Contraindications for examination
Indications for gastroscopy are quite wide. It allows the doctor to obtain important information about the condition of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, identify pathological changes in them and take tissue sections for analysis . The study is recommended for any complaints that may be associated with dysfunction of the upper digestive tract. However, not all patients are prescribed this diagnostic procedure, even if it is needed.
There are a number of contraindications to FGDS :
- pathology of the esophagus, in which it is impossible to insert a probe into the stomach or there is a high risk of damage to the wall of the organ (scar strictures, burns);
- mediastinal tumors , mediastinitis;
- severe kyphoscoliosis (curvature of the spine and displacement of the chest organs makes it difficult to insert an endoscope);
- severe cardiovascular or respiratory failure;
- shock of various origins;
- acute cerebrovascular accident;
- complicated myocardial infarction in the acute period;
- suspicion of perforation (violation of the integrity) of the organ.
also undesirable to use gastroscopy in pregnant women and people with the following diseases:
- acute infections;
- acute inflammation of the upper respiratory tract;
- glaucoma;
- unstable angina;
- hyperthyroidism.
Contraindications from the last list are considered relative. This means that it is better to refuse the procedure, but in extreme cases the doctor may prescribe it.
Please note: In each specific situation, the need to use gastroscopy is determined by its diagnostic value. If a patient develops a life-threatening condition and it is impossible to help him without FGDS, then it is carried out without paying attention to contraindications.
Indications for the procedure
Capsule endoscopy is prescribed for all pathologies that are indicated for classical gastroscopy. In most cases, such a check of the condition of the stomach and the entire gastrointestinal tract is used when there are contraindications to tube diagnostics using the FGDS method. Capsule endoscopy is indicated for patients with the following pathologies:
- cardiac ischemia of the third degree;
- stage III hypertension;
- pronounced curvature of the spine;
- aortic aneurysm;
- history of heart attack, stroke;
- varicose veins of the esophagus;
- narrowing or ulcer of the esophagus;
- hemophilia;
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- obesity;
- anorexia;
- thyroid goiter.
Probeless endoscopic examination is recommended for people with mental disorders who are at risk of experiencing attacks of lack of air or suffocation due to a panic attack.
The method can successfully replace the standard FGDS method with the same diagnostic value.
In what cases are there no analogues?
Among the indications for gastroscopy, there are several particularly important ones, in the presence of which it cannot be avoided :
- gastrointestinal bleeding (vomiting "coffee grounds" or black stools);
- bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus (bloody vomiting);
- foreign bodies in the esophagus or stomach.
This is due to the fact that in such cases FGDS is performed not only for diagnostic purposes, but also for therapeutic purposes. it is not possible to eliminate the problem using other methods , it is impossible to replace the procedure.
It is also important to perform gastroscopy in patients with suspected gastric cancer and the need for a biopsy . After all, the patient’s management tactics depend on the results of the study.
What alternative methods are there?
If it is impossible to perform FGDS, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- ultrasound examination of the stomach;
- X-ray examination with contrast;
- endoscopic examination using a video capsule;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
These techniques cannot be considered to completely replace FGDS. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages over the endoscopy procedure. Nevertheless, as an alternative method when diagnosis is necessary, these methods are actively used. What will help in diagnosis, besides FGDS?
Anesthesia and sedation
If performing gastroscopy is difficult due to the psychological status of the patient or the presence of epilepsy or organic diseases of the central nervous system, then the study is best carried out under sedation or intravenous anesthesia.
For everyone else, this may be a good way to get through the procedure without unnecessary worry and stress. Sedation for EGD is widespread throughout the world. Read more about it in our article.
General anesthesia is often used in young children, which makes the procedure easier tolerable and easier.
Is gastroscopy possible without swallowing the probe?
In order to answer this question, you need to understand - what is gastroscopy? Translated from ancient Greek “γαστήρ” - stomach and “σκοπέω” - I look. Of course, classic gastroscopy without swallowing a probe is impossible , because it involves examining the stomach from the inside using an endoscope.
Currently, there are other methods for examining the stomach that allow visualization of the organ without penetrating into the cavities of the human body. They, of course, cannot completely replace FGDS, but with their help you can obtain useful information about the anatomy of an organ and its functional activity:
- assess the condition of the stomach wall , its inner surface;
- identify changes in the relief of the mucous membrane, the presence of neoplasms;
- characterize his motor activity and much more.
Help Using probeless methods, it is impossible to perform any diagnostic or therapeutic procedures, such as biopsy, analysis of gastric acidity, removal of polyps , etc.
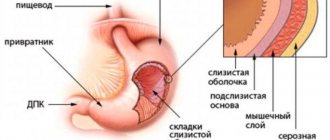
Gastroscopy of the stomach
This is a procedure for which a fibrogastroscope is used. This device is connected to a video monitor and it clearly shows the condition of the internal organs of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
In addition, if necessary, it can be used to collect material for histological examination.
Gastroscopy of the stomach is performed by swallowing a flexible gastroscope hose, at the end of which a small video camera is mounted (among the population, such manipulation is referred to as intestinal swallowing).
Before checking the stomach, a liquid anesthetic is injected to reduce the gag reflex. Most often it is Lidocaine.
What can be replaced?
If the patient has contraindications to FGDS, the doctor prescribes an examination using alternative methods. It is considered advisable to combine several diagnostic procedures to obtain more accurate data and prevent errors at the diagnostic search stage.
Sometimes patients themselves look for an alternative to gastroscopy, experiencing discomfort or fear of the study. In such cases, it is better to coordinate your actions with your doctor and choose a diagnostic method together . After all, to make a diagnosis in each case, a different amount of examination may be required. Below we list the main alternative studies and briefly discuss each of them.
How to check the stomach without swallowing a tube in an adult: conclusion
Thus, FGS is not the only research method, but it is still the most accurate and informative. Alternative methods only complement it. Most often they are prescribed to patients with contraindications to gastroscopy, but not instead of FGDS. Therefore, the patient should be concerned not with the question of how to avoid probing, but with how to overcome fear and tune in to the diagnostic event. Attention. The article is for informational purposes only. A doctor's consultation is required. Currently, gastroscopy of the stomach is already performed without swallowing the probe. This procedure will appeal to those patients who do not want to experience a lot of unpleasant sensations due to the use of endoscopic equipment by specialists.
Sources
https://zhivotneboli.ru/diagnostika-i-lechenie/metody-diagnostiki/gastroskopiya-zheludka-bez-glotaniya-zonda.html
https://wb health.ru/lechin-zhivot/kak-proverit-zheludok/
https://med-inffo.ru/proverit-zheludok-kak-nazyvaetsja-procedura.html
https://jely udok.ru/sposoby-proverki-zheludka-bez-glotaniya-zonda.html
How to check the esophagus without swallowing the intestine?
Transnasal route of administration
The principle of transnasal gastroscopy
In people with a clearly defined gag reflex , as well as in children, the endoscope can be inserted through the nose. This method allows you to avoid irritation of the root of the tongue and all the unpleasant symptoms associated with it. This is written in detail in a separate article.
Using a thin probe
The diameter of modern endoscopes does not exceed 6-8 mm. But, if necessary, thinner probes - 3-5 mm - can be used for research. They are indispensable in pediatric practice; if necessary (for example, in case of difficulties when inserting an endoscope into the gastrointestinal tract), they can also be used in adults.
Video capsule
This is the first painless method of high-quality visualization of all parts of the digestive tube, which does not require additional sedation of patients and is characterized by a high level of safety.
Its essence lies in the introduction of a special video capsule into the body, which, moving through the gastrointestinal tract along with its contents, takes a series of pictures that are transmitted to a recording device.
Initially, it was used only for diagnosing intestinal diseases, but thanks to improvements in equipment, it is now successfully used to diagnose pathologies of the esophagus and stomach. Read about video capsule endoscopy here.
Probeless methods for endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract
Ultrasound
Ultrasound diagnosis of diseases of the stomach and intestines is a relatively new phenomenon in gastroenterology, as it was previously used only for examining parenchymal organs (liver, spleen, kidneys, pancreas) and bile outflow tracts.
The method is safe and informative. Ultrasound allows you to visualize the organ through the anterior abdominal wall and provides the doctor with a spatial image of it in different projections.
Usually ultrasound is prescribed in any case as an addition to FGDS. It is excellent as the first stage of examining the gastrointestinal tract system and can identify emergency cases . A detailed analysis and comparison of these two methods: FGDS and ultrasound can be read here.
X-ray
X-ray techniques are widely used to detect pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. They are distinguished by their accessibility, ease of use, and sufficient information content , but, at the same time, they are associated with radiation exposure.
Some of them are carried out with contrast enhancement, which puts additional stress on the body and causes unwanted reactions. X-rays are most often prescribed for emergencies in hospitals . A detailed comparison of stomach X-rays and FGDS can be found in this article.
CT and MRI
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are prescribed in gastroenterology as additional research methods when there is a need to confirm the diagnosis or clarify the nature of pathological changes, as well as when a tumor process is suspected.
Computed tomography (CT) exposes body tissue to radiation that is several times higher in dose than conventional radiography. MRI has certain limitations in use. You can learn more about this in a separate article.
Electrogastroenterography
The method is absolutely safe and non-invasive. It is used in clinical practice to assess the motor function of the stomach and intestines by recording the electrical potentials emanating from them. The absence of contraindications and side effects makes it possible to prescribe it to different categories of people - young children, seriously ill patients, pregnant women.
Capsule gastroscopy
This research method is based on replacing the probe with a special capsule equipped with a video camera. The device allows for a thorough examination of the gastric mucosa and detects the disease in the early stages of development.
Capsule gastroscopy does not cause discomfort or unpleasant sensations
To make a diagnosis, the patient must swallow the capsule. For the inspection to be successful, you should prepare for it:
- The patient must adhere to a diet for 2 days before the procedure. It is recommended to exclude fatty, heavy foods, alcohol and dishes that cause flatulence from the diet. Food should be well chopped and steamed or boiled.
- The study is carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach. The capsule can be taken with ½ glass of plain liquid.
The process does not take much time and does not cause any discomfort to the person. During the examination, the patient can return to normal life, limiting physical activity. After 7–8 hours, the patient visits the doctor’s office again, where the doctor transfers the indicators recorded by the capsule into the computer and makes a diagnosis.
After a certain time, the device leaves the body naturally. The advantages of this procedure are obvious, but the method has not found wide application due to the rather high price of the device. In addition, such an examination does not allow you to perform a biopsy, remove polyps, or stop bleeding.
You can see how the stomach is examined using the capsule method in the video:
Desmoid test
Gastroenterologists often use a desmoid test to determine the degree of gastric juice activity. During the test, the patient swallows a bag filled with methylene blue powder and tied with catgut thread.
Using methylene blue to check the acidity of gastric juice
After the thread dissolves, the dye is gradually absorbed into the blood and no later than 18–20 hours later it is eliminated from the body. The study is based on assessing the intensity of urine staining. If the first portion of urine acquires a bright blue-green color, it means that the acidity of the stomach is increased.
Radiation research methods
You can check the gastrointestinal tract in an adult using both invasive manipulation and radiation diagnostics.
Such examination methods make it possible to obtain information about the configuration of the stomach and the presence of neoplasms, but do not make it possible to assess the condition of the mucous membrane. Of the radiation methods, X-ray is the most widely used. Equipment for examination is available in almost every medical institution, so the examination is available to all segments of the population.
MRI and ultrasound are more modern research methods and pose less of a threat to the health of patients.
You can learn about the differences between these procedures from the video:
X-ray
Using radiography, a stomach ulcer is detected, its configuration is checked, and its size is assessed. R-graphy is carried out using a contrast agent - barium suspension. It is prescribed when the patient complains of rapid weight loss, the appearance of blood in the stool, frequent and debilitating diarrhea, and constant pain in the gastrointestinal tract.
X-ray of the gastrointestinal tract is informative and does not take much time, but has contraindications
The procedure is completely painless and not very complicated, but requires compliance with some rules:
- For 2–3 days before the examination, you should exclude alcohol, thick, fatty and solid foods from your diet.
- On the eve of the test, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines using an enema or special means with a laxative effect.
- Before the procedure, the patient is prohibited from eating or drinking colored drinks.
An X-ray of the stomach lasts 30–40 minutes. All this time, the doctor asks the patient to take certain positions and takes six pictures of the gastrointestinal tract in different projections.
The procedure has its advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include the possibility of obtaining information that is not available when using a fiber gastroscope. For example, using FGS it is impossible to detect narrowing of the intestinal lumen or stenosis of the pylorus of the stomach.
Attention. Contraindications to x-rays are the first trimester of pregnancy and internal bleeding. In addition, x-rays are undesirable if you are allergic to iodine preparations.
Ultrasonography
Today, ultrasound is performed if bleeding or the presence of cancer in the organ cavity is suspected. This is a fairly popular, but not very informative diagnostic method.
Ultrasound is an uninformative method of checking the stomach
The procedure helps to identify only the main disorders in the gastrointestinal tract. For a more accurate diagnosis, the patient will have to use other diagnostic methods. Therefore, ultrasound is most often prescribed not to identify the disease, but to confirm an existing diagnosis.
Advice. Ultrasound examination is completely safe and can therefore be recommended for women at any stage of pregnancy.
Other
Desmoid test
It is a simple way to tentatively diagnose pathological conditions associated with achlorhydria (lack of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice). For this purpose, the patient swallows a thin rubber bag with methyline blue, tightly tied with catgut. If there is free HCl in the stomach, catgut dissolves and the dye enters the body and is excreted in the urine, based on the color change of which a conclusion is made.
Gastropanel
a complex of laboratory tests
to diagnose stomach diseases
To do this, blood is taken from a vein, in which the content of gastrin (a hormone produced in the stomach), pepsinogen types 1 and 2 (precursor of the gastric enzyme - pepsin), and antibodies to H. Pylory are determined.
How to check the stomach without swallowing a probe: desmoid test
Gastroenterologists often use a desmoid test to determine the degree of gastric juice activity. During the test, the patient swallows a bag filled with methylene blue powder and tied with catgut thread.
Gastroenterologists often use a desmoid test to determine the degree of gastric juice activity.
After the thread dissolves, the dye is gradually absorbed into the blood and no later than 18–20 hours later it is eliminated from the body. The study is based on assessing the intensity of urine staining. If the first portion of urine acquires a bright blue-green color, it means that the acidity of the stomach is increased.
What pathologies can be identified?
Various alternative diagnostic methods reveal signs of many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, but often cannot confirm the diagnosis due to the lack of biopsy and morphological examination.
Table 1. Diagnostic capabilities of each method.
| Gastritis | Peptic ulcer | Stomach cancer | |
| Ultrasound | Indirect signs, it is not possible to accurately diagnose | Determines the presence of an ulcerative defect, but does not have the ability to assess the benignity of the process | Assumes but does not confirm |
| X-ray | Same | Same | Same |
| Video capsule endoscopy | Same | Same | Same |
| CT, MRI | Same | Same | The same Evaluates the prevalence of the process |
| Gastropanel | Detects H. Pylory infection | Assess risk | Same |
| Electrogastroentnerography | Detects only disorders of motor function of the gastrointestinal tract. | ||
| Desmoid test | Determines the presence or absence of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. | ||
| GERD | Foreign bodies | Benign tumors, polyps | |
| Ultrasound | Yes | Yes | Yes, but cannot reliably distinguish from a malignant process |
| X-ray | Yes, but the sensitivity is low | Yes | Same |
| Video capsule endoscopy | Yes (detects Barrett's esophagus) | Yes | Same |
| CT, MRI | — | Yes | Same |
| Gastropanel | Same | — | — |
| Electrogastroentnerography | Detects only disorders of motor function of the gastrointestinal tract. | ||
| Desmoid test | Determines the presence or absence of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. | ||
How can you check your stomach without gastroscopy?
Today, ultrasound is performed if bleeding or the presence of cancer in the organ cavity is suspected. This is a fairly popular, but not very informative diagnostic method.
The procedure helps to identify only the main disorders in the gastrointestinal tract. For a more accurate diagnosis, the patient will have to use other diagnostic methods. Therefore, ultrasound is most often prescribed not to identify the disease, but to confirm an existing diagnosis. Advice. Ultrasound examination is completely safe and can therefore be recommended for women at any stage of pregnancy.
Price
The cost of examining the stomach using the above methods in the Russian Federation varies depending on the region, the prestige of the clinic and the qualifications of the specialist and equipment.
The price for the same procedure can differ significantly in the center of the capital and on the outskirts. Therefore, if there is a need to undergo examination in private clinics, it is better to familiarize yourself with their capabilities and pricing policy in advance.
Table 2. Cost of FGDS and other studies in the Russian Federation (in rubles).
| Moscow | St. Petersburg | Voronezh | Ekaterinburg | Krasnoyarsk | Ufa | |
| Ultrasound of the stomach | 800-3300 | 800-2800 | 540-1500 | 500-1500 | 450-1200 | 150-3080 |
| X-ray of the stomach | 1000-13000 | 1450-4500 | 650-2400 | 200-2500 | 200-1900 | 400-4200 |
| FGDS | 1000-36000 | 200-12000 | 400-3000 | 730-6800 | 250-2000 | 500-3030 |
| Video capsule endoscopy | 6000-111000 | 10000-78000 | From 55000 | 37000-50000 | From 53000 | From 65000 |