Why does stomach churning and diarrhea occur at the same time?
If a person simultaneously feels rumbling in the stomach and is tormented by diarrhea, the causes of this condition may be infectious or non-infectious in origin. Despite the fact that seething in the stomach and watery loose stools rarely cause significant harm to the human body, it is necessary to get rid of them as soon as possible.
Dysbacteriosis
The disease can develop after taking certain medications, most often antibiotics. With this phenomenon, the intestinal microflora is disrupted. Medicines destroy it, killing both pathogenic and beneficial bacteria.
Because of this, food ceases to be processed normally, a person develops diarrhea, increased gas formation occurs, and the stomach begins to rage. Therefore, most doctors, when prescribing antibiotics, try to prescribe drugs that prevent the development of dysbacteriosis (Linex, Bifiform and others).
Salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is an intestinal infection. It often affects people who eat unprocessed foods. The disease is transmitted through meat, dairy products and eggs of an infected animal or bird.
With this disease, the patient suffers from vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence, fever, and less often convulsions.
To avoid infection, doctors advise people not to purchase products from unverified places and not to try them. In addition, you should wash your hands thoroughly when preparing food with meat or eggs.
Food intolerance
Food allergies can also cause stomach grumbling and diarrhea. Unpleasant symptoms develop due to the fact that the immune system refuses to process certain types of foods.
Often, such a reaction occurs to legumes, dairy products, seafood, and chicken eggs. They are not processed in the gastrointestinal tract of the allergic person, the stomach grumbles, flatulence and diarrhea occur. To prevent this from happening, doctors advise not to eat dangerous foods.
Dysentery
The causative agent is the dysentery bacillus, which is transmitted through food, water, and feces of an infected person. With this disease, people may experience the following symptoms:
- weakness;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- slimy stool;
- temperature increase.
The disease is especially dangerous for young children and the elderly. You can protect yourself by thoroughly washing your hands after visiting public places, the toilet, etc.
Poisoning
Having been poisoned by food, a person may also experience upset stools and rumbling in the stomach. Poisoning is often caused by food that has been stored in improper conditions. The most dangerous products are the following:
- cakes;
- sausages;
- minced meat;
- mushrooms;
- fish;
- meat and pates.
Botulism
A rare but dangerous disease is caused by the bacillus Clostridium botulinum. The disease is accompanied by diarrhea, paralysis, bloating, blurred vision, loss of space, and pale skin. You can become infected with the disease through meat, mushrooms, fish and home preserves. The bacterium, which produces a poison dangerous to humans, can enter the body through an abrasion or scratch from contaminated soil.
If you suspect botulism, a person should immediately consult a doctor. It is advisable to call an ambulance.
Enteric viruses
With this infection, in addition to diarrhea and bloating, a person experiences symptoms of acute respiratory viral infections or acute respiratory infections, and is bothered by a runny nose, cough, and sore throat. You can become infected with intestinal viruses through airborne droplets or the fecal-oral route.
Product incompatibility
Loose stools and rumbling stomach are observed if a person has eaten incompatible foods. For example, someone who ate herring and washed it down with milk or combined borscht with kvass will have to encounter these symptoms.
Cholera
The causative agent of the disease is Vibrio cholerae. The disease has the ability to spread quickly, so epidemics often occur. The infection is transmitted through food, water, and household contact.
Cholera is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- muscle pain and cramps;
- thirst;
- the patient’s facial features become sharper;
- the skin becomes dry;
- weakness.
Sedentary lifestyle
If a person leads an inactive lifestyle, then the microflora in the intestines is disrupted, fat plugs form, and food is poorly absorbed. All this leads to diarrhea and bloating. To avoid such phenomena, a person should move more, for example, take walks, visit the pool, and do exercises.
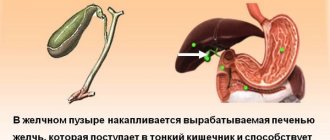
Pancreatitis
Flatulence and other disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract can be caused by pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). The disease can cause serious complications, so it needs to be treated as soon as possible. In addition to bloating, the patient may be bothered by:
- pain;
- dehydration;
- yellowness of the skin;
- temperature;
- breathing problems;
- vomit;
- pancreatic colic.
Other reasons and factors
In addition to the above reasons, other factors can contribute to the occurrence of diarrhea and stomach grumbling:
- Irritable bowel syndrome. Flatulence and diarrhea develop against the background of stress and emotional distress.
- Medicines. In addition to antibiotics, diuretics, oral contraceptives, and antirheumatoid medications can cause watery stools.
- Gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining). The disease develops against the background of poor nutrition and is accompanied by nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Read about diarrhea as a manifestation of gastritis here.
- Dyspepsia. The disease is manifested by rumbling in the stomach, nausea, rapid satiety, and painful sensations.
Infectious causes
Intestinal infections are common, especially in the summer. Pathogenic bacteria can cause not only food poisoning and diarrhea, but also a number of serious diseases, including death.
Some of them:
Salmonellosis
Transfer products are meat from an animal with salmonellosis, milk, bird eggs.
Manifested by vomiting, diarrhea, less often convulsions and a strong rise in temperature. The stomach is rumbling, flatulence is pronounced. You should not buy products at spontaneous markets, much less try them. It is important to wash your hands. Subject meat and fish to thorough heat treatment.
Dysentery
Transmission agents are food, water, feces of a sick person. The causative agent is dysentery bacillus. General intoxication of the body and weakness occurs, which is very dangerous for children in the first year of life and the elderly. Accompanied by frequent urge to go to the toilet, rumbling in the stomach, mucous stools and elevated body temperature.
Dysentery is called the disease of “dirty hands”. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain personal hygiene, always wash your hands after using the toilet, and periodically wash the toys of small children.
Botulism
The causative agent is the spore-forming bacillus Clostridium botulinum. A rarer, but more dangerous type of intestinal infection. The botulinum toxin produced is a powerful poison that affects the human nervous system. In addition to diarrhea, there is pronounced loss of space, paralysis, bloating, gas, blurred vision, pale skin; the temperature is normal and about 37 °C. Sources: mushrooms, meat products, fish, home canning. Infection through a wound surface (cuts, scratches) from contaminated soil is also possible.
To prevent disease, boil opened cans of homemade preserves for half an hour. Keep the kitchen clean. Treat wounds with antiseptic solutions upon contact with soil. If you suspect botulism, you must urgently call an ambulance. Failure to contact a medical facility in a timely manner can result in death!
Enteric viruses
The difference from other infectious intestinal disorders in this case is that manifestations such as liquid stool, flatulence, seething in the stomach and bloating are accompanied by signs of acute respiratory infections - cough, inflammation of the tonsils and runny nose. These viruses (rotaviruses, reoviruses, enteroviruses, adenoviruses) are transmitted from an infected person to another by airborne droplets and fecal-oral routes, mainly in the autumn-winter period, like all viruses.
Cholera
An extremely dangerous infection (causative agent Vibrio cholerae), capable of causing epidemics, spreads instantly. The picture of the patient’s condition is severe diarrhea and vomiting, severe dehydration, muscle cramps, shrinking of the skin into small folds. A distinctive feature is the absence of elevated temperature. Infection occurs from a sick person; the pathogen can be on the surface of vegetables and fruits, or in water.
To avoid infection, it is imperative to wash your hands after using the toilet and before eating; do not drink raw water; Pour boiling water over vegetables and fruits.
You should not self-medicate if your temperature rises above 38 °C and diarrhea persists for more than a day - you must urgently call a doctor!
Source
Associated symptoms
One of the main signs of diarrhea, regardless of its cause, is a rumbling stomach. A person may also experience other manifestations in which one should be wary:
- Increased gas formation due to a malfunction of the digestive system.
- Some infections cause vomiting and increased body temperature.
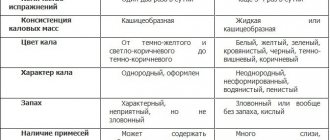
- Very loose stools mixed with mucus or blood.
- If the diarrhea is of an infectious nature, it may be watery. A person's skin turns pale and dehydration begins.
Enteric virus
The pathology in its manifestations is somewhat different from previous infectious diseases. The differences are that diarrhea, rumbling in the stomach and bloating are accompanied by a cough, runny nose and sore throat.
Rotavirus, reovirus, enterovirus or adenovirus can enter the human body through airborne droplets during contact with an already infected patient.
In addition, intestinal viruses can be transmitted through the fecal-oral route. An exacerbation of these pathologies is observed in autumn and winter.
Only a qualified specialist can determine the true reason that a person’s stomach is rumbling and diarrhea appears.
Therefore, it is recommended to contact a medical facility immediately after the symptoms in question appear.
In what cases should you visit a specialist?
There are several main points, when they appear, you should immediately see a qualified specialist. They are:
- Constant pain in the stomach.
- Retching and vomiting that does not go away after taking medications.
- Rumbling in the stomach and diarrhea that does not go away for several days.
- Excessive gas formation, which is not eliminated by specialized medications.
- The appearance of green stool mixed with mucus or blood.
Don't wait for the problem to go away on its own. The earlier the disease is diagnosed and treated, the better the prognosis.
First aid
You can provide first aid to yourself by taking activated carbon at the rate of one tablet per 10 kg of body weight.
Polysorb is also an excellent enterosorbent, but it is not always available. The drug is available in powder form and is taken in accordance with the table given in the instructions for it. For example, an adult weighing more than 60 kg needs to dilute two heaping tablespoons in 150 ml of water and drink. Take the suspension 3-4 times a day. The medication successfully fights food allergies, poisoning, intoxication, and acute intestinal infections of various origins.
In addition to taking any of the above medications, a person suffering from diarrhea and stomach turmoil should drink as much clean water as possible.
Which doctor should I contact?
If diarrhea and stomach churning are of a non-infectious nature, then you can contact a nutritionist. He will create the right diet for every day and tell you which foods are best not to eat.
If problems with the gastrointestinal tract are caused by infections, you should consult a gastroenterologist or infectious disease specialist. Be sure to go to these specialists if the following symptoms are present:
- periodic cramps in the abdomen;
- nausea;
- fatigue due to constant diarrhea;
- elevated temperature for several days;
- cloudy urine;
- yellowish tint to the whites of the eyes;
- constant gurgling in the stomach;
- increased gas emissions;
- mucus in stool, green stool.
Diagnostics
If you have abdominal problems that do not disappear within 2-3 days, you should go to a therapist who will prescribe an initial examination. Diagnostics is carried out using the following methods:
- Palpation. The doctor examines the patient, palpates his abdomen, pressing on certain points. In this way, painful areas of the digestive system are detected.
- Lab tests. This examination helps to clarify the reasons that caused diarrhea and rumbling in the stomach. For this purpose, stool, urine, and blood are collected from the patient. Tests allow you to determine the type of pathogenic microbe that has entered the body.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS). The essence of the method is to use a special probe, which helps to examine the walls of the gastrointestinal tract and analyze tissue samples.
These methods together allow the doctor to determine the original source of the problem and prescribe the most effective therapy.
How to eliminate diarrhea and stomach turmoil?
Depending on the severity of the disease, the patient is prescribed treatment. As a rule, therapy for diarrhea and rumbling in the abdomen is combined and combines taking medications and folk remedies, as well as following a diet.
Taking medications
To eliminate diarrhea and its accompanying symptoms, doctors prescribe drugs from the following pharmacological groups:
- Antibiotics (Levomycetin, Metronidazole). They are necessary to destroy intestinal infections.
- Probiotics (Bifidumbacterin, Linex). Prescribed to maintain normal microflora in the intestines.
- Drugs that slow down peristalsis (Loperamide, Imodium). Reduces the urge to diarrhea.
- Antidiarrheal medicines of herbal origin (cherry or pomegranate fruits). Act as astringents and tannins, stopping diarrhea.
- Enterosorbents (Polysorb, activated carbon and Smecta). Prescribed to remove toxins from the body.
Nutritional Features
For diarrhea and rumbling in the stomach, gentle nutrition is necessary. You should adhere to a special diet. Doctors allow you to drink kefir with bifidobacteria, eat crackers and porridge (oatmeal and rice) cooked in water. The next day, if the symptoms of the disease decrease, you can introduce omelettes and porridge cooked with milk into your diet. If such nutrition is perceived normally by the body, then you can eat meat and fish dishes with side dishes of vegetables.
It is also worth paying attention to the temperature of the food - it should be warm, but not hot. It is not recommended to eat cold food. Portions should be moderate so as not to overload the stomach with work.
Traditional methods
You can stop loose stools and eliminate rumbling in the stomach using folk remedies. As an auxiliary therapy, doctors allow:
- A decoction of blackberry leaves. The crushed raw material in the amount of one tablespoon is poured into a glass of boiling water. Then the broth is infused for 15-20 minutes and filtered. The healing drink is taken three times a day, 100 ml.
- Burnet decoction. The crushed root of the plant (one tablespoon) is poured with a glass of boiling water. The resulting mixture is simmered over low heat for at least half an hour, then cooled and filtered. Take the resulting drink six times a day, one tablespoon.
- Blueberry tea. To prepare it, you need to pour 250 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of berries and let the drink brew for 20 minutes. When it cools down, you can drink it without adding sugar.
Abdominal turmoil and diarrhea in pregnant women
During pregnancy, diarrhea and stomach turmoil can be caused by the same reasons as in other people. Also during this period, problems with the gastrointestinal tract may arise due to hormonal changes in the body and changes in the anatomical location of internal organs. Increased levels of progesterone in pregnant women reduce muscle tone not only of the uterus, but also of the intestines, and its peristalsis changes.
In late pregnancy, rumbling in the abdomen is due to compression of the intestines by the growing uterus. At the same time, the stomach also suffers, which manifests itself in a feeling of heaviness after eating and the appearance of heartburn. After childbirth, bowel function quickly returns to normal.
In addition, rumbling in the stomach in pregnant women can occur due to polyhydramnios. This pathology is considered obstetric, threatens complications, and its treatment is carried out by the doctor leading the pregnancy.
Folk remedies
Seething in the stomach and diarrhea are eliminated using recipes that our grandmothers knew. These formulations are used only in combination with proper nutrition and drug treatment. Decoctions of the following ingredients have beneficial properties:
- chamomile;
- oak bark;
- black tea;
- dill seeds;
- pomegranate peel;
- mint;
- rice
The following medicinal drinks prevent bloating and diarrhea, and also have a beneficial effect on the body.
Stomach turmoil and diarrhea in children
In childhood, problems with the gastrointestinal tract can also be caused by infectious and non-infectious causes. It is worth considering that the body of a child under one year is different from that of an adult. The baby's immune and digestive systems are not fully developed, so they often have loose stools, which should be distinguished from diarrhea. Loose stools are not dangerous, as they occur due to the characteristics of baby food (mother's milk or formula).
Diarrhea in a child under one year of age is a dangerous phenomenon that requires immediate medical attention. In a baby, diarrhea most often occurs due to non-compliance with the diet by the nursing mother (up to a year), infection with worms, poisoning with household chemicals, inability to digest certain foods, food allergies, and eating unwashed foods.
Gastrointestinal disorders and accompanying symptoms worsen a person’s quality of life. To prevent their occurrence, you should follow preventive measures and eat only at trusted food outlets. If problems with the intestines have already arisen and are protracted, then you should not waste time by self-medicating, but consult a doctor.
Previous post How to prepare and take saline solution for diarrhea?
Next entry Why does diarrhea with vomiting occur during pregnancy and what to do about it?
Prevention
For each specific patient, the selection of therapy is individual; the doctor is based on the presence of concomitant diseases and symptoms.
To prevent intestinal diseases, it is necessary to comply with a number of requirements regarding diet and general lifestyle:
- reduce the consumption of salty, fatty, smoked foods;
- avoid excessive drinking of alcohol;
- maintain a drinking regime (at least 1.5 liters per day of clean water);
- monitor the freshness of food;
- periodically consume fermented milk products;
- Consult a doctor in a timely manner if unwanted symptoms appear.
Prevention is the best treatment, especially when it comes to the digestive organs, the examination of which causes psychological discomfort and unpleasant sensations.