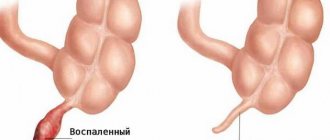
Thanks to prompt diagnosis of acute appendicitis, it is possible to detect the disease in time and begin its treatment. This pathology is dangerous due to the appearance of serious complications, which is why it is so important to carry out surgical intervention as early as possible. To detect the disease in a timely manner, you need to know how to identify appendicitis at home.
Symptoms of appendicitis
To diagnose pathology at an early stage of development and distinguish it from other problems in the digestive system, you need to pay attention to the symptoms of appendicitis:
- Pain in the abdomen. With the development of appendicitis, pain is first felt in the navel area, after which it gradually moves to the right lower abdomen. Discomfort appears suddenly and is vague. Usually there is a dull aching pain that does not allow you to take a deep breath. In addition, they increase significantly when coughing or laughing.
- Forced body position. When appendicitis develops, a person cannot straighten up or move normally - this is due to abdominal pain. Another sign of inflammation is the forced posture of an adult or child - the patient lies on his side and raises his legs.
- Nausea and vomiting. With the development of appendicitis, abdominal pain is almost always accompanied by nausea. Debilitating vomiting that does not bring relief may also occur. Sometimes it happens once, but in most cases this condition lasts quite a long time. It is worth considering that in a child or teenager, vomiting is frequent, while in adults this symptom can occur literally 1-2 times. In old age there are no such symptoms.
- Increased body temperature. Usually this figure is 37.5-38 degrees, but in a child it can rise to 40 degrees. If the temperature increases significantly in an adult, this indicates the progression of inflammation.
- Abnormal stool. In most cases there is no this symptom. But if the appendix in an adult or child is located abnormally, constipation may occur. In rare cases, diarrhea may also develop. It is worth considering that in case of poisoning, loose stools bring temporary relief to a person, while in case of appendicitis the condition remains the same - abdominal pain does not disappear after defecation.
- Dry mouth. If abdominal pain is accompanied by this symptom, we can talk about the development of appendicitis.
Increased pain and increased body temperature
Over the course of four to five hours, pain gradually increases, body temperature rises to >37.3° C. When there is acute inflammation of the appendix, the patient suffers from severe pain. It becomes difficult for him to move. Even breathing can cause increased pain. At the same time, it subsides if you take a certain body position: lying on your right side.
Remember! Pain subsides when lying on the right side, sharply intensifies when turning over to the left side - a key symptom of appendicitis.
Poses for appendicitis pain relief
Several characteristic symptoms
Let us identify a few more symptoms characteristic of appendicitis. They often manifest themselves in complex ways.
- Painful sensations are sometimes accompanied by severe nausea, vomiting and urge. In this case, we can talk about reflex vomiting. When vomiting occurs before the onset of pain, most likely the problem is not inflammation of appendicitis. Typically, reflex vomiting after abdominal pain due to appendicitis is observed in children and elderly patients.
- Also, pain may be accompanied by gastric disorders.
- With inflammation of appendicitis, signs of malfunctions in the genitourinary system appear. Sometimes there is a frequent urge to urinate, pain in the ureters, and nagging pain in the bladder area.
- The cardiovascular system also reacts to appendicitis. Heart rhythm disturbances, tachycardia occur, and blood pressure can drop or jump sharply.
- An increase in low-grade fever may be observed. Indicators are approximately 37-39 degrees. As a result, a person feels weak, drowsy, and loses appetite. It is this temperature that indicates the development of an inflammatory process in the body.
Main symptoms of appendicitis
When a patient has concomitant illnesses, symptoms characteristic of the existing disease are likely to appear. It is important to pay attention to any nuances.
Appendicitis can be not only acute, but also chronic. With it, pain occurs from time to time. This disease is difficult to diagnose; it does not pose a serious threat in itself, but it can potentially provoke acute inflammation.
How to determine appendicitis at home: self-determination methods
How to recognize appendicitis? To check for yourself whether you have inflammation in the appendix, you can do the following:
- Lie down on a flat surface - bed or floor. Place your arms along your body, spread your legs slightly, and then bend your knees. In this case, the second person should lightly press the area in the lower right corner of the abdomen with the fingers of his right hand, and then sharply remove his hand. If pain occurs at this point, you should consult a doctor. With appendicitis, the groin, navel or left side often hurts.
- Lie on the floor, place your arms along your body, and straighten your legs. First, raise your right leg 50-60 degrees. At this moment, the second person should remove the edge of his hand quite strongly along the heel. Similar actions need to be done with the left leg. Pain in the right side of the abdomen is a characteristic symptom of appendicitis.
- To understand whether a child has a stomach ache, you should look for specific symptoms. If the baby suddenly squats down and cries a lot, this indicates the development of inflammation.
- To diagnose appendicitis yourself, you can try coughing. Echoes of pain will occur in the right corner of the abdomen.
- If appendicitis is suspected, the person should be asked to walk. When the appendix is inflamed, the stomach hurts while walking. If every step is accompanied by discomfort, we can talk about the development of appendicitis.
- It is worth carefully palpating the stomach. Tightness of the abdominal wall will help identify appendicitis.
The listed symptoms in an adult or child should be a signal to consult a doctor, since there is a risk of appendix rupture or chronic inflammatory process.
Appendicitis in women, elderly and children
Clinical manifestations in females resemble certain gynecological pathologies. The anomaly is associated with the close location of the appendages, and pain syndrome is present:
- with ectopic pregnancy;
- ovarian rupture;
- apoplexy, etc.
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to pay attention to the presence of gynecological diseases and the menstrual cycle.
Some specific manifestations of appendicitis are present in the elderly, children, pregnant women and with an abnormal location of the appendix.
The following clinical signs are typical for babies:
- diarrhea with frequent vomiting;
- febrile temperature indicators;
- decreased activity - the child loses interest in toys;
- lethargy, moodiness;
- anxiety - with increasing discomfort.
In old age, the symptomatic picture is different:
- temperature rise does not always occur;
- the pulse remains within standard limits - without increasing heart rate;
- there are mild signs of abdominal irritation.
At an older age, the clinical manifestations of appendicitis resemble a neoplasm located in the area of the cecum. During pregnancy, the pain syndrome is localized over the iliac region - due to the upward elevation of the intestines against the background of an enlarged uterus.
What should you not do if you suspect appendicitis?
In such situations, it is strictly prohibited:
- Take laxatives or painkillers. Such actions will prevent the doctor from diagnosing inflammation of the appendix in a timely manner.
- Take medications for the intestines or stomach. They can cause an intense chemical reaction that can cause the appendix to rupture.
- Eat food before consulting a doctor. If the appendix is inflamed, emergency surgery may be required, and before surgery, you must refuse to eat. In addition, food can cause intestinal irritation, which will lead to increased pain.
- Apply a heating pad or warm compress to your stomach. Heat exposure will cause an acceleration of the inflammatory process.
If your stomach hurts and your temperature rises, under no circumstances should you hesitate. In such a situation, you should call an ambulance.
What not to do if you have appendicitis
If appendicitis is suspected, a number of restrictions come into force. Compliance with them allows you to avoid a sharp deterioration in health before receiving medical help. With such symptoms, the use of laxatives and painkillers is strictly prohibited. All this will create difficulties in diagnostics. The list of contraindications includes drugs for the stomach, as they can lead to rupture of the appendix.
Since the detection of this disorder is followed by surgery, you should refrain from eating before visiting a doctor. This will allow you to begin surgery faster. This restriction will also help avoid increased pain caused by increased load on the intestines. In case of appendicitis, thermal effects on the source of inflammation will become dangerous. Therefore, you should not apply a heating pad or anything warming to your stomach.
Diseases with similar symptoms
To determine inflammation of the appendix, additional examinations are often required. This is explained by the fact that the primary symptoms of the disease resemble signs of other pathologies. These include:
- pyelonephritis;
- Crohn's disease;
- inflammation of the uterus, tubes or ovaries;
- renal colic;
- peptic ulcer;
- colitis and enterocolitis;
- inflammation of the testicle;
- inflammation of small intestinal nodes;
- tear or stretch of the anterior abdominal muscles.
Appendicitis in men
The primary signs of developing pathology include:
- pain syndrome;
- elevated temperature;
- one-time vomiting;
- white coating on the tongue;
- state of general weakness;
- dryness of the oral mucosa;
- rapid heartbeat, diarrhea;
- refusal to eat.
The intensity and nature of the manifestations are different for each patient. Age and individual characteristics of the body are of great importance. Sharp and diffuse abdominal pain becomes the reason for an urgent visit to the local clinic.
Diagnosis of appendicitis
To identify inflammation of the appendix, it is imperative to analyze the symptoms and conduct additional research:
- Urine and blood tests. When the appendix is inflamed, urine analysis remains normal, and this makes it possible to exclude kidney pathologies. Through a blood test, it will be possible to identify the inflammatory process, but the exact localization cannot be established.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. This is the fastest and most reliable method for diagnosing appendicitis.
- CT scan. This study is prescribed when there is doubt about the correctness of the diagnosis.
Now you know how to identify appendicitis at home in adults and children. This is very important for timely surgical intervention. Therefore, the very first symptoms of the disease should force a person to call an ambulance - the slightest delay can provoke dangerous complications.
Which doctor treats inflammation of the cecal appendage?
If you have appendicitis, you should consult a surgeon, gastroenterologist or therapist. If signs occur in a pregnant woman, it is recommended to consult a gynecologist. A patient with inflammation of the appendix of the cecum should go with appendicitis to a doctor with a surgical focus. This is due to the fact that the treatment of the disease proceeds alone - removal of the appendage.
Regardless of the doctor, if the appendix is inflamed, the patient is diagnosed. This is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis. This is especially required for women during pregnancy. Sometimes symptoms are confused with inflammation of the ovary or other pelvic organs.
For appendicitis, the doctor palpates and interviews the patient. To do this, he examines the intestine and ileal region. If signs of the disease are confirmed, the patient is referred for removal of the appendix.
For any development of the disease, the patient undergoes an appendectomy. However, surgical intervention has contraindications and is performed only by a surgeon. If the patient does not seek help in a timely manner, complications of appendicitis may arise. Therefore, surgery to remove the appendage is carried out using different techniques. To prepare the patient for the intervention, he is admitted to a surgical hospital.
To achieve this, the following intervention methods are distinguished:
- minimally invasive operations;
- classic dissection;
Carrying out diagnostics and determining the location of inflammation
When visiting a doctor with signs of appendicitis, the patient undergoes additional laboratory tests. To accurately identify the inflammatory process, you will need to undergo a general blood and urine test. To determine the size of the appendix, radiography and ultrasound are performed.
In some cases, intestinal irrigoscopy is used. Diagnosis is carried out with the introduction of a contrast agent through the rectum. The procedure is necessary for radiography. In addition, CT or laparoscopy of the abdominal cavity is used.
Diagnostic methods are used to exclude inflammation of other organs. After treatment of acute appendicitis, a recovery period of up to 30 days is required. If no complications are observed in an adult or child, then rehabilitation reaches 2 weeks.
If you experience persistent pain accompanied by vomiting due to appendicitis, consult a therapist or gastroenterologist. After diagnosis, the patient is referred to a surgeon. However, pregnant women should consult a gynecologist. Signs can accompany other diseases. In addition, there are a number of contraindications in treatment with the classical method. The attending physician will advise you on this.
We recommend: What is abdominal peritonitis and why is it dangerous?
Causes of appendicitis
Diagnosis of appendicitis
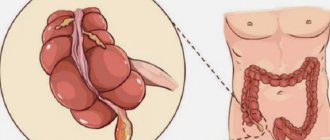
In order to understand the causes of the disease, it is necessary to have at least a small understanding of such an organ as the appendix.
The appendix is nothing more than an extension of the cecum, up to ten centimeters in length. It is the border zone between the large and small intestines.
In addition, it protects the body from all kinds of infections by boosting the intestinal immune system. But the appendix is not a vital human organ, so at the slightest inflammation it must be removed.
The causes of inflammation can be completely different for each person. The disease may never occur in a person who has suffered from a stomach ulcer for a long time, but, at the same time, it can appear in a completely healthy person.
Based on numerous observations, doctors have identified three obvious reasons:
- Mechanical. Occurs when there is blockage (obstruction) of the lumen, which is blocked by fecal stones, foreign objects or any neoplasms.
- Infectious. Occurs when the intestines are damaged by a number of diseases and infections, which leads to inflammatory processes in the cecum and, accordingly, can cause problems with appendicitis. There are frequent cases of inflammation of the appendix in infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
- Vascular. There is an opinion that a number of vascular diseases can provoke the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the appendix.
Another likely factor is indiscriminate eating habits. This is especially true for children. When eating seeds with shells, chips and all kinds of fast food, a blockage of the lumen may well occur.
Everything in the body is interconnected, so the reasons can be very different; they can lead to inflammation of the appendix, even to chronic forms. The chronic form of appendicitis is very difficult to diagnose, so in most cases it manifests itself in an acute form.