Causes of pathology
Obviously, the trigger for any blood loss is a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane of the lower intestine (colon and rectum). This is a very serious pathology, regardless of the underlying cause, since it can result in the development of anemia with severe, sometimes fatal, consequences.
The presence of blood in the stool is a reason to immediately consult a doctor, so as not to aggravate the situation, but to prevent massive blood loss by establishing the cause of the pathology.
The most common reasons for bleeding from the butt are:
- hemorrhoidal disease with nodes of different localization (discharge during defecation is scarlet and does not mix with stool);
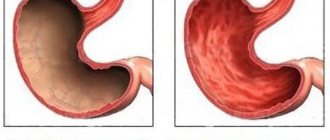
- inflammation of the large intestine - colitis with erosive phenomena;
- fissure of the anus - blood is released in portions during bowel movements, against the background of pain, accompanied by a burning sensation immediately after defecation;
- blood from the anus appears with constipation, polyps, rectum cancer;
- Gastritis can cause heavy bleeding (profuse blood, but the stool is formed, without pathological inclusions);
- with proctitis, bloody discharge comes with mucus, mixed with feces, a similar picture is given by diverticulosis;
- an ulcer of the stomach and duodenum is accompanied by profuse bleeding, which turns the stool a tar color and is visualized in the vomit;
- HIV, due to reduced immunity, provokes an exacerbation of many pathologies, which are accompanied by bloody discharge from the anus;
- varicose veins of the esophagus - a trigger for bleeding from the anus;
- The cause of bleeding from the rectum may be taking medications or systemic pathologies.
In any case, the causes require differentiation so that adequate therapy can be prescribed.
The main causes of rectal bleeding in men and women do not differ by gender, but have some characteristics.
Among women
Blood from the anus (anus) in women requires differentiation of anal and vaginal discharge. To do this, you need to inspect the toilet paper and see if there are any blood streaks in the stool. Regular panty liners can serve as a marker.
Pathology in women may occur due to:
- infections;
- pathological changes in the digestive system;
- pathologies of the circulatory system;
- injuries
This phenomenon can become dangerous if you cannot stop the bleeding on your own, and it increases in strength, volume, becomes painful, and appears:
- nausea, turning into vomiting, sometimes uncontrollable, mixed with blood;
- bruises on the body without injury to the area of the bruise;
- nasal hemorrhages.
The general condition worsens, signs of prodrome appear: low-grade fever, pain in the lower abdomen, pain is sometimes very strong, dagger-shaped.
It should be emphasized that the reason why blood comes from the anus in women can be anal sex. In this case, the bleeding is minor and goes away within minutes after coitus. Anal bleeding is a sign of early pregnancy.
In men
Rectal bleeding is more common in men than in women. The reason is that in men, more cellular space is anatomically concentrated in the pelvic area, which in women is occupied by the uterus and vagina. Because the male pelvic organs are not able to contract like the uterus, men's discharge is less abundant. Pain occurs only due to inflammation.
A peculiarity of male anal discharge is its development against the background of alcoholism, which disrupts the functions of the central nervous system and the digestive system and provokes pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract.
The nature and color of blood traces
Black blood on paper after using the toilet is an alarming symptom. You should consult a doctor immediately. This clinical picture may indicate an exacerbation of gastric ulcer. Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages can also cause discharge. To accurately determine the provoking factor, it is necessary to be examined by a specialist.
Traces of blood on toilet paper are not always accompanied by pain.
After defecation, scarlet blood on paper is cause for concern. Diseases characterized by scarlet bleeding:
Read also
How is a colonoscopy performed?
- Haemorrhoids. Most often, after stool, blood on paper or underwear indicates the presence of hemorrhoids. During the passage of dense feces, the nodes are injured.
- Malignant neoplasms. Discharge does not always appear after bowel movements. They can be found later on underwear.
- Rectocele, advanced stage of hemorrhoids. You may find scarlet drops or mucous discharge on your underwear. If there was no provoking factor (for example, heavy lifting), then there may be a tumor in the rectum. Clinical tests are prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
- Rectal fissure. Traces of blood found on men's toilet paper may be a sign of pathology. It is often caused by constipation. Anal sex can also cause it. Cracks can heal on their own, or you can speed up the process with the help of ointments and lotions.
- Diverticulitis. Blood on paper after bowel movements in men may be a symptom of this disease. It is characterized by: elevated temperature, pain in the left abdomen, vomiting, difficult bowel movements.
The doctor will determine which disease caused the scarlet discharge after receiving the results of clinical studies.
Classification of bleeding according to blood color
Based on the shade of blood that is released from the anus, one can suspect the cause of the pathology:
- cherry - the colon is affected;
- red – indicates the formation of a tumor or polyp;
- scarlet - indicates a fissure, hemorrhoids or intestinal injury;
- dark clots - warn of a diverticulum or colon tumor;
- black (tarry) - indicate pathology of the stomach, duodenum, and initial parts of the intestine.
The color of bloody discharge is a valuable diagnostic sign.
When do you urgently need a doctor and who to contact?
Blood from the rectum in men and women is always a reason for consultation with a proctologist, general practitioner, gastroenterologist or infectious disease specialist. At the same time, the presence of pain is absolutely optional. Rectal discharge without pain can indicate a variety of diseases, from a harmless fissure to cancer or leukemia.
And yet, there are a number of manifestations that require emergency intervention from a specialist. Calling an ambulance is required when:
- a combination of bleeding with high fever and symptoms of peritoneal irritation (pain in the abdominal area);
- a sharp deterioration in the patient’s well-being;
- the appearance of subcutaneous hematomas, nosebleeds in combination with rectal bleeding;
- prolonged bleeding with clots and without signs of stopping;
- admixtures of bloody discharge in vomit.
All of the above symptoms are signs of danger to human health; they pose a threat to life. Self-treatment or visiting a doctor in a clinic under such circumstances is simply unacceptable.
Before the doctor arrives, you must:
- provide the patient with complete rest by placing him comfortably on his back;
- You can’t drink or eat;
- cold on the stomach - indicated (a heating pad with ice), can be changed every quarter of an hour;
- If available, it is very good to give the patient a spoonful of 10% calcium chloride.
In case of severe hemorrhages, you should not give an enema, wash out the stomach, and in case of fainting, revive the patient with ammonia. The only thing you can do is monitor your heart rate and breathing.
Blood during defecation without pain is not a reason to calm down. If the patient has had stool, you need to examine the stool in order to understand the location of the source of bleeding by color (the upper sections will give a dark brown or black color). Scarlet discharge from the anus - most often speaks of injury to the intestinal mucosa or polyp.
The urgent hospitalization suggested by doctors cannot be refused, since delay in stopping the bleeding can be fatal. The clinic uses the most modern examination methods for examination:
- sigmoidoscopy;
- colonoscopy;
- irrigoscopy;
- FGDS;
- laparoscopic techniques.
It’s paradoxical, but true: the smaller the portion of blood released, the more dangerous the prognosis. This does not apply only to bowel cancer or infectious processes. Hemorrhoids, anal fissures, polyposis in advanced cases lead to anemia, the need for emergency surgical intervention, create a risk of malignancy,
Diseases that cause anal bleeding
There are enough pathological conditions that can cause hemorrhagic discharge from the anus. All of them are associated with a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract at different levels. But their main danger is the development of iron deficiency anemia, which can provoke severe metabolic disorders, hypoxia of the heart and brain, resulting in a heart attack or stroke.
Anal fissure
Anorectal fissures are directly related to dysfunction of the digestive tract: dyspepsia, constipation, the formation of fecal stones, which injure the surface of the inner lining of the intestine. The main symptom is blood in the stool. In second place is pain during bowel movements. A carefully collected anamnesis, visual examination of the anus, and, if possible, digital and rectal examination of the rectum, which allows one to detect a fissure, helps to make the correct diagnosis.
Treatment is complex based on normalization of bowel movements. To treat pathological manifestations, anti-inflammatory, analgesic drugs, and regenerants are used. Diet is the second mandatory aspect of treating pathology. The third is regular hygienic treatment of the anus and nearby tissues. Without such a tirade, any set of therapeutic measures will be temporary. Even with full compliance with the recommended algorithm, relapses are inevitable due to intestinal dysfunction.
If the cause of the crack was an injury, the situation is easier: it is possible to get rid of the pathology with the help of hygiene of the rectal area, regenerants and antiseptics.
Polyposis of the colon
A polyp is a benign tumor of various sizes, the main feature is the presence of a stalk, which is injured when a bolus of food, feces or stones passes through the intestines. The danger of polyps lies in their latent course. Dyspepsia rarely appears: constipation or diarrhea that disrupts peristalsis. The patient simply does not pay attention to minor troubles, which in a very short period of time can degenerate into cancer.
The surface of polyps, as a rule, bleeds, which explains the situation when blood comes from the butt. Moreover, the larger the size of the polypous neoplasm, the more easily its surface is damaged.
Haemorrhoids
Hemorrhoidal disease occurs most often in the age category from 45 to 50 years or during pregnancy, after childbirth. It is based on a hormonal imbalance of various properties, which provokes a violation of the elasticity of blood vessels. In combination with high blood pressure due to age or purely mechanical compression of blood vessels by the growing uterus, arterial-venous blood flow is disrupted, congestion occurs, including in the pelvic organs, and hemorrhoids form.
Varicose veins of hemorrhoidal cavities are aggravated by constipation, the formation of fecal stones, and straining during bowel movements. All this provokes mucosal injuries and bleeding from the rectum. The pathological process is accompanied by pain, the addition of a secondary infection, inflammation of the hemorrhoids, itching, and a feeling of discomfort.
Advanced hemorrhoids can only be treated with radical methods, but even in this case there is no complete guarantee of cure, and relapses are possible. Insurance can be a radical change in lifestyle (giving up bad habits), changing eating habits (balanced diet).
Hemorrhoids in the early stages can be corrected using minimally invasive techniques, diet, and a reasonable alternation of dosed physical activity and rest.
Inflammation
Bloody discharge that appears periodically from the anus, provoked by inflammation, is characterized by pathogenetic symptoms: pain in the abdomen, stool disorders, blood in the stool. Additionally, systemic diseases are diagnosed: arthritis, dermatitis, liver dysfunction. This is typical, for example, for exacerbation of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
If pathologies are left without proper attention, then without adequate therapy, tumors and large ulcerations of the intestinal mucosa are formed, often leading to rupture of different parts of the digestive tube.
Therapy is dominated by hormones, immunosuppressants, painkillers, and agents that normalize stool and digestion.
Worms
Helminthic infestation is a likely cause of bleeding from the rectum, which is accompanied by injury to the mucous membrane and disruption of its integrity. Perhaps this is the most common pathology that can gradually provoke the development of serious anemia and sharply reduce the quality of life of patients.
Parasites significantly disrupt human immunity and are therefore dangerous. They cause allergies up to anaphylaxis against the background of apparent health, provoke constant colds, acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, and dysfunction of internal vital organs. Bloody discharge is a late symptom of helminthic infestation, requiring hospital treatment.
Crohn's disease
Discharge mixed with blood from the anus may be a consequence of autoimmune processes affecting the mucous membrane of the digestive system. An example is Crohn's syndrome.
Erosive-ulcerative defects in this pathology cause bleeding of the intestinal lining, abdominal pain, lack of appetite, hyperthermia, a feeling of malaise, and weakness. Stool in this condition is called milena - black stool; it is formed under the influence of systematic brushing or one-time heavy intraintestinal bleeding.
Bowel cancer
Intestinal tumors, unless we are talking about polyps, are usually malignant. This is a cancer that can bleed at any stage of its development and spread through the intestines. Discharge from the rectum can be either primary or secondary, sometimes it is a symptom of a late stage of a malignant process.
In cancer, bleeding is accompanied by the development of intestinal obstruction (obstruction of the intestinal lumen by a tumor). Diagnosis is aided by digital examination (anal cancer) or instrumental techniques with histological examination of the biopsy specimen.
The color of the blood varies: from scarlet to mixed with feces, dull. The intensity of bleeding also varies, it all depends on the number of vessels involved in the process of tumor disintegration.
Diverticulosis
The process of protrusion of the intestinal mucosa through its outer layer is called diverticulosis. This disease often gives complications in the form of bleeding and peritonitis, which is life-threatening, so you need to know the first signs of pathology:
- abdominal pain (in the lower left corner of the abdominal wall);
- bloody discharge from the anus;
- low-grade fever.
The most important task in this case is to correct bowel movements to prevent the formation of new diverticula. Sometimes conservative, medicinal treatment is enough for this, sometimes surgery is indispensable.
Acute infection
Infections of any etiology provoke anal bleeding, which is characterized by intestinal irritation, dyspepsia with the formation of mucosal erosions. This gives symptoms of bleeding at the time of defecation or may have nothing to do with it.
Typhoid fever, dysentery, hemorrhagic fevers of various origins change the blood formula, provoke anemia, and require inpatient treatment in a specialized clinic to exclude death.
Pancreatitis
Bloody discharge from the anus may appear against the background of pancreatitis, an inflammatory pathology of the pancreas. The disease involves many organs and systems, often causing their bleeding.
The loss of biofluid is insignificant, but if there is bloody impurities in the stool, it is necessary to urgently determine the cause. Advanced pancreatitis cannot be treated, the mortality rate is more than 90%.
Blood in the stool in pregnant women
During pregnancy, women often experience bloody discharge after bowel movements. Most often the cause is constipation.
The act of defecation is difficult due to:
- Weight gain. As the child develops, the woman gains weight. Physical activity decreases. Stagnation occurs. It is difficult for feces to move through the intestines.
- Not drinking enough water. Swelling of the extremities is common in pregnant women. Therefore, gynecologists often advise limiting fluid intake. But water is necessary for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The stool dries out and thickens. In the process of moving through the intestines, it injures its walls.
- High levels of progesterone. The hormone negatively affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Read also
Why does a burning sensation occur in the anus?
The causes of blood in the stool of a pregnant woman can be different.
The above factors can cause scarlet spots to appear on underwear. Try to eliminate the provoking factor.
If a pregnant woman's stool is dark in color, this may indicate the presence of serious pathologies. Taking multivitamins can cause stool to turn dark. You should take a break from taking the medication and observe. If the color of the stool has returned to normal, there is no reason to panic. Otherwise, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Ways to stop bleeding
The occurrence of bleeding from the rectum can frighten many. There are enough reasons for this, so you should understand how to behave in a given situation.
Minor bleeding does not require hospitalization; it can be stopped with cold or methyluracil suppositories, which should be present in every home medicine cabinet. Suppositories will help speed up the healing of the wound - the source of bleeding, raise the body's defenses at the local level, prevent the development of inflammation and the addition of secondary flora. The medications contain sea buckthorn and lidocaine, which guarantees an analgesic effect, relief of itching, and improvement of blood clotting properties.
In the early stages of pathology development, cold compresses, lotions, and baths are effective. Ice spasms blood vessels and stops bleeding, relieves pain. Ice compresses are most effective for external hemorrhoids. The special device “Krinus” can replace lotions or ice candles. If the patient has problems with the kidneys, pancreas, bladder, then cold is excluded (it can provoke an exacerbation of nephritis, cystitis, pancreatitis). In this case, tablet hemostatic agents are used: Detralex, Vikasol, Dicynon.
Good results are achieved by using porous hemostatic sponges. Impregnated with Furacilin, boric acid, Miramistin, they stop bleeding at the local level when applied to the source of bleeding.
You cannot ignore a balanced diet with a predominance of easily digestible foods (fruits, vegetables, fish, seafood, lean meats), regular, dosed physical activity (exercises “cat”, “birch”, scissors).
Today there is not a single drug that could alone reliably stop pathological manifestations, since the cause of bleeding is diseases of several internal organs, which can only be treated comprehensively. Antihemorrhoidal medications help well in the treatment of hemorrhoids, for example, they relieve pain and promote the resorption of nodes.
Rectal bleeding can be stopped with suppositories if the only reason for its occurrence is chronic constipation, which contributes to the formation of fecal stones that injure the mucous membrane of the digestive system. In this case, the use of laxative suppositories is indicated.
However, in any development of events, the appearance of bleeding from the anus is a reason to seek qualified medical help in a specialized clinic. To preserve health (and sometimes life), it is necessary to conduct a full clinical and laboratory examination, establish an accurate diagnosis and carry out a set of appropriate treatment measures.
Diagnostics
- Digital examination of the rectum. Already at the stage of preliminary examination of the perineum and anus, anal fissure and hemorrhoids can be diagnosed. Digital examination allows you to evaluate the mobility of the rectal wall and the condition of the lymph nodes.
- Anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy. Allows visual examination of the rectum and distal sigmoid colon. Using these methods, the presence of neoplasms of the mucous membrane, erosions, ulcers, cracks, and signs of inflammation is determined. These methods also allow tissue biopsy followed by coagulation of the bleeding area.
- Colonoscopy. The most informative method that allows you to examine the large intestine along its entire length. Thanks to its high resolution, colonoscopy can detect pathological changes in the intestines at the earliest stages, perform multiple tissue biopsies, remove polyps, and coagulate a bleeding vessel.
- Irrigoscopy. X-ray method for examining the large intestine. Using this method, it is impossible to determine the source of bleeding, but it allows one to obtain information about the underlying disease (diverticula, neoplasms) that likely caused the bleeding.
Be sure to read:
Consistency of stool in an adult: where is the norm and where is the pathology?
Features of treatment
Discharge mixed with blood from the rectum is a symptom of various diseases, and therefore requires careful attention. With such a variety of causes provoking pathology, there can be no question of the existence of a single treatment regimen for all patients.
To eliminate bleeding, you need to treat the disease that caused it. Blood from the anus is not always a serious pathology, but in all cases without exception, this is a reason to visit a doctor.
Ways and methods of combating bleeding are correlated with the cause of the pathology:
- Medication – applicable for the treatment of infections, including helminthic infestations, when it is possible to accurately determine the pathogen and its sensitivity to prescribed antibacterial or antiviral therapy. Elimination of the cause entails the disappearance of the alarming symptom.
- Surgery is appropriate for polyps, malignant neoplasms, and advanced hemorrhoids.
- Cauterization or contact therapy is carried out if it is necessary (and possible) to cauterize the affected area of the mucosa in the upper or lower segment of the digestive system.
- Combined - greatly enhances the intended effect (for example, cauterization in combination with antibacterial therapy).
Prevention of bleeding from the rectum can only be a careful and reasonable attitude towards your own health. Medical examination is to help everyone who wants to maintain active longevity.