What it is?
Computed tomography with contrast has been actively used in domestic medicine for more than 15 years. This diagnostic method remains one of the most informative , since it allows you to detect even minor structural changes in tissue.
Its essence is quite simple - before the start of the study, the patient is intravenously injected with a special drug that contains iodine salts.
Their molecules are capable of almost completely absorbing X-ray radiation, while they accumulate well in certain types of tissues and are also quickly eliminated from the body without causing harm.
Initially, contrast was used to study the lumen of the digestive tract, thyroid gland and blood vessels. But over time, experts noticed that there are patterns in the accumulation of the drug that make it possible to detect a malignant process, the proliferation of connective tissue and other changes.
The procedure for administering contrast is simple. The patient lies down on the tomograph table in the required position. Then a catheter is placed on the ulnar vein, through which a contrast agent is injected manually by a nurse or using an infusion pump (an automatic device). At this time, the doctor monitors the general condition of the patient (to avoid allergic reactions).
Help An important advantage of computed tomography with contrast is the ability, during one session, to diagnose not only the abdominal cavity, but also the chest, pelvic organs, limbs, and head. In this case, the diagnostic time is extended by only a few minutes. This is especially important in emergency situations when it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis as quickly as possible.
How is an abdominal CT scan done?
To conduct the examination, the patient is placed on a retractable tomograph table in a supine position. Your hands will need to be placed behind your head. You will have to lie still for 15-30 minutes, so the patient’s body is fixed using special pillows and belts. In order to lie comfortably, you need to choose comfortable, loose-fitting clothes.
During the examination, the doctor may ask the patient to hold his breath for 1-2 seconds in order to prevent displacement of organs during breathing and to obtain clearer and more informative images.
Types of contrast
To examine the abdominal organs with contrast, initially Barium preparations were used, which the patient had to drink. However, this made it possible to better visualize only the cavity of the esophagus, stomach and intestines. Therefore, after the introduction of iodine preparations into clinical practice, which must be administered intravenously, they are used for CT scanning in the vast majority of cases.
Barium preparations are increasingly being abandoned , since they pass exclusively into the cavity of the stomach and intestines and do not accumulate in the walls and tissues of the abdominal organs. In fact, they are only suitable in situations where there is a pathological process on the surface of the mucous membrane.
Contrast agents with Iodine differ from each other due to different physical and chemical properties (osmolarity, viscosity, solubility in water).
Usually the CT specialist works with only one of them.
At the same time, there are different types of diagnostics, which affects the method of contrast administration:
- Classic . The patient is slowly injected with the drug intravenously, after which diagnostics of the abdominal cavity begins. Allows you to study its accumulation in organs (liver, spleen, pancreas, intestinal wall, stomach). The technique is used if there is no need to visualize the flow of contrast into the vessels.
- Bolus contrast enhancement.
- Permanent . A drip with a contrast agent is connected to the venous catheter. This allows you to maintain its concentration in the body at a constant level during the entire diagnosis. Used to visualize the abdominal aorta and its branches.
- Double . The patient is given a double dosage of contrast once before starting the CT scan. This technique is used in specialized cancer centers to search for metastases in lymph nodes and soft tissues.
- Rectal . The patient is given contrast using an enema, after which the study begins. Used in proctological practice.
Bolus organ boost
This is a technique that is considered the standard in CT. Its peculiarity is that the contrast agent is administered intravenously to the patient using a special device , which makes it possible to control the dose and speed of injection. Before starting the procedure, the doctor calculates the individual amount of contrast for a particular patient. The examination of the patient begins a few seconds after the start of administration.
Thanks to this, the specialist is able to clearly observe two phases of contrast distribution:
- vascular - when the drug sequentially fills large arteries, small arterioles, and then veins;
- parenchymal – accumulation of contrast in the patient’s organs (the speed of this process depends on the type of tissue).
As a result, it is possible to examine all the anatomical structures of the abdominal cavity with maximum information.
CT scan of the abdomen with contrast
In most cases, to obtain high-quality and detailed images, computed tomography of the abdominal cavity is performed with a contrast agent. To enhance the clarity of the image of the organs being examined, special preparations containing iodine are used.
There are two ways to introduce a contrast agent into the patient’s body.:
- intravenous administration is used to increase the contrast of blood vessels, hypervascular tumors, vascular malformations, and organs of the urinary system;
- oral administration of contrast helps to obtain more information about the structure and functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Also, contrast can be injected into the fistula tracts, if the patient has any and it is not possible to study them in any other way.
Drugs
As already emphasized, almost all preparations used for computed tomography contain iodine salts. However, they differ from each other in the following important indicators:
- Concentration of the active substance. On the one hand, the more contrast molecules in the preparation, the better, since this should improve image quality. But an interesting paradox was discovered - with increasing concentration, the viscosity of the drug also increased, which negatively affects its distribution in the vascular bed. Therefore, in all modern contrasts this figure does not exceed 350 mg/ml.
- Hydrophilicity (ability to absorb water). Contrasts with high hydrophilicity do not penetrate cell walls well, but are less likely to cause adverse reactions, and therefore are ideal for CT angiography (Urografin, Telebrix). Drugs with low hydrophilicity (Omnipak, Ultravist, Vizipak, Imagopak) penetrate well into the middle of the cells, so they are used if it is necessary to examine individual organs of the abdominal cavity.
- Osmolarity (an indicator that shows the concentration of active molecules in the drug). The toxicity of contrast is directly related to it. The highest osmolarity is in Urografina, the lowest in Vizipak.
"Urografin"
The drug of choice for CT angiography is a study in which the vessels of the abdominal cavity are visualized. Contrast does not penetrate well from the vascular bed into tissues and organs. The recommended dose of Urografin for adult patients for oral administration before CT is 20-50 ml, but in certain situations it can be further increased. The dosage of Urografin for children is presented in the following table:
| Age | Contrast volume, ml |
| Up to a year | 7-10 |
| 1-2 years | 10-12 |
| 2-6 years | 12-15 |
| 6-12 years | 15-20 |
| Over 12 years old | 20 |
The drug is administered intravenously slowly so that the procedure lasts 5-10 minutes. The only exception to this rule is patients with uncompensated pathologies of the cardiovascular system (20-30 minutes).
The study begins a minute before the end of the administration of Urografin. The diagnostic window lasts 20 minutes in patients without kidney pathologies.
The drug "Urografin"
"Omnipak"
The drug is used both for angiography and for contrast enhancement in CT. Its particles penetrate well through the cell membrane and accumulate in peripheral tissues. Therefore, with its help it is easier to detect areas of inflammation or oncological processes . For adult patients, 100-200 ml of the drug is administered intravenously, and for children, an individual dosage is calculated based on the ratio of 2-3 ml per 1 kg of body weight.
The drug "Omnipak"
Indications for abdominal CT scan
You can get a referral from your doctor for an examination in the following cases::
- oncological search: detection of tumors in the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, in the bones and soft tissues of the area being examined;
- determining the stage of the oncological process, searching for metastases, obtaining information about the structure and spread of the tumor before surgical removal or starting radiation therapy;
- determining the cause of obstructive jaundice;
- clarification of data obtained using ultrasound or x-ray examination;
- identification and control of the dynamics of development of aortic aneurysm;
- identification of damage to the abdominal organs, hematomas, free fluid, foreign bodies that may appear after abdominal trauma;
- determination of the condition of the lymph nodes in cases of lymphogranulomatosis, lymphosarcoma and some other diseases of the hematopoietic system.
For what symptoms is it prescribed?
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography is prescribed if the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- abdominal pain of various localization and nature;
- the appearance of blood or pus in the stool;
- nausea, repeated vomiting;
- abdominal muscle tension;
- reducing body weight without changing the nature of nutrition or physical activity;
- decreased appetite, aversion to certain foods;
- chronic constipation;
- detection of enlarged lymph nodes;
- severe weakness;
- closed or penetrating abdominal injury;
- decreased blood pressure and increased heart rate (signs of hemorrhagic shock without external bleeding).
This imaging method allows you to diagnose a number of pathologies of the digestive tract and other body systems:
- acute and chronic pancreatitis;
- pancreatic cysts and adenomas
- abnormalities of the digestive tract
- Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis;
- acute appendicitis
- cholelithiasis;
- acute and chronic cholecystitis;
- cholangitis;
cirrhosis of the liver;- acute and chronic hepatitis;
- increased pressure in the portal vein system
- detachment of the wall of the abdominal aorta;
- aortic rupture;
- thrombosis of arterial or venous vessels;
- splenomegaly (enlarged spleen);
- lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes);
- oncological process in the abdominal organs and/or its metastases.
Tomography of the peritoneal organs - what is it?
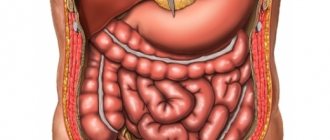
CT scan of the entire abdominal cavity is a highly informative diagnostic procedure that can show an accurate three-dimensional image of parenchymal and hollow organs, vessels and the lymphatic system of a given anatomical zone. This method involves the use of small doses of X-ray irradiation, giving minimal radiation exposure, while allowing to obtain layer-by-layer sections of tissue with a pitch of 0.5-10 mm, depending on the type of tomograph.
CT is indispensable in cases of suspected oncology, acute and chronic diseases of the peritoneal organs and blood vessels, because the accuracy of the study is much higher than that of ultrasound and radiography. What does this procedure show, what organs are visible during it? This:
- Organs related to the gastrointestinal tract system - large, small intestine (overview), pancreas.
- The organs of the hepatobiliary system are the liver, gallbladder and ducts.
- Spleen.
- The organs of the retroperitoneal space are lymph nodes and ducts, kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Vessels of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space.
Nowadays, CT of the abdominal organs is often replaced by MSCT, an even more modern research method. It is a multislice computed tomography, which is favorably distinguished by its technical capabilities and the number of sections when scanning organs. The image quality during this examination is higher, the duration is shorter, and the radiation dose is lower.
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
The main advantages and disadvantages of the technique are summarized in the following table:
| CT scan with contrast of the abdomen | |
| Advantages | Flaws |
| 1. Highly informative research (especially vascular changes, bones and intestinal wall).2. Ability to detect small tumors and their metastases. 3. Speed of the procedure (compared to MRI), which is necessary in emergency situations. 4. Painless. 5. Possibility to simultaneously conduct an examination of the entire body. | 1. Radiation exposure to the patient’s body.2. Toxic effect of contrast. 3. The need to pre-assess renal function. |
How often can an abdominal CT scan be done?
CT scanners use X-rays to produce images. The radiation dose a patient receives varies depending on the extent and timing of the examination.
Studies conducted in a number of clinics providing CT services indicate that the average dose received by patients per abdominal examination is about 7±2 mSv. For comparison, the permissible radiation exposure from background radiation for a person is 3-4 mSv per year.
This implies a number of restrictions regarding the volume and frequency of CT scanning. The optimal interval between examinations is 12 months. In cases where the potential risk from radiation is lower than the value of the information that can be obtained using CT, the procedure can be repeated 6 months after the first examination.
Harm of computed tomography with an enhancing agent
Computed tomography is an x-ray diagnostic method, therefore, the patient is susceptible to radiation. In this case, the radiation exposure is much higher than with radiography. Typically, with an abdominal CT scan, the patient receives 5-14 mSv (depending on the type of machine). Although this dose exceeds the recommended dose for an ordinary healthy person (1-2 mSv), it remains safe.
Without emergency indications, it is recommended to conduct the next study no earlier than 6 months after the previous one. If you do CT scans frequently, you can increase the risk of developing malignant neoplasms.
Important The contrast used for the procedure is not radioactive. But during its administration and 30 minutes after, medical monitoring of the patient’s condition is required. It is during this period that undesirable reactions most often develop.
Side effects
The vast majority of patients tolerate the procedure well. But in a small number of cases the following side effects may occur:
- Allergic reactions (rash, bronchospasm, anaphylactic shock, disturbances in heartbeat and breathing).
- Increased body temperature.
- Dyspeptic disorders (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting).
- Pain in the head or peripheral muscles.
- Systemic fibrosis (skin, muscles, liver, heart, lungs).
- Nephrotoxicity and acute renal failure.
- Thyroid dysfunction (hyperthyroidism).
What do abnormal CT results mean?
An abdominal CT scan can show some types of cancer, including:
- Cancer of the renal pelvis or ureter
- Colon cancer
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Lymphoma
- Melanoma
- Ovarian cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
- Pheochromocytoma
- Kidney cancer
- Cancer metastases from other areas of the body
An abdominal CT scan may reveal problems with the gallbladder, liver, or pancreas, including:
- Acute cholecystitis
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Cholelithiasis
- Pancreatic abscess
- Pancreatic pseudocyst
- Pancreatitis
- Bile duct blockage
An abdominal CT scan may reveal the following kidney problems:
- Kidney blockage
- Hydronephrosis (swelling of the kidney from urine backflow)
- Kidney infection
- Stones in the kidneys
- Damage to the kidneys or ureters
- Polycystic kidney disease
Indications and contraindications
There are a number of conditions when CT scanning using contrast allows not only to increase the diagnostic information, but has practically no alternatives. Among these indications it is necessary to highlight:
- oncological pathologies of the abdominal organs, as well as regional or distant metastases;
- liver disease, as well as the presence of ascites or jaundice of unknown origin;
- presence of contraindications to MRI;
- traumatic injury to the abdomen;
- hematological pathologies (leukemia, lymphoma);
- aneurysm or dissection of the abdominal aorta;
- developmental abnormalities of the digestive or urinary systems.
The diagnostic procedure cannot be carried out if patients have the following conditions:
- intolerance to iodine-containing contrast agents;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, which are accompanied by thyrotoxicosis;
- period of pregnancy or breastfeeding;
- end-stage renal failure (decrease in GFR<15 ml/min);
- acute heart failure.
Children can undergo contrasting from the first year of life.
Contraindications to CT with contrast
Contraindications to CT with contrast include:
- presence of a confirmed allergy to iodine;
- acute or chronic renal failure due to the possibility of complications due to the administration of a contrast agent;
- blood creatinine level above 100 µmol/l;
- severe diabetes mellitus (risk of complications from contrast enhancement while the patient is taking medications containing metformin);
- some thyroid diseases.
It is possible to do a computed tomography scan with contrast during breastfeeding. You just need to exclude lactation within 48 hours after the study.
Questions
Is it possible to do a CT scan during pregnancy?
Any form of X-ray diagnostics is contraindicated at any stage of pregnancy. Computed tomography uses well-known x-rays, which have a negative effect on the fetus. Therefore, CT scanning for pregnant women is performed only in exceptional cases when it comes to saving the life of the mother. If there is a threat to the life of a pregnant woman, they will try to carry out a tomography using a low-dose program, covering the tummy as much as possible with a special lead blanket that reflects X-rays. But even these precautions cannot exclude the possibility of the development of abnormalities in the fetus. The likelihood of this threat depends on the stage of pregnancy. The use of computed tomography in the early stages of pregnancy is strictly undesirable, since this may be fatal to the embryo, and the woman will have to terminate the pregnancy. According to the observations of expert radiologists:
- in pregnant patients who were irradiated at 1-2 weeks due to radiation from CT scans, in 98% the fetus died or stopped developing;
- in women irradiated at 2-5 weeks of pregnancy, in 70% of cases there was a miscarriage or frozen pregnancy, and in 20% the fetus had malformations of the liver, heart, and thyroid gland;
- In pregnant women who underwent computed tomography at 6-12 weeks, in 80% of cases the child developed multiple pathologies of organ development.
Is it possible to do a CT scan after x-rays and fluorography?
In case of medical necessity, an X-ray or fluorography examination can be combined with a computed tomography session on the same day. The main thing is to ensure that the total radiation dose does not exceed 15-20 mSv. On average, X-rays provide 0.2 mSv of radiation exposure per scanning session. The level of radiation exposure on MSCT is significantly higher and depends on the scanning area. It can range from 1 mSv to 15 mSv per examination.
Is it possible to do CT scans for children?
Computed tomography is a radiological form of diagnosis. It is not recommended for children under 14 years of age unless absolutely necessary. X-rays have a negative impact on the formation of the central nervous system in a child and increase the chances of cancer in children under 5 years of age. The dose of radiation that a child receives during a tomography session leads to an increase in the number of cells with mutations in the P53 gene, which is responsible for the development of cancer, and increases the chance of developing leukemia and brain cancer by 35%. Therefore, a child’s CT scan is performed only as prescribed by a doctor and in the presence of compelling medical reasons, when the benefits of the examination outweigh the health risks associated with it. Doctors strive, whenever possible, to replace computer scans with safer forms of diagnostics - ultrasound or MRI.
Is it possible to do a CT scan at a temperature?
Temperature is not a contraindication to native tomography, but it may be a limitation for contrast-enhanced CT. Changes in a person's temperature may indicate an inflammatory process in the body, and in such a state, the introduction of iodine-containing contrast can provoke a crisis.
Can I do a CT scan with dental implants and braces?
The short answer is yes. X-rays do not in any way affect dental implants, crowns and braces, no matter what material they are made of. Dental implants also cannot affect the quality of the tomograms obtained. They do not produce any artifacts on CT images.
Is it possible to do CT with titanium and metal plates?
Metal in the body is not a contraindication to CT, regardless of the alloy composition of your metal inclusion. Therefore, computed tomography can be used as an alternative form of diagnosis when, due to the metal in the patient’s body, magnetic resonance imaging cannot be performed on the patient.
Is it possible to do a CT scan with a pacemaker?
If you have a pacemaker of any model, you can do a CT scan. CT scans use X-rays and they do not have any negative effect on any artificial pacemakers. Therefore, CT is used as an alternative to MRI if the patient has a pacemaker, neurostimulator, or insulin pump, which can fail in the magnetic field of the magnetic resonance imaging scanner. But it is safe for such patients to undergo examination with a CT scanner.
Is it possible to do a CT scan after chemotherapy?
A CT scan may be ordered after a series of chemotherapy treatments to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. The decision about when control images need to be taken is made by the attending physician. Chemicals used in oncological treatment are not a contraindication to CT. The only thing you should always remember is that X-rays tend to accumulate in the human body, so the recommended interval between CT examinations for an oncological diagnosis should be 2-3 months. For diagnostics, you should also choose spiral low-dose units.
Preparation
If a more thorough examination of the vessels of the abdominal cavity, retroperitoneal space or intestinal wall is planned using computed tomography with contrast, then the patient must be prescribed a diet , the purpose of which is to reduce the production of gases in its lumen. This makes it possible to increase the information content of diagnostics.
You can only eat foods that do not cause increased gas formation. The preparation also includes a study on the tolerability of the contrast agent and kidney function. This allows you to avoid complications during the procedure. You can read more about preparing for a CT scan here.
Please note: If the examination is carried out in emergency conditions, then diet and preliminary water load can be neglected.
Preparing for the study
The patient should learn about how to prepare for an abdominal CT scan from the doctor who gave the referral for the study. The individual characteristics of the patient and his parameters must be taken into account.
It is necessary to prepare for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity in advance - undigested food, feces, and gases significantly reduce the level of diagnosis. In addition, the introduction of contrast into an unprepared body can provoke negative reactions - nausea, vomiting, and volvulus.
Therefore, the three-day preparation for the procedure is based on a strict diet.
Allowed to eat:
- oatmeal with water;
- boiled white chicken meat;
- light, non-rich broths with crackers;
- lean steamed fish;
- Egg omelet cooked in a slow cooker without oil.
Prohibited:
- vegetables that cause increased gas formation - cabbage, legumes, beets.
- berries, fruits and dried fruits;
- baked goods using yeast;
- any cereals;
- dairy products;
- fatty meats;
- smoked meats;
- carbonated drinks, strong tea, coffee;
- confectionery, chocolate;
- alcohol.
By following such a diet, adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract are minimized. Diagnosis is carried out on an empty stomach.
The intestines are also prepared for computed tomography:
- the night before and in the morning, on the day of the procedure, cleansing enemas are given;
- 18 hours before the examination, you can cleanse the intestines using medications recommended by your doctor, if there are no contraindications - enterosorbents, laxatives, antihistamines. They should be stopped 4 hours before the procedure.
When preparing for an abdominal CT scan using contrast, the attending physician may temporarily stop taking medications that the patient takes systematically.
During the procedure, the patient needs to relax, breathe freely and comply with all requests of the diagnostician. The likelihood of discomfort for the patient during the examination is very small.
Computed tomography of the abdominal organs is effective no earlier than 14 days after an x-ray using barium, which can distort the parameters.
Price
How much a contrast-enhanced procedure costs depends on the region in which the patient lives. In Moscow, you can undergo an abdominal CT scan with contrast in many private medical centers. The cost of the examination ranges from 4,500 (“Be Healthy”) to 11,500 (“Pokrovsky Gate”) rubles. In state clinics, the price of stomach diagnostics is slightly lower - 4500-8000 rubles (Research Institute of Rheumatology, Scientific Center for Children's Health of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Clinical Hospital No. 85).
In St. Petersburg, the cost of a CT scan with contrast in private clinics is 5,500-10,500 rubles. In the Pokrovskaya Hospital the price for diagnostics is 7,000, and in the City Clinical Hospital No. 31 - 7,500 rubles.
In Yekaterinburg, the procedure costs 5,500 (“Diagnostics Plus”), and in Kazan – 7,500 rubles (“Expert+”).
Often, an abdominal tomography with contrast is done simultaneously with an examination of other organs, such as the chest or pelvis, and the price for both procedures is more favorable.
Diagnostics can be done under the compulsory medical insurance policy in all public and some private clinics. In this case, the patient must undergo a preliminary full examination and receive a referral from the attending physician in the prescribed form (valid for 3 months after discharge).