How to cure the disease
Before starting treatment, the doctor must determine the cause that led to the onset of the disease.
There are several types of therapy. The doctor chooses the most appropriate one depending on the severity of the disease and the severity of symptoms. Treatment is accompanied by the use of drugs that normalize the acidity of the stomach, as well as drugs that protect the mucous membrane.
If the cause of the disease is severe poisoning, the patient is prescribed gastric lavage and an enema. This will allow the effect of the irritating factor to be neutralized in the near future, which means the treatment will be faster and more successful.
The patient is recommended to rest in bed, even if treatment is carried out at home. This state will allow the patient to relax and calm down.
Traditional medicine is widely used to treat catarrhal gastroduodenitis. However, it should be remembered that these methods can be considered as auxiliary measures that complement the treatment prescribed by the doctor. Decoctions of herbs that relieve inflammation (coltsfoot, chamomile) help well. But they can be used if the symptoms of the disease are moderate. Otherwise, it is better to use traditional medications.
The rhythm of life of a modern person is so intense that many serious diseases appear against its background. Most often, the stomach suffers due to improper diet and bad habits. Among the main problems of the gastrointestinal tract are catarrhal gastroduodenitis.
Treatment with folk remedies
Congestive duodenopathy
Alternative medicine methods can help reduce unpleasant symptoms and restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract at home. Treatment of gastroduodenitis in adults with folk remedies helps to quickly cope with the disease and improve the quality of life. Natural products are used for this. The most commonly used agents are presented in Table 5.
Table 5. Folk remedies for the treatment of gastroduodenitis
| Herbal remedy | Properties |
| Linseed oil | Envelops the epithelium, promotes healing of the mucous membrane, eliminates constipation |
| Potato juice | Has a regenerating effect, reduces pain, creates a protective layer on the inner surface of the digestive tract |
| Carrot juice | The product is useful for atrophic gastritis, helps restore the epithelium |
| Chamomile, mint, elecampane flowers | They have an anti-inflammatory effect, eliminate swelling, soothe irritated mucous membranes, and reduce nausea |
| Sea buckthorn oil | Heals damaged epithelium, reduces swelling and inflammation |
Patients with gastroduodenitis should understand that, once diagnosed, the disease can be treated successfully in most cases.
It is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations to quickly get rid of unpleasant symptoms and prevent the development of unpleasant consequences of gastroduodenitis
Medical nutrition
Treatment of duodenitis of this form must necessarily include various types of products. At the same time, the patient's carbohydrate intake is limited. But the main emphasis is on proteins. There are several recommendations for the nutrition of a patient with catarrhal duodenitis.
- Doctors recommend that patients consume a lot of compotes and fruits or berries. You can also consume juices that contain large amounts of vitamin C.
- Chewing food thoroughly means protecting the stomach from unnecessary mechanical injuries. You need to eat in small portions (5-6 times), and the serving size should not exceed the volume of an average apple.
- The diet includes vegetable broths and soups from various cereals. When preparing first courses, be sure to include cream or milk in their recipe.
- It is not necessary to exclude meat and fish. These products are without a doubt important for a speedy recovery. The main condition is that they must be steamed. This way, excess fat will be removed from future dishes, and their structure will become softer, which will simplify the digestion process.
- For breakfast it is recommended to eat fermented milk products: sour cream, cottage cheese, milk, kefir and low-fat fermented baked milk. Fruit purees, baked apples and hard-boiled eggs are also great for breakfast.
- For a faster recovery, you need to give up sweets. Chocolate is especially dangerous. It is better to replace it with honey or sweetened fermented milk products.
- As for spices and salt, they must be removed from the diet completely. Spices can cause some damage to the stomach and provoke gastritis.
- Drinks include jelly, compotes, fresh juices and herbal teas.
According to doctors' forecasts, if you follow these rules, you can cope with the symptoms of catarrhal duodenitis within a week. But it is also worth knowing about products whose consumption is strictly prohibited:
- Canned food.
- Sausages and other smoked meat products.
- Fast food products: pies, hamburgers, belyashi and everything you can eat in fast food.
- Crackers, chips, snacks, instant noodles are foods that are generously seasoned and can irritate the stomach and duodenum.
- Coffee and strong tea should be removed from the menu for not one, but a couple of weeks. Afterwards, these drinks should be introduced into the diet gradually. The main thing again is not to overdo it with their use.
- Drinks that are too hot or cold. Hot food injures the mucous membrane, but cold food slows down the digestion process, leading to fermentation of undigested foods in the stomach. As a result - intestinal upset, bloating, belching, heartburn.
By adhering to these exceptions, you can eat calmly, forgetting about the possible danger to the gastrointestinal tract. The diet must be prescribed by the attending physician, along with drug treatment. These two components of excellent well-being are also often supplemented with some folk remedies for the treatment of duodenitis.
Basic rules of treatment
Erythematous gastropathy against the background of mucosal atrophy
Therapy for gastroduodenitis is always individual for each patient. The doctor takes into account the symptoms of the disease, the general condition of the patient, the severity of the pathology and the presence of concomitant diseases. The specialist determines what kind of treatment the patient needs to undergo, that is, he makes the choice of outpatient or inpatient therapy. Next, the doctor determines what regimen the patient should follow: ward, bed or semi-bed. Then dietary nutrition is prescribed and the necessary medications are prescribed.
Usually, all patients with severe pain, bleeding in the stomach or intestines, as well as in cases of erosive gastroduodenitis or in the presence of concomitant pathologies that are severe, are hospitalized. Exacerbation of the disease requires strict adherence to bed rest (from three to five days).
Medicines to normalize acidity
There are many factors that cause an imbalance in the acid balance in the stomach. In this case, the pH may be either increased or significantly decreased. Effective treatment can be prescribed only after determining the quantitative content of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
You can alleviate the condition with medications, for example, Gaviscon
Drugs that help normalize pH balance include:
- Antacids. These medications are used for superficial gastroduodenitis. They have enveloping and acid-neutralizing properties. These are Gaviscon, Omez, Phosphalugel, Omeprazole or Maalox. Doctors give preference to drugs that are not absorbed into the body, and the drugs do not negatively affect a person and do not cause side effects. These medications are available in various forms. These are suspensions and tablets, as well as powders, which allows each patient to choose a convenient option. The medicine is taken four times a day, each time an hour after meals. The last use of the medication should be before bedtime.
- Enzyme agents are prescribed for gastroduodenitis, which is accompanied by low acidity. These medications promote additional acid production, raising its level to normal. Among these medications, Betacid, Proserin or Calcium Gluconate are often used.
- M-anticholinergics. Drugs are used to reduce the secretion of gastric glands. Among the drugs in this group, there are both non-selective and selective drugs. The first of them, blocking cholinergic receptors, include Metacin and Atropine sulfate. Due to the non-selective effect, a large number of side effects occur. The use of selective drugs (Pirene, Pirenzepine, Gastrozem) reduces the release of acid and helps reduce the amount of pepsinogen released. The blood supply to the stomach and the motor activity of its walls improve.
In some cases, taking Omeprazole is indicated
- H2-histamine blockers. These are antisecretory medications. These drugs include Cimetidine, Famotidine, Ranitidine. Available in the form of solutions or powder for their preparation, as well as tablets. In terms of effectiveness, H2 blockers are inferior to proton pump inhibitors, but are used due to genetic characteristics or for cost-saving reasons.
- Proton pump inhibitors. They are used in the treatment of acid-dependent pathologies and are classified as antisecretory drugs. This is a modern group of medications, also used in the detection of Helicobacter pylori. One of the most commonly used drugs from this group is Omeprazole.
Antibiotics
When the disease develops due to bacteria (most often Helicobacter pylori), antibiotics are prescribed that can affect many microorganisms. Among them: Amoxicillin or Alpha Normix. Metronidazole is often used. Antibiotics reduce the risk of secondary infection by identified bacteria.
Enveloping drugs (cytoprotectors)
Enveloping medicines based on bismuth are quite popular. Among them are Bismofalk, Vikair, De-Nol. Bismuth promotes the formation of a protective coating on mucous membranes. The substance has an enveloping, astringent and slight antiseptic effect on the gastrointestinal tract. For the erosive form of gastroduodenitis, De-Nol is often prescribed. The medicine promotes effective healing of damaged mucosa.
De-Nol is a modern drug that will help protect the mucous membranes
Treatment of atrophic gastroduodenitis
The goal of treatment of atrophic gastroduodenitis is to prevent further development of intestinal metaplasia, destruction of the epithelium and its transformation into atypical cells (cancerous transformations). This goal can be achieved within 5 years of careful therapy.
A prerequisite for complete treatment is dietary nutrition. Food should be gentle in composition, temperature, and mechanical structure. After a short period of time, it is allowed to include low-concentrated lemon, cranberry, and cabbage juice in the diet. Bananas are the only acceptable fruit for this diet. Food should not be cold or hot, the diet should be frequent meals, small portions. Smoking and drinking alcohol in any dose are absolutely unacceptable during and after treatment.
Medicines for the treatment of atrophic gastroduodenitis:
- Antibiotics for eradication of the bacteria Helicobacter pylori;
- Proton pump inhibitors;
- Bismuth preparations;
- Glucocorticosteroids;
- Iron supplements;
- Vitamins;
- Enzymes;
- Mineral waters with high mineral content;
- Gastroprotectors;
- Antacids;
- Stimulators of cellular regeneration;
- Agents that stimulate peristalsis.
Additionally, physiotherapeutic treatment (electrophoresis, magnetotherapy, thermal procedures) and sanatorium treatment at a balneological resort are used.
Basic rules of complex treatment
Chronic diarrhea or when diarrhea does not stop
In the process of treating gastroduodenitis, the causative agent of which is the Helicobacter bacterium, first treatment is carried out with drugs such as Omeprazole and Phosphalugel. They are used in conjunction with Amoxicillin. The patient takes these medications for about seven days, then the doctor conducts a re-examination. In cases where the bacterium is still present in the patient, they say that there is no expected result from the treatment. In this case, a second line of therapy is performed. Medicines are replaced.
Remember that if you have any problems, you should first consult a doctor; you cannot take medications on your own
It is possible to prescribe De-Nol together with Alpha Normix and Metronidazole. Approximate treatment regimen: De-Nol three times a day, and antibiotics twice a day. Only a specialist can indicate the exact dosage. Therapy is carried out for up to two weeks until the patient is completely cured. We must not forget about maintaining proper dietary nutrition. Only with complex therapy can a quick recovery be achieved. The diet will allow you to quickly restore the affected mucous membrane. For a quick recovery, you must follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
The video contains information about the drug De-Nol and existing analogues:
Symptoms of the disease
Each type of gastroduodenitis has its own symptoms, which are manifested by both external and internal changes. Based on a comprehensive examination of the patient, a complete picture of the disease is established and treatment is prescribed. Let's consider the main symptoms based on the classification of gastroduodenitis.
• The chronic form of the disease is characterized by variable states of exacerbation and remission, that is, temporary improvement. Acute forms mainly occur seasonally, that is, in spring and autumn. This is due to many factors that provoke the disease at this time of year. In the presence of such a disease, a person constantly feels heaviness in the stomach, nausea, and drowsiness, which increase with exacerbation and often take on the character of antispasmodic pain.
Each type of gastroduodenitis has its own symptoms, which are manifested by both external and internal changes
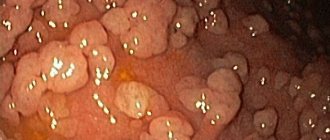
• Catarrhal gastroduodenitis can be considered a condition when the duodenum is also involved in the inflammatory process. Its symptoms, in particular, resemble those of acute gastroduodenitis, but a complete examination of the patient using an endoscope can determine a more accurate diagnosis, which is established on the basis of a complete picture of damage to the digestive organs.
• The initial stage of the disease can be called superficial gastroduodenitis, characterized by the onset of inflammation of the organs, which has not yet led to serious changes in their functionality. Its symptoms are less pronounced and more reminiscent of a common digestive disorder, but if these kinds of body prompts persist for a long time, you should definitely contact a gastroenterologist for timely treatment.
• The presence of erosive gastroduodenitis means a real threat to your life. It is worth understanding that the presence of such wounds on the flora of the stomach or duodenum is fraught with serious consequences and bleeding, which can significantly affect your health and cause death. Symptoms of this disease include blood in the vomit or in the stool, dizziness, weakness, elevated body temperature, frequent stomach pain, reminiscent of contractions, which mainly occur before lunch.
Based on a thorough diagnosis, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes treatment, which is not carried out on the basis of one “cure for all diseases”, but is prescribed comprehensively and taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the type of disease.
What it is
Atrophic duodenitis is a chronic inflammation in the small intestine or duodenum. Complicated form of catarrhal and erosive duodenitis. With prolonged inflammation, the deep tissues of the digestive organ are affected and the mucous membrane atrophies, the intestines begin to work worse, and discomfort appears.
It is recurrent in nature. Exacerbations begin due to external and internal factors: diseases of the digestive tract, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, stomach.
ethnoscience
For gastroduodenitis, traditional medicine has a good therapeutic effect.
Mint
Mint leaves (fresh or dry) are poured with hot water and infused in a thermos for 24 hours. The resulting infusion is taken before meals and after meals, 50 ml. Mint will have a disinfectant and soothing effect on the digestive system. It is impossible to increase the indicated dose and frequency of taking the drug, since in large quantities it can provoke the development of heart diseases.
Celandine
The plant is poured with alcohol and infused for two weeks. Alcohol tincture is taken a few drops per day. Every day the amount of medicine is gradually increased to 50 drops per day, then the countdown begins.
Linen
A tablespoon of crushed flax seed is poured with water and placed on low heat, brought to a boil and boiled for several minutes. The resulting product is taken in 50 g doses for a month.
Clinical picture, symptoms of atrophic duodenitis
Based on the predominant set of symptoms, the following variants of the disease can be distinguished.
- The neurovegetative variant is characterized by the appearance after eating of tremors of the limbs, palpitations, diarrhea, shortness of breath, sweating, and weakness. All of the above, as a rule, is associated with hormonal dysfunction of the duodenum and prevails in the female population.
- An ulcer-like variant accompanies acute duodenitis with erosions and ulcers of the duodenum. Not relevant for atrophic duodenitis.
- The more common type of duodenitis will be gastritis-like. In this form of the disease, the resulting pain is localized in the epigastrium (in the epigastric region) and the right hypochondrium, nausea and heaviness in the stomach, belching and other signs of impaired patency of the duodenum, flatulence and diarrhea, and weight loss in the patient are common.
- There are also frequent cases of duodenitis, similar in clinical picture to inflammation of the biliary tract and pancreas - cholecysto- and pancreatic-like. With them, symptoms of damage to the liver, biliary tract, and pancreas will come to the fore. These are bitterness in the mouth, hepatic colic, vomiting mixed with bile, nausea, pain in the liver or pancreas, flatulence, bloating, alternation of various defecation disorders, yellowness of the skin and discoloration of stool. All the symptoms here are associated with the reflux of food into the bile ducts, disruption of the outflow of juices and bile, and spasm of the sphincter of Oddi.
- When duodenitis and enteritis are combined, intestinal symptoms will have an advantage, i.e. dyspepsia, stool disorders and duodenostasis (bloating and pain in the right hypochondrium, gas retention).
From the above it follows that the clinical picture of atrophic duodenitis is nonspecific and has many manifestations, often under the guise of other diseases. Therefore, mixed and latent forms of the disease are also distinguished, when it is impossible to identify a specific set of symptoms or the clinical picture is extremely poor.
Acute duodenitis
Acute duodenitis usually occurs in combination with acute inflammation of the stomach and intestines as acute gastroenteritis, gastroenterocolitis. There are:
- catarrhal acute duodenitis;
- erosive-ulcerative acute duodenitis;
- phlegmonous acute duodenitis.
Etiology, pathogenesis
Acute duodenitis occurs as a result of exposure to the following factors on the body: food toxic infections, poisoning with toxic substances that have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, excessive intake of very spicy food, usually in combination with a large amount of strong alcoholic drinks, damage to the mucous membrane of the duodenum by foreign bodies.
Symptoms, course
Acute duodenitis is characterized by pain in the epigastric region, nausea, vomiting, general weakness, pain on palpation in the epigastric region, weakness, and fever. The diagnosis is confirmed by duodenofibroscopy, which detects inflammatory changes in the duodenal mucosa. With a very rare phlegmonous duodenitis, the patient’s general condition sharply worsens, tension of the abdominal wall muscles in the epigastric region, a positive Shchetkin-Blumberg sign, fever, neutrophilic leukocytosis, and increased ESR are determined.
Acute catarrhal and erosive-ulcerative duodenitis usually ends with self-healing in a few days; with repeated duodenitis, a transition to a chronic form is possible. Possible complications: intestinal bleeding, perforation of the intestinal wall, development of acute pancreatitis.
Treatment
For acute catarrhal and erosive-ulcerative duodenitis, 1-2 days of fasting, bed rest, and gastric lavage are indicated. In the following days - diet No. 1, astringents and enveloping agents inside, for pain - antispasmodic and anticholinergic drugs. For phlegmonous duodenitis, treatment is surgical in combination with antibiotic therapy.
Peculiarities
Catarrhal duodenitis is presented in two forms: acute and chronic. It is in the nature of superficial damage. The peculiarity of the disease is that the inflammation is localized on the surface at the junction of the duodenum and the catarrhal opening of the stomach. It is not pathological in nature and does not lead to structural changes in tissue or swelling.
Chronic duodenitis leads to the development of pathologies. This form is characterized by the presence of mucosal degeneration. Dystrophy of the walls of the organ becomes the result of long-term negative effects of microorganisms.
The result of catarrhal duodenitis is thickening of the affected walls. Wrinkles form. The acute form of the disease can be easily and effectively treated. The cause of the development of this form of the disease is Helicobacter. Helicobacter pylori resists the acidic environment of the digestive system. The danger lies in the aggressive effect on the mucous membranes. The bacteria destroys it. The result of the activity is an inflammatory process.
Symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the course of the disease. Acute gastroduodenitis is characterized by pronounced symptoms. The first symptoms appear 10-12 hours after the action of the irritating factor. Sometimes the disease develops within 1-2 hours.
The following symptoms appear:
- pain in the stomach and intestines;
- nausea turning into vomiting; bile is present in the vomit;
- feeling of heaviness and fullness;
- belching rotten food, bitter taste in the mouth;
- weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- headache and dizziness;
- loss of appetite;
- white coating on the tongue;
- rash on lips.
The attack lasts 1-2 days. With normalization of nutrition and taking medications, it quickly stops. Without treatment, after a couple of days, gastroduodenitis becomes chronic. It is characterized by severe vomiting. Cleansing the stomach does not bring relief to the patient. Constipation or diarrhea, heartburn, and bloating appear.
Chronic catarrhal gastroduodenitis is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission. An attack can occur even with the slightest errors in nutrition.
It is necessary to contact a gastroenterologist.
Diagnostics
The doctor studies the person’s medical history and listens to his complaints. The diagnosis is made on the basis of laboratory and instrumental methods, which include:
- clinical and biochemical blood test;
- stool blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- bacteriological examination of vomit;
- intragastric pH-metry to determine the acidity of gastric juice;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy - endoscopic examination to assess the condition of the gastric mucosa;
- radiography using a contrast agent;
- electrogastrography - a technique for assessing the peristalsis of the stomach and intestines;
- multislice computed tomography;
- biopsy.
What happens with atrophic gastroduodenitis
The disease is a mixed inflammatory process involving the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. Often, gastroduodenitis progresses against the background of sluggish gastritis, which is not treated. As a result, the glands that produce gastric juice wear out, stop functioning, and then atrophy.
The mucous membranes lose their protective abilities, so favorable conditions are created for the proliferation of infections and the growth of malignant tumors. Inflammatory disease leads to slow digestive processes and poor absorption of nutrients.
Over time, the pathological process spreads to the intestines and chronic atrophic gastroduodenitis develops. In the absence of timely treatment of gastroduodenitis, it will spread to internal organs located nearby.
Treatment
A patient with an acute attack of catarrhal gastroduodenitis should be treated in the gastroenterology department
An important component of therapy is diet. The first days of illness, fasting is indicated, but drinking plenty of fluids should be done.
After the symptoms have eased, you can eat pureed and steamed foods.
It is necessary to avoid animal fats, tea, coffee and carbonated drinks. You should not eat spicy, fried or fatty foods. Products must be fresh and healthy. It is necessary to drink still water from Borjomi or Essentuki.
The patient should follow diet No. 5 and bed rest
Along with dietary nutrition, it is important to undergo drug treatment, which includes:
- antibiotics (for bacterial infection);
- enzyme preparations – Festal;
- adsorbents (in case of poisoning) – Smecta or activated carbon;
- drugs to reduce the synthesis of hydrochloric acid - Kvamatel or Omeprazole;
- products that soothe irritated mucous membranes - Maalox;
- probiotics.
If you experience severe pain, you cannot do without antispasmodics and analgesics. To prevent dehydration in case of profuse vomiting, saline solution is administered intravenously. The course of treatment is 7-10 days, already on the 3-4th day of therapy the patient’s condition should improve significantly.
Prevention
Preventive measures are as follows:
- eat right, follow a routine, eat only high-quality and healthy food;
- do not overeat or starve, eat often, but in small portions;
- stop drinking alcohol;
- treat gastrointestinal diseases in a timely manner and prevent exacerbations of chronic diseases;
- take medications only after consulting a doctor.
If a patient is diagnosed with catarrhal gastroduodenitis, then he must follow the above preventive measures in order to prevent the development of complications.
The prognosis for recovery is favorable with timely diagnosis and treatment. The patient can get rid of catarrhal gastroduodenitis, but to prevent relapses of the disease, he needs to change his lifestyle and review his diet.
Erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis
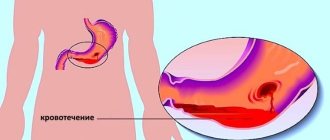
Due to its persistent and long-lasting course, erosive gastritis often results in complications. One of them is gastric bleeding from eroded mucosa. Such gastritis is called erosive-hemorrhagic. The mechanism of their development is related to the size, depth and localization of erosions. Superficially located defects in the area of the anterior, posterior walls and fundus of the stomach bleed extremely rarely. The most dangerous in this regard are extensive and multiple erosions that extend to great depths. Their most dangerous localization is the area of lesser curvature due to the location of large vessels in this area and the high intensity of the general blood flow.
For the transition of erosive gastritis to erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis, erosions must reach the depth of the vascular bed. Each person's small vessels have different characteristics of their branching, structure and level of pressure in them. Therefore, individuals with the same diagnosis have different degrees of risk of developing erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis. To a greater extent, these are patients with any form of arterial hypertension and diseases of the blood coagulation system. The risk group also includes patients taking anticoagulant drugs (aspirin and its analogues, warfarin, heparin), non-steroidal painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ibuprofen).
The symptoms of the transition from erosive gastritis to erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis are quite clear. All of them indicate the presence of gastric bleeding of varying severity.
These signs include:
Reducing the intensity of pain. This sign is more pronounced the more intense the bleeding. This phenomenon is due to the fact that erosion destroys sensitive receptors behind which the vessels are located. Therefore, first the pain decreases, then bleeding occurs;
Vomiting is an obligatory sign of erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis. Its nature depends on the intensity of bleeding, the diameter and number of bleeding vessels. If the vomit contains bloody contents, this indicates active ongoing bleeding. The presence of brown contents in the vomit is evidence of blood leaking from the vessels into the stomach cavity or slight bleeding;
Symptoms of anemia are a decrease in the amount of blood in the vascular space. Their severity depends on the amount of blood loss: pale skin, dizziness, decreased blood pressure, increased heart rate;
Dark colored stool. Sometimes erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis is accompanied by so little bleeding that vomiting does not occur. But, destroyed by acid, blood elements entering the intestines cause the dark color of the stool.
Treatment
With inflammation of the upper digestive tract, the patient requires comprehensive care.
How to treat duodenitis of the duodenum?
After a thorough analysis of the patient’s data, the specialist develops an individual treatment plan, which includes the following areas:
- Treatment with medications - antibiotics, drugs that eliminate symptoms and affect the pathogenetic mechanisms of the disease.
- Diet during periods of exacerbation and remission.
- Physiotherapy, exercise therapy.
- Treatment with folk remedies.
Drug treatment
The main direction of assistance for inflammatory processes is the use of medications. Drug treatment of duodenitis is prescribed based on objective examination data and additional research methods. Options for remedies depend on the patient’s complaints, the severity and stage of the process, and the presence of concomitant conditions.
Etiological treatment is required if the causative agent of the disease is confirmed by laboratory methods. When nonspecific bacterial flora is detected, antibacterial agents are used according to the obtained sensitivity to the group of drugs. If Helicobacter pylori is diagnosed, an eradication regimen is used. It includes antibiotics, antiprotozoal agents, proton pump blockers and bismuth subcitrate compounds.
Additionally, symptomatic and pathogenetic therapy is prescribed, which are represented by the following groups:
- Antispasmodics - eliminate spasm of smooth muscle cells and pain.
- Antacids - coat the inner surface of the mucous membrane, reduce irritation and inflammation.
- H2-histamine blockers - reduce acidity in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
- Alginates - form a film on the surface of the digestive tract, preventing the aggressive effects of digestive juices.
For concomitant diseases of the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder, enzymes, choleretics, and sedatives are recommended.
Important!
In cases of severe duodenitis, infusion therapy is used to improve microcirculation and rehydration (replenish lost fluid).
Folk remedies
When unpleasant symptoms appear, not only pills help. Along with the traditional approach, experts can recommend treatment of duodenitis with folk remedies. Preparations made from natural raw materials reduce the inflammatory process and promote tissue restoration. At home, you can prepare infusions and decoctions based on:
- caraway fruit;
- chamomile;
- fireweed leaves;
- honey;
- yarrow;
- dill seeds;
- horseradish root;
- aloe juice;
- flax seeds;
- oatmeal;
- lavender;
- shepherd's purse;
- cinquefoil;
- sea buckthorn oil.
Diet
If the doctor suspects inflammation of the duodenum, the first thing the patient is recommended is a therapeutic diet. Before the examination, menu 1a is prescribed, which is prescribed during an exacerbation. You can eat pureed soups and cereals, mashed potatoes with water, chopped or paste-like lean meat, dried bread, jelly, decoctions of sweet fruits, and tea. When duodenitis is established, you should not eat food that irritates the gastrointestinal mucosa. Prohibited foods include fried, fatty, spicy, pickled foods, juices, strong coffee, alcohol, and yeast baked goods.
As the condition improves, the diet is expanded, adding new foods. Go to tables 1, 1b. If atrophic changes in the epithelium with a low level of acidity occur, table 2 is prescribed. During the period of remission, they move to table 5.
Causes
In addition to the specified microorganism, the reasons are:
- Daily abuse of strong coffee drinks.
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Poisoning from low-quality products.
- Constant consumption of fatty and fried foods.
- Poisoning by toxins of any organ of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Mechanical injury, intentionally or not, to the mucous membrane of the duodenum as a result of the entry of a foreign body.
- Undiagnosed and neglected condition of gastritis or pancreatitis.
Any of the above reasons can cause the onset of an inflammatory process in the duodenum. The bacterium can infect the mucous membrane of the duodenum even in childhood. Signs of the disease can appear only in the presence of provoking factors. When they are combined, the occurrence of catarrhal duodenitis becomes natural.