Stomach diseases are diagnosed in children and adults at any age; these pathologies are quite dangerous because they can cause the development of disorders in other systems and organs. Timely diagnosis will help identify the disease at an early stage, and proper treatment, diet and folk remedies will quickly get rid of unpleasant sensations.
Stomach diseases can appear at any age
Stomach diseases
The cause of the development of diseases of the digestive system in adults is most often poor nutrition, bad habits, stress, and hereditary factors. All diseases have certain characteristic symptoms, which greatly simplifies diagnosis; each of them is assigned a code in the international classification.
Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa; this disease is the leader among pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and occurs in acute or chronic form. There are autoimmune and Helicobacter types; inflammation can be accompanied by an increase or decrease in the acidity of the juice.
Acute gastritis is a one-time inflammation that can be triggered by medications, junk food, chemicals and bacteria. The chronic form is characterized by a long course, remission is replaced by exacerbation. The disease code according to ICD-10 is K29.
Causes of gastritis:
- damage to the stomach by pathogenic microorganisms, the main pathogen is the bacteria Helicobacter pylori;
- poor nutrition, fasting, overeating;
- alcoholism;
- long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticoids;
- duodenal reflux;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- hormonal imbalance, vitamin deficiency;
- helminthiasis, stress.
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is the causative agent of gastritis
With gastritis with high acidity, the patient complains of discomfort in the solar plexus area or near the navel; the discomfort decreases after eating. The main symptoms are heartburn, belching with the taste and smell of rotten eggs, diarrhea, metallic taste, stomach pain, and morning sickness.
Gastritis with low acidity is accompanied by deterioration of peristalsis, frequent constipation, bad breath, rapid satiety, heaviness in the abdomen, and increased gas formation.
A dangerous consequence of the chronic form of the disease is atrophic gastritis, which gradually begins to destroy the glands that are responsible for the synthesis of gastric juice.
Peptic ulcer
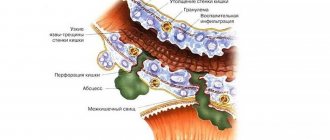
An ulcer is a consequence of chronic gastritis; deep wounds form in the gastric mucosa; the disease is chronic. With an ulcer, destructive processes affect the deep layers of the mucous membrane, and scars appear after healing. The ICD-10 code is K25.
The reasons for the development of peptic ulcer disease are similar to gastritis, but sometimes an ulcer develops against the background of diabetes, tuberculosis, hepatitis and cirrhosis, lung cancer, and syphilis.
Main features:
- pain in the upper abdomen - a symptom manifests itself in 75% of patients;
- constipation;
- heartburn, nausea, sometimes vomiting;
- lack of appetite, weight loss;
- bitter or sour belching, flatulence;
- coating on the tongue, constantly sweaty palms;
- feces with mucus.
The ulcer is often hereditary; the risk of developing the disease is high in men and women with blood group I.
Frequent coating on the tongue may indicate a stomach ulcer
Gastroparesis
The disease is characterized by slow motility - the stomach muscles weaken, food does not move well through the gastrointestinal tract. The symptoms of the disease are in many ways similar to other gastric pathologies - nausea, vomiting after eating, pain and cramping in the abdomen, rapid satiety. The ICD-10 code is K31.
Causes of the disease:
- diabetes;
- inflammatory processes in the pancreas;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- micronutrient deficiency;
- surgical interventions on the stomach, removal of a bladder for cholelithiasis, during which the vagus nerve was affected;
- chemotherapy, radiation exposure.
Against the background of gastroparesis, there is a failure in metabolic processes, vitamin deficiency, and sudden weight loss.
People with diabetes are more likely to experience gastroparesis
Gastroptosis
Stomach prolapse due to weakened muscle tone; the pathology is often congenital. The acquired form develops due to sudden weight loss, constant lifting of heavy objects, childbirth, the disease has an initial, moderate and severe stage. The ICD-10 code is 31.8.
Disease syndromes:
- a strong feeling of heaviness, especially after overeating;
- unstable appetite, craving for spicy foods, dairy products can cause disgust;
- nausea for no apparent reason;
- frequent belching, increased gas formation;
- constipation;
- acute pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies with changes in body position;
- the stomach sags.
Against the background of gastroptosis, prolapse of the kidneys and liver often occurs.
Adenocarcinoma
Stomach and esophageal cancer are the most dangerous, often fatal diseases of the digestive system; malignant neoplasms are formed from the epithelial tissues of the gastric mucosa. The disease is common among people aged 50–70 years; the pathology is diagnosed in men more often than in women. The ICD-10 code is C16.
Causes of the disease:
- excessive consumption of salt, food additives category E, smoked, pickled, canned, fried foods;
- alcohol, smoking, unsystematic use of Aspirin and hormonal drugs;
- deficiency of ascorbic acid, vitamin E;
- the destructive effects of Helicobacter pylori, streptococci, staphylococci, Candida fungi, Epstein-Bar virus;
- chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer, polyps, surgery or gastric resection;
- hereditary factor - cancer develops more often in people who have inherited blood group II;
- lack of immunoglobulin Ig in the tissues of the gastric epithelium.
Chronic gastritis can develop into stomach cancer
The main danger of cancer is that the disease can occur for a long time without any special symptoms. At the initial stage, there is a decrease in performance, a general deterioration in well-being, heaviness and discomfort in the abdomen. As the tumor grows, the abdomen increases in size, weight decreases sharply, the person suffers from frequent constipation, severe thirst, abdominal pain intensifies, radiates to the back, blood appears in the stool, and pain in the anus is bothersome.
Helicobacter pylori is transmitted through saliva, contaminated food and water, poorly disinfected medical instruments and dirty dishes, from mother to fetus.
Pneumatosis
The disease is characterized by increased gas formation; excess gas leaves the body along with loud belching. Neurological pneumatosis develops in hysterics and neurasthenics, who often involuntarily swallow large portions of air. The ICD-10 code is K31.
Causes of organic pneumatosis:
- hernias, increased intra-abdominal pressure;
- respiratory diseases, which are accompanied by difficulty breathing, dry mouth;
- talking while eating, snacking on the go, babies swallow a lot of air during feeding;
- some pathologists of the heart and blood vessels;
- smoking, chewing gum.
In addition to belching, a person is worried about bloating, rapid heartbeat, heart pain after eating, hiccups, and difficulty breathing.
Smoking can cause gastric pneumatosis
Gastric volvulus
A rare and serious disease in which the stomach rotates around its anatomical axis. The ICD-10 code is K56.6.
Causes of the disease:
- anatomical malformations, elongation of ligaments, sudden weight loss;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- lifting weights;
- abuse of rough food - the disease often develops in vegetarians;
- changes in intra-abdominal pressure indicators.
At the initial stage of the disease, there is a sharp pain in the abdomen, which radiates to the left hypochondrium, bloating and a feeling of heaviness, and sometimes there are problems with swallowing.
At the initial stage of gastric volvulus, there is severe pain in the left hypochondrium
With acute volvulus, the pain occurs sharply, can radiate to the back, shoulders, and shoulder blade, accompanied by severe nausea and vomiting, regurgitation occurs even after a sip of water. Against the background of gastric pathology, disruptions in the functioning of the heart occur, severe intoxication, and death are possible. Any form of the disease is characterized by a lack of stool, severe thirst, and a sharp increase in temperature.
Important!
Abdominal pain is not always a sign of stomach disease. In a child, such symptoms often appear with a sore throat, a cold, or against a background of stress and nervous experiences.
Reflux stomach disease
One of the most common chronic pathologies of the digestive system, it develops due to regular penetration of the contents of the abdominal cavity and duodenum into the esophagus. The disease is accompanied by severe sore throat, sour belching, heartburn, discomfort in the solar plexus area, and diseases of the bronchi and trachea may occur. The ICD-10 code is K21.
Causes of the disease:
- decreased muscle tone of the lower sphincter due to alcohol abuse, caffeine, taking certain medications, smoking, hormonal imbalance during pregnancy;
- increased intra-abdominal pressure;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- eating on the go;
- duodenal ulcer.
Excessive consumption of animal fats, mint tea, spicy and fried foods can provoke the development of reflux disease.
Duodenal ulcers can cause gastric reflux disease
Gastroenteritis
Intestinal flu, a rotavirus infection, develops when pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the digestive system; the disease is often diagnosed in children and the elderly. The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets, through contact and household contact, but most often the bacteria enter the body through dirty vegetables and hands. The ICD-10 code is K52.
Symptoms:
- cough, runny nose, red throat, pain when swallowing - these symptoms appear a few hours before dyspepsia and pass quickly;
- diarrhea 5–10 times a day - gray-yellow stool has a pungent odor, no inclusions of pus or blood;
- vomiting, increasing weakness;
- pain near the navel or lower abdomen;
- temperature increase;
- dehydration.
Such symptoms may indicate either ordinary poisoning or the development of cholera or salmonellosis, so you need to call a doctor and get tested.
Gastroenteritis is characterized by frequent diarrhea
Gastritis
Gastritis is called inflammation of the gastric mucosa, which occurs due to exposure to bacteria, poor nutrition, alcoholism, as well as abuse of diets and fasting (especially snacking on sandwiches and dry food), spices and spicy foods. The most common symptoms of this stomach disease (treatment and signs of gastritis depend on the causes that cause it) are characterized by an increased level of acidity, heartburn, and sore throat when swallowing. In addition, signs of gastritis include intestinal disorders: constipation or, conversely, diarrhea. If the cause of gastritis is pathogenic bacteria, then it progresses quite quickly, erosion and destruction of the walls of the gastric muscle are noted.
In addition, the cause may be an acute autoimmune process, when the body perceives its own stomach as something foreign. Antibodies produced by the body begin to attack it and eat away the walls and mucous membranes. During treatment of the disease, it is important to take medications only after meals, when gastric juice is produced. In this case, the patient must be prescribed a diet for stomach disease, which completely excludes the consumption of alcoholic beverages, hot, spicy and fatty foods. Diagnosis is carried out by endoscopy.
Diagnosis of stomach diseases
If signs of gastric diseases appear, you must visit a gastroenterologist, the doctor will conduct an external examination, listen to complaints, collect anamnesis, and prescribe the necessary studies to clarify the diagnosis and identify the cause of the pathology.
Diagnostic methods:
- general and biochemical analysis of blood, urine, bile;
- coprogram - stool analysis;
- gastropanel is a modern method of blood testing. Allows you to identify hypothetical risks of developing gastric pathologies;
- probing allows you to examine the secretory function of the stomach;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity - used for biopsy, the method allows you to determine the location of tumors;
- CT scan – the images show hematomas, abscesses, cysts;
- MRI - prescribed for suspected stomach cancer, gastritis, ulcers, the method allows you to determine the size and shape of the stomach, its position;
- gastroscopy - study of the stomach from the inside, allows you to identify tumors at the initial stage of development, the presence of bleeding;
- endoscopy – during examination of the stomach and intestines, a biopsy sample is taken using a special camera;
- X-ray - use contrast liquid, which allows you to see malformations, neoplasms, ulcers, narrowing of the lumen;
- parietography is a method of x-ray examination in which gas is introduced into the organ, which makes it possible to determine the degree of tumor growth in the tissue;
- colonoscopy – diagnosis of all parts of the intestine using an endoscope;
- FGDS – reveals pathologies of the digestive organs.
It is almost impossible to avoid stomach and liver diseases in the modern world, so experts recommend undergoing a preventive examination annually.
Probing helps to identify abnormalities in the functioning of the stomach
Methods for treating stomach diseases
Based on the results of the study, the doctor prescribes medications, gives recommendations on proper nutrition, and there are special schemes and standards for the treatment of diseases of the digestive system. Alternative medicine and exercise therapy will help enhance the effect of medications.
Diet
Preparation of the correct diet, adherence to the daily routine and nutrition are an essential component of therapy in the treatment of diseases of the stomach and pancreas. For treatment, diet 1, 1a, 1b is used.
During treatment, you should exclude from the menu all unhealthy and heavy foods that can cause irritation of the gastric mucosa. The diet should not contain vegetables and fruits with high acidity, spicy, salty, fried and fatty foods, canned food, and semi-finished products. You need to give up fast food, carbonated drinks, sweets, minimize the consumption of tea and coffee, legumes, cabbage, and mushrooms.
What can you eat if you have stomach problems?
- the menu must include puree soups, milk soups and liquid porridges;
- seasonal vegetables and fruits with low acidity - carrots, zucchini, beets, pumpkin;
- lean meat and fish;
- yesterday's white bread;
- vegetable oils;
- boiled eggs, steam omelet;
- fermented milk products with medium fat content.
If you have stomach problems, you are allowed to consume low-fat dairy products.
→ Proper nutrition for stomach and duodenal ulcers
All food should be boiled, baked, or steamed; food should be consumed in small portions at regular intervals; it should be at a comfortable temperature. You need to follow a drinking regime - drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day, this can be plain or alkaline water, jelly, rosehip decoction, herbal teas.
→ Details about the diet for pancreatitis
Medicines
In the treatment of diseases of the stomach and duodenum, drugs are used that help eliminate pain, inflammation, nausea, and normalize stool.
Main groups of medicines:
- antispasmodics – No-shpa, Papaverine, tablets eliminate spasms and have a mild analgesic effect;
- binding agents – Imodium, Loperamide, help cope with diarrhea;
- antiemetics – Cerucal, Ondansetron;
- gastroprotectors - Rennie, Phosphalugel, neutralize hydrochloric acid and eliminate the burning sensation in the esophagus;
- alginates - Gaviscon, Laminal, neutralize pepsin in the stomach, help strengthen the immune system;
- carminatives - Espumisan, help eliminate bloating;
- antihistamines – Cetrin, Fexofenadine;
- antibiotics – Ceftriaxone, Amoxicillin;
- anthelmintic drugs – Vermox, Nemozol;
- enzymes to improve digestion - Creon, Festal;
- antienzymes - Gordox, Ingitril.
Creon improves the digestion process
Most drugs for the treatment of stomach diseases are well tolerated; sometimes there is a change in the color of the tongue, the color of urine and feces, dizziness, children may have problems sleeping, and increased excitability. After completing therapy, you need to drink vitamin complexes and drugs to restore intestinal microflora - Linex, Bifiform.
Folk remedies
Traditional treatment of stomach and intestinal problems involves the use of herbs, some available remedies and products that help quickly eliminate pain and inflammation, have an enveloping effect, and help heal erosions and ulcers.
What can be used in therapy:
- potato juice, oat decoction, flaxseed - they normalize acidity, coat the mucous membrane, relieve pain and inflammation;
- Chaga is an effective remedy for treating ulcers, accelerates the healing process, and has an anti-inflammatory effect;
- St. John's wort, chamomile, plantain. aloe – plants have an astringent, healing effect, eliminate foci of inflammation;
- mumiyo - restores the immune system, quickly relieves pain, spasms, has an antibacterial effect, accelerates regeneration processes;
- honey, propolis - beekeeping products have a pronounced antimicrobial, healing and anti-inflammatory effect;
- badger fat – coats the walls of the stomach, preventing belching and bloating.
Non-traditional treatment methods should be wisely combined with drug therapy; it is impossible to get rid of serious gastrointestinal pathologies using traditional medicine alone.
Mumiyo gets rid of bacteria and strengthens the immune system
Causes of stomach problems
Most of the causes of disorders in the organ can be completely avoided if you monitor your diet and lifestyle. The following factors can cause problems.
- Poor nutrition. If the patient refuses or cannot eat protein foods, he experiences a significant decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid. As a result, this leads to fermentation processes and the development of gastritis.
- Infection of the body with helminths, which can clog the stomach cavity and gastrointestinal tract.
- Having bad habits. Alcohol is especially dangerous. When mixed with gastric juice, it weakens the digestive function, making digestion impossible.
Alcohol negatively affects stomach function
- Eating very cold or too hot foods. Alternating temperatures over a short period of time is especially dangerous.
- Binge eating. Due to the constant consumption of large amounts of food, the volume of the stomach begins to increase, which leads to its distension.
- Prolonged or intermittent fasting. Acid in the stomach is produced on a constant basis. If she has nothing to digest, she begins to decompose the walls of the stomach. This can cause ulcers and gastritis.
- Consuming low-quality or expired food. Such food causes severe fermentation and possible inflammation of the walls of the organ.
- Eating fatty, highly seasoned foods, smoked meats and pickles. Such food is difficult to digest, causing heartburn, bloating, and burns of the mucous membrane.
Attention! Sometimes overeating leads to severe fermentation inside the stomach cavity. Because of this, the organ swells so much that it comes out into the chest, and the patient dies.
Video - Causes of stomach problems
Possible complications
If treatment for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is not started in a timely manner, then dangerous and sometimes fatal consequences cannot be avoided. In the initial stages, medications and diet will help cope with the disease; in advanced forms, surgical intervention will be required.
Consequences of stomach diseases:
- Peritonitis is the most common complication, which is accompanied by severe pain, a sharp increase in temperature, vomiting, and severe intoxication. Complete intestinal atony develops, arterial values decrease, and the person may lose consciousness. Without timely medical care, there is a high probability of death.
- Internal bleeding is a consequence of an ulcer. There are blood impurities in the blood and feces, symptoms of increasing anemia appear - weakness, sticky cold sweat, dizziness, loss of consciousness.
- Dysbacteriosis is a disorder of the intestinal microflora that can cause sudden weight loss.
- Intestinal obstruction – develops in the presence of tumors, polyps, prolonged constipation, and increased intestinal motility.
- Gastric resection.
Self-diagnosis and uncontrolled use of medications are the main reasons for the development of complications of stomach diseases.
If stomach diseases are not treated in time, intestinal obstruction may occur.