas-forming ones).
The menu includes low-fat fermented milk products, soups with lean meat, meatballs or cutlets made from home-made minced meat, and drinking plenty of fluids. Food is prepared by boiling, stewing, baking. During the acute period, food in ground, liquid or semi-liquid form is recommended. It is recommended to dilute natural juices with water first.
Physiotherapeutic methods
Physiotherapy for colitis is prescribed carefully to avoid the development of complications and negative consequences. For chronic intestinal colitis with constipation, physical therapy, warming, and mud therapy are indicated.
Prevention of constipation in ulcerative colitis
The best way to cope with constipation due to ulcerative colitis is to take care of your intestinal health in advance and prevent an exacerbation of the disease. To do this, it is important to maintain a healthy microflora, not to violate the diet and method of nutrition, and to visit a doctor in a timely manner for a routine examination, as well as in case of any complaints.
Moderate physical activity, fresh air, daily walks - all this improves intestinal motility and prevents difficult patency.
The right foods are just the basis for preventing constipation. With UC, it is important to monitor the amount of food eaten and the frequency of meals. Gastroenterologists advise eating small meals 5 times a day.
Some patients with UC note improvement after long-term consumption of boiled beets with prunes, dried apricots and garlic. During periods of calm disease, homemade low-fat kefir (1 glass daily) will benefit.
Follow us on social networks
How does spastic colitis with constipation manifest?
The absence of spastic bowel movements occurs periodically. There are cases when, with colitis, constipation does not bother the patient or occurs quite rarely. In the intervals when they stop, loose or normal stools may be observed. Most often, a mild form of diarrhea is observed, which is the intestinal reaction to prolonged stagnation of feces and muscle spasm.
Constipation with spastic intestinal colitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- bloating;
- the presence of a painful syndrome accompanied by cramping;
- periodic absence of bowel movements;
- the presence of mucus in the stool;
- increased emotionality;
- apathy;
- chronic fatigue.
The patient also often suffers from insomnia, headaches and increased gas formation. In addition, patients often complain of mild nausea, constant rumbling in the stomach and pain that worsens after eating.
Often with constipation, partial excretion of feces is observed, but in very small quantities. Such an attempt to defecate is accompanied by a feeling of incomplete emptying. The patient has heaviness in the abdomen and discomfort. Appetite disappears, a feeling of irritability appears. All these symptoms allow you to suspect the disease at the very beginning of its development and consult a doctor. If this is not done, the problem may become chronic.