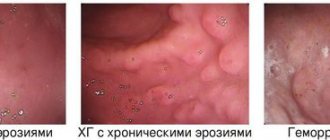
Many people wonder, when they hear the diagnosis “gastropathy,” what it is, and quite often confuse it with gastritis, although these provisions in medicine are completely different.
If gastritis is a pathology of the gastric mucosa, accompanied by its inflammation, then gastropathy is the name of various gastric diseases that are characterized by damage to the epithelium and vascular system of the stomach with possible minor inflammation. With this disease, studies will show redness of the surface of the organ.
According to ICD-10, the code for this disease is the same as for gastritis - K29.
Epidemiology
Currently, every second person on the planet has diseases of the digestive system. More than 60% of people are over fifty years of age. The picture takes on enormous proportions if we take into account the fact that the disease does not manifest itself in the initial stages.
Gastropathy occurs in both men and women, and it is also observed in children. In the fairer sex, the disease is diagnosed a little more often, this is due to problems at the hormonal level.
Classification
In medicine, there are several classifications of gastropathy. According to one of them, the disease is divided into acute and chronic, according to another, the disease is distinguished by stages, and still others distinguish the degrees of development of the pathology. According to the degree of development of the disease, gastropathy is:
- 1st degree, which manifests itself in a slight change in the gastric mucosa, as well as a slight decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid,
- 2nd degree, which is caused by more severe pathological processes, cell damage and necrosis of the gastric epithelium passes faster than in the first case. But these changes are convertible if treatment is started in a timely manner.
Olga system international histological classification of gastritis
The international classification of chronic gastritis (Sydney system and its Houston modification) in recent years has been supplemented by an integral indicator of the severity of inflammation - the degree and severity of atrophy of the gastric mucosa - the stage of chronic gastritis. This interpretation of morphological features was developed by an international group of expert pathologists (Atrophy Club) and the Working Group on Gastritis Assessment (OLGA - Operational Link on Gastritis Assessment).
In 2008, a group of experts involved in gastric pathology and a number of clinical gastroenterologists proposed a new system for assessing gastritis - the OLGA (Operative Link for Gastritis Assessment) system. This system uses an assessment of the histological severity of atrophy and inflammation in the antrum and body of the stomach, followed by the determination of integral indicators - the stage and degree of chronic gastritis.
The degree of gastritis is the manifestations of all infiltration, and the stage of gastritis is the extent of the severity of atrophy (the higher the stage, the greater the likelihood of developing non-cardiac gastric cancer). For practical use, an international group has proposed a new visual analogue scale of the OLGA - 2008 system. The OLGA system is a modern international histological classification of chronic gastritis. The study is used in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases.
The OLGA system has two significant advantages over previous classifications. Firstly, determining the stage of atrophy allows you to stratify the patient’s risk of developing gastric cancer, and secondly, the integral approach allows you to objectively determine the presence and severity of regression of the degree of inflammation and the stage of atrophy of the gastric mucosa as a result of treatment.
The OLGA system allows one to judge the dynamics of gastritis and make correlations with non-invasive diagnostic methods. Thus, assessment of the stage and degree of chronic gastritis turns into a characteristic that determines the individual prognosis and treatment tactics for a patient with chronic gastritis, ensuring the prevention of ulcers and the prevention of stomach cancer.
Sources:
- https://www.rosmedlib.ru/doc/ISBN9785970451755-0008/-esf2k2z11-tabrel-mode-pgs.htm
- https://autogear.ru/article/343/560/kod-po-mkb—erozivnyiy-gastrit-simptomyi-i-lechenie/
- https://gastritinform.ru/peptic.ru/gastrit/vidy/kody-tipov-gastrita-po-klassifikacii-mkb.html
- https://gastritinform.ru/www.mif-ua.com/archive/article/14947
- https://gastritinform.ru/www.grantimed.ru/services/uslugi-vzroslogo-otdeleniya/gastroenterologiya/
Causes and risk factors
Different types of the disease are currently diagnosed frequently. Doctors divide the causes of the disease into internal and external. These include:
- Poor diet, consumption of alcohol and nicotine, coffee, infections,
- Insufficient secretion of enzymes in the body that are needed for digestion,
- Long-term use of medications, burns and other injuries,
- Reflux of bile into the stomach, stagnation,
- Incomplete blood supply to the stomach due to the formation of internal pathologies,
- Genetic predisposition.
Symptoms
At first, the disease shows no signs. In frequent cases, the first symptoms are covered by those that are inherent in other ailments in which gastropathy develops. After some time, gastropathy has symptoms, as with gastritis, it is accompanied by pain and heaviness in the stomach, flatulence, nausea and heartburn.
In addition, appetite is disrupted, vomiting appears, after which the patient’s well-being becomes better. In half of the patients, there is a disturbance in the formation of bile, the tone of the large intestine is disturbed, and constipation occurs.
If there is a pathology of the antrum of the stomach, then bleeding may occur in the organ, the stool becomes reddish in color, and there is an admixture of blood in the vomit.
Erosive gastritis ICD 10
The healthcare system uses the international classification of diseases ICD-10. But the average person does not always understand how this phrase is related to the disease. Everything is very simple. This classification is intended to provide statistics on all existing diseases and health-related problems. And the number 10 in this phrase indicates the frequency with which this statistical information is collected (10 years).
Very often among the types of gastrointestinal tract there is erosive (hemorrhagic) gastritis or bulbitis. This disease is not only unpleasant, but also dangerous. Indeed, with its development, the entire gastric mucosa is affected by small, but quite numerous erosions, which not only cause pain, but also bleed quite often.
If a sick person sees the ICD-10 code, erosive gastritis, in his medical documents, a description of it, if desired, can be found in a reference book containing information about various diseases. But it is worth firmly remembering that any self-medication for this disease is fraught with serious complications. All medical prescriptions are the prerogative of the doctor! And the ICD was created only for medical specialists.
According to the ICD, the code for chronic gastritis is K-29.0. For the average person, this is an ordinary set of letters and numbers, but for a doctor it says a lot. Just seeing it in a medical document, a gastroenterologist will immediately say that it is acute erosive gastritis, complicated by bleeding.
It is dangerous because it is a precursor to an ulcer, and if treatment is ignored, it quickly develops into one. Its development is accompanied by inflammation in certain areas of the stomach and focal lesions appearing there, which have very thin, often bleeding, vessel walls.
It is needed in order to have optimal conditions for processing and analyzing all statistical data obtained from different regions and countries on morbidity and mortality. In ICD-10, verbal diagnoses are converted into an alphanumeric code, which greatly facilitates not only analysis, but also storage and retrieval of data.
Gastropathy in children
In childhood, this disease ranks second after ARVI. In this case, the disease usually occurs suddenly and progresses rapidly. Gastropathy can be observed in infancy during the transition to artificial feeding or as an allergic reaction to food. The disease is also often provoked by infections, medications, infant formula and expired products.
Gastropathy is manifested by weakness, anxiety, pain in the abdomen, lack of appetite, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. The acute form often becomes chronic, characterized by pain and a feeling of discomfort in the stomach.
Symptoms of NSAID gastropathy
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
Clinical manifestations of the disease vary. In 40-50% of cases, the pathology is asymptomatic, and the disease can be diagnosed at the stage of development of complications. In other cases, nausea, a feeling of heaviness and pain in the epigastric region, flatulence, and loss of appetite are noted. The pain occurs on an empty stomach, more often at night. The discrepancy between the results of endoscopic examination and the clinical picture of the disease is noteworthy. In a number of patients, in the absence of pain and dyspeptic symptoms, multiple ulcerations of the gastric mucosa are observed and, conversely, in patients with severe symptoms there are no endoscopic changes in the mucous membrane.
Varieties
Considering what gastropathy is, it should be noted that this term refers to a large number of stomach diseases. The types of these ailments depend on the description, interpretation of the disease, as well as on the final conclusion.
When describing, they evaluate the gastric mucosa, the size of its walls, and the presence of pathologies. The interpretation is made on the basis of clinical diagnosis, the conclusion is made based on the results of the biopsy. Today there are many types of gastropathy.
Antral gastropathy
This type of gastropathy develops in the atrium of the stomach, which is responsible for grinding food and its further movement into the duodenum. Here, mucus is secreted, which helps neutralize hydrochloric acid, as well as the production of the hormones serotonin, gastrin and endorphin.
This pathology causes a decrease in the rate of food processing, resulting in stagnation and fermentation. The patient begins to feel heaviness and pain. Untimely treatment leads to the development of ulcers that are easy to heal.
Associated and induced gastropathy
These types of diseases include pathologies that appeared as a result of taking NSAIDs in the treatment of various diseases. Such drugs can cause damage to the gastric mucosa, the development of ulcers and erosions, bleeding, and create obstruction of the organ.
Typically, these types of gastropathy do not show symptoms, so they are often diagnosed when complications occur.
Atrophic gastropathy
With this type of disease, the cells of the gastric glands lose the ability to cope with their tasks, they give birth to their own kind as a result of an autoimmune reaction, a mutation occurs that leads to the production of mucus instead of hydrochloric acid. A particular danger in this case is the development of malignant neoplasms.
Hyperemic gastropathy
This pathology is characterized by an increase in the flow of blood to the stomach, which leads to redness of the mucous membrane, its swelling and bruising. Hyperemic gastropathy can spread to various parts of the organ or be located in small areas.
Diagnosis of erosive gastritis
Although signs and symptoms as well as the patient's medical history may indicate gastritis, further testing is needed to confirm the diagnosis of erosive gastritis. Blood and stool tests can confirm anemia with blood loss, infection, and blood in the stool. However, imaging studies such as upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy or gastroscopy will confirm the diagnosis of erosive gastritis.
Ulcers and erosions will be visible, as well as other changes in the stomach, such as enlarged folds and nodules of the stomach. Other tests may include a double-contrast barium x-ray, where the patient takes a radiopaque dye and the stomach is highlighted on the x-ray.
Treatment
Any gastropathy requires treatment with enzymes, painkillers and gastrocytoprotectors. Medications that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach may also be prescribed.
If Helicobacter bacteria are detected, doctors prescribe antibiotics to the patient. Surgery is performed when there is bleeding in the stomach that cannot be stopped. In this case, laparoscopy is used.
Prognosis and prevention
If the disease is treated promptly and effectively, it does not pose a threat to life. A negative prognosis will occur when the disease is advanced and leads to the development of malignant neoplasms, as well as in the presence of pernicious anemia.
Having studied the causes of the development of gastropathy, it is recommended to design prevention methods in such a way as to protect your body from negative external and internal influences. First of all, you need to monitor your diet, give up bad habits, not abuse medications, and avoid stressful situations.
Loading…