Duration of digestion of food in the human stomach
To be absorbed, complex food compounds must first be broken down into simple molecules. Processing begins in the oral cavity with its mechanical grinding - chewing.
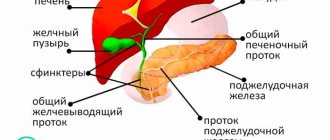
Food undergoes a more active effect in the stomach; its juice contains hydrochloric acid and special enzymes that break down proteins.
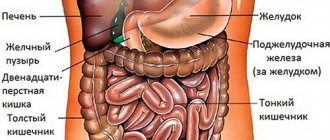
Food can remain in it from 30 minutes to 6 hours. Digestion is completed in the intestines. Enzymes are also actively working in the small intestine, and in the large intestine the absorption of nutrients and water is completed. It takes from 20 hours to several days until the residues are completely removed from the body.
The chemical composition determines how long it takes for food to be digested. The body absorbs simple sugars faster, then proteins; the body has to work the longest on fats. Fiber is not digested at all, but passes through the gastrointestinal tract in transit, but it activates the intestines.
How much food is digested on average depending on a person’s age
In the stomach of a newborn baby, which is able to digest only milk, food remains for no more than 3 hours. At this age, the volume of the organ is small, food comes in small portions and leaves the stomach quickly, hence the need for frequent intake of nutritional formula or milk.
In an adult, the time a bolus of food remains in the stomach depends on its volume, the quality composition of the products, their compatibility, and the state of the digestive organs.
How long does it take for different types of food (raw and cooked foods) to be digested in the human stomach?
On average, in a healthy state of the digestive system - from half an hour to 5-10 hours. In older people, the elasticity of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract decreases, acidity and the amount of enzymes produced change. These changes increase the period of processing of the food eaten and its evacuation into the intestines.
What affects the rate of food digestion over time?
To prevent the fermentation of undecomposed food from starting in the stomach, and to prevent the formation of gases and toxic compounds, a new portion can be eaten after disposing of the previous one. The rate of transformation of products is determined not only by their chemical composition.
How quickly food is digested depends on the following factors:
- Cooking method. For most foods, heat treatment prolongs their absorption time. So, a raw egg breaks down faster than an omelet. But some tricks can speed up the process: soaking seeds and nuts makes them easier to digest. When cooking, it is better to practice boiling, but not frying or baking.
- Meal time. Everything eaten at lunch breaks down much faster than dinner or breakfast. Therefore, in the evening you should give preference to light dishes.
- Combination of products. If the mixture contains “slow” ingredients, then the entire dish will take a long time to digest.
- Appearance. An attractively designed and aromatic portion stimulates the secretion of digestive juices.
- Consistency. Dense, especially fatty foods take longer to break down than liquid carbohydrate foods. Puréed dishes are easier to digest, which is why soups are so useful for dietary nutrition.
The health of the gastrointestinal tract is of great importance. All of its organs, including the stomach, intestines, liver and pancreas, contribute to metabolism.
The influence of age and gender on duration
From the moment a person is born, his gastrointestinal tract actively develops and is finally formed in a child by about 3 years. At the same time, the speed of food digestion changes with age. A newborn absorbs mother's milk in 2-3 hours. In an infant, the entire process lasts from 6 to 18 hours, and in an adult, complete digestion takes from 24 to 36 hours.
The maximum concentration of digestive enzymes occurs in the period from 20 to 40 years, then it decreases. Moreover, in men the amount of hydrochloric acid in the stomach is higher, so the breakdown of products occurs faster in them.
Food temperature
Which is better: cold or hot food - it all depends on its composition.
Protein foods are better digested when they are warm.
Without heating, food breaks down faster, but proteins need at least 2-3 hours to convert to amino acids.
Cold protein does not have time to be digested and leaves the body without bringing any benefit.
It’s not for nothing that all infant formula is given warm.
Product groups by digestibility time
Depending on how many hours a dish remains in the digestive system, there are three categories:
- Easily digestible food. Carbohydrates (mostly fast carbohydrates) fall into this group. The average time to digest food is 30-40 minutes. This includes most fruits and vegetables, except potatoes. And also juices, fresh salads, low-fat broths, kefir.
- Products of medium digestibility. This is a protein food that includes little fat. It is absorbed in up to 2 hours. This includes fish, poultry, eggs, most dairy products and seafood. Fruits include bananas and avocados. In this category there is chocolate, and only oatmeal.
- Heavy products. Such food remains in the stomach after eating for 3-4 hours, and sometimes more. This is a food rich in slow carbohydrates and a significant amount of fat. This group includes potatoes and mushrooms, all cereals, pasta and legumes (beans, lentils), corn. This also includes bread. Also fatty cottage cheese and hard cheese, nuts and seeds without heat treatment. Red fatty meat and canned food take a long time to digest.
The worst options are coffee or tea with added milk, cream, beans, chips, pizza. Such difficult-to-digest foods take a very long time to break down, which leads to various types of discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract (bloating, gas, constipation, etc.).
“Average” products in terms of digestion time
Medium digestion times include those foods that are digested from 1 hour to 3 hours. As a rule, they contain almost no fat, since the fat components significantly lengthen the digestion time. These are cereal porridges, bread, as well as dairy and vegetable proteins - cottage cheese, nuts, legumes. This also includes eggs and dishes based on them.
Protein food: cottage cheese
This protein is absorbed almost completely in the human body. How long does it take to digest cottage cheese? Typically, the time it takes to break down in the stomach is 1.5-2 hours. But liquid dairy products - milk, kefir, are digested faster, in 40 minutes, and are easily digestible foods.
Grain foods: bread, rice, buckwheat
Complete absorption of porridges, cereals, bread lasts about 6 hours. Moreover, the time for their breakdown in the stomach is up to 2 hours. This long-term absorption is explained by the need to break down, “disassemble” the resulting food into simple carbohydrates.
How long does it take to digest buckwheat and rice? The digestion process differs by 20-30 minutes. Buckwheat breaks down in 2 hours. Rice is “heavier”; it is digested in 2.5 hours.
Bread moves faster from the stomach to the intestines, but lingers longer in the intestinal cavity. Yeast bread causes an imbalance of intestinal flora. It causes fermentation, delayed evacuation of intestinal masses, as well as gas formation, bloating, and incomplete digestion of food.
How long does it take for bread to be digested in the stomach? Up to 2 hours.
Starches
Starch and starchy vegetables – potatoes take longer to digest than grain porridges.
Thus, the digestion time of potatoes in the stomach is 3 hours. However, jelly, a liquid food containing potato starch, is digested faster, about an hour.
Table of digestion times for individual foods in the stomach
| Products | Digestion time |
| Water | Immediately enters the intestines |
| Fruit juice | 15-20 min |
| Vegetable juice | 15-20 min |
| Vegetable broth | 15-20 min |
| yogurt | 2 hours |
| Full fat kefir | 2 hours |
| Low-fat kefir | 1.4 hours |
| Raw vegetables | 30-40 min |
| Vegetable salads without oil | 30-40 min |
| Vegetable salads with vegetable oil | up to 1 hour |
| Fruits containing a lot of water and berries | 20 minutes |
| Watermelon | 20 minutes |
| Orange, grapes, grapefruit | 30 min |
| Apples, cherries, peaches, pears | 40 min |
| Banana | 45 minutes |
| Boiled vegetables | 40 min |
| Cabbage, zucchini, corn | 45 min |
| Root vegetables (turnips, carrots, beets) | 50 min |
| Potatoes, Jerusalem artichoke | 1.5-2 hours |
| Porridge: buckwheat, rice, millet | 2 hours |
| Legumes | 2 hours |
| Nuts | 3 hours |
| Sunflower seeds, pumpkin | 3 hours |
| Cottage cheese | 2 hours |
| Hard cheese | 3-4.5 hours |
| Smoked sausage cheese | 3.4 hours |
| Ice cream | 2.3 hours |
| Egg | 45 min |
| Fish | 1 hour |
| Sea kale | 2 hours |
| Shrimp (krill meat) | 2.3 hours |
| Mussels | 3 hours |
| Canned fish | 3-3.5 hours |
| Poultry meat | 2.5-3.3 hours |
| Rabbit meat | 3.1 hours |
| Beef | 3.3 hours |
| Mutton | 3.3 hours |
| Pork | 5.5-6 hours |
| Boiled sausage Doctorskaya | 3 hours |
| Smoked sausage | 4 hours |
| Raw smoked sausage | 4.2 hours |
| Milk sausages (sausages) | 3 hours |
| Meat or liver pate | 3 hours |
| Dumplings | 3.3 hours |
| Butter | 3.2 hours |
| Mayonnaise | 3.2 hours |
| Beer, wine, vodka, cognac | 1.3 hours |
| Chocolate without additives | 2-2.2 hours |
| Halva | 3 hours |
| Candies | 2-2.5 hours |
| Marshmallow, marmalade | 2 hours |
| Natural honey | 1.2 hours |
| Cookies, gingerbread, bagels | 2.2-2.4 hours |
| Cakes, pastries | 3-4 hours |
| Bread made from wheat or rye flour | 3.1-3.3 hours |
This is how long it takes for your stomach to digest all the foods you eat.
Many people, even those who monitor their diet, do not take into account such a factor as the time it takes for food to be digested in the stomach and what it affects, so in this article we will look in detail at how long it takes for food to be digested in the human stomach and what affects the speed of digestion.
What determines the rate of food digestion over time?
- Drinking water and other liquids during meals. It is not recommended to drink water and drinks during meals, as they dilute the gastric juice and the digestion time of food increases (or the food is not completely digested).
- Many products after heat treatment (cooking, frying, stewing) take longer to be absorbed in the human body (the time for assimilation of products increases).
- Cold food is digested faster over time.
- Food eaten at lunch is digested faster than food eaten in the morning and evening.
- The speed of digestion in the stomach and absorption in the body is greatly influenced by the type and amount of food consumed, since different foods are absorbed at different speeds (from several minutes to several hours), and when they are mixed, the digestion time can increase.
Of the listed factors that significantly influence how quickly the food eaten and drinks drunk will be digested, let us dwell in more detail on the speed of digestion of all products separately and consider how many hours various foods are digested (meat, fish, cereals, vegetables, fruits, etc. .) in the human stomach.
Dairy
Raw milk leaves the stomach slowly, pasteurized milk even slower, and boiled milk even slower. Milk that is rich in fat passes through the stomach more slowly than milk that is low in fat.
Skim milk, ricotta, low-fat cottage cheese, feta cheese, and homemade cheese are digested in about 90 minutes.
Milk is completely digested within 12 hours. Tea or coffee with milk: 24 hours.
Whole milk cottage cheese - 2 hours
- Hard cheese made from whole milk, such as Dutch and Swiss, will require 4 to 5 hours to digest.
- Fermented milk drinks – 1 hour
- https://youtu.be/wIQddQZKzk4
Table: how much food is digested in the human stomach
| The product's name | Product digestion time |
| Water and drinks | |
| Water (drink on an empty stomach) | immediately enters the intestines |
| Vegetable and fruit juices | 15-30 minutes |
| Tea | About 60 minutes |
| Broth (vegetable, chicken, meat) | 20-40 minutes |
| Vegetables and greens | |
| Jerusalem artichoke (earthen pear) | 1.5-2 hours |
| Potatoes (new potatoes) | 2 hours |
| Boiled potatoes | 2-3 hours |
| Fried potato | 3-4 hours |
| Carrots (fresh) | 50-60 minutes |
| White cabbage (fresh) | 3 hours |
| Sauerkraut | 4 hours |
| Beetroot (boiled) | 45-55 minutes |
| Tomatoes | 30-40 minutes |
| Cucumber | 30-40 minutes |
| Bulgarian pepper | 30-40 minutes |
| Salad | 30-40 minutes |
| Greenery | 30-40 minutes |
| Zucchini (boiled) | 40-50 minutes |
| Corn (boiled) | 40-50 minutes |
| Corn (canned) | partially digested for at least several hours |
| Salads dressed with vegetable oil | 50-60 minutes |
| Mushrooms | 5-6 hours |
| Fruits and berries | |
| Orange | 30 minutes |
| Grapefruit | 30 minutes |
| Grape | 30 minutes |
| Cherry | 40 minutes |
| Peach | 40 minutes |
| Pear | 40 minutes |
| Apple | 40 minutes |
| Kiwi | 20-30 minutes |
| Banana | 45-50 minutes |
| A pineapple | 40-60 minutes |
| Mango | 1.5-2 hours |
| Legumes | |
| Lentils | 3 hours |
| Peas | 2-2.5 hours |
| Green peas | 2-2.5 hours |
| Beans | 3 hours |
| Soybeans | 2 hours |
| Dried fruits and nuts | |
| Dates | 2 hours |
| Raisin | 2 hours |
| Prunes | 3 hours |
| Nuts (walnuts, pine, hazelnuts, peanuts) | 3 hours |
| Seeds (seeds) of sunflower, pumpkin, sesame | 2 hours |
| Cereals and porridges | |
| Millet | 60-80 minutes |
| Rice | 60-80 minutes |
| Buckwheat (buckwheat porridge) | 60-80 minutes |
| Barley porridge | 60-80 minutes |
| Oatmeal | 60-80 minutes |
| Milk and dairy products | |
| Milk | 2 hours |
| Fermented milk drinks (for example, kefir) | 60 minutes |
| Homemade cheese | 90 minutes |
| Brynza | 90 minutes |
| Low-fat cottage cheese | 90 minutes |
| Fat cottage cheese | 2 hours |
| Hard cheese | 4-5 hours |
| Yogurt | 2 hours |
| Ice cream | 2-2.5 hours |
| Meat | |
| Chicken meat | 1.5-2 hours |
| Turkey | 2 hours |
| Pork | 3.5-5 hours |
| Beef | 3-4 hours |
| Mutton | 3-3.5 hours |
| Salo | At least 5-6 hours |
| Dumplings | 3-3.5 hours |
| Fish and seafood | |
| Lean fish (eg cod) | 30 minutes |
| Fatty fish (herring, trout, salmon) | 50-80 minutes |
| Shrimps | 2-2.5 hours |
| Seafood Cocktail | 2.5-3 hours |
| Flour products | |
| Bread (wheat, rye) | 3-3.5 hours |
| Pasta, spaghetti | 3-3.2 hours |
| Eggs | |
| Egg white | 30 minutes |
| Egg yolk | 45 minutes |
| Scrambled eggs (fried eggs), omelet | 2-3 hours |
| Boiled egg | 2-2.5 hours |
| Sweets | |
| Chocolate | 2 hours |
| Honey | 1-1.5 hours |
| Marshmallow | 2 hours |
| Halva | 3 hours |
| Gum | not digested (leaves the body within 12-36 hours) |
With a detailed review of the table presented, we can conclude that the digestion time in the stomach for various categories of products is:
- Water and drinks are absorbed within 20 minutes.
- Vegetables are digested within 30-60 minutes (with the exception of vegetables containing large quantities of starch).
- Fruits and berries are digested within 20-40 minutes.
- Legumes are digested within 2 hours (120 minutes).
- Cereals and porridges are digested within 2 hours (120 minutes).
- Nuts and seeds are digested within 3 hours (180 minutes).
- Milk and dairy products are digested within 2 hours (120 minutes).
- Fish and seafood are digested within 1 hour (60 minutes).
- Poultry meat is digested within 2.5-3 hours.
- Cattle meat is digested within 4-6 hours.
- Eggs are digested within 40-45 minutes.
Tips on how to speed up the process of digesting food
If food is slowly digested, it causes a feeling of heaviness, drowsiness, and malfunction of many organs. To avoid long stay of food in the stomach and intestines, the following recommendations should be taken into account:
- Do not eat foods with different digestion times at the same time, adhere to the principles of separate nutrition. In this case, even fast food will take a long time to break down.
- Dressing salads from fresh vegetables with oil is a common, but not the best technique; it extends the time food stays in the stomach by 2 times. Fat breaks down slowly, and due to the fact that it envelops vegetables, they are also in no hurry to be disposed of.
- Drinking after lunch increases the load on the gastrointestinal tract. Any liquid dilutes gastric juice and reduces the concentration of enzymes. Therefore, water should be drunk before meals, on an empty stomach.
- To improve the breakdown of substances, you need to eat slowly and chew everything thoroughly. This technique ensures that hunger is satisfied with a smaller portion, which protects against overeating.
- Metabolism is activated by eating in small portions. For example, the one glass diet has shown its effectiveness due to this intake.
- Foods rich in fiber make the intestines work more actively. Fermented milk drinks are also useful; they contain bacteria important for this organ, which prevent putrefactive processes.
- A healthy lifestyle with regular exercise eliminates constipation, since when playing sports there is a natural massage of the gastrointestinal tract. But you can’t do physical exercise immediately after eating.
- You should not eat at night, the optimal time is 2 or 3 hours before going to bed. In the evening you can eat easily digestible foods. During sleep, the gastrointestinal tract should rest. For better digestion, you should sleep on your left side.
Advice
Adding mint or ginger to dishes activates metabolism. Another assistant in this process is enzyme preparations.
Table of the most favorable combination of products
The compatibility of foods will depend on which enzymes and how long the food is digested in the human stomach.
Food Compatibility Chart:
| Products | Favorable combination |
| Protein (meat, legumes, cheese, nuts, mushrooms, fish) | Non-starchy vegetables, greens |
| Animal proteins (meat, eggs, fish) | Animal fats |
| Plant proteins (nuts, legumes, mushrooms) | Vegetable fats |
| Carbohydrates (cereals, bread, pasta, potatoes, cereals, etc.) | Vegetables, fats, greens. |
| Fats (vegetable oil, lard, animal butter, sour cream) | Starchy foods, greens, vegetables |
| Starch-free vegetables, greens (parsley, onions, cucumbers, peppers, cabbage) | Combination with almost all products |
| Cottage cheese | Sour cream, herbs |
| Milk | Dried fruits |
| Melon, fruit | Self-administration |
Composition and properties
Meat is rich in proteins, fats, carbohydrates, cholesterol and essential amino acids. This product contains microelements such as iron, sodium, zinc, magnesium. Meat foods also contain vitamins of groups A, B, E, D, which regulate the functions of neurotransmitters, thereby guaranteeing performance and activity for humans. These substances are needed for the proper functioning of the body.
Meat contains proteins foreign to the human body. When consuming this product in large quantities, the natural intestinal microflora is disrupted.
Animal products can and should be included in your diet. Only they should be fresh and in moderation. The benefits of meat depend on the way it is processed. Nutritionists do not recommend eating fried and smoked meat; it is better to bake or boil the product. It is recommended to eat any meat product simultaneously with vegetables or porridge, due to which the absorption of the product will be complete.
In the intestines
The intestines have their own enzymes, adapted to the specific local conditions and no less effectively coping with the task of digesting meat proteins. These are trypsin, erepsin, chymotrypsin, steapsin, which work with the proteins and fats of the meat lump.
At the same time, a portion of meat should already be absorbed in the intestines, and therefore all the enzymes here should quickly complete the work of digesting meat, which began in the stomach. Both the pancreas and the intestines themselves produce enzymes, focusing on signals from the stomach about the quantity and quality of meat entering it.
And the breakdown products of all the structural components of meat - amino acids, vitamins, fatty acids, mineral components - are absorbed by the intestines and distributed in the blood throughout the body.