Description
Stomach cramps are uncomfortable sensations and a feeling of heaviness, often occurring in combination with pain symptoms and other very unpleasant sensations.
In fact, cramps are involuntary muscle contractions of the stomach walls. This organ initially has a well-developed muscle layer, which, thanks to active contraction, softens and moves food.
When digestion begins, muscle contraction stops for it to proceed fully, but after processing the food it begins again to move the food masses into the intestines.
Such reductions occur only when necessary, so we do not notice them.
But under the influence of certain factors, the stomach muscles begin to contract involuntarily. Such contractions cause discomfort because the stomach works and produces juice in vain when there is no food supply.
Causes
Quite a variety of reasons can provoke the appearance of stomach cramps, although neurological or digestive disorders most often lead to such disorders.
- Food or alcohol intoxication;
- Long-term or frequently disturbing stressful conditions;
- Irregular and unhealthy diet, overeating;
- Prolonged hypothermia;
- Tobacco smoking, especially if you have the habit of smoking on an empty stomach;
- Having a food allergy;
- Abuse of strong coffee, especially on an empty stomach;
- Frequent consumption of foods containing too much fiber (roughage), spicy foods and too fatty foods, etc.;
- Long-term anti-inflammatory therapy with NSAIDs;
- Intoxications associated with occupational hazards or chemical exposure.
More often, stomach cramps are detected in people who are emotionally unstable, prone to depression and have a labile nervous system. Provoking factors for spasms can also be conditions such as VSD or neuroses, gastrointestinal pathologies such as ulcerative lesions, duodenitis or gastritis, etc.
Causes of spasms
Most often, pain in the stomach appears due to pathological factors. This is how the body reacts to disturbances in the digestive system. Gastroenterologists distinguish two types of causes of spasmodic sensations: primary, or organic, and functional.
Organic
Organic spasms indicate damage or progression of acute and chronic gastrointestinal diseases. Often organic changes in tissues signal the presence of a serious illness, such as:
- Gastritis. Caused by insufficient or excessive production of hydrochloric acid. Spasms occur during an exacerbation of the disease and can radiate to the back.
- Ulcer or erosive lesion of the stomach walls. The pain is accompanied by belching, heartburn and appears most often after eating.
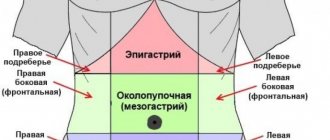
- Gastroduodenitis. The intensity of spasms depends on the degree of impairment of secretory and motor functions. Pain is felt in the epigastric or umbilical region.
- Pancreatitis. Patients perceive colic as gastrospasm. In such a situation, you will need to consult a doctor to determine an accurate diagnosis.
In order to find out the nature of stomach cramps, sometimes doctors administer myotropic drugs to the patient intravenously or subcutaneously. If the deformation of the organ does not disappear against the background of medication, then this indicates an organic cause.
Functional
The functional causes of stomach cramps are determined by the individual characteristics of a person. They are a reaction to a specific stimulus. The occurrence depends on a person’s lifestyle, his habits and emotional state. The main factors of negative disorders include:
- prolonged stress;
- intoxication with chemicals;
- lack of adequate nutrition, overeating;
- drinking alcohol and smoking;
- genetic predisposition;
- food allergies;
- metabolic disease;
- presence of parasites;
- taking medications that cause stomach cramps;
- mechanical influences;
- hypothermia.
Associated symptoms
Stomach pain is caused by loss of muscle tone, disorders of the neuro-autonomic system and metabolism. It can be paroxysmal or intermediate. Symptoms of stomach spasms may include:
- discomfort and painful attacks in the abdomen;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea;
- periodic vomiting;
- general weakness of the body;
- a sharp increase in body temperature.
Unpleasant sensations can occur during any physical activity. In addition, the patient suffers from prolonged constipation or diarrhea, constant seething and bloating after eating. The most dangerous symptoms of spasms include:
- regular increase in pain;
- labored breathing;
- change in color of feces;
- severe chills;
- pale skin;
- vomiting with blood and bile secretion.
If you experience such symptoms, you should immediately seek help from a doctor, as ignoring the signs can lead to serious consequences.
Classification
Gastroenterologists classify stomach cramps into several groups. According to the etiology, spasms are:
- Primary or organic – formed when the gastrointestinal tract is damaged;
- Functional - arise as a result of a reaction to a certain irritant such as alcohol or medications;
- Secondary – formed against the background of damage to intraorganic structures (except for the gastrointestinal tract).
Depending on the type of course, stomach cramps can be total or regional.
Regional are characterized by localization in a specific area of the stomach, can occupy a large area, and often appear in the upper half of the organ. Total stomach spasms are very rare in gastroenterological practice and are associated with pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract or nervous system.
Diet for cramps
To prevent the occurrence of repeated spastic contractions of the stomach in the future, in addition to a gastroenterological examination, you should:
- Move more.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Review your diet.
Products that you should avoid eating are all products that are mechanically, thermally or chemically capable of overloading the gastrointestinal tract:
- Heavy, fatty, spicy food. Steaming is preferable.
- Products containing large amounts of coarse fiber.
- Carbonated drinks.
- Pastries, pies, pies.
- Fatty, thick meat and mushroom broths, mushrooms.
- Sour, pickled and pickled vegetables and fruits – they increase acidity.
Drinking excessively is prohibited. And of course, you should follow the general rules of a healthy diet: no stale foods (sometimes harmless bread bought yesterday can become a source of pathogenic microorganisms), normal (3-4 hours) intervals between meals, fasting days (they are arranged once a week, eating only light meals during the day), moderation in diet (avoid overeating, and if bouts of “gluttony” are regular, you should think about the possible psychological underpinnings of this phenomenon), no food that is too hot or too cold.
The dietary regime is observed for at least 2 months.
Most common reasons
Among the reasons include functional stomach disorders (aerophagia, pylorospasm, dyspepsia), food allergies. But, as a rule, patients with such features are aware of their disorder.
Sudden convulsive sensations against the background of complete gastroenterological health are usually caused by stress and severe emotional experiences. In body language, pain in the stomach is a pinched, very strong anger. There are techniques for relieving this anger, but you will need to work with a specialist.
In addition to stress, neurosis, and an emotionally difficult situation, hypothermia, a large fatty dinner, or eating a new, unusual food can cause unreasonable unpleasant sensations. The disorder can be provoked by diseases of other organs of the gastrointestinal tract, blood diseases, cardiovascular and endocrine diseases.
Symptoms
Stomach cramps are characterized by pronounced clinical manifestations, so it is simply impossible not to notice them:
- Discomfort and pain symptoms appear, radiating to different areas of the abdomen;
- Nausea-vomiting reactions are a concern; sometimes the vomit contains blood impurities, which indicates hidden internal bleeding;
- Sudden occurrence of a hyperthermic reaction;
- The patient complains of difficulty bending;
- The general condition of the patient is depressed, migraines, etc.;
- Swelling in the peritoneum;
- Pain symptoms radiating to the umbilical zone;
- General exhaustion, weakness, chronic fatigue.
Discomfortable symptoms occur with any activity, and the attacks are of an interval nature. The difficulty is that it becomes difficult for the patient to eat, because he cannot chew and swallow solid food.
After meal
After eating, stomach cramps occur less often than on an empty stomach. If such symptoms occur, there is reason to suspect pathological conditions such as pancreatitis or peptic ulcer.
With an ulcer, painful symptoms occur approximately half an hour to an hour after eating, then as the food masses are digested, the painful spasms gradually subside.
On an empty stomach, the stomach does not hurt with an ulcer. If pain is caused by pancreatitis, then it occurs immediately after eating, and pain symptoms can be felt in the liver or lumbar region.
Diarrhea
A similar clinical picture occurs with irritable bowels, consumption of stale or poor-quality food. The pain appears within an hour after eating, occurs with diarrhea and increased gas formation, and disappears after defecation.
Temperature
If spastic gastric discomfort is accompanied by a hyperthermic reaction, the causes are usually associated with infectious pathology or acute poisoning.
When eating unwashed or spoiled foods, patients experience characteristic symptoms of food intoxication, stool disorders, hyperthermic reactions and paroxysmal pain.
If there is a digestive infection, then there may be signs of intestinal bleeding, which are found in the stool in the form of bloody impurities. In such a situation, the patient should urgently contact a gastroenterologist.
With nausea
Stomach cramps coupled with nausea characterize the development of inflammatory lesions in the bile and ductal canals or indicate gall bladder dyskinesia. In this case, the pain syndrome is localized in the hypochondrium on the right. It usually occurs after eating smoked meats, fatty foods, sweets or salty foods.
With belching
If spasmodic pain in the stomach occurs with sour belching, then the causes are associated with inflammation of the walls of the duodenum and stomach. The pathology is characterized by a long course with periodic attenuation of symptoms and exacerbations.
The pain is periodic in nature, located in the epigastric and umbilical zone, there is a feeling of fullness and heaviness.
Nervous
The origin of such spastic discomfort is due to the weakness of the autonomic nervous system structures.
Attacks of stomach cramps in such patients usually occur after deep stressful experiences, emotional overload, etc. Often such attacks occur after exams, severe fears or public speaking.
Sometimes painful symptoms in the stomach of nervous origin are accompanied by severe diarrhea, gastric heaviness, excessive gas formation, etc. After defecation and taking sedatives, the painful symptoms subside.
Pyloric spasm
This condition is called pylorospasm. Pain syndrome of pylorospastic origin, i.e., arising against the background of contraction of the gastric pylorus, usually appears in people prone to depression and neurasthenia, neuroses, often experiencing stress, etc.
A characteristic manifestation of such pain is a nausea-vomiting attack, which occurs for about half an hour after eating. Only after the gastric cavity has been emptied will the patient feel relief.
In general, spasmodic gastric soreness can also bother healthy patients, and there may be no pathological reasons for this phenomenon.
Such signs may include errors in the diet, poorly prepared dishes, or a large number of various additives in the foods consumed. But if spasms occur regularly, then competent diagnosis is necessary to identify the exact causes.
How to relieve pain with stomach cramps?
During the treatment of gastritis, it is necessary to direct all efforts to the causes of the disease, most often this is an incorrect diet. How to relieve pain when stomach pain occurs? A properly selected diet will help eliminate irritation of the mucous membrane, medications, and folk remedies. But, all these methods can aggravate the problem if you prescribe treatment yourself. Only the attending physician can choose the right liver and prescribe medications to relieve pain.
Drugs
Considering the cause of the disease, gastroenterologists prescribe a remedy for pain and cramps. But, in case of severe pain, you can take painkillers such as Tempalgin, Ibuprofen.
The most commonly used antispasmodics are:
- "Omez";
- "Omeprazole";
- "Famotidine";
- "Dibazol";
- "Baralgin";
- "Mebeverine."
Omez is an antiulcer drug that effectively fights the disease. It is used to treat erosive colitis, duodenal and gastric ulcers, and to prevent exacerbation of gastroesophageal reflux.
For ulcers that bleed, the dose in the infusion solution is 80 ml, administered slowly. After stopping the bleeding, it can be used in the form of tablets of 20 mg per day. The course of treatment is 14 days.
Omeprazole is also a medicine against stomach ulcers, duodenal ulcers, and also to prevent relapses. It should be taken 20 mg at a time, once a day with meals or before meals.
When you purchase medicine in capsules, you cannot chew them and wash them down with a small amount of water. Treatment lasts from 2 weeks to a month. When there is an exacerbation of GERD, the doctor prescribes taking the medicine 20 ml per day for one to two months.
Famotidine , an antiulcer substance, suppresses exacerbations, treats erosive and reflux esophagitis. The tablet must be swallowed whole, chewing is not recommended, and washed down with water.
In the acute phase, 20 mg is prescribed in the morning and evening or 40 mg at night. If there is a need for this, the dose is increased to 80 mg. You need to drink it from a month to two, and if reflux esophagitis, then 20 or 40 mg 3 times a day for 1.5 - 2 months.
Dibazol , relieves spasm of smooth muscles of the stomach, intestinal colic, stimulates the immune system. Causes muscle relaxation by reducing free calcium levels. Prescribed for peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum.
Take orally after meals 2 hours later or at the same interval before meals. Dose – from 20 to 50 mg 2 or 3 times a day for one month.
Baralgin is an antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, and also antispasmodic agent. Relieves moderate and mild pain, weakens spasm of smooth muscles of the stomach, intestinal colic.
Adolescents over 15 years of age should take 2–5 ml intravenously or intramuscularly once a day. The medicine is administered intravenously very slowly, approximately 1 ml per 1 minute. The patient must lie down. Tablets for adults are prescribed 4 times a day, 500–1000 mg.
Mebeverine is an antispasmodic agent that has a direct effect on the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract. Eliminates stomach cramps without pain, positively affecting intestinal motility.
Take one tablet in the morning and evening 20-30 minutes before meals, no need to chew, drink 150 ml of water. The duration of treatment is prescribed by the attending physician.
Alternative methods and traditional medicine
In addition to medications, there is an alternative method of treatment with herbs and decoctions. What is the best thing to drink to relieve severe cramps? Folk remedies that you can prepare yourself at home will help relieve symptoms:
Medicinal marshmallow , which relieves inflammation. For stomach pain, take a cold decoction. In addition, it restores the intestinal microflora after food poisoning. The basis of plants is mucilage. One tsp. dry powder pour a glass of cold water. Prepare immediately before use. Take 1 glass three times a day. It is not recommended to sweeten it, or drink it hot.
Swamp calamus . The name is not attractive, but a decoction of the root of this plant perfectly soothes the gastrointestinal tract, restores stomach function, and relieves pain. Grind the dry root in a coffee grinder. Place a teaspoon of powder in a cup of boiling water, let it brew for 10-15 minutes. Take 25-30 drops per 200 ml of water three times a day.
Red viburnum (garden) relaxes the intestines and relieves stomach cramps. However, before use, be sure to consult a doctor, especially during pregnancy, so as not to provoke a miscarriage. There is a 1:5 tincture, take 40-50 drops, or a 1:1 liquid extract, 10 drops per cup of water. Take one dose three times a day.
Common calendula , an essential substance during spasms, irritation of the rectum, during constipation or bloating. You can take it every day. Drink 1:5 tincture 25–30 drops per 80–100 ml of water. Take one dose 3 or 4 times a day.
Cinnamon – this spice copes well with diarrhea and moderate food poisoning. The product kills germs that cause stomach upset. In addition to its pleasant taste, cinnamon is a lifesaver against food poisoning. Pour half a teaspoon of powder into 200 ml of boiling water. Take one glass of the prepared drink three times a day.
Melissa (lemon balm) helps with indigestion, relieves cramps, and fights the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Use as tea. Brew in the proportion of 3 teaspoons per cup of boiling water. It is not only a healthy decoction, but also tastes good, improves digestion and lifts your mood.
Massage for stomach cramps
When acute pain syndrome occurs in the stomach, it is not recommended to perform any exercises. Only after two weeks have passed, classes with a small load are prescribed, gradually increasing it. Abdominal exercises should be avoided during this period.
Massage helps well to get rid of colic and abdominal pain:
- At the base of the palm, near the wrist, there is a point responsible for the stomach. It should be massaged for 3 minutes.
- Place your palm on your stomach so that your little finger is above your navel. The desired point is located near the index finger. You need to press on it, but not hard.
- Symmetrically to the first current there are two more. Finding them is not difficult, just measure 4 fingers in one direction or the other from the previous point. You need to massage at the same time, but so as not to feel pain.
- Place the palm of your right hand on your stomach, exhaling deeply and making circular movements with your hand in a clockwise direction. Perform a massage for 2 – 3 minutes.
Seeing a doctor and diagnosis
If it is necessary to establish a diagnosis, you should undergo a complete examination of the body. When visiting a doctor with stomach cramps, the following is most often prescribed:
- Gastroscopy to determine whether there is damage to the mucous membrane, to examine the condition of the surface of the stomach and digestive organs. Using an endoscope, determine acidity, as well as microbial contamination of the surface of the stomach.
- Colonoscopy to examine the surface of the large intestine as well as the rectum.
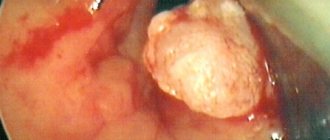
- A biopsy, where the surface of the gastrointestinal tract is examined under a microscope. It is prescribed if it is necessary to detect the presence of a tumor.
- Zoning of the stomach, with the help of which gastric juice is taken, determining the composition of acidity and the presence of parasites.
- An X-ray is prescribed for acute pain in the stomach to see the condition of the organs located in the chest area and the presence of air under the diaphragm. Its absence may indicate intestinal obstruction.
- Ultrasound is a safe, painless procedure. Prescribed for abdominal pain to establish a diagnosis.
- Computed tomography to identify inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity, examine the condition of organs: small and large intestines, stomach, pancreas.
Analyzes
After receiving information about the condition of the stomach, the doctor prescribes blood, urine and stool tests.
If after a general blood test it is not possible to establish a diagnosis, a biochemical test is prescribed to check the level of bilirubin and leukocytes, indicating the presence of infection in the body.
A urine test allows you to visually determine the presence of infection. If the urine is not clear and has an unpleasant odor, an infection is most likely present. If blood is found in the urine, it indicates kidney disease.
Analysis of stool during abdominal cramps will help identify parasites or infection, provide information about diseases of the stomach and intestines, and check for dysbacteriosis.
Additional diagnostic procedures
The above tests will tell you about the patient’s condition. After this, the doctor may require an examination of the integument to determine the breathing pattern. He will palpate, percussion, touch the abdomen in different places, tap it to find out the degree of tension.
Additionally, a rectal examination may be performed to determine hemorrhoids or the presence of blood in the rectum. Check the color of the whites of the eyes and the mouth to determine dehydration.
During pregnancy
Pregnant girls often have various types of digestive disorders, most typical in the 2nd-3rd trimester of gestation.
- It is during these periods that the uterus quickly and significantly increases, squeezing the organs of the digestive system.
- Therefore, pregnant women often experience bloating and flatulence, heartburn and difficulty digesting.
- As pregnancy progresses and the fetus enlarges, motor skills are disrupted, and food stagnation occurs, causing constipation.
- Often in the later stages, fermentation processes occur, which increase bloating, aggravating the patient’s condition.
- Spasms in the stomach develop as a result of all the above-described transformations in the mother’s body.
To normalize the gastrointestinal tract, mothers are advised to avoid overeating and stagnation of food in the intestines. To do this, you need to eat fermented milk and plant foods. But pregnant women should not take laxatives.
Consequences
Periodic painful sensations are usually not dangerous, but it is still necessary to tell a specialist about them in order to exclude the probable onset of the development of a pathological process.
If spastic painful discomfort is a constant concern, interspersed with short periods of remission, then in the absence of therapy and poor nutrition, this condition can lead to pathological complications.
Such complications include ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, bleeding or perforation of the stomach, oncology, atrophy of the stomach walls, etc.
Any digestive pathology immediately affects the condition of teeth, nails, hair and skin, and sharp jumps in body weight are observed. If previously digestive complications occurred mainly in people over 40, now they have begun to occur more and more often in young people, which is associated with modern rhythms of life and the lack of a healthy diet and regimen, frequent dieting or overwork, etc.
Diagnosis of the disease
A blood test will help determine the cause of abdominal colic.
When admitting a patient with complaints of colic, first of all, the gastroenterologist collects and analyzes the medical history and life history of the patient himself, as well as the life history of his family. To do this, the doctor may ask the following questions:
- Duration and nature of pain.
- Having problems with bowel movements (constipation, bleeding).
- The occurrence of nausea and vomiting, increased body temperature.
- The fact of taking painkillers and the positive effect of taking them.
- The patient's lifestyle and eating habits.
- Past and present presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in the patient and his family members.
- Next, if this is a primary appointment, the doctor examines the patient, performs percussion (palpation and tapping) of the abdominal area and, especially carefully, the epigastric region (the area of the anterior abdominal wall corresponding to the projection of the stomach onto this wall).
The patient is then sent for laboratory tests. You may need:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- stool occult blood test;
- a routine stool test is a coprogram.
To clarify the picture of the disease, the patient undergoes the necessary instrumental diagnostic procedures:
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal area allows you to assess the general condition of the organs.
- An X-ray examination does not provide an accurate picture of the condition of the tissues and organs of the abdominal cavity, but allows one to see the presence and distribution of gases and liquids in the image. Based on this information, some conclusions can be drawn about the pathologies occurring in the area of the patient’s body being studied.
- Computed tomography is the most accurate and informative method of instrumental diagnostics. On a computed tomogram, the image of organs is visualized in a three-dimensional projection. Images of individual organs are not superimposed on each other, unlike an X-ray. Each organ is visible in cross-section, you can evaluate its shape, size, and condition of the tissues. Computed tomography allows you to determine the presence of foreign bodies in the studied part of the body, pathological changes in cells and tissues of organs.
Based on the data obtained during the examination of the patient, his attending physician draws up a treatment program. It should be remembered that therapeutic procedures (including maintenance therapy) can last for quite a long time.
In this case, you need to periodically visit your treating specialist so that he can assess the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy and, if necessary, adjust the treatment.
Diagnostics
The causes of stomach cramps can only be identified through competent and thorough diagnosis. To do this, various manipulations are carried out:
- The patient's medical history is studied and an examination is carried out;
- Laboratory tests of biomaterials such as urine and blood, blood biochemistry, stool microscopy, and a breath test to detect pathogenic bacterial microorganisms are prescribed;
- Ultrasound examination of the peritoneum and endoscopy are performed;
- X-ray examination with or without contrast;
- Probing of the duodenal area;
- Computed or magnetic resonance imaging;
- Ultrasound diagnostics of renal tissues;
- Gastroscopic examination, etc.
In some cases, it is necessary to conduct additional consultations with such highly specialized specialists as an endocrinologist or nephrologist, pediatrician or gynecologist, etc.
First aid
If an acute and sudden attack of cramps in the stomach begins, you need to call an ambulance. Before the doctor arrives, you can alleviate the patient’s condition by providing first aid.
In case of acute stomach cramps, it is recommended to take plenty of plain drinking water at room temperature, which will help cleanse the gastrointestinal tract. You can take a pain reliever to dull the spasms.
The patient is advised to take a position in which spastic sensations will be minimal and remain in this position until the doctor arrives. Similar actions are appropriate as first aid for adult patients. If a painful attack occurs in a child, then you need to give him an anesthetic and send the patient to the hospital.
How to relieve stomach spasms on your own?
You can take any measures only if your stomach hurts with cramps and is not due to an existing chronic or acute disease. For assistance measures you need:
- drink a glass of warm clean water;
- 5 minutes after this, take 1 tablet of no-shpa or drotaverine hydrochloride at a dosage for an adult of 80 mg;
- place a warm heating pad on the stomach area.
If you have heartburn, you must take an antacid. But you need to drink it no earlier than 20 minutes after taking no-shpa. Before you relieve stomach spasms on your own, you need to make sure that you do not have stomach bleeding. In this case, emergency medical care is required.
If these measures do not bring you relief within an hour and a half, seek emergency medical attention.
Treatment
Therapy for stomach cramps does not have any single scheme; usually therapeutic measures are prescribed individually to each patient.
In general, the treatment process is based on data obtained during diagnostic studies and is determined depending on the root cause of spastic pain in the stomach.
In general, medications and traditional medicine are used, and diet therapy is prescribed with a diet in accordance with the clinical picture of spasms.
The patient’s lifestyle is also important in the therapeutic process; it is necessary to give up unhealthy habits such as cigarettes, alcohol, etc.
Medicines
Drug therapy is prescribed in accordance with the diagnosis that caused stomach cramps. In general, drugs from the following pharmaceutical groups are used:
- Antispasmodics (Baralgin, No-shpa, Papaverine or Akabel, Datiscan, etc.);
- Probiotics like Lactobacterin, Sporobacterin, Linex and Acipol, Bifidumbacterin, etc.;
- Antimicrobial medications (Amoxicillin, Levofloxacin, Flemoxin, Clarithromycin).
Additional methods of treating spastic gastric syndrome include homeopathic medicines, herbal medicine and reflexology.
Surgical interventions for spastic pain may be necessary only in particularly complex cases such as advanced ulcerative pathology, extensive gastric erosive lesions or oncological processes.
Folk remedies
Good results in the treatment of stomach cramps can be achieved with the help of traditional recipes and herbal medicine. In general, it is recommended to prepare herbal decoctions or medicinal infusions based on St. John's wort and meadowsweet, mint and valerian, chamomile or nettle, rose hips and yarrow, ginger, dill, plantain and calendula.
Peppermint tea is excellent for relieving spastic pain; you need to add a teaspoon of crushed mint to a glass of tea. Also, stomach cramps can be removed with the help of motherwort juice, a teaspoon of which should be dissolved in 100 ml of water and drunk.
Spastic pain can be eliminated by frequent consumption of freshly squeezed carrot juice with the addition of honey. You can also make a carrot salad by grating the vegetable and seasoning it with honey. This salad should be eaten about half an hour before meals. It is also recommended to prepare an infusion of carrot seeds (250 ml of boiling water per large spoon of seeds).
Diet
Treatment of spasms cannot be done without diet therapy. In general, the principles of a dietary nutrition program for gastric spastic discomfort boil down to the following:
- It is necessary to exclude spices and mayonnaise, spicy and smoked foods, garlic from the diet;
- Also prohibited are fatty foods and hot sauces, bakery products, animal fats and confectionery products, onions;
- You cannot eat cabbage, radishes and sorrel, radishes and spinach;
- You should also not drink strong coffee, black tea, or alcoholic beverages;
- The food consumed should be warm or at room temperature; too cold and hot foods should also be avoided.
Meals should be balanced, 3-4 times a day. Patients also need to stop smoking.
How does the treatment work?
A prerequisite for eliminating pain in the stomach is to follow the diet prescribed by a specialist.
Of course, you should never eat fried, spicy or salty foods. In addition, you should not drink coffee or carbonated drinks. This diet should be followed not only until the symptoms disappear, but also for a month afterwards.
Medicines are prescribed by a gastroenterologist. Any medications should be taken depending on the diagnosis made by the specialist.
To relieve discomfort in the stomach, antispasmodics like No-shpa and Baralgin are prescribed. The doctor must determine which medicine should be used. Also, you should not get carried away with taking these medications on your own. Remember that they only eliminate pain, but do not get rid of its cause.
If bacteria are found in the stomach, then, accordingly, antimicrobial drugs and antibiotics are prescribed.
Along with these medications, the doctor prescribes probiotics. They are prescribed to restore intestinal microflora. If you do not take them, there may be dysbacteriosis, which is very difficult to treat.
Homeopathic medicines are not entirely trusted in modern medicine. But if you are sure that they help, then you can also use them.
Prognosis and prevention
Spasmodic pain in the stomach does not pose a threat to the patient’s life; however, if the problem is ignored, it can provoke the development of serious complications, worsening the prognosis for recovery.
In order not to encounter stomach cramps, it is necessary to completely eliminate unhealthy habits, avoid psycho-emotional and stressful situations, and physical overexertion.
Proper and healthy nutrition should become the norm of life, and not a temporary measure. In addition, it is necessary to avoid hypothermia, and medications should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor.
Periodically it is necessary to undergo a medical examination to exclude possible gastrointestinal pathology.
Such spasms, if they have a pathological origin, can be treated for quite a long time, so preventive measures will help to avoid many problems.
Prevention
Spasmodic pain in the stomach is a reason to consult a gastroenterologist
Preventing problems with the stomach and other organs of the digestive tract is the best way to avoid pain. Preventive measures come down to several rules:
- Proper nutrition. If a person has had acute attacks of gastritis and other similar diseases in the past, or these diseases remain in a chronic form, he must follow the diet prescribed by the doctor for almost his entire life. But even for a healthy person, not all food is healthy.
- Strong tea and coffee, fatty, spicy, salty foods, fast food and canned food, sweet soda, confectionery - you should try to consume these foods as rarely as possible. A balanced diet and a normal eating pattern are important - no snacks on the go, heavy dinners before bed, or overeating during the day.
- If you suspect the development of diseases of any origin, you need to undergo diagnostics at a medical institution and consult a doctor. Many diseases not related to the digestive system have a detrimental effect on the condition of its organs.
- In everyday life and at work, you should avoid stressful situations whenever possible. A weakened nervous system can cause sudden pain in the stomach and even diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Moderate physical activity is beneficial for people with any health condition. This could be walking in the fresh air, cycling, swimming. Depending on how you feel, you can indulge in active sports. But in this case, you need to monitor your diet especially carefully in order to compensate for the lack of nutrients in the body in time.
It should be noted that with incipient but not yet noticeable disturbances in the functioning of the stomach, lifting weights can provoke the rapid development of stomach diseases.
You also need to get rid of bad habits - smoking and alcohol abuse. The sooner this happens, the better, since the body needs quite a long time to recover from the harmful effects of toxic products.
A useful activity to prevent stomach cramps is breathing exercises. Spasmodic pain in the stomach is a serious symptom indicating disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system.
The pain syndrome includes both diseases of internal organs and external factors. To determine the source of pain, you need the qualifications of a specialist - a gastroenterologist, who, after a series of tests and studies, will prescribe effective treatment.
Did you know that some foods can help treat stomach problems? About this in the video:
The stomach as an organ plays a huge role in the life of the human body. Along with the heart, it can be called a kind of engine - by processing food, it provides energy support to the entire body, giving it strength to function.
But, like any organ, the stomach is susceptible to various diseases or simply temporary functional disorders. One such disorder is colic.