The occurrence of stabbing pain is a sign of multifunctional or organic diseases of the stomach or diseases of nearby organs. The stomach is an innervated organ directly connected to the human central nervous system. Minor errors in nutrition, violation of the usual menu, secondary effects of pharmaceutical substances on him and nearby organs of the gastrointestinal tract can disrupt his condition.
Causes
The main causes of stabbing pain in the stomach and abdominal area:
- Eating disorder.
- Severe psycho-emotional state.
- Intense loads.
- Introduction of pathogenic microorganisms, infections.
- The influence of harmful substances.
- Injuries to the abdominal organs.
- Congenital pathologies of the stomach and intestinal tract.
- Allergy.
It is quite possible that such a receptive organ as the stomach is capable of feeling pain that occurs in other organs, even those that do not belong to the digestive system. For example, myocardial infarction. He, in turn, manifests himself with stabbing pains not in the heart, but in the stomach, radiating to the arm.
Classification of abdominal colic
Classification of colic is carried out depending on the etiology and accompanying symptoms. Stitching pains can be true, false or symptomatic. In the first case, the condition is a symptom of a specific disease. The false type occurs with diseases of any organs, but not the digestive system (kidneys, liver, respiratory organs, genitourinary system).
Symptomatic pain is secondary. They can be caused by operations, infections, or other pathological processes.
Types of colic:
- appendicular type (localized on the right side of the abdomen, accompanies acute appendicitis);
- lead type (spasmodic pain, increased body temperature);
- renal type (pain syndrome extends to the lumbar and stomach areas)4
- pancreatic type (pain takes on a girdling character);
- hepatic type (pain occurs in the area of the right hypochondrium, gradually spreading to the shoulder or scapula).
Diseases that cause pain
Stomach colic accompanied by pain are signs of damage to the stomach or organs close to it:
- Gastritis – prolonged pain is felt after digesting sour or rough foods, and there is also a feeling of heaviness, weakness and nervousness.
- Stomach ulcer – 30% of patients may experience mild pain that occurs after eating; relapses of this disease are replaced by seasonal exacerbations.
- Duodenitis – projects pain from the small intestine to the stomach. In addition to stabbing and cutting pain in the stomach, inflammation of the intestinal tract is accompanied by hyperthermia, depression, vomiting and lightheadedness.
- Appendicitis - an attack begins with the appearance of stabbing pains in the stomach, later they shift to the iliac region on the right side. Signs: slight nausea, slight increase in temperature.
- Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a disorder of the blood supply to the myocardium, sometimes radiating to stabbing pain in the stomach area. Additional signs are shortness of breath, tachycardia, impotence.
Diseases
Pathology of the gastrointestinal tract is common and occupies a leading place in medical statistics. A detailed examination can reveal the true cause of acute, stabbing pain.
Gastritis
This is a disease caused by inflammatory processes in the gastric mucosa. There are two types of disease: acute and chronic.
During the first period, the disease does not manifest itself with external signs. Rare pain sensations appear, which are attributed to a heavy dinner or a spicy dish. Symptoms appear unexpectedly and are severe:
- Severe, sharp pain in the upper part of the digestive tract. Manifestations do not depend: after eating or before eating.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Feeling of heaviness, fullness. If you take food in small portions, the feeling does not go away, digestion leads to an uncomfortable state.
- Appetite decreases until it disappears completely. Weight loss in a short period of time. Problems with bowel movements - constipation.
- Weakness, pale skin, white coating on the oral mucosa. Possible heart rhythm disturbances, high temperature, low blood pressure.
- Heartburn and a feeling of dry mouth or increased salivation.
The chronic stage occurs quickly, in the absence of treatment for gastritis. The patient has the following symptoms:
- Feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
- Heartburn.
- Belching with an unpleasant aftertaste.
- Vomit.
- An undulating state of the intestines, resulting constipation is replaced by diarrhea.
- Bloating, flatulence.
- Bad breath.
The causative agent of the disease is considered to be Helicobacter pylori infection. Attaching to the wall of the stomach, the microorganism multiplies, producing ammonia, which destroys the protective mucous layer of the walls of the organ. As a result, foci with inflammation and pain syndromes arise.
Stress, poor diet, bad habits and alcohol abuse lead to disruption of the stomach.
Stomach ulcer
The disease appears during a chronic inflammatory process on the mucous membrane of the organ. Exacerbations occur in the spring and autumn periods. The causative agent is considered to be Helicobacter pylori. This is an infection that enters the body through unwashed hands and poor-quality food. Causes destruction of the protective layer on the walls of the stomach and the appearance of tissue necrosis. As a result, a wound forms in the wall of the stomach - an ulcer, which periodically bleeds and is painful. At the same time, the muscles are constrained by spasms, which forces the person to bend.
Severe stress can cause peptic ulcers. Disruptions in the nervous system reduce the contractile movements of the stomach. Hydrochloric acid, which makes up gastric juice, is retained in the epigastrium. The lack of food forces the organ tissue to recycle, which leads to the formation of non-healing ulcers. The pain is characterized as stabbing and radiating to the back.
Duodenitis
Damage to the duodenum. Inflammatory processes occurring in the upper parts of the organ resemble an ulcer in terms of symptoms, and in the lower parts they resemble pancreatitis or cholecystitis. External signs that occur: weakness, acute pain in the stomach, severe heartburn, nausea and vomiting.
Duodenitis occurs in two forms: acute and chronic. The acute form of the disease passes quickly, and with proper treatment does not change the structure of the organ mucosa. The chronic form is more dangerous. Foci of the inflammatory process develop with periods of relapse and irreversible changes in the protective membrane of the organ.
Appendicitis
The first signs of an inflamed appendix of the colon are sharp pains in the stomach. Gradually, the pain syndrome moves to the iliac region, on the right side. The nature of the symptoms: vomiting, slight increase in body temperature.
Cardiac ischemia
Serious heart disease leads to disruption of the blood flow supplying the digestive organs. The occurrence of spasmodic phenomena and pain is observed. Associated symptoms: shortness of breath, irregular heart rhythm, general weakness.
Characteristics of pain
Acute stabbing pain in the stomach most often occurs not as a symptom of an incipient disease, but as a sign of a complication of a previously developed pathology. To make a correct diagnosis, the patient must provide the doctor with detailed information about the nature and frequency of pain attacks, because:
- The time of occurrence of severe stabbing pain in the stomach varies with different pathologies of the organ; it may be associated with food that has entered the stomach, or may be determined by the daily menu.
- The pain occurs at different times of the day and night and can be felt as a series of stabbing sensations or individual manifestations.
- The location is of great importance for appropriate diagnosis. It can be in the upper or lower lobe of the stomach, and can radiate to the back or arm.
- Intensity. The pain may be mild, or it may remind the patient of a “dagger prick.” The intensity of pain can be so high, for example, when a stomach ulcer is perforated, that the patient periodically loses consciousness from painful shock.
- Duration - one day or several, months and even years. For example, stabbing pain in the stomach after eating can last from several minutes to several hours, return or end in the absence of any therapy.
Under the left and right shoulder blade
In most cases, the main cause is diseases of the pancreas, which cannot cope with the load. Pain occurs 10-15 minutes after eating, and also intensifies when drinking alcohol. An attack of acute pancreatitis is always accompanied by severe colic in the left hypochondrium. Additional symptoms may include the following:
- nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal spasm;
- increase in body temperature.
In the case where there are no problems with the pancreas in the form of diseases and pathologies, the cause of colic should be sought in food. Abuse of fatty and sweet foods devoid of fiber puts increased stress on the pancreas, which is accompanied by painful sensations after eating.
Colic in the shoulder blade area is rarely associated with diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Usually the causes are pathologies such as:
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system - acute heart failure, thrombocytosis, arrhythmia and tachycardia can provoke colic in the area of the shoulder blades and between them.
- Kidney disease - if colic gets worse when you inhale, and your back hurts in the area of the shoulder blades, which is accompanied by frequent painful urination, then the problem is in the kidneys. This could be a symptom of a urinary tract infection or cancer.
- Biphasic rupture of the spleen is a dangerous pathological condition characterized by a violation of the integrity of the organ.
Sometimes colic in the area of the shoulder blades is a sign of a chronic type of peptic ulcer, which is in the acute stage.
Symptoms
Painful sensations arising in the stomach area can be of a very different nature; in addition, they can be paroxysmal or regular. Many people often complain of stabbing pain in the stomach, which can occur for a variety of reasons. In any case, you should not figure out the cause of such pain on your own. If you experience stabbing pain in your stomach, you should immediately contact a specialist. Only he will be able to identify the true cause of these pain sensations.
Sharp stabbing pain in the stomach can be a sign of various diseases, and a particular disease can be identified by additional symptoms accompanying these painful sensations, as well as by the location of the pain. So, for example, if pain occurs not in one place, but over the entire surface of the abdomen, then this may indicate the presence of some kind of chronic disease; sometimes such pain goes away on its own after using mild painkillers or after proper rest. If colic appears in the lower part of the gastrointestinal tract, this may indicate the development of a new disease. In this case, stabbing pain is often accompanied by severe discomfort in the stomach area.
Stitching pain in the stomach can occur in women with certain gynecological diseases. Severe stress can also trigger their appearance. Often, stabbing pains in the stomach area appear with severe poisoning, in which case they are accompanied by vomiting or diarrhea, as well as bloating and discomfort.
How to eliminate colic in the stomach area?
Surgery
If the patient suddenly develops severe pain, stomach pain, nausea and vomiting, this may indicate acute appendicitis. Intense pain in the presence of blood in the stool or vomit indicates an ulcer and internal bleeding. In both cases, neglecting a visit to the hospital can be fatal. To save the life and health of the patient, urgent surgery is required.
Nutrition rules
To eliminate inflammation and prevent recurrent attacks, it is important to stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
Carbonated drinks should be excluded from the diet, as they irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Any gastrointestinal disease requires lifestyle changes and diet. If colitis occurs in the stomach, you should avoid foods that can irritate the mucous membranes. Spices and sauces, fatty and fried foods, and carbonated drinks are prohibited. Food needs to be boiled, baked or steamed. Before use, the dish should be crushed using a blender. The patient must rest thoroughly. It is important to avoid stress and take walks.
Drug therapy
If there is severe pain in the stomach, nothing can be done until the ambulance arrives. In the absence of signs of ulcer perforation and internal bleeding, it is allowed to take an antispasmodic. No-spa is often used to eliminate pain. Antacids, for example, Maalox, can relieve inflammation and stop an attack of colic. The pathological symptom can be completely eliminated only with the help of complex therapy selected by a doctor based on the diagnostic results. To combat a number of gastrointestinal diseases, the patient is prescribed antispasmodics, antacids, and enzyme preparations. Emotional people are additionally prescribed sedatives.
Diagnostics
At the first sensation of pain, you should immediately contact a specialist, since in some cases the cause may be quite serious and require emergency surgical intervention. The first thing the doctor does is conduct a full examination, after which he sends the patient for additional tests. The patient may be prescribed the following procedures:
- Ultrasound;
- gastric probing;
- X-ray;
- biopsy;
- gastroscopy;
- MRI;
- colonoscopy;
- computed tomography;
- irrigoscopy,
- angiography;
- cholescintigraphy.
Drug treatment
Stitching pain in the stomach can be caused by various reasons, but in no case should you self-medicate it or take pills without consulting a doctor. If the feeling of pain is too strong, then before the specialist arrives, it is allowed to take an antispasmodic or analgesic. Any irrational use of medications causes a distortion of the overall picture of the problem, which significantly complicates diagnosis. Quite often there are patients who, at the first sign of pain, drank an anesthetic drug, and this created a long-term effect of recovery. But this only temporarily relieved them of pain.
The doctor prescribes medications, but only after all examinations and an accurate diagnosis. Many people are advised to take only painkillers. For example, if the pain is associated with cramps in the intestines, the specialist will suggest giving an injection in the arm, leg or thigh. In the absence of a gag reflex, it is allowed to drink a painkiller along with an antacid.
Medications
Pharmacies have freely available medications aimed at relieving symptoms and treating various gastrointestinal diseases.
Almagel
The feeling of heartburn and stabbing pain can be relieved by Almagel. The action of the drug is aimed at neutralizing the accumulated hydrochloric acid in the stomach, creating an additional protective layer on the mucous membrane. Uniform distribution of medicinal components throughout the organ.
No-shpa
A popular antispasmodic drug. Acts on the smooth muscles of the organ, reducing tone. Thanks to the expansion of blood vessels, the stomach is better supplied with blood, and antispasmodic effects gradually decrease. Does not affect the human central nervous system.
Source: GastroTract.ru
The best means
You can do without medication if pain in the abdominal area is not accompanied by vomiting, bleeding or high fever. It usually goes away after some time. To relieve abdominal pain, it is recommended to use antacids. Some of them can be purchased in pharmacies without a doctor's prescription. For example, “Maalox”, “Almagel” or “Phosphalugel”. The listed medications do a good job of eliminating pain. But they can only be used if the pain is actually directly related to problems of the digestive tract. If discomfort in the abdominal area occurs due to food poisoning or drug overdose, then activated carbon will be the best remedy.
What should you not take?
It is forbidden to take Aspirin or Ibuprofen if you have an ulcer or liver problems. They act as an irritant to the mucous membranes, and the pain will only intensify. If a woman experiences stabbing pain during pregnancy, then experts recommend that it is best to refrain from using any medications. Each of them contains certain chemical elements that have a negative impact on the further development of the fetus. The most suitable option is a homeopathic remedy.
Traditional treatment
The most common problem for most people living in big cities is pain in the stomach, which is accompanied by various unpleasant symptoms such as vomiting, bloating or simply severe discomfort. Most often, people complain of stabbing pain in the stomach, which can occur from time to time or be constant. People who have pain in the stomach prefer folk remedies, and this is not surprising, since such drugs are more effective, and they have practically no side effects. True, before using any folk remedies, even the safest ones, you must undergo a mandatory consultation with a doctor. The fact is that stabbing pain in the stomach may be a sign of some serious disease, for the treatment of which any traditional medicine may be completely useless. It turns out that the pain will be eliminated, but the disease that caused the appearance of such a symptom will remain.
Causes of stomach pain
Pain in the stomach is a sign of inflammatory, ulcerative or degenerative changes in internal organs, as well as irritation of nerve receptors. It can be acute or aching, bother the patient constantly, appear suddenly or at certain hours. In some cases, it is accompanied by nausea, vomiting and other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Sometimes the discomfort is associated with eating - the pain intensifies on an empty stomach or after eating.
Stomach pain can be divided into several categories:
- visceral - irritation of nerve receptors on the walls of the abdominal cavity and internal organs occurs;
- parietal - occurs when the peritoneum is irritated;
- inorganic pain (neurogenic, psychogenic and others not associated with damage to the digestive tract).
The causes and treatment of stomach pain are interrelated, so it is important to determine which pathology triggered its development. The difficulty of diagnosis lies in the fact that in some diseases it radiates, that is, it is transmitted along the nerves from distant areas. This is why self-medication at home can be not only ineffective, but also dangerous.
Gastritis
Gastritis is one of the most common causes of stomach pain, inflammation of its mucous membrane. The disease can occur in acute or chronic form. In the second case, it manifests itself only during periods of exacerbation, which may be due to irregular and unhealthy diet, taking certain groups of drugs, stress or other factors.
All gastritis is conventionally divided into microbial and non-microbial. A complete classification of this disease identifies several main types:
- type A - autoimmune, associated with the development of an allergic reaction to one’s own organs and tissues;
- type B - exogenous, occurs when the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is activated;
- type C - can be triggered by chemical irritation of the mucous membranes with drugs (NSAIDs), chemicals or bile;
- inflammation due to an increase or decrease in the concentration of hydrochloric acid;
- special forms of gastritis.
There are two more types of gastritis that require radically different treatment tactics. They can be distinguished by the results of laboratory tests of gastric contents:
- hyperacid - occurs with intense release of hydrochloric acid and increased acidity of gastric juice;
- hypoacid - accompanied by a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice.
Inflammatory processes can also be triggered by abnormalities in the structure of the stomach. Thus, when the pyloric sphincter is weak, the contents of the duodenum are thrown into the stomach, which does not occur normally, and causes pain. It is also necessary to take into account the nature of inflammation. It can be aseptic, purulent, fibrinous, hemorrhagic (with bleeding) or mixed.
Peptic ulcer
The appearance of an ulcer on the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum may be associated with a long-term chronic course of gastritis, as well as other diseases. Among other things, it can be triggered by weakness of blood vessels and disruption of blood flow in a certain area. Peptic ulcer disease occurs in a chronic form with periodic relapses. It manifests itself with a number of characteristic symptoms:
- hunger pains - discomfort in the stomach during long breaks between meals;
- night pain;
- nausea and vomiting;
- digestive disorders, including flatulence or diarrhea;
- the appearance of blood impurities in the stool, that is, its coloration in a black tint.
The most dangerous condition is perforation of the ulcer. This condition is accompanied by severe pain in the stomach and deterioration in well-being, including loss of consciousness. If the contents of the stomach or duodenum enter the abdominal cavity, there remains a risk of purulent inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis) with all the manifestations of sepsis.
Hungry (night) stomach pain
Hunger pain in the stomach is usually called those that occur 5-6 hours after the last meal. It is during this period of time that the food bolus passes through the stomach and duodenum so that they remain completely empty. This can be easily prevented during the day (including by drinking water), which is why hunger pain is also called night pain. They often occur between 3 and 5 am.
The main cause of hunger pain in the stomach is irritation of the mucous membrane by the organ’s own contents. Here it constantly secretes gastric juice, which digests food into small components. However, it affects its own mucosa in a similar way. If it is initially damaged, it will react to irritation with acute pain.
The causes and treatment of nighttime stomach pain may vary. In most cases, this syndrome is caused by gastritis of various origins. However, it can also be caused by a more dangerous condition - peptic ulcer disease.
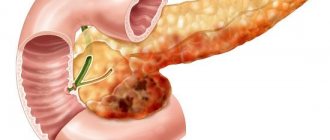
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas, which is closely related to the functions of the stomach and duodenum. Its main function is the production of pancreatic juice. It is released into the lumen of the small intestine and neutralizes the acidic contents that come from the stomach and contain hydrochloric acid. Pain with pancreatitis is caused by inflammatory processes and dysfunction of the organ - if pancreatic juice is produced in insufficient quantities, the mucous membranes of the digestive tract are irritated by acids.
Among the causes of pancreatitis are:
- disruption of the outflow of pancreatic juice and its accumulation in the organ cavity;
- non-compliance with the diet, consumption of large amounts of animal fats, alcohol and other unhealthy foods;
- hormonal factors;
- gastritis, hepatitis, cholecystitis.
The pain with pancreatitis is acute and spreads to the upper abdomen. It can be encircling in nature and located in the area of the left and right hypochondrium. Discomfort increases after eating or prolonged fasting.
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder can also be one of the causes of pain in the stomach. This organ is a hollow sac in which bile accumulates. Then it enters the bile ducts into the lumen of the small intestine and participates in the digestion (emulsification) of fats. Violation of this process leads to pathologies of the digestive system, gastritis and duodenitis.
All cholecystitis can be divided into two groups:
- calculous - associated with the formation of stones in the cavity of the gallbladder, irritation of its walls and blockage of the bile ducts with stones;
- non-calculous - develops due to poor diet, injuries, or infection activity.
The work of the gallbladder, unlike the pancreas, is directly related to the digestive processes. Its sphincter relaxes when food enters the stomach so that bile can flow freely into the intestines. If a long period of time passes between meals, the liquid fills the bladder and causes its walls to stretch.
In digestive pathology, the composition of the food consumed is important. An abundance of animal fats, which contain excess cholesterol, provokes the formation of stones. They can be of different shapes and sizes, have smooth or sharp edges. Stones can clog the bile ducts and injure the mucous membrane of the biliary system. The pain with cholecystitis is acute, spreading to the area of the right hypochondrium, stomach and intestines. It is accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, and increased gas formation.
Infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
One of the main causes of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is the activity of pathogenic and opportunistic microflora. The main gastric infection is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which can remain in its cavity for a long time and cause irritation of its mucous membrane. It is part of the gastric microflora of most of the population, but its activation occurs only with a confluence of favorable factors. These include mutations and increased virulence of individual strains, decreased body resistance and irritation of the gastric mucosa with food or drugs.
The bacterium is a trigger for the development of a number of pathologies:
- gastritis;
- stomach ulcer;
- adenocarcinomas and lymphomas of the stomach.
The pain is localized in the epigastrium and mesogastrium and can be sharp, cutting or aching. The clinical picture is complemented by characteristic symptoms of diseases of the digestive tract: decreased appetite, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea. Infectious inflammation can also be triggered by other pathogens, including staphylococci or streptococci.
Neoplasms
Gastric tumors are a group of neoplasms that differ in origin, size and degree of danger to the patient. All of them can be divided into two groups: benign and malignant. The former are limited in size, do not grow into organ tissue and do not affect large vessels, and do not form metastases. The danger of benign tumors is that during the process of their growth they can become malignant, that is, become malignant.
Benign tumors include:
- polyps - rounded formations on a stalk that are easily removed surgically;
- leiomyomas - originate from the muscular layer of the organ wall;
- lipomas - from the submucosal layer;
- angiomas - vascular tumors;
- Neuromas - develop from nervous tissue.
Among the malignant neoplasms of the stomach are:
- adenocarcinomas - stomach cancer that originates from the epithelium;
- carcinoid - has a neuroendocrine origin, can secrete hormones;
- leiomyblastomas - develop from cells of epithelial and muscle tissue;
- malignant lymphomas and others.
All neoplasms are manifested by constant pain in the stomach area. There may be a decrease in appetite and a quick feeling of filling the stomach with food while eating. The patient's general condition worsens, accompanied by headaches and general intoxication. Small benign tumors may not appear for a long time and are only discovered then. when they reach significant sizes.
Other reasons
Painful sensations in the stomach can occur with more rare conditions, which must be taken into account during diagnosis. These include pathologies not only of the gastrointestinal tract, but also of other organs. So, pain can have the following causes:
- diaphragm spasm - discomfort increases with certain body positions;
- colitis (inflammation of the large intestine) - also manifests itself in the upper abdomen;
- appendicitis - pain can occur not only on the right, but also in any part of the abdominal cavity;
- coronary heart disease - pain radiates to the stomach;
- pathologies of blood vessels (thrombosis of intestinal vessels, dissection of the abdominal aorta and others).
All these pathologies are manifested by chronic or acute pain in the stomach, which can spread to other areas. So, it can be encircling, that is, also covering the area of the left and right hypochondrium, or one-sided. Painful sensations that primarily arise in the stomach area and then spread to the back are often interrelated.
Ginger
So, if a stabbing pain appears in the stomach area, it is recommended to use medicines prepared on the basis of asafoetida, fennel or ginger root. Medicines based on ginger are especially effective, since this aromatic root contains substances that normalize the functioning of the digestive system. In addition, ginger root has anti-inflammatory properties and helps reduce pain and inflammation.
To prepare a healing potion, it is recommended to use fresh, rather than dried, ginger root, which must first be peeled and then cut into small pieces. Next, place the chopped ginger root in a small saucepan of boiling water. Boil the ginger for no more than five minutes over low heat, strain the prepared broth, add a little honey to it and consume when a stabbing pain occurs.
Fennel
To reduce pain in the stomach, it is recommended to use a decoction of fennel seeds, which have antimicrobial and carminative effects. Pour a spoonful of fennel seeds into a small saucepan, pour in one and a half glasses of hot water, boil the mixture for three minutes, strain and cool. Use fennel infusion as tea if you have stomach pain.
Surgery
One of the most unpleasant types of pain, the cause of which is difficult to determine, is pain in the abdominal area. There are many reasons for its occurrence, but what exactly hurts can only be determined by a doctor, who will also prescribe treatment.
When the cause is established, the doctor prescribes a course of treatment or sends for emergency surgery. Surgical intervention occurs mainly for inflammation of the gallbladder and appendicitis. In some cases, surgery is not possible for intestinal obstruction. Stitching pain in the abdominal area may occur due to perforation of internal organs or their rupture. In these cases, surgery cannot be avoided; it is performed by a surgeon with assistants under general anesthesia.
Examination for stabbing pain
Only on the basis of the patient's complaints of discomfort in the abdominal cavity, the doctor will not be able to make a correct diagnosis.
The patient must undergo a series of examinations, as a result of which the doctor will be able to determine the causes of pain and prescribe the correct treatment.
Video:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=k6s3GWu3mlo
In some cases, a specialist may prescribe therapy with hormonal drugs and regenerative agents. Such medications will heal wounds and reduce pain.
If a patient is diagnosed with stomach cancer, then treatment should only be surgical. The patient may be prescribed narcotic analgesic therapy, which will help relieve the patient of severe pain.
Stitching pain can also occur with methyl alcohol poisoning.
In this case, the patient’s stomach must be rinsed, after which he will be prescribed drugs that cleanse the body of toxins.
If a patient gets mercury into his stomach, he needs to urgently take an antidote. Treatment should only take place under the supervision of a doctor.
Elimination of stabbing pain should be carried out not only with medications prescribed by the doctor. The patient must adhere to certain rules to alleviate his condition.
The patient must:
- start following a diet - do not eat fried, spicy, sour, fatty foods, it is advisable not to include whole milk in your diet;
- You should eat food slowly and chew it thoroughly;
- portions for one meal should be small;
- it is important to eliminate stress;
- get rid of bad habits.
By following all the doctor’s recommendations, the patient will be able to quickly get rid of stabbing pain in the abdomen and cure the organ that brings discomfort.
After treatment, you should eat right. Even on holidays, the diet must be followed. Otherwise, the acute abdominal pain will return.
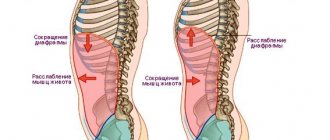
When the stomach hurts with cramps, this is a signal that there is a malfunction of the digestive organ. Contractions of the smooth gastric muscles are repeated at intervals from three minutes to several hours. In addition to pain, a disorder in the secretion of the gastrointestinal tract occurs. How does this happen and for what reasons? Let's talk about this in this article.
Nutrition
During treatment, you should adhere to special dietary restrictions:
- It is prohibited to include fried fish or meat in the diet.
- Do not eat foods that will lead to intense secretion of gastric juice.
- Avoid salty and sour foods.
- Do not eat cold or hot foods.
- Eat in doses, fractionally.
- Chew each piece thoroughly.
- Eat 3 hours before bedtime.
- Do not torment yourself with hunger and do not overeat.
- Fermented milk products perfectly restore the function. Milk can be taken with light tea. All dairy products should not be fatty.
- In general, the menu should not exceed the 3000 kcal level.
- When applying oil, you should take olive oil, as it heals all scratches from the inside.
- It is recommended to take teas and herbal infusions, drink more mineral waters, and also use folk recipes for pain.
During the treatment period, you should abstain from cigarettes, as they only interfere with healing.
Often, the course of drug treatment will last at least 2 weeks, everything will depend on what disease the person suffers from.