Why does the spleen hurt, where does it hurt: causes of pain, what diseases can there be?
Human Spleen
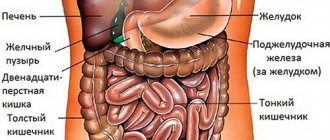
The spleen is one of the most underrated organs of the human body. Many people think that this is some kind of rudiment that can be easily dispensed with. In fact, the spleen is an important organ responsible for metabolism. One of the main functions of this organ is hematopoiesis, that is, the formation of red blood cells and white blood cells. The spleen is also a kind of filter that cleanses the blood of viruses, bacteria, and helps maintain a strong immune system in the body.
Why does the spleen hurt? What diseases can there be? There are several causes of pain in the spleen:
- The first reason is trivial - mechanical damage. Most often, a rupture of the spleen is a consequence of a fracture of the ribs on the left side of the body. Often, a ruptured spleen is accompanied by profuse internal bleeding, severe pain, and in some cases even painful shock.
- The next reason is parasites. One of the most common is echinococcus. Detecting the presence of parasites is difficult. At the moment, ultrasound and tomography studies show the best results in this process.
- Also, this organ can be affected by benign and malignant tumors, the identification of which at an early stage is almost impossible. Therefore, at the first pain on the left side of the side, you should immediately consult a specialist.
The main symptoms of problems with the spleen are: low blood pressure, constant nausea and sometimes vomiting, and breathing problems. Where does it hurt?
- Often the spleen makes itself felt in the form of severe pain in the left hypochondrium.
- Sometimes the pain spreads all the way to the shoulder blade area.
It is not surprising that an organ that performs so many functions is susceptible to a host of diseases. The spleen does not have pain receptors; problems with it can only be identified through a full examination by a specialist. Therefore, at the first discomfort, immediately consult a doctor. The clinic will conduct a diagnosis, and the doctor will prescribe treatment.
How does the spleen hurt?
The organ begins to hurt only in the third and fourth stages of enlargement. The patient experiences acute cutting or aching pain in the left side, which radiates to the shoulder blades and upper limbs. Its appearance is preceded by a deterioration in appetite, the appearance of heartburn, and an increase in body temperature. At night, a person begins to sweat a lot. If nothing is done, the pathology develops according to the following scenario:
- The patient's skin turns yellow.
- Nausea constantly sets in, and the urge to vomit appears.
- Weight decreases quickly.
When the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment begins. It is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease. This may be a bacterial infection, the development of myeloproliferative neoplasms, portal hypertension, hemolytic anemia, acute leukemia, cysts, abscesses, malignant tumors.
Ultrasound of the spleen in adults: what it shows, preparation for the procedure
Ultrasound of the spleen in adults
The spleen is an organ responsible for the protective properties of the body. With the help of the spleen, the immune system and metabolism are formed. If there is a malfunction in its operation, this leads to disruption of many important systems of the human body. In this case, diagnostic procedures are prescribed, namely ultrasonic examination. What does it show?
- Ultrasound of the spleen in adults is one of the safest diagnostic methods.
- It gives an almost complete, and most importantly, objective picture of the health of this organ.
- Ultrasound allows you to determine the size and function of the spleen.
- Both adults and children from an early age can be subject to such examination.
- There is no risk in this procedure.
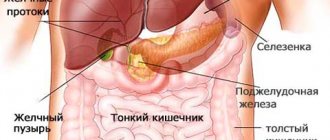
The spleen is a kind of filter of the body that absorbs bacteria and diseased blood cells, and other pathological particles that enter the body or are produced in it.
An ultrasound is done to determine a number of abnormalities. Reasons to do an ultrasound include:
- Determination of organ size or abnormalities of its development
- Detection of neoplasms
- Pain in the lower back or side
- Pain in the left side of the back
- Pain in the shoulder blade
- Nausea
- Reduced blood pressure readings
- Liver diseases
- Injuries
- Diseases of the blood or lymph nodes
How to prepare for the ultrasound ? Here is the answer:
- An important task is to prevent excess gas formation. A loaded bowel may make examination difficult.
- Three days before the ultrasound you should follow a small diet. Legumes (including peas and beans), sweet foods (confectionery sweets), fresh white bread and vegetables that have not been thermally processed should be excluded from the diet.
- Nine hours before the ultrasound , you should stop eating altogether. Sometimes, to improve the digestion of food, doctors prescribe the evening before the procedure to drink a Filtrum or Smecta . This is necessary in order to neutralize the gases.
The ultrasound examination itself is carried out strictly on an empty stomach, with the exception of diabetics. If you have diabetes, your doctor will recommend how to go about this procedure correctly and what you can eat and when.
Functions of the spleen
All functions of the spleen have not yet been fully studied. It is currently believed to exert hormonal regulation of bone marrow activity. In the first months of pregnancy, the spleen is the main hematopoietic organ of the fetus. In the last month of pregnancy, the bone marrow of the fetus fully matures, in which leukocytes of the granulocyte series and erythrocytes begin to form. From this moment on, only monocytes and lymphocytes are formed in the spleen. However, with some blood diseases, hematopoietic sites begin to form again in the spleen.
In adults, the spleen performs several other functions:
- Here, the destruction (phagocytosis) of outdated platelets and red blood cells occurs, as well as the conversion of hemoglobin into hemosiderin and bilirubin. The iron contained in hemoglobin is deposited in the cells of the spleen, which is the main depot of this element in the human body;
- The spleen is one of the most important sources of lymphocytes circulating in the blood, especially in children, adolescents and young adults;
- Produces antibodies and acts as a filter that traps foreign particles and microbial agents. It is a well-known fact that after removal of the spleen, people become very susceptible to various bacterial infections;
- It is a kind of reservoir of red blood cells that enter the general bloodstream in critical conditions.
Spleen in children: size of the organ, treatment if the spleen in a child is enlarged?
Spleen in Children
As children grow older, the normal size of the spleen varies in children. Usually, an increase in this organ in a baby indicates a specific physiological phenomenon, but it is important to exclude pathologies. The dimensions of the organ are described below.
- The process of formation of this organ begins approximately 5 weeks after conception.
- The spleen of a small baby is round in shape and weighs about 9 grams .
- By the first year of life it increases 3 times.
- Much depends on the child's growth. If the baby is between 60 and 70 centimeters , then the diameter of the splenic vein will be 3.3 mm , the length of the organ 54.6 mm , the width will be 26.2 mm , and the thickness will be 24.3 millimeters .
- With a height of 100 cm, the diameter of the splenic vein will already be 4.2 mm , and with a height above 170 cm - 6.1 . Accordingly, the size of the gland itself will increase. That is, a lot depends on the child’s growth and age.
An enlarged spleen occurs when there are rapid changes in the growth of the child's body, or there may be diseases. Ailments due to problems with the spleen are as follows:
- Abscesses
- Bacterial infections
- Problems with the blood-forming organs
- Liver problems
- Tuberculosis
- Syphilis
- Problems in metabolic processes
- Heart defects
- Oncology
- Cysts
- Measles
- Rubella and more
Typically, an enlarged spleen in a child is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Pain in the left hypochondrium
- Increasing temperature
- Increased fatigue
- Apathy
- High sweating at night
Diagnostics includes:
- Ultrasound
- Blood, urine and stool tests
If the spleen is enlarged and there are the symptoms described above, you should consult a doctor.
Worth knowing: Doctors in this case will take a wait-and-see approach, since the child’s body changes quickly. However, if the symptoms do not go away for a long time and the baby’s well-being worsens, then there is a serious pathology. You will need special medications, or even surgery.
The diet of such a child should include the following foods:
- Bird
- Beef
- Fish
- Beef and chicken liver
- Cereal porridges and soups with milk
- Buckwheat
- Boiled and baked potatoes
- Chicken eggs
- Fresh vegetables and fruits
Advice: The main diet should consist of these foods. Do not allow your baby to eat a lot of sweets and fried foods. It is also worth protecting your child from eating fatty foods.
Prevention consists of scheduled vaccination against various diseases. It is also important to be careful when traveling to exotic countries. Do not give your baby unfamiliar fruits or other foods. It should be simple and useful. Introduce moderate amounts of physical activity into your life.
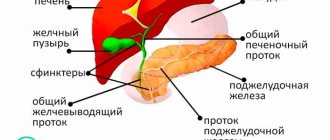
Anatomy and structural features of the organ
The spleen is shaped like a bean.
Its contours are clear and even. It stretches 15 cm in length, 8 cm in the crossbar. Fastening occurs with the help of pressure formed inside the peritoneum and two ligaments: the phrenic-splenic and phrenic-colic. The blood supply is carried out by a large branch of the celiac trunk - a muscular artery. It has a powerful internal elastic membrane. Its diameter can reach up to 12 mm.
The top of the spleen is covered with a membrane in two layers. The first - serous - consists of mesothelial cells. The second is fibrous tissue. All trabeculae are attached to it. They stretch from the gate of the parenchymal organ (the point of entry of the splenic artery and the exit of the lymphatic vessels and splenic vein). Veins, lymphatic vessels and fibers of nervous tissue are located inside the trabeculae; the anatomy of the organ stroma is presented:
- a capsule consisting of connective tissue;
- septa (trabeculae) with a network of reticular fibers (all this together is the contractile apparatus of the spleen, which allows it to stretch and contract);
- pulp - the main part (it occupies 95% of the organ).
The pulp is divided into red and white. The share of red pulp is 75% of the total volume. It consists of separate elements - venous sinuses. They are completely surrounded by reticular tissue. The spaces between the septa (trabeculae) are called “pulp cords.” The space between them and the sinuses is filled with blood cells. A large number of macrophages that participate in the recycling of iron atoms live here. This is where old red blood cells die.
White pulp occupies 22% of the total volume of the organ. Its anatomy is simple. Clusters of lymphocytes are located along the arterial vessels emerging from the trabeculae. They come in two types:
- PALM – periarterial lymphoid couplings – T-lymphocytes;
- Malpighian bodies – lymphatic follicles – B-lymphocytes.
Each type has its own accumulation zone, so different lymphocytes “live” separately, without mixing with each other. Where the red and white pulp intersect is the marginal area. Antibodies accumulate in it. They are produced by plasma.
In children, the structure of the spleen is different. In newborns it is round and has a lobed structure. White pulp makes up only 5-10% of the total volume. The organ weighs on average 9.5 g. In the third month of life, the mass increases to 14 g, by the end of the first year it reaches 28 g, by six years it doubles, by ten it begins to weigh 70 g.
Knowing these structural features of the spleen in children, pediatricians are able to timely diagnose an enlarged organ and prescribe adequate treatment. By the age of 17, the mass of the organ becomes like that of adults. And here, already approved standards are used to identify deviations.
Internal structure of the spleen
Spleen in a dog: location, functions
Spleen in a dog
In dogs, the spleen is located on the left and fits tightly to the abdominal wall and stomach. The location of this organ is in the abdominal cavity, and it does not contact the sternum. However, the location of the spleen may change, since due to the stomach being filled with food, it is able to “float”.
Worth knowing: When an organ fills with blood, it may hang (lower edge) to the right side. The spleen extends a couple of fingers beyond the arc when the stomach is moderately filled with food, and this is considered normal for a dog.
The functions of this internal organ in dogs:
- One part of the spleen, called the “red pulp,” is responsible for recycling old red blood cells.
- Another section, called the “white pulp,” is involved in the synthesis of antibodies necessary for the functioning of the immune system.
- The dog's spleen is capable of holding up to 16% of the blood in the dog's body.
- The spleen processes blood cells that contain viruses and bacteria.
In an adult, child or animal, the spleen performs important vital functions. Do not underestimate this organ and it is important to monitor its health. At the first symptoms of illness, immediately contact a specialist.
Structure of the spleen
The dimensions of the spleen in an adult are 8 cm wide, 10–12 cm long, and its thickness does not exceed 4 cm. During the digestion process, an enlargement of the spleen is usually observed.
The shape of the spleen resembles a coffee bean. Its surface color is dark red, with a distinct purple tint. It has two edges - upper and lower and two ends - anterior and posterior. In the area of the spleen adjacent to the stomach there is a groove - a gate through which nerves and blood vessels enter it.
Outside, the spleen is covered not only with a serous membrane, but also with a dense connective tissue capsule. This capsule also penetrates into the organ, dividing the spleen tissue into small separate sections.
Spleen hurts - treatment
There is no specific treatment regimen. It is selected individually and depends on provoking factors and the general condition of the body.
Drug therapy
- Antibiotics depending on the pathogen.
- Probiotics. Bifidumbacterin, Linex.
- Antiviral. Remantadine, ribavirin.
- Vitamins. Multi-tabs, complivit.
- Painkillers. Pentalgin, Ketanov.
- Antipyretic. Efferalgan, Nurofen.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Diclofenac.
- Enzymes. Festal, pancreatin.
- If necessary, chemotherapy or drainage is performed to drain pus.
Diet
Food intake is carried out 4-6 times a day in small portions.
- You can: iron-containing foods, pomegranate, nuts, honey, cabbage, fatty fish, citrus fruits, avocados, apples.
- Not allowed: salt, sour fruits and vegetables, butter, smoked meats, marinades, pickles, caviar. Alcohol is strictly prohibited.
Treatment of the spleen with folk remedies
Natural herbal ingredients cannot replace traditional therapy, but in consultation with a doctor and choosing appropriate remedies, they alleviate the condition and speed up recovery.
They have hypotensive, antacid, antidiarrheal, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiviral and analgesic effects. In addition, they reduce cholesterol levels, eliminate poisons and toxins, speed up metabolism, improve the absorption of beneficial components and strengthen the immune system.
Such remedies include onions, blueberries, apples, ginger, chicory, strawberries, horseradish, nettles, violet flowers, string and others. Extracts, infusions, compresses and tea are prepared from these plants.
Surgery
It is prescribed urgently for rupture of the spleen or bleeding from it. What happens after road accidents, fights, falls from a height.
If there is pathology of the organ, surgery is performed only if conservative methods are ineffective, this is either removal of tumors, cysts laparoscopically, or complete removal of the spleen with traditional splenectomy.
Consequences after removal of the spleen
Although the spleen is unofficially considered not a vital organ, there will still be consequences for a person after splenectomy. Since the organ belongs to the immune system, overall immunity will inevitably decrease, so flu and colds will definitely occur more often. There is a risk of becoming more easily infected with hepatitis, meningitis, pneumonia, and malaria.
Since the functions of the removed organ are taken over by the lymph nodes and liver, disturbances in the functioning of the liver and gallbladder occur more often.
The diet will also have to be changed; fried foods, fatty meats and offal, canned food, eggs, seasonings, alcohol, sour foods, and sweets will be prohibited. You can eat cereals, soups, lean meat and fish, vegetables, non-sour fruits, day-old bread, nuts, honey.
Prevention
To prevent diseases of the spleen, you need to lead an active lifestyle, engage in light physical activity, give up bad habits and consumption of low-quality food, undergo timely medical examination and treatment of various diseases, strengthen the body’s defenses and protect the abdominal area from injury.
Of course, it is possible to live without a spleen. But in this case, the body is left without a significant part of its defenses. An increased load is placed on the liver and bone marrow, which leads to their accelerated “wear and tear.” A person will be registered with a hematologist throughout his life and take anticoagulants to prevent thrombosis.