Feelings of heartburn and bitterness in the mouth are extremely unpleasant symptoms that indicate certain problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Separately, both of these symptoms can indicate a variety of diseases, but their joint occurrence narrows the range of possible pathologies and simplifies the diagnostic process.
To understand the nature of the occurrence of these symptoms, it is necessary to understand their etiology, the characteristics of their manifestation, and find out which diseases are accompanied by similar symptoms. In addition, it is important to direct all efforts to fight not only these unwanted sensations, but also the disease itself.
What is heartburn?
Such an unpleasant burning sensation as heartburn is familiar to many people. Calling this pathology a disease is fundamentally incorrect; rather, it is a symptom that can be caused by certain diseases and disorders of the functions of the gastrointestinal tract.
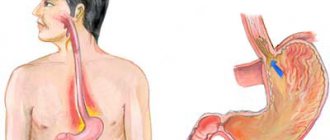
As for the definition, heartburn is a burning sensation in the esophagus that radiates to the throat and epigastric region. Burning sensations are caused by gastric juice entering the esophagus, which damages the unadapted mucous membrane, burning it and forming erosions, otherwise this phenomenon is called reflux.
In no case should you tolerate heartburn, however, the use of all kinds of means aimed at suppressing painful sensations is also not an option, because this way you only get rid of the burning sensation, while the underlying disease cannot be treated and can even progress.
About the mechanism of heartburn
A burning sensation in the epigastric region of the anterior abdominal wall can appear at different periods. Usually its appearance depends on food intake (after ingestion). In this case, the discomfort spreads in an upward direction. This combination of characteristics indicates that heartburn is occurring.
The development of this symptom is associated with incoordination of the activity of the stomach and esophageal sphincter. This condition is typical during the development of reflux disease. The lower esophageal sphincter does not perform its obturator function, thereby not preventing the antegrade spread of the bolus. The contents of the stomach enter the esophagus.
Reflux esophagitis (left); normal (right)
Gastric juice has a relatively low pH value. It is not surprising, because it contains a large amount of hydrochloric acid. Getting inside the esophagus, it irritates its mucous membrane and causes pain and burning.
Bitterness in the mouth and heartburn are characteristic of gastroesophageal reflux disease. But the appearance of these symptoms is more likely with the coexistence of gastroesophageal and pyloroduodenal reflux.
Causes of unpleasant taste during heartburn
Heartburn and bitterness in the mouth are related symptoms; they very often occur at the same time, that is, together. Often we do not pay due attention to such symptoms, thinking that this is a normal phenomenon for heartburn itself. This judgment is fundamentally incorrect; the simultaneous manifestation of both pathologies indicates more severe damage to various parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
There are several main reasons for the “tandem” of these symptoms:
- Increased acidity of the stomach and associated damage to the esophageal mucosa. At the same time, increased acidity can also provoke attacks of heartburn, as you can see, everything is really very closely connected.
- Another reason that heartburn is accompanied by bitterness in the mouth is the reflux of bile into the stomach , which occurs due to disruption of the biliary system. The flow of bile may also be impaired, and the person may also experience a bitter taste in the mouth.
- Gastroesophageal reflux is a chronic disease in which the sphincter between the esophagus and the stomach is disrupted, as a result of which the reflux of gastric contents along with gastric juice occurs regularly, causing increasing damage to the esophagus, leading to heartburn and bitterness in the mouth.
- Stomach ulcers and gastritis - both diseases, among other things, can cause severe bouts of burning, accompanied by a characteristic bitterness.
As you can see, the simultaneous manifestation of the two symptoms discussed may indicate truly dangerous diseases. Ignoring such pathologies increases the risk of harm to your health, so do not put off visiting a doctor for too long.
Endocrine diseases as a cause of bitter taste in the mouth
Heartburn and bitterness in the mouth are related symptoms; they very often occur at the same time, that is, together.
Often we do not pay due attention to such symptoms, thinking that this is a normal phenomenon for heartburn itself. This judgment is fundamentally incorrect; the simultaneous manifestation of both pathologies indicates more severe damage to various parts of the gastrointestinal tract. There are several main reasons for the “tandem” of these symptoms:
- Increased acidity of the stomach and associated damage to the esophageal mucosa. At the same time, increased acidity can also provoke attacks of heartburn, as you can see, everything is really very closely connected.
- Another reason that heartburn is accompanied by bitterness in the mouth is the reflux of bile into the stomach, which occurs due to a disruption in the functioning of the biliary system. The flow of bile may also be impaired, and the person may also experience a bitter taste in the mouth.
- Gastroesophageal reflux is a chronic disease in which the sphincter between the esophagus and the stomach is disrupted, as a result of which the reflux of gastric contents along with gastric juice occurs regularly, causing increasing damage to the esophagus, leading to heartburn and bitterness in the mouth.
- Stomach ulcers and gastritis - both diseases, among other things, can cause severe bouts of burning, accompanied by a characteristic bitterness.
As you can see, the simultaneous manifestation of the two symptoms discussed may indicate truly dangerous diseases. Ignoring such pathologies increases the risk of harm to your health, so do not put off visiting a doctor for too long.
Bitterness, not associated with the consumption of low-quality food or poisoning, is provoked by various dysfunctions. If this symptom is regular and stable, contacting a doctor will help identify the cause of its occurrence.
This symptom is most common in diseases of the bile-forming and biliary system: liver and gallbladder. The function of the liver is to produce bile; after it is produced by the liver tissue, the bile accumulates in the cavity of the gallbladder and is excreted through the bile ducts into the duodenum, where it participates in the digestion process.
In the presence of dysfunction of the gallbladder, motility of the biliary tract, mechanical obstacles (stones, calculi, obstruction of the ducts due to hypertrophy or degeneration of their tissues, compression due to inflammation and pathologies of surrounding organs), improper functioning of the liver, bile reflux into the esophagus and a bile or bitter taste are possible on the tongue.
In particular, the release of bile is often observed in patients with cholelithiasis and liver dysfunction during physical activity, muscle contractions of the stomach and/or duodenum due to diet violations, etc. At the same time, other symptoms indicating pathological processes in the liver (lack of pain in the right side, normal skin color and organ size) may not appear.
The feeling of a bitter taste is part of the symptom complex of cholecystitis, a disease accompanied by an inflammatory process of the membranes of the gallbladder. The metallic taste of bitterness in this case will be accompanied by discomfort and pain on palpation in the area of the right hypochondrium. Attacks of cholecystitis are accompanied by severe pain in the right side with possible irradiation to the back, shoulder blade, right collarbone, as well as nausea and vomiting without dependence on food intake.
Impaired removal of bile from the gallbladder cavity can also be caused by diseases of the stomach and intestines. Periodic disturbances in the process of production, excretion and absorption of bile accompany gastric ulcers, gastritis, duodenitis, colitis, enteritis, pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). To determine the cause, a fibrogastroscopy examination is recommended.
Gastroesophageal reflux, in which the acidic contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus as a result of spasm, irritating its upper sections, is better known as the cause of sour taste and heartburn, but can also provoke the occurrence of unpleasant tastes in the mouth. Most often, spontaneous spasm occurs due to poor nutrition and the habit of “lying down after lunch,” but it may indicate the presence of pathological processes in the stomach or esophageal tissues (pyloric stenosis) or neurological symptoms.
If the bitter taste persists while following a diet, avoiding foods that are unbalanced in composition and/or quantity, excluding fatty, fried, spicy, citrus fruits, chocolate, then an examination is necessary to diagnose pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract tissues or increased excitability of the nerve endings in the esophagus and upper section of the stomach.
Dyspeptic stomach disease is often accompanied by bitterness after eating. Added to the feeling of “bitter in the mouth” are morning heartburn, nausea, flatulence, as well as a feeling of discomfort, heaviness in the stomach and decreased appetite due to accelerated saturation.
The presence of Giardia, helminths and other parasites that disrupt the structure of the lining of the small intestine can lead to disturbances in the digestive process and the appearance of a bitter taste. By attaching to the inner lining of the intestine, parasites cause reflex irritation, damage tissue, provoke digestive disorders, increased gas formation, and dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
A bitter taste may be a consequence of the development of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. The proliferation of pathogenic bacteria due to non-compliance with hygiene rules, inflammation of the gum tissue, teeth, mucous membrane, surface of the tongue, stomatitis, gingivitis, innervation disorders can be accompanied by an unpleasant taste, bad breath, ulceration, tissue swelling and necrotic processes. A bitter taste may also occur due to allergic reactions and neurological disorders.
Implants, incorrectly selected filling materials, crowns, or an individual paradoxical reaction to them can also cause bitterness and a metallic taste, while the dental material does not necessarily have to be made of metal.
We suggest you read: Pus from the gums near the tooth treatment
Involutional or pathological disorders of taste buds can lead to a feeling of “bitterness in the mouth.” In this case, it is recommended to treat the underlying disease or use mouth rinses with a pleasant taste.
Thyroid dysfunction may be accompanied by excessive production of the hormones adrenaline and norepinephrine, which cause spasm of muscle tissue and promote the reflux of bile into the lower esophagus. This mechanism is the cause of the feeling of bitterness in the mouth during stress, but if there is a bitterness in the mouth regardless of nervous overstrain and other causes are excluded, this symptom may indicate the presence of hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and thyroid dysfunction.
With these pathologies, therapy for biliary dysfunction does not bring the expected effect: a bitter taste occurs as a consequence of hormonal imbalance against the background of the health of the biliary system.
In diabetes mellitus, bitterness in the mouth can be accompanied by dryness of the oral mucosa, increased sweating, increased blood supply to the palms and feet, which indicates a sharp increase in blood sugar levels. The presence of such symptoms requires immediate intervention and normalization of the patient's condition.
Often a person cannot correctly interpret that he has a bitter taste in the mouth and heartburn. The patient complains of an unpleasant taste and dryness of the oral mucosa. However, recognizing these symptoms is not difficult.
- Heartburn is one of the symptoms of diseases of the digestive tract. It manifests itself as discomfort in the stomach, a burning sensation in the esophagus and behind the sternum. People compare this discomfort to an internal fire.
- Dysgeusia – bitterness in the mouth, a feeling of acidity and an unpleasant aftertaste. It occurs when taste sensations are distorted and is one of the forms of taste disorders.
Taken together, these symptoms significantly worsen the patient's quality of life. Therefore, it is important to find out what disease they appear in. Treatment will depend on what caused the illness.
Secondary origin and predisposing factors
Above we have listed the most likely cases of bitterness in the mouth and heartburn, however, there are many more factors, some of them only contribute to the unpleasant sensations discussed, others provoke them directly:
- Adverse habits – primarily we are talking about smoking and alcoholism. Abuse of tobacco products and strong drinks causes serious harm to the digestive system, reduces the protective mechanisms of the esophageal and stomach mucosa, and causes heartburn and bitterness.
- Diet - fatty, fried, smoked, spicy and sour foods, as well as fruits and vegetables with a high acid content are no less harmful to our body. Such foods force the stomach to work harder and increase the secretion of gastric juice, increasing acidity, leading to known consequences.
- Bacterial infection - the Helicobacter bacterium, as it remains in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, contributes to the destruction of the gastric mucosa, as a result of which its walls are not able to withstand the acid contained in the gastric juice. The causes of the development of gastritis and peptic ulcers in some cases also depend on the vital activity of this bacterium; all types of pathology are accompanied by heartburn and bitterness.
- Damage by parasites – some harmful parasitic organisms, when they enter the stomach, have a detrimental effect on the functioning of the entire digestive system. They can stay there for a long time without showing any signs at all, and the only symptom of infection will be a feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
Feeling of bitterness in the mouth: causes
Many people complain of a periodic feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
Under normal conditions, the body perceives bitter taste through irritation of receptors in the area of the root of the tongue. It is this area that is believed to react to foods containing bitter compounds. But in some conditions, this taste in the mouth does not arise due to the consumption of the corresponding foods.
The development of inflammation in the oral cavity causes a perversion of taste sensations. This situation is medically called dysgeusia. One of the manifestations is the appearance of bitterness in the mouth. After eliminating the causative factor during a visit to the dentist, the discomfort goes away.
Dysgeusia accompanies cancer. It is especially typical for stomach cancer. You should pay close attention to symptoms of bitterness in the mouth and weight loss, constant fatigue, pale skin, and impotence.
Dyshormonal conditions can also be a factor causing bitterness in the mouth. This applies not only to diseases, but also to physiological conditions. For example, bitterness can accompany pregnancy.
Most patients complain of the described symptom in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In most cases, they become the etiological factor of heartburn.
Bitterness, a feeling of rancidity, a taste of bile can be a situational phenomenon associated with eating low-quality food. Some products, in particular pine nuts and other gifts of nature rich in fats, after consumption, cause a bitter taste in the mouth due to fat oxidation processes that began during storage, which negatively affects the liver.
However, if such a bitter taste appears after eating a large meal or including a large amount of fatty, fried, or smoked foods in the diet, then in most cases this indicates the development of diseases of the liver, bile ducts, and gall bladder. A bitter taste after a night's sleep also indicates disruption of these organs.
If you feel bitterness in your mouth when eating any type of food and following the principles of proper nutrition, then it is necessary to undergo an examination to identify pathological processes in the stomach, diseases or pathologies of the intestines, especially the duodenum, as well as abnormalities in the functions of the liver and biliary system.
Long-term bitterness not associated with food intake can occur in older people due to a natural decrease in the number and activity of taste receptors. Also, bitterness can be felt constantly if there are inflammatory processes in the oral cavity (gingivitis, stomatitis), diseases of the endocrine system, oncological tumors in the organs of the digestive system, cholelithiasis. Some mental illnesses may also be accompanied by a feeling of bitterness on the lips or tongue.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Thrush on the tongue in children: how to treat it
Some dental procedures can provoke bitterness as an individual reaction to the appearance of foreign objects, for example, during dental implantation. With episodic and short-term bitter taste in the mouth, the cause is most often a side effect of taking certain medications, in particular from the groups of choleretic drugs, antibiotics, antifungals and antihistamines.
Stress and increased neuro-emotional tension can affect the tone of the gallbladder, leading to excessive release of bile and causing dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and causing bitterness in the mouth. In such cases, it is necessary to correct the reactions of the nervous system and monitor and/or support the digestive organs: stress often provokes the development of gallbladder dyskinesia.
It is worth remembering that the reasons that cause such a taste in the mouth are diverse and range from healthy processes of natural involution of the taste organs to extensive parasitosis and cancerous tumors. Therefore, if this phenomenon occurs repeatedly, you should pay close attention to this symptom and be sure to undergo examination and treatment from a specialist.
Causes not related to the gastrointestinal tract
Of course, in most cases, heartburn and bitter taste have a direct connection with the gastrointestinal tract. However, there are certain factors in which the appearance of the symptoms discussed is not associated with stomach or intestinal problems.
First of all, we are talking about diabetes. A bitter taste is accompanied by significant increases in plasma glucose. A person may not even develop diabetes yet, in which case bitterness and attacks of heartburn can become harbingers of a terrible disease, which can still be prevented by testing and urgent treatment.
Individual manifestations of bitterness
In medical practice, there are cases when both pathologies appear separately; the causes of their occurrence lie not only in gastrointestinal problems; the symptoms are caused by two different diseases that appear simultaneously.
The point is that heartburn attacks are provoked by stomach diseases or reflux, while bitterness can occur due to the development of the following diseases of the oral cavity:
- Gingivitis or stomatitis;
- Other inflammatory processes of the gums;
- Reaction to unsuccessful prosthetics or specific filling materials;
- Consequences of dental operations;
- Trivial lack of oral hygiene.
In such cases, a person not only needs the help of a gastroenterologist, but should also contact a dentist or orthodontist.
Diagnostic measures
Of course, diseases that cause heartburn and bitterness in the mouth cannot be treated blindly. First, you need to pinpoint the underlying problem causing these unpleasant symptoms by subjecting yourself to a series of diagnostic procedures.
To establish the main cause of bitter taste and heartburn due to pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (FEGDS) is first performed. This procedure involves examining the upper gastrointestinal tract by inserting an elastic hose with a camera at the end. In this case, the doctor receives a visual picture of the condition of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum and sphincters. This method also allows for a biopsy of internal tissues and sampling of gastric juice for further research and obtaining a more accurate picture of the disease.
In some cases, an ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is required, which is especially important for identifying stagnant processes and pathological changes in the channels of the biliary system, and detecting cancer.
Laboratory blood tests (general analysis) make it possible to detect certain diseases, for example, to diagnose inflammatory processes of various types, followed by their detection and treatment.
Bitterness and accompanying symptoms
What to do if bitterness in the mouth is accompanied by other symptoms? You should definitely tell your doctor about this.
When, in addition to bitterness, pain occurs in the right side, this may indicate cholecystitis or other liver diseases. The pain may be constant or occur only after intense physical exertion.
Bitterness in the mouth in the morning and a yellow coating are a sign of diseases of the biliary tract, impaired liver function, exacerbation of peptic ulcers, gastritis, cholecystitis. If the yellow plaque has a greenish tint, and the feeling of bitterness increases significantly after eating fatty foods, you should check the bile ducts, gallbladder and liver for pathologies.
A white coating on the tongue indicates a violation of the microflora of the oral cavity, dental problems, or an allergic reaction to medications and materials used during prosthetics.
An unpleasant odor, bitterness, a gray-white coating, heartburn - these are all signs of problems such as peptic ulcers, dyspeptic disorders, gastritis. A thick white coating indicates thrush and problems with the immune system. The accumulation of brown plaque in the area of the root of the tongue is typical for heavy smokers with intestinal intoxication and iron deficiency in the body.
Accompanying bitterness with nausea means problems of the gastrointestinal tract, such as:
- Nastroesophageal reflux disease.
- Eating too heavy, poorly digestible food.
- Viral hepatitis, gastric dyspepsia, gastric ulcer, biliary dyskinesia.
- Poisoning. Poisoning with heavy metals (lead, cadmium, cobalt, mercury, manganese, copper) can occur not only with food, but also through clothing, household chemicals, and water.
If, in addition to the appearance of a bitter taste, a person complains of constipation or too frequent loose stools, decreased appetite, increased gas formation, sleep disturbances, it is worth examining the intestines and ruling out the possibility of allergies. If measures are not taken in time, the patient's condition may worsen significantly.
Chills, fever, heaviness in the abdomen, hot palms and feet, feeling dry - all this indicates inflammation of the gallbladder or cholecystitis.
Depending on the cause, bitter belching may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain or discomfort in the right hypochondrium;
- heartburn;
- nausea;
- weakness in the body;
- vomiting with bile;
- bloating;
- increased body temperature;
- drowsiness;
- hair loss as one of the complications of liver cirrhosis.
In addition, there is a constant unpleasant taste in the mouth and an unpleasant odor, despite high-quality oral care.
Methods to combat heartburn and bitterness
For effective treatment, it is necessary not only to deal with the symptoms, it is very important to consult a doctor, undergo examinations and, based on the diagnostic data obtained, begin to fight directly the underlying disease that caused the unpleasant sensations.
But as mentioned earlier, enduring bitterness and constant bouts of heartburn is extremely harmful; symptomatic treatment is also necessary. To do this, you can use both traditional and folk remedies, the most effective of which are:
- Medicines containing antacids. This group of drugs was created specifically to relieve burning in the esophagus, because they have a calming and enveloping effect on the mucous membrane. In addition, these medications neutralize the effects of gastric juice, slightly reduce acidity, that is, they will help remove bitterness. It is better to buy antacid medications in liquid or gel forms, they act faster and more effectively.
- Soda solutions – using regular baking soda helps a lot, especially when you don’t have the necessary medications nearby. It is enough to dilute a small amount of soda in a glass of warm water and drink slowly. The alkali will react with the acid of the gastric juice, “quenching” it. However, this reaction produces excess carbon dioxide, so don't be alarmed by the resulting bloating.
In any case, you cannot neglect your health, ignore the bitterness in your mouth and burning in the esophagus. If there are systematic manifestations of pathologies, immediately go to the doctor, because the sooner you start fighting the disease, the less damage it will cause to your health. In addition, you should not self-medicate either, because this can only aggravate your current condition, greatly harming yourself.
Treatment
To get rid of heartburn and bitterness in the mouth, it is necessary, first of all, to undergo a full medical examination to find out the true cause of these symptoms. Self-medication can only worsen the patient’s condition and lead to an exacerbation of the underlying disease.
Drug therapy
Prescribed based on the underlying disease. However, to alleviate the patient’s condition, the doctor may prescribe the following groups of drugs:
- Inhibitors are medications that protect the mucous membrane from the harmful effects of gastric juice and bile. They are taken before meals.
- Prokinetics are drugs that gently stimulate the gastrointestinal tract.
- Antacids are medications in the form of gels and suspensions that are taken symptomatically to eliminate an attack of heartburn.
- Enzymes are a group of medications that help a weakened stomach digest food better. Take with food.
Sometimes a doctor may prescribe sorbents to remove toxins from the body.
Folk remedies
Herbal medicine alone will not be enough in this case. It can be combined with medications, after consulting with your doctor. Neglecting this advice threatens to worsen the patient’s condition, including emergency hospitalization.
To alleviate the patient's condition, you can use the recipes below. They have a beneficial effect on the activity of the gastrointestinal tract, help reduce inflammation and protect the mucous membrane from the aggressive effects of gastric juice and bile:
- Flax jelly. A teaspoon of flaxseeds purchased at a pharmacy is steamed with a glass of boiling water (250 ml) and allowed to brew. Take according to the following scheme: drink 0.5 glasses in the morning before meals, the second half in the evening.
- Potato juice. Fresh, hard potato tubers are thoroughly washed, peeled, punched in a blender or passed through a juicer. The resulting pulp is squeezed out. Drink ¼ glass of potato juice 2 times a day, half an hour before meals. It is necessary to consume only freshly squeezed juice; after 10 minutes its beneficial properties begin to disappear. When drinking, it is preferable to use a straw, as the drink can negatively affect the condition of tooth enamel.
- Oatmeal broth. To prepare it, take half a glass of oats, add 2 liters of water and simmer over low heat until half the liquid has evaporated. The resulting volume of liquid should be drunk per day. Take half a glass of decoction between meals. The course of treatment should not exceed 10 days.
Diet and lifestyle
In addition to taking medications, you should reconsider your lifestyle and diet. It is important to establish a daily routine so that you have enough time to sleep. You need to give up bad habits.
- You should walk in the fresh air and engage in light sports. Thus, there is a fight against stagnation in the body, which can arise against the background of physical inactivity and oxygen starvation.
- Stress and nervous strain should be avoided; if it is impossible to cope with traumatic situations on your own, you should consult a psychologist.
- You will need to adjust your diet - you need to eat several times a day, but at least 3 times, so that food enters the stomach evenly. This will reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract and not provoke heartburn.
- The food itself should be dietary if possible; only warm food should be consumed, since hot or cold food can provoke inflammatory processes in the stomach. You need to avoid fried, smoked, salted, spicy, pickled and canned foods, as well as from eating sour berries and fruits.
- Fermented milk products, liquid cereals, low-fat broths and light soups based on them should be included in the diet. The meat should be dietary, dishes based on it should be steamed or baked.
Thus, bitterness in the mouth and heartburn, the causes and treatment of these pathologies depend on many factors and require a complete examination of the patient. Only then can you find out the true cause of these symptoms and eliminate it so that heartburn and bitter taste stop bothering the patient.