Screening studies for colorectal cancer
Screening studies are diagnostic measures that are carried out in patients without symptoms of colon cancer. All these studies are divided into two types:
- Tests that can detect colorectal cancer and polyps. These methods assess the structure of the colon. For this purpose, endoscopic equipment or fluoroscopy is used. If a polyp is identified, it can be removed before it develops into cancer.
- Tests that are primarily designed to detect cancer. These methods are aimed at examining stool for signs of a malignant tumor in the intestine. These methods do not detect polyps.
How does the procedure work?
Sigmoidoscopy is not a complex procedure. It takes about 15 minutes and does not cause pain in the patient; it is performed without anesthesia. However, if necessary, anesthesia may be used.
The patient lies on his left side, and the doctor performs a digital rectal examination of the rectum. Men undergo, among other things, a thorough examination of the prostate to detect the presence of cancer. Then a sigmoidoscope is inserted into the anal canal and gradually advanced to a depth of 30–60 cm. Sometimes the patient experiences discomfort during the procedure - in such cases, only 30 cm of the intestine is examined.
In cases where small polyps are found in the area under study, the doctor performs a biopsy of the formations for further histological examination of the obtained material. If there is a large polyp, a colonoscopy is prescribed to remove it.
After completion of the procedure, minor bleeding may be observed, which passes fairly quickly. There are no restrictions on diet or other habits after the examination, so the patient can immediately return to their normal lifestyle.
Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic examination that allows you to evaluate the inner surface of the rectum and sigmoid colon, the condition of their mucosa and identify the various presence of both polyps and malignant tumors, as well as perform a biopsy. In addition, this method allows you to identify other reasons for the presence of blood in the stool. A sigmoidoscope is used to perform sigmoidoscopy. It is a flexible probe with a light bulb and a camera lens at the end. The doctor can see the surface of the intestine with his own eyes. The length of the sigmoidoscope is approximately 60 cm, so the doctor can examine only the rectum and sigmoid colon.
Before performing a sigmoidoscopy, a cleansing enema is required. In addition, your doctor may prescribe a special diet for you to make it easier to prepare for the examination. Sigmoidoscopy takes on average 10-20 minutes. The procedure is painless and does not require anesthesia. The patient lies on a special table, on his left side, with his knees tucked to his chest. The sigmoidoscope is lubricated and then slowly inserted into the rectum. During the examination, the patient may feel some discomfort associated with the intestines distending with air.
Details
Sigmoidoscopy is performed by a proctologist and takes 15-20 minutes. Examination with a sigmoidoscope is usually painless and is therefore performed without anesthesia. The patient is examined on the left side, if he is a man, and the prostate is examined at the same time. Before inserting the device into the anus, the rectum is palpated using the finger method.
The tube of the device is slowly inserted into the anal canal and carefully passed into the depths of the intestine 30-60 cm. If polyps are detected in this area during sigmoidoscopy, a biopsy of the tumors is immediately performed. During the examination, the doctor examines the mucous membranes of the intestines.
Among the unpleasant aspects of sigmoidoscopy is minor discomfort associated with the advancement of the endoscope tube during the examination. Sometimes some bleeding may occur after the examination.
Reviews from doctors and statistical data confirm the reliability of sigmoidoscopy: 90% of all pathologies of the colon and sigmoid colon are detected by this method.
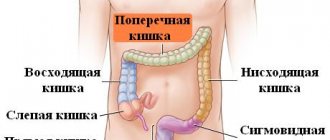
Colonoscopy is prescribed when it is necessary to study the entire large intestine, which has a length of 120-150 cm. Such capabilities are available in a colonoscope - a special device that is similar in principle to a sigmoidoscope, but has a longer fiber optic cable.
Advancement of the endoscope during sigmoidoscopy is accompanied by the supply of air into the lumen of the intestine, which by the time of the examination should be completely free of feces. This explains the difference in preparation: cleansing before colonoscopy should be more thorough. The duration of the procedure is often determined by anatomical features, the presence of physiological bends and adhesions. In some cases, colonoscopy is performed under general anesthesia.
Sigmoidoscopy procedure
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is similar in principle to sigmoidoscopy, the only difference being that it allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the entire large intestine, and not just its final sections. Colonoscopy is the same endoscopic examination. A colonoscope is used for this. This is a thin probe with a light bulb and a video camera at the end. The colonoscope also allows you to biopsy suspicious areas of the intestinal mucosa. Colonoscopy is performed, like sigmoidoscopy, with the patient positioned on the left side, with the legs tucked to the chest. Before inserting it into the patient's rectum, it is lubricated. Colonoscopy makes it possible to visually assess the condition of the entire large intestine, since the length of the colonoscope is 120–152 cm. During colonoscopy, as with sigmoidoscopy, a feeling of discomfort is possible. Colonoscopy also allows for a biopsy if a polyp or tumor is found.
Preparing for a colonoscopy
Careful bowel preparation is very important for colonoscopy. The study itself is usually carried out in the first half of the day. If necessary, the study can be performed in the evening. Before a colonoscopy, you need to switch to a slag-free diet 3-4 days before. On the eve of the study, the patient should not have dinner. In addition, two enemas are performed on the eve of the study at 20.00 and 22.00. On the day of the study, two enemas are also performed at 07.00 and 08.30.
Preparation for the procedure
Nutrition
Before the procedure, the patient must adjust his diet. A few days before the test you should stop using:
- flour and confectionery products;
- meat;
- legumes;
- alcohol and sweet soda.
It is recommended to create a daily menu of liquid vegetable soups and water porridges. You can eat vegetables and fruits, but in moderation.
You cannot eat directly on the day of the procedure; you can only drink water or juices.
Cleansing procedures
In the evening before the study, it is necessary to perform a standard cleansing enema, which must be repeated the next morning. To cleanse the intestines, you can use a special drug – Fortrans (see more details here). It is available in paper bags containing 64 grams of active ingredient. Each sachet must be diluted in 1 liter of water.
The dosage of the drug is 1 liter per 15-20 kg of body weight, so usually for a single use it is necessary to dilute 3-4 liters. The laxative can be used at one time, in the evening - drink 1 liter per hour. Another method of administration is fractional, 2 liters in the evening and 2 liters in the morning before the procedure. It is important to stop using the solution 4 hours before the test.
Cleaning with Fortrans is considered more convenient for the patient than classic enemas. However, the use of laxatives has a number of limitations. It is not recommended for use by elderly people, weakened patients, or patients with heart pathologies. It is strictly prohibited to administer the solution if any form of intestinal obstruction is suspected.
Irrigoscopy with double contrast barium suspension
Irrigoscopy is a method of X-ray examination of the large intestine using a radiopaque substance - a suspension of barium sulfate, which is administered through the rectum. This is a completely painless procedure, it is non-traumatic and involves a lower radiation dose compared to computed tomography. Therefore, if there is a need for an X-ray examination of the large intestine, this technique is used. Irrigoscopy is indicated for bleeding from the rectum, intestinal discharge, pain in the anus, chronic constipation or diarrhea. It is also used to detect polyps and colon and rectal cancer. Preparation for irrigoscopy is the same as for other intestinal examinations.
The contrast agent for irrigoscopy - barium sulfate - is heated to 33 - 35 degrees. Carrying out irrigoscopy usually requires the use of not an enema, but a special device for intestinal lavage. The jar of the device is filled with contrast, and then the substance is pumped into the intestine with a bulb.
X-rays are taken as the intestinal lumen fills with a suspension of barium sulfate. After filling, a survey of the abdominal cavity is taken. The rectal tube is then removed and the patient goes to the toilet to have a bowel movement.
After the barium suspension has been released, another survey of the abdominal cavity is performed to visualize the intestinal mucosa and assess its evacuation function.
Irrigoscopy with double contrast is performed immediately after the end of the barium study.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy examines the intestinal mucosa
Author Alexandra Balan-Senchuk
22.09.2019 15:03
Health
Flexible sigmoidoscopy is a medical technique that allows visualization of the intestinal mucosa, particularly the rectum and part of the colon (up to approximately 60 cm). This is done using a sigmoidoscope, which is a flexible tube with a camera at the end.
Indications for flexible sigmoidoscopy
There are several reasons why this procedure may be recommended. Patients with bowel signs and symptoms such as bleeding, abdominal pain, changes in bowel behavior and/or weight loss are the main reasons for evaluation. The procedure helps to study and confirm or refute intestinal pathologies that may be associated with these symptoms.
GS can also be used to detect colon cancer.
One limitation of the procedure is that it does not visualize the entire colon, and cancer that is outside the area may not be detected. Other imaging techniques, such as colonoscopy, are the preferred screening method in these cases because the entire colon can be examined. The advantage of HS is that the procedure usually requires less time to prepare and perform.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy procedure
The entire procedure takes approximately half an hour, and the patient usually does not require anesthesia. The sphincter may be lubricated with gel to allow easy insertion of the sigmoidoscope into the anus and then slowly guided through the rectum into the sigmoid colon. As the sigmoidoscope is inserted, it inflates the colon with air to optimize visualization of the colon. The resulting images are sent to the computer screen in real time.
The target is gradually advanced until it reaches the transverse colon, and then the abstinence process also slowly decreases as the exploration of the colon continues. If any areas of the intestinal wall appear suspicious, a biopsy is taken for further analysis.
Virtual colonoscopy
This is a type of CT scan that was developed to replace endoscopy. The essence of virtual colonoscopy is to conduct a CT scan of the large intestine. In this case, unlike colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy, there is no need to insert a long probe into the patient.
The indication for virtual colonoscopy is to screen for polyps and other tumors in the colon at an early stage in order to remove them before they become malignant.
Preparing for a virtual colonoscopy
Virtual colonoscopy also requires bowel preparation. For this purpose, cleansing enemas are performed, or laxatives are prescribed. On the eve of the study, a slag-free diet is prescribed. Pregnant patients should notify the doctor performing the virtual colonoscopy before taking laxatives.
A virtual colonoscopy is performed like a regular abdominal tomography, except that air is introduced into the patient's rectum through a special tube to improve image quality and straighten the colon.
During the procedure, the patient is sometimes asked to hold his breath. First, the patient lies on his stomach, then he needs to roll over onto his back, sometimes vice versa. A virtual colonoscopy takes about 15 minutes. The entire procedure is painless, but there may be some slight discomfort from distending the rectum with air.
Differences from other types of procedures
There are differences between sigmoidoscopy and other procedures. The appointment of each procedure is carried out after examination and medical history by a doctor. Each requires clinical indications.
Unlike colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy provides a view of only 60 cm of the colon. Colonoscopy makes it possible to view the entire colon, take tissue from it for examination, and immediately remove a polyp if present, but it is more difficult for patients to tolerate. The use of local anesthetics is required.
The main difference from irrigoscopy is the presence of an X-ray image of the colon. This is not the case with sigmoidoscopy.
Sigmoidoscopy does not provide the necessary information about the condition of the intestinal walls. The main subject of her study is the condition of the rectum. Preparation for the procedure is not so thorough, it takes a minimum amount of time - from 10 minutes.
Endoscopic examination of the large intestine makes it possible to prevent serious consequences of the disease, identify cancerous tumors in time and treat them.
Fecal occult blood test
The essence of this research method is to identify “hidden” blood in the stool, which is not visible during microscopic examination. The presence of hidden blood in the stool indicates the presence of bleeding from any part of the gastrointestinal tract.
A fecal occult blood test is indicated if there is a suspicion of bleeding from any part of the gastrointestinal tract, which can occur, for example, with bleeding polyps or colon cancer.
Preparing for analysis
Typically, medications (especially bismuth and iron preparations) should be discontinued a week before a stool occult blood test. In addition, it is not recommended to perform enemas, and at least 2 days should pass after X-ray examinations of the stomach and intestines. Before performing a stool occult blood test, meat, liver, and all foods containing iron should be excluded from the diet.
Indications for rectosigmoidoscopy
Diseases of the large intestine are a common pathology, so videorectosigmoscopy is widely used in the following pathological conditions:
- persistent disturbances in bowel function in the form of alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- the presence of mucous or purulent impurities in the stool;
- discharge of blood during defecation or during pushing;
- suspicion of hemorrhoids or already diagnosed pathology to determine the stage of the disease;
- causeless loss of body weight;
- discomfort in the intestines in the form of incomplete emptying after defecation;
- the presence of anemia, low hemoglobin and weakness without obvious reasons;
- determination of a tumor formation along the intestine upon palpation of the abdomen;
- frequent and persistent constipation that cannot be corrected with diet and medications;
- positive stool occult blood test;
- the presence of polyps that must be removed.
The appointment for examination of the large intestine is based on the patient’s complaints, objective and laboratory data. The procedure for examining the rectum and sigmoid colon does not present any particular difficulties compared to colonoscopy, that is, a complete examination of the large intestine.
Preparing the patient for sigmoidoscopy.
This technique gives the doctor the opportunity to examine the patient’s intestines from the inside and accurately diagnose the disease - this is necessary for drawing up the most effective treatment plan.
For the examination to be successful, the intestines should be completely free of feces. To do this, the patient is recommended to start following a slag-free diet two days before the sigmoidoscopy:
- refuse: baked goods, potatoes, mushrooms;
- consume in moderation: vegetables, fruits, berries;
- recommended: liquid soups, porridges, boiled meat, fermented milk products (with the exception of cottage cheese).
On the eve of the examination (preferably late in the evening), the patient should undergo a cleansing enema. It is then repeated immediately before the procedure (2-3 hours).
You can drink water or apple juice before having a sigmoidoscopy. Any food and dairy products must be completely abandoned.
Preparing for sigmoidoscopy
To get the most accurate results, before the procedure you need to clear the intestines of feces and gases. To do this you should:
- Two days before the test, avoid bread and baked goods, berries, fruits, sauerkraut, carbonated drinks and legumes, which cause gas formation. Light foods, low-fat soups and other foods that do not emit large amounts of gases are allowed.
- The last meal should be at 12:00 the day before the procedure. After this, you cannot eat food. You can drink water in unlimited quantities.
- Before the examination, a cleansing enema is done in the evening and in the morning. You can prepare the intestines using a drug like Fortrans.